Abstract
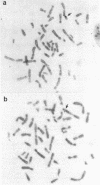
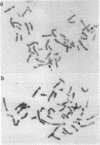
The multigene procollagen family encodes probably greater than 20 genetically distinct but structurally related polypeptide chains. Recent characterization of human procollagen clones has allowed determination of functional domains within the proteins, genomic organization, and chromosomal location. Previously, we assigned the coordinately expressed type I genes (alpha 1 and alpha 2) to chromosomes 17 and 7, respectively, and now other investigators have mapped the type II gene to chromosome 12 [Strom, C. M., Eddy, R. L. & Shows, T. B. (1984) Somatic Cell Genet. 10, 651-655]. Recently, we isolated cDNA clones encoding the fourth interstitial procollagen, type III, and the alpha 2 chain of the type V cytoskeletal components. To determine whether these genes were clustered with alpha 1(I), alpha 2(I), or alpha 1(II) or were further dispersed in the genome, in situ hybridization of the alpha 1(III) and alpha 2(V) probes to metaphase chromosomes was carried out. Here we report a fourth autosome with procollagen gene loci but the first cytological evidence for linkage. By using normal and translocated cell lines, our results show that both the alpha 1(III) and alpha 2(V) procollagen genes map to the q24.3----q31 region of chromosome 2.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentz H., Morris N. P., Murray L. W., Sakai L. Y., Hollister D. W., Burgeson R. E. Isolation and partial characterization of a new human collagen with an extended triple-helical structural domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3168–3172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard M. P., Chu M. L., Myers J. C., Ramirez F., Eikenberry E. F., Prockop D. J. Nucleotide sequences of complementary deoxyribonucleic acids for the pro alpha 1 chain of human type I procollagen. Statistical evaluation of structures that are conserved during evolution. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5213–5223. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard M. P., Myers J. C., Chu M. L., Ramirez F., Eikenberry E. F., Prockop D. J. Structure of a cDNA for the pro alpha 2 chain of human type I procollagen. Comparison with chick cDNA for pro alpha 2(I) identifies structurally conserved features of the protein and the gene. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1139–1145. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage H. Structurally distinct collagen types. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:957–1003. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson R. E. Genetic heterogeneity of collagens. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Jul;79 (Suppl 1):25s–30s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson R. E., Hebda P. A., Morris N. P., Hollister D. W. Human cartilage collagens. Comparison of cartilage collagens with human type V collagen. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7852–7856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., Balian G., Ross R., Bornstein P. Synthesis of types I and III procollagen and collagen by monkey aortic smooth muscle cells in vitro. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3243–3249. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Emanuel B. S. An improved method for G-banding chromosomes after in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(4):308–309. doi: 10.1159/000132079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., de Wet W., Bernard M., Ding J. F., Morabito M., Myers J., Williams C., Ramirez F. Human pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene structure reveals evolutionary conservation of a pattern of introns and exons. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):337–340. doi: 10.1038/310337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Shander M., Martinis J., Cicurel L., D'Ancona G. G., Dolby T. W., Koprowski H. Chromosomal location of the genes for human immunoglobulin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3416–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisseroth A., Nienhuis A., Lawrence J., Giles R., Turner P., Ruddle F. H. Chromosomal localization of human beta globin gene on human chromosome 11 in somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1456–1460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisseroth A., Nienhuis A., Turner P., Velez R., Anderson W. F., Ruddle F., Lawrence J., Creagan R., Kucherlapati R. Localization of the human alpha-globin structural gene to chromosome 16 in somatic cell hybrids by molecular hybridization assay. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Martinis J., Croce C. M. Assignment of the genes for human lambda immunoglobulin chains to chromosome 22. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):173–175. doi: 10.1038/294173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard D. S., Kawasaki E. S., Bancroft F. C., Szabo P. Localization of a unique gene by direct hybridization in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3755–3759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. J., Kielty C. M., Garner C., Schor S. L., Grant M. E. Identification and partial characterization of three low-molecular-weight collagenous polypeptides synthesized by chondrocytes cultured within collagen gels in the absence and in the presence of fibronectin. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):417–426. doi: 10.1042/bj2110417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Saunders G. F. Localization of single copy DNA sequences of G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00327364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Myers J. C., Ramirez F. Localization of the human 2(I) collagen gene (COL1A2) to chromosome 7q22. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1983;36(3):586–587. doi: 10.1159/000131978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huerre C., Junien C., Weil D., Chu M. L., Morabito M., Van Cong N., Myers J. C., Foubert C., Gross M. S., Prockop D. J. Human type I procollagen genes are located on different chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6627–6630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jander R., Rauterberg J., Glanville R. W. Further characterization of the three polypeptide chains of bovine and human short-chain collagen (intima collagen). Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Craig I. W., Francke U. Localisation of the G gamma-, A gamma-, delta- and beta-globin genes on the short arm of human chromosome 11. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):606–608. doi: 10.1038/281606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junien C., Weil D., Myers J. C., Van Cong N., Chu M. L., Foubert C., Gross M. S., Prockop D. J., Kaplan J. C., Ramirez F. Assignment of the human pro alpha 2(I) collagen structural gene (COLIA2) to chromosome 7 by molecular hybridization. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 May;34(3):381–387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Eddy R. L., Henry W. M., Haley L. L., Byers M. G., Shows T. B. Human metallothionein genes are clustered on chromosome 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5494–5498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Woo S. L., Dugaiczyk A., O'Malley B. W. The ovalbumin gene: alleles created by mutations in the intervening sequences of the natural gene. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loidl H. R., Brinker J. M., May M., Pihlajaniemi T., Morrow S., Rosenbloom J., Myers J. C. Molecular cloning and carboxyl-propeptide analysis of human type III procollagen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9383–9394. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm S., Barton P., Murphy C., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Bentley D. L., Rabbitts T. H. Localization of human immunoglobulin kappa light chain variable region genes to the short arm of chromosome 2 by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4957–4961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne R., Vail M. S., Miller E. J., Blose S. H., Chacko S. Collagen polymorphism in cell cultures derived from guinea pig aortic smooth muscle: comparison with three populations of fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jun;181(2):462–469. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullagh K. A., Balian G. Collagen characterisation and cell transformation in human atherosclerosis. Nature. 1975 Nov 6;258(5530):73–75. doi: 10.1038/258073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Gay S. Collagen: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):3–32. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Dickson L. A., de Wet W. J., Bernard M. P., Chu M. L., Di Liberto M., Pepe G., Sangiorgi F. O., Ramirez F. Analysis of the 3' end of the human pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Utilization of multiple polyadenylation sites in cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10128–10135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Loidl H. R., Stolle C. A., Seyer J. M. Partial covalent structure of the human alpha 2 type V collagen chain. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5533–5541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan A. S., Page R. C. Biosynthesis and regulation of type V collagen in diploid human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11694–11699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooshima A. Collagen alpha B chain: increased proportion in human atherosclerosis. Science. 1981 Aug 7;213(4508):666–668. doi: 10.1126/science.7256267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I. Heritable diseases of collagen. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 9;311(6):376–386. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408093110606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyeritz R. E., Stolle C. A., Parfrey N. A., Myers J. C. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome IV due to a novel defect in type III procollagen. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Nov;19(3):607–622. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Trüeb B., Bornstein P. Biosynthetic and structural properties of endothelial cell type VIII collagen. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13391–13401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Covalent structure of collagen: amino acid sequence of alpha 1(III)-CB9 from type III collagen of human liver. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2621–2627. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Hiorns L., Dalgleish R., Tolstoshev P., Crystal R., Sykes B. Regional localization of the human alpha 2(I) collagen gene on chromosome 7 by molecular hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1983;35(1):64–66. doi: 10.1159/000131838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom C. M., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B. Localization of human type II procollagen gene (COL2A1) to chromosome 12. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Nov;10(6):651–655. doi: 10.1007/BF01535232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom C. M., Upholt W. B. Isolation and characterization of genomic clones corresponding to the human type II procollagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1025–1038. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate V., Finer M., Boedtker H., Doty P. Procollagen genes: further sequence studies and interspecies comparisons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1039–1049. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Avvedimento V. E., Mudryj M., Ohkubo H., Vogeli G., Irani M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. The collagen gene: evidence for its evolutinary assembly by amplification of a DNA segment containing an exon of 54 bp. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):887–892. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90565-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet W. J., Chu M. L., Prockop D. J. The mRNAs for the pro-alpha 1(I) and pro-alpha 2(I) chains of type I procollagen are translated at the same rate in normal human fibroblasts and in fibroblasts from two variants of osteogenesis imperfecta with altered steady state ratios of the two mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14385–14389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]