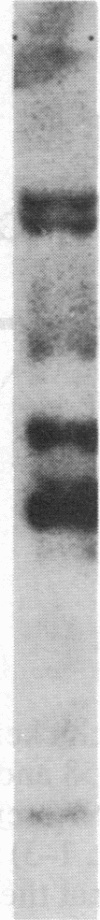
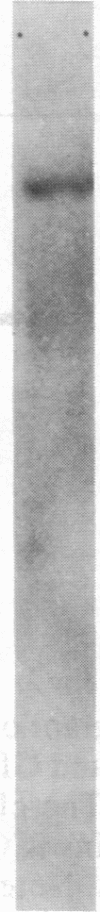
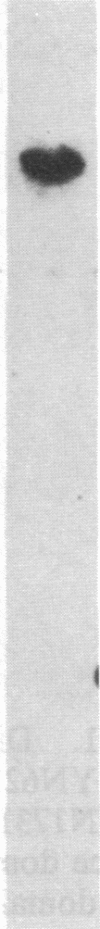
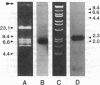
Abstract
Type IX collagen is a disulfide-bonded protein first isolated from hyaline cartilage. The structure of this collagen is unusual in that the molecules contain three triple-helical domains interspersed with noncollagenous regions. The molecules are heterotrimers composed of three genetically distinct polypeptide chains. In our laboratory, cDNAs specific for two of these polypeptide chains have recently been isolated. Here we report on the isolation of genomic clones by use of these cDNAs as probes for screening a chicken genomic library. Nucleotide sequence analysis of these clones shows that the exon structure of type IX collagen genes is fundamentally different from the exon structure of the genes for the fibrillar collagen types I-III. Whereas the sizes of exons in fibrillar collagen genes are related to a basic 54-base-pair coding unit, the exons of type IX collagen genes show a large variation in size and do not appear to be related to a 54-base-pair unit. We propose, therefore, that type IX collagen genes belong to a class of vertebrate collagen genes distinct from that of fibrillar collagens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd C. D., Tolstoshev P., Schafer M. P., Trapnell B. C., Coon H. C., Kretschmer P. J., Nienhuis A. W., Crystal R. G. Isolation and characterization of a 15-kilobase genomic sequence coding for part of the Pro alpha 2 chain of sheep type I collagen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3212–3220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., de Wet W., Bernard M., Ding J. F., Morabito M., Myers J., Williams C., Ramirez F. Human pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene structure reveals evolutionary conservation of a pattern of introns and exons. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):337–340. doi: 10.1038/310337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson L. A., Ninomiya Y., Bernard M. P., Pesciotta D. M., Parsons J., Green G., Eikenberry E. F., de Crombrugghe B., Vogeli G., Pastan I. The exon/intron structure of the 3'-region of the pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8407–8415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M., Cox G. N., Hirsh D. Comparisons of the complete sequences of two collagen genes from Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):599–606. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne R., van der Rest M., Weaver D. C., Butler W. T. The structure of a small collagenous fragment isolated from chicken hyaline cartilage. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(2):133–141. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson J. M., Friedman J., McCarthy B. J. DNA sequence analysis of a mouse pro alpha 1 (I) procollagen gene: evidence for a mouse B1 element within the gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1362–1371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson J. M., Natzle J., Friedman J., McCarthy B. J. Expression and novel structure of a collagen gene in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1761–1765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Dickson L. A., de Wet W. J., Bernard M. P., Chu M. L., Di Liberto M., Pepe G., Sangiorgi F. O., Ramirez F. Analysis of the 3' end of the human pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Utilization of multiple polyadenylation sites in cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10128–10135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya Y., Olsen B. R. Synthesis and characterization of cDNA encoding a cartilage-specific short collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Vogeli G., Mudryj M., Avvedimento V. E., Sullivan M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Isolation and characterization of overlapping genomic clones covering the chicken alpha 2 (type I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7059–7063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek P. A., Merlino G. T., Peters N. K., Cohn V. H., Moore G. P., Kleinsmith L. J. Characterization of five members of the actin gene family in the sea urchin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 28;656(2):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandell L. J., Prentice H. L., Kravis D., Upholt W. B. Structure and sequence of the chicken type II procollagen gene. Characterization of the region encoding the carboxyl-terminal telopeptide and propeptide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7826–7834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandell L. J., Yamada Y., Dorfman A., Upholt W. B. Identification of genomic DNA coding for chicken type II procollagen. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11617–11621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate V., Finer M., Boedtker H., Doty P. Procollagen genes: further sequence studies and interspecies comparisons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1039–1049. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Cheah K. S., Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., Solomon E., Flavell R. A. Isolation and characterization of a human collagen alpha 1(I)-like gene from a cosmid library. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1981–1994. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Morimoto R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Fine structural analysis of the chicken pro alpha 2 collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):712–716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Avvedimento V. E., Mudryj M., Ohkubo H., Vogeli G., Irani M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. The collagen gene: evidence for its evolutinary assembly by amplification of a DNA segment containing an exon of 54 bp. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):887–892. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90565-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Liau G., Mudryj M., Obici S., de Crombrugghe B. Conservation of the sizes for one but not another class of exons in two chick collagen genes. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):333–337. doi: 10.1038/310333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Mudryj M., Sullivan M., de Crombrugghe B. Isolation and characterization of a genomic clone encoding chick alpha 1 type III collagen. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2758–2761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Rest M., Mayne R., Ninomiya Y., Seidah N. G., Chretien M., Olsen B. R. The structure of type IX collagen. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):220–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]