Abstract
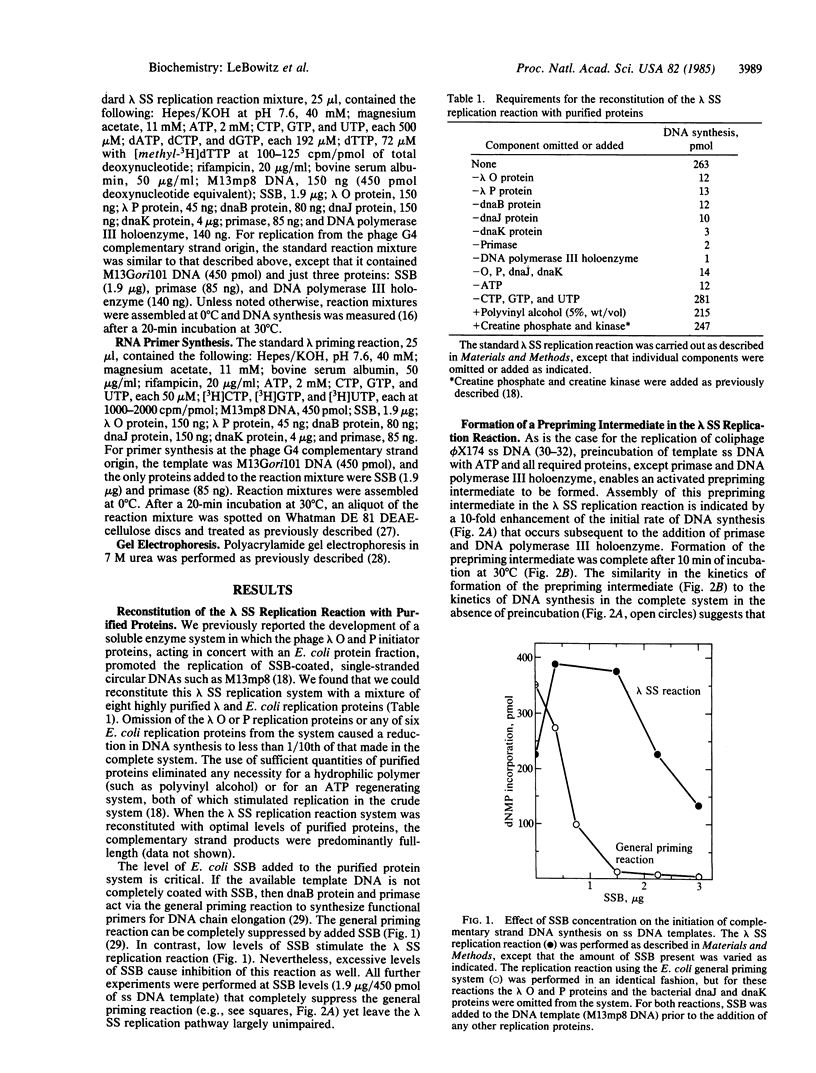
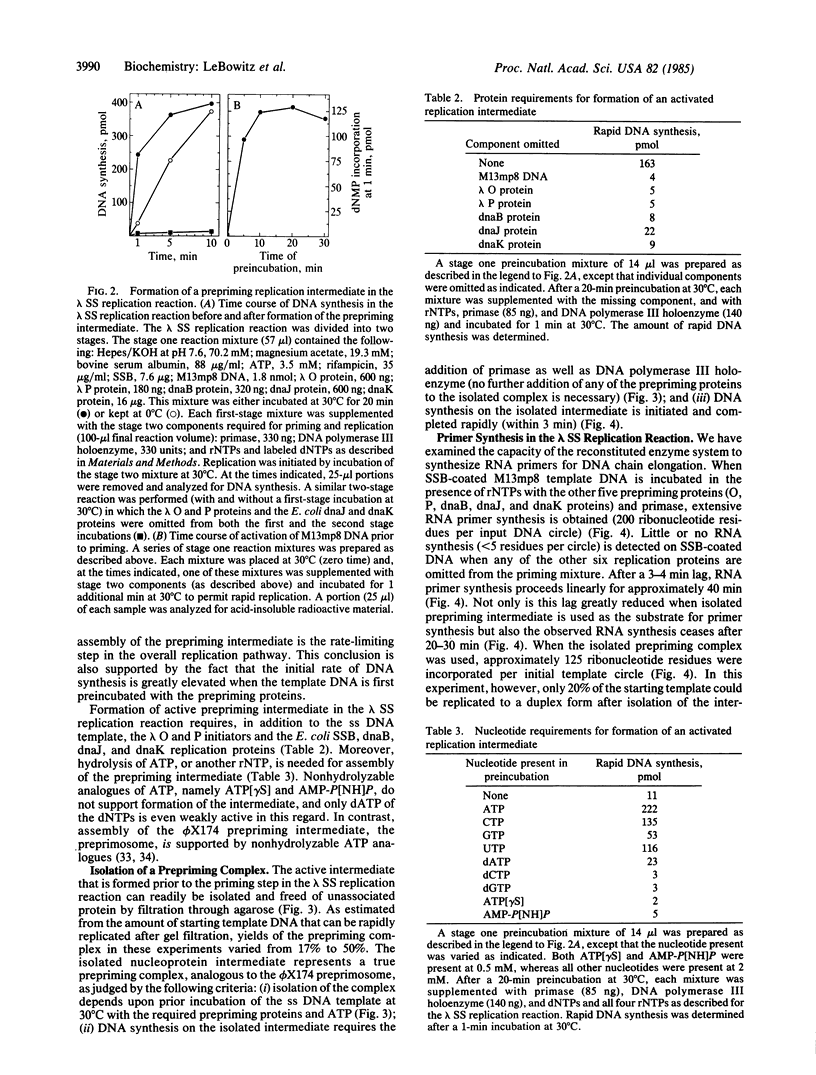
Initiation of bacteriophage lambda DNA replication at the chromosomal origin depends on the lambda O and P replication proteins. These two viral initiators, together with an Escherichia coli protein fraction, promote the replication in vitro of single-stranded circular DNA chromosomes such as that of bacteriophage M13. This nonspecific strand initiation reaction, which we have termed the "lambda single-strand replication reaction," has now been established with eight purified proteins, each of which is also required for replication of the phage lambda chromosome in vivo. An early rate-limiting step in the overall reaction is the ATP-dependent assembly of an activated nucleoprotein prepriming complex. In this step the lambda O and P initiators cooperate with the E. coli dnaJ and dnaK proteins to transfer the bacterial dnaB protein onto M13 DNA that is coated with the single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Multiple RNA primers are synthesized on each DNA circle when isolated prepriming complex is incubated with primase and rNTPs. In the complete system, DNA polymerase III holoenzyme extends the first primer synthesized into full-length complementary strands. Because the properties of this system are closely analogous to those found for the replication of phi X174 viral DNA by E. coli proteins, we infer that a mobile prepriming or priming complex (primosome) operates in the lambda single-strand replication reaction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderl A., Klein A. Replication of lambda dv DNA in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1733–1740. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Kornberg A. A general priming system employing only dnaB protein and primase for DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4308–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Kornberg A. Unique primed start of phage phi X174 DNA replication and mobility of the primosome in a direction opposite chain synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):69–73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Low R. L., Kornberg A. Movement and site selection for priming by the primosome in phage phi X174 DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):707–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Low R., Kobori J., Shlomai J., Kornberg A. Mechanism of dnaB protein action. V. Association of dnaB protein, protein n', and other repriming proteins in the primosome of DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5273–5280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Dodson M., Better M., Roberts J. D., McMacken R. The role of specialized nucleoprotein structures in site-specific recombination and initiation of DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:727–733. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., McLeester C., Dove W. F. Specificity determinants for bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. I. A chain of interactions that controls the initiation of replication. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 5;126(2):195–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C. P. A new bacterial gene (groPC) which affects lambda DNA replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Feb 28;151(1):35–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00446910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein A., Lanka E., Schuster H. Isolation of a complex between the P protein of phage lambda and the dnaB protein of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R. The bacteriophage lambda O and P protein initiators promote the replication of single-stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3069–3088. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry C., Kornberg A. DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. Purification and resolution into subunits. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6478–6484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMacken R., Kornberg A. A multienzyme system for priming the replication of phiX174 viral DNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3313–3319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMacken R., Ueda K., Kornberg A. Migration of Escherichia coli dnaB protein on the template DNA strand as a mechanism in initiating DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray D. S., Hines J. C., Kim M. H., Imber R., Nomura N. M13 vectors for selective cloning of sequences specifying initiation of DNA synthesis on single-stranded templates. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90160-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., McMacken R. The bacteriophage lambda O replication protein: isolation and characterization of the amplified initiator. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7435–7452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowen L., Kornberg A. Primase, the dnaG protein of Escherichia coli. An enzyme which starts DNA chains. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):758–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Uchida H. Initiation of the DNA replication of bacteriophage lambda in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A. M. DNA replication--bacteriophage lambda. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;78:201–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Matsubara K. Purified bacteriophage lambda O protein binds to four repeating sequences at the lambda replication origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1789–1799. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Matsubara K. Replication of lambda dv plasmid in vitro promoted by purified lambda O and P proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7639–7643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., McMacken R., Kornberg A. dnaB protein of Escherichia coli. Purification and role in the replication of phiX174 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):261–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner J. H., McMacken R., Kornberg A. Isolation of an intermediate which precedes dnaG RNA polymerase participation in enzymatic replication of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):752–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner S. H. DNA replication proteins of Escherichia coli and phage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):303–310. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner S., Hurwitz J. Conversion of phiX174 viral DNA to double-stranded form by purified Escherichia coli proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Mallory J. B., Roberts J. D., LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R. Initiation of bacteriophage lambda DNA replication in vitro with purified lambda replication proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6176–6180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., McMacken R. Regulation of expression of the Escherichia coli dnaG gene and amplification of the dnaG primase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4907–4911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yochem J., Uchida H., Sunshine M., Saito H., Georgopoulos C. P., Feiss M. Genetic analysis of two genes, dnaJ and dnaK, necessary for Escherichia coli and bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Aug 4;164(1):9–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00267593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli dnaK replication protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8820–8825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Gorska I., Taylor K., Georgopoulos C. Bacteriophage lambda replication proteins: formation of a mixed oligomer and binding to the origin of lambda DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):401–406. doi: 10.1007/BF00436186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein of Escherichia coli possesses an ATPase and autophosphorylating activity and is essential in an in vitro DNA replication system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6431–6435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




