Abstract
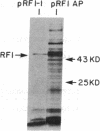
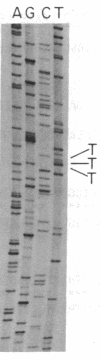
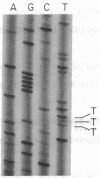
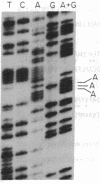
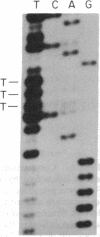
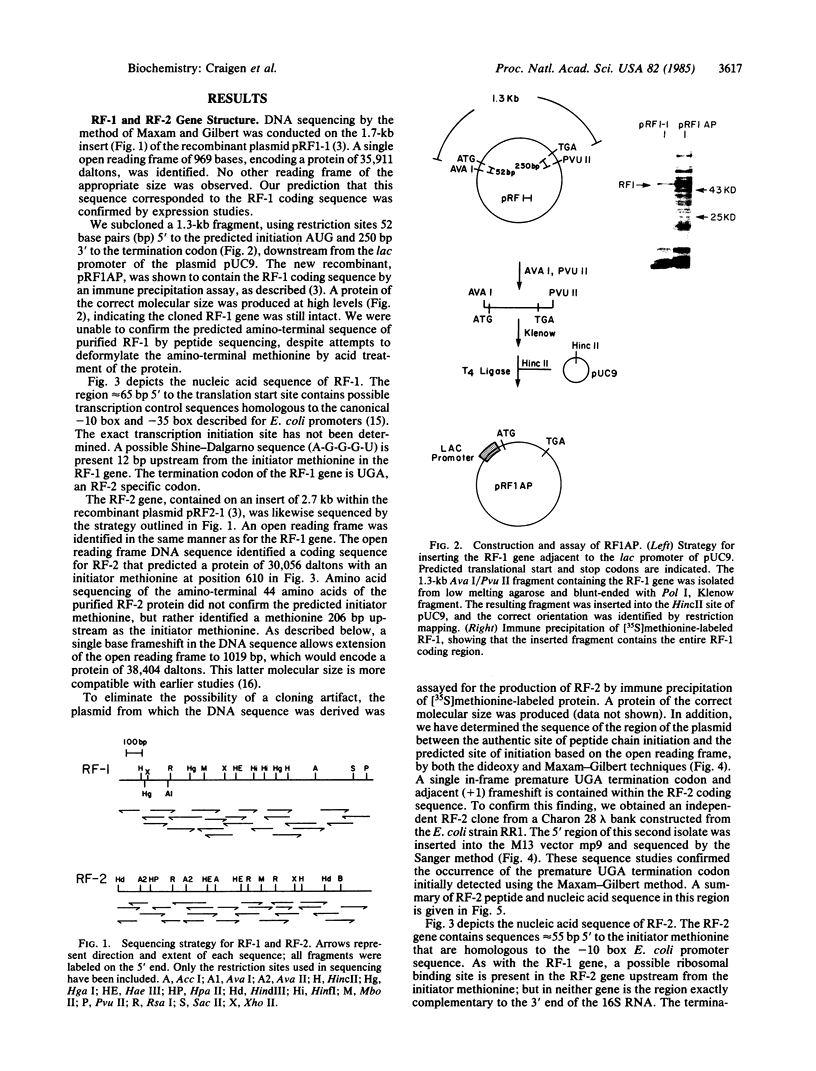
Escherichia coli peptide chain release factors are proteins that direct the termination of translation in response to specific peptide chain termination codons. The mechanisms of codon recognition and peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis are unknown. We have characterized the genes encoding release factor 1 (RF-1) and release factor 2 (RF-2) to study the structure-function relationships of the proteins and their regulation in the bacterium. In this report, we present the gene structure of RF-1 and RF-2, and a partial peptide sequence of RF-2. RF-1 and RF-2 are highly homologous in their primary structure. In addition, an in-frame premature opal (UGA) termination codon is located within the RF-2 coding region at amino acid position 26. This region of the protein was sequenced by automated Edman degradation to confirm the predicted reading frame, and a second independent isolate of the RF-2 gene was identified and sequenced to confirm the DNA sequence. These results imply that a frameshift occurs prior to the premature termination codon, thus allowing for translation of RF-2 to be completed. This may represent a mechanism of translational control of RF-2 expression. An alternative possible means of translational regulation is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins J. F., Nichols B. P., Thompson S. The nucleotide sequence of the first externally suppressible--1 frameshift mutant, and of some nearby leaky frameshift mutants. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1345–1350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01590.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caskey C. T., Forrester W. C., Tate W., Ward C. D. Cloning of the Escherichia coli release factor 2 gene. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):365–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.365-368.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Beaudet A. L., Caskey C. T. Peptide chain termination with mammalian release factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):99–106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratliff J. C., Caskey C. T. Immunologic evidence for structural homology between the release factors of Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jun;181(2):671–677. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm D. L., Horness D., Kucera J., Blattner F. R. Construction of coliphage lambda Charon vectors with BamHI cloning sites. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(3-4):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E., Milman G., Rosman M., Caskey T. Transesterification by peptidyl transferase. Nature. 1970 Jan 10;225(5228):152–154. doi: 10.1038/225152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate W. P., Schulze H., Nierhaus K. H. The Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L11 suppresses release factor 2 but promotes the release factor 1 activities in peptide chain termination. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12816–12820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Murphy J. P., Gallant J. A. Genetic screen for cloned release factor genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):362–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.362-364.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R., Gallant J. Mechanism of ribosome frameshifting during translation of the genetic code. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):389–393. doi: 10.1038/302389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]