Abstract
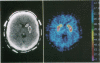
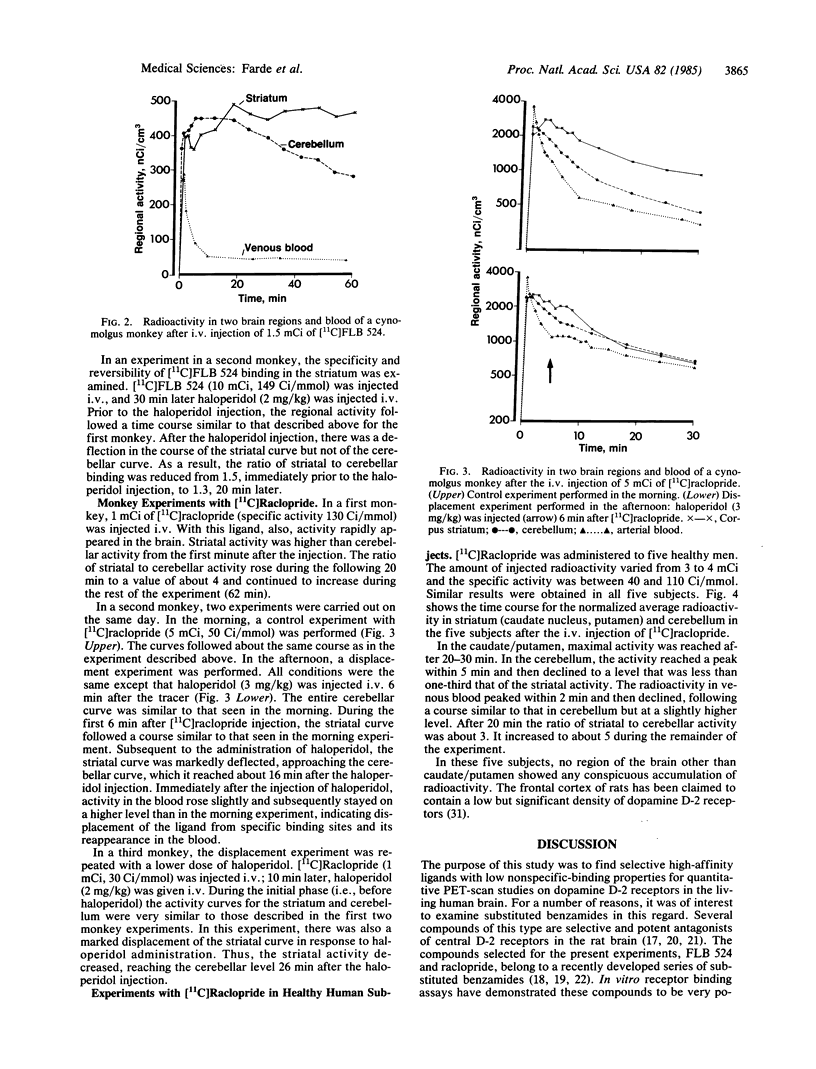
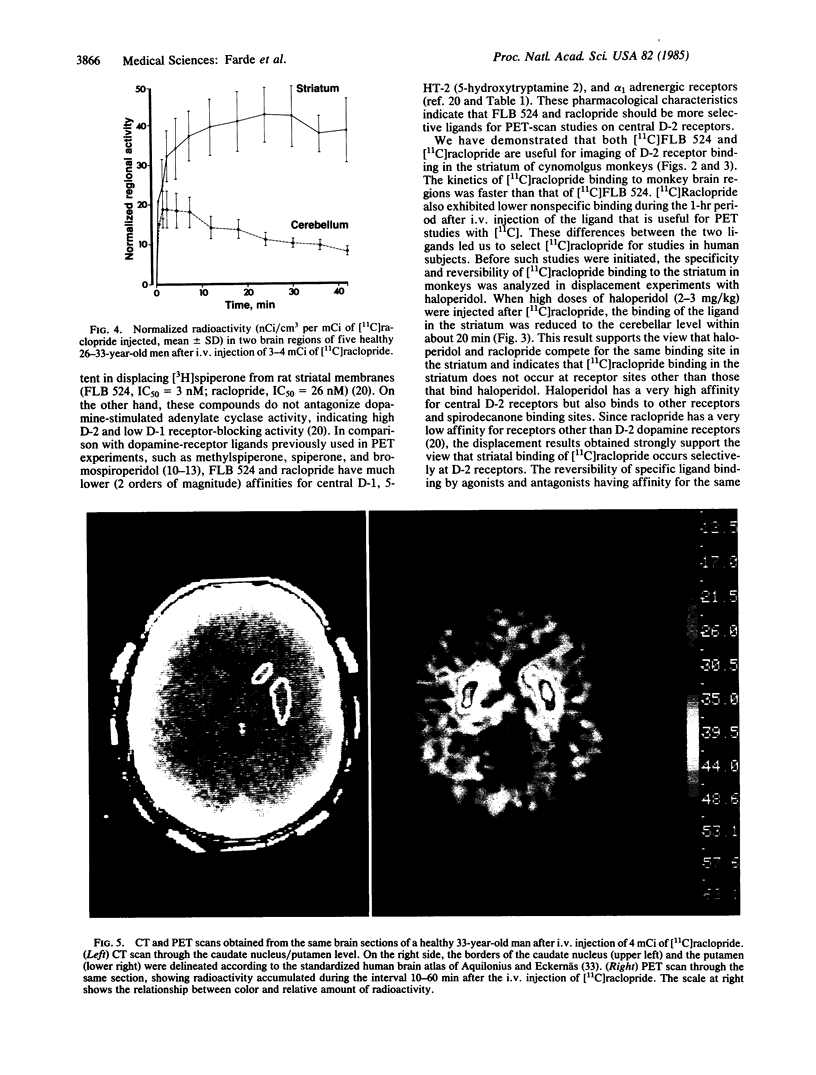
Two substituted benzamides, FLB 524 and raclopride, were labeled with 11C and examined for their possible use as ligands for positron emission tomography (PET)-scan studies on dopamine-2 (D-2) receptors in the brains of monkeys and healthy human subjects. Both ligands allowed the in vivo visualization of D-2 receptor binding in the corpus striatum caudate nucleus/putamen complex in PET-scan images. [11C]Raclopride showed a high ratio of specific striatal to nonspecific cerebellar binding, and the kinetics of binding of this ligand made it optimal for PET studies. The in vivo binding of [11C]raclopride in the striatum of cynomolgus monkeys was markedly reduced by displacement with haloperidol. This and previous in vitro data indicate that [11C]raclopride binds selectively to striatal D-2 dopamine receptors. In healthy human subjects, [11C]raclopride binding in the caudate nucleus/putamen was 4- to 5-fold greater than nonspecific binding in the cerebellum. In comparison with previously available ligands for PET-scan studies on central dopamine receptors in man, [11C]raclopride appears to be advantageous with regard to (i) specificity of binding to D-2 receptors, (ii) the high ratio between binding in dopamine-rich (caudate, putamen) and dopamine-poor (cerebellum) human brain regions, and (iii) rapid association and reversibility of specific binding. [11C]Raclopride should be a valuable tool for characterizing D-2 receptors in the brains of patients with neuropsychiatric disorders.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudry M., Martres M. P., Schwartz J. C. In vivo binding of 3H-pimozide in mouse striatum: effects of dopamine agonists and antagonists. Life Sci. 1977 Oct 15;21(8):1163–1170. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cools A. R., Van Rossum J. M. Excitation-mediating and inhibition-mediating dopamine-receptors: a new concept towards a better understanding of electrophysiological, biochemical, pharmacological, functional and clinical data. Psychopharmacologia. 1976 Feb 2;45(3):243–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00421135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. C., Smith T., Veall N., Zanelli G. D., Crow T. J., Owen F. Dopamine receptors displayed in living human brain with 77Br-p-bromospiperone. Lancet. 1983 Oct 22;2(8356):975–975. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90497-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett D. R., Morris H., Nahorski S. R. Anomalous properties of [3H]spiperone binding sites in various areas of the rat limbic system. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 May;15(3):506–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höllt V., Czlonkowski A., Herz A. The demonstration in vivo of specific binding sites for neuroleptic drugs in mouse brain. Brain Res. 1977 Jul 8;130(1):176–183. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90855-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Petzold G. L., Greengard P. Dopamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in caudate nucleus of rat brain, and its similarity to the "dopamine receptor". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2145–2149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Murrin L. C., Malouf A. T., Klemm N. Dopamine receptor binding in vivo: the feasibility of autoradiographic studies. Life Sci. 1978 Jan;22(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90538-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laduron P., Leysen J. Specific in vivo binding of neuroleptic drugs in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 May 15;26(10):1003–1007. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90486-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leysen J. E., Niemegeers C. J., Tollenaere J. P., Laduron P. M. Serotonergic component of neuroleptic receptors. Nature. 1978 Mar 9;272(5649):168–171. doi: 10.1038/272168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litton J., Bergström M., Eriksson L., Bohm C., Blomqvist G., Kesselberg M. Performance study of the PC-384 positron camera system for emission tomography of the brain. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1984 Feb;8(1):74–87. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198402000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazière B., Loc'h C., Hantraye P., Guillon R., Duquesnoy N., Soussaline F., Naquet R., Comar D., Mazière M. 76Br-bromospiroperidol: a new tool for quantitative in-vivo imaging of neuroleptic receptors. Life Sci. 1984 Sep 24;35(13):1349–1356. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90391-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Iwata K. [3H]Ro 22-1319 (piquindone) binds to the D2 dopaminergic receptor subtype in a sodium-dependent manner. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):430–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J., Synder S. H. Relationship of neuroleptic drug effects at brain dopamine, serotonin, alpha-adrenergic, and histamine receptors to clinical potency. Am J Psychiatry. 1980 Dec;137(12):1518–1522. doi: 10.1176/ajp.137.12.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Ulpian C., Bergeron C., Riederer P., Jellinger K., Gabriel E., Reynolds G. P., Tourtellotte W. W. Bimodal distribution of dopamine receptor densities in brains of schizophrenics. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):728–731. doi: 10.1126/science.6147018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Drug and neurotransmitter receptors in the brain. Science. 1984 Apr 6;224(4644):22–31. doi: 10.1126/science.6322304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Martres M. P., Schwartz J. C. Three classes of dopamine receptor (D-2, D-3, D-4) identified by binding studies with 3H-apomorphine and 3H-domperidone. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980;315(2):89–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00499251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spano P. F., Govoni S., Trabucchi M. Studies on the pharmacological properties of dopamine receptors in various areas of the central nervous system. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1978;19:155–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoof J. C., Kebabian J. W. Opposing roles for D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors in efflux of cyclic AMP from rat neostriatum. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):366–368. doi: 10.1038/294366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H. N., Jr, Burns H. D., Dannals R. F., Wong D. F., Langstrom B., Duelfer T., Frost J. J., Ravert H. T., Links J. M., Rosenbloom S. B. Imaging dopamine receptors in the human brain by positron tomography. Science. 1983 Sep 23;221(4617):1264–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.6604315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M. J., Kilbourn M. R., Mathias C. J., Mintun M. A., Raichle M. E. Comparison in animal models of 18F-spiroperidol and 18F-haloperidol: potential agents for imaging the dopamine receptor. Life Sci. 1983 Oct 24;33(17):1687–1693. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90725-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]