Abstract
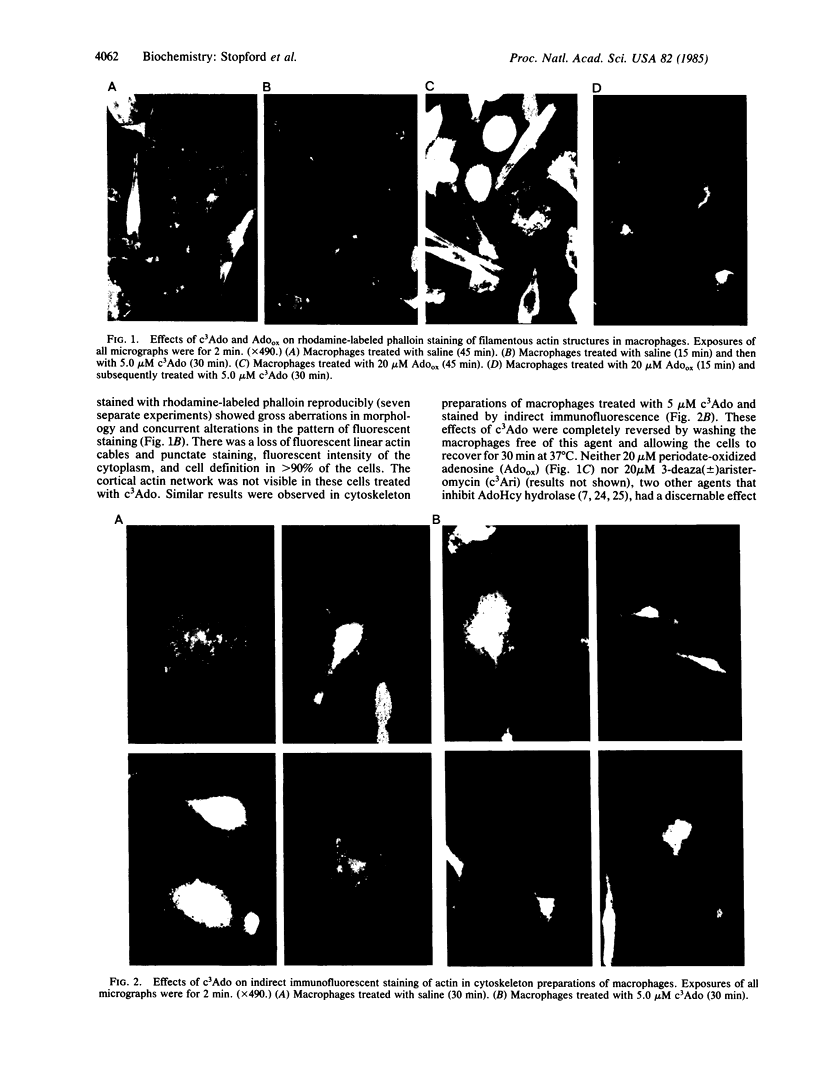
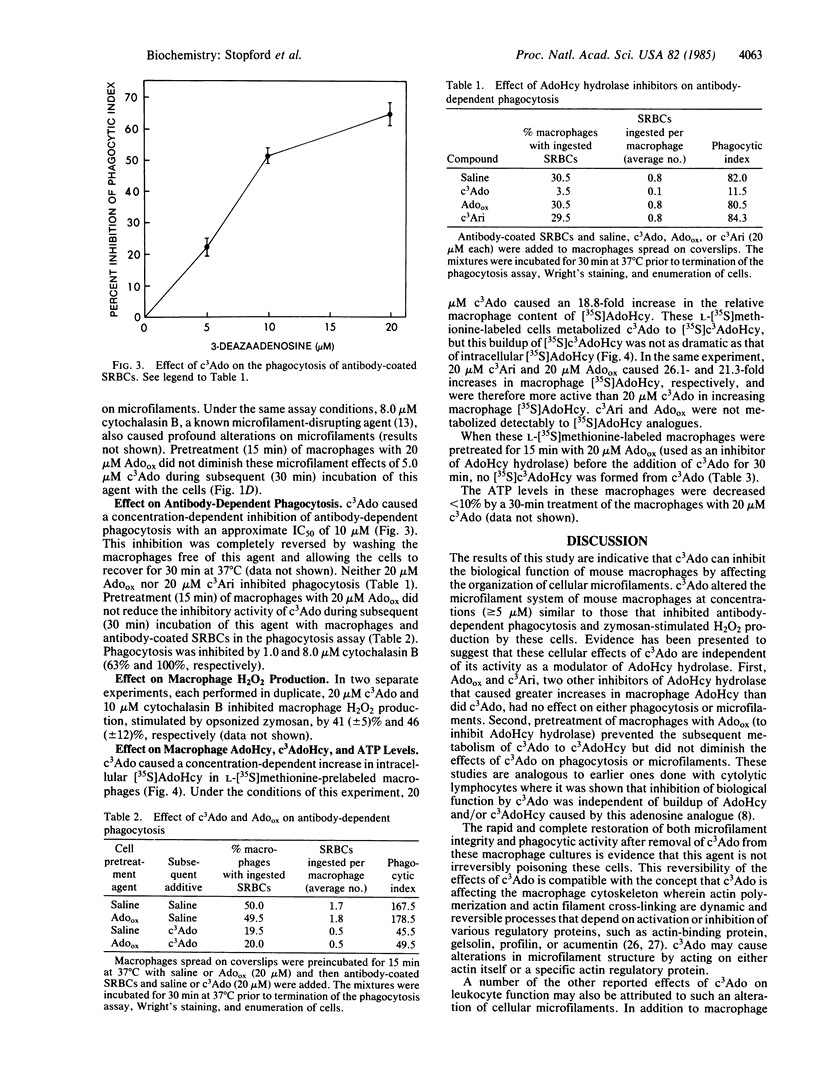
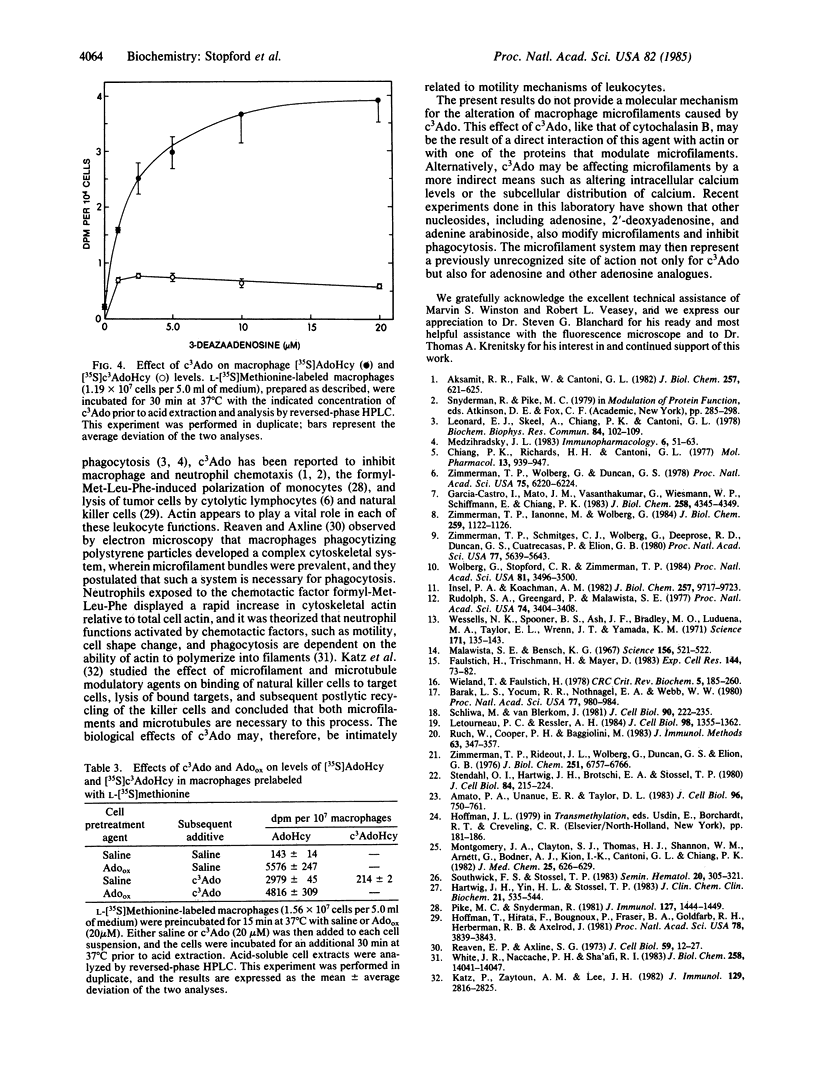
3-Deazaadenosine (c3Ado) has been reported to inhibit a number of cellular functions. These biological effects of c3Ado have generally been attributed to its ability to act as inhibitor and substrate of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. In this report, it is revealed by fluorescence microscopy that c3Ado caused disorganization of the microfilament system of mouse macrophages at concentrations (greater than or equal to 5 microM) similar to those that inhibited antibody-dependent phagocytosis and zymosan-stimulated H2O2 production by these cells. Inhibition of phagocytosis and perturbation of microfilaments by c3Ado were completely abrogated by washing the macrophages free of this agent and allowing the cells a 30-min recovery period. Furthermore, these effects of c3Ado on phagocytosis and microfilaments appeared to be independent of the increase in S-adenosylhomocysteine and S-3-deazaadenosylhomocysteine that occurred in these macrophages. First, periodate-oxidized adenosine and 3-deaza(+/-)aristeromycin, two other inhibitors of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase that caused greater increases in macrophage S-adenosylhomocysteine than did c3Ado, had no effect on either phagocytosis or microfilaments. Second, pretreatment of macrophages with periodate-oxidized adenosine (to inhibit S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase) prevented the subsequent metabolism of c3Ado to S-3-deazaadenosylhomocysteine but did not diminish the effects of c3Ado on phagocytosis or microfilaments. These results demonstrate that c3Ado can perturb the microfilament system of cells and provide an alternative mechanism for the biological effects of c3Ado.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksamit R. R., Falk W., Cantoni G. L. Inhibition of chemotaxis by S-3-deazaadenosylhomocysteine in a mouse macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):621–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amato P. A., Unanue E. R., Taylor D. L. Distribution of actin in spreading macrophages: a comparative study on living and fixed cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):750–761. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak L. S., Yocum R. R., Nothnagel E. A., Webb W. W. Fluorescence staining of the actin cytoskeleton in living cells with 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-phallacidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang P. K., Richards H. H., Cantoni G. L. S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase: analogues of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine as potential inhibitors. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;13(5):939–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulstich H., Trischmann H., Mayer D. Preparation of tetramethylrhodaminyl-phalloidin and uptake of the toxin into short-term cultured hepatocytes by endocytosis. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Mar;144(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Castro I., Mato J. M., Vasanthakumar G., Wiesmann W. P., Schiffmann E., Chiang P. K. Paradoxical effects of adenosine on neutrophil chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4345–4349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. How phagocytic leukocytes move. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1983 Sep;21(9):535–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman T., Hirata F., Bougnoux P., Fraser B. A., Goldfarb R. H., Herberman R. B., Axelrod J. Phospholipid methylation and phospholipase A2 activation in cytotoxicity by human natural killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3839–3843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Koachman A. M. Cytochalasin B enhances hormone and cholera toxin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation in S49 lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9717–9723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Zaytoun A. M., Lee J. H., Jr Mechanisms of human cell-mediated cytotoxicity. III. Dependence of natural killing on microtubule and microfilament integrity. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2816–2825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Skeel A., Chiang P. K., Cantoni G. L. The action of the adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase inhibitor, 3-deazaadenosine, on phagocytic function of mouse macrophages and human monocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 14;84(1):102–109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneau P. C., Ressler A. H. Inhibition of neurite initiation and growth by taxol. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1355–1362. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E., Bensch K. G. Human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: demonstration of microtubules and effect of colchicine. Science. 1967 Apr 28;156(3774):521–522. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3774.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medzihradsky J. L. Effects of 3-deazaadenosine on antibody-dependent cellular cytoxicity and phagocytosis: reciprocal inhibition and augmentation of these functions in various effector cell populations. Immunopharmacology. 1983 Jun;6(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(83)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery J. A., Clayton S. J., Thomas H. J., Shannon W. M., Arnett G., Bodner A. J., Kion I. K., Cantoni G. L., Chiang P. K. Carbocyclic analogue of 3-deazaadenosine: a novel antiviral agent using S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase as a pharmacological target. J Med Chem. 1982 Jun;25(6):626–629. doi: 10.1021/jm00348a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike M. C., Snyderman R. Transmethylation reactions are required for initial morphologic and biochemical responses of human monocytes to chemoattractants. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1444–1449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Axline S. G. Subplasmalemmal microfilaments and microtubules in resting and phagocytizing cultivated macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1973 Oct;59(1):12–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruch W., Cooper P. H., Baggiolini M. Assay of H2O2 production by macrophages and neutrophils with homovanillic acid and horse-radish peroxidase. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Oct 28;63(3):347–357. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph S. A., Greengard P., Malawista S. E. Effects of colchicine on cyclic AMP levels in human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3404–3408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M., van Blerkom J. Structural interaction of cytoskeletal components. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):222–235. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southwick F. S., Stossel T. P. Contractile proteins in leukocyte function. Semin Hematol. 1983 Oct;20(4):305–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O. I., Hartwig J. H., Brotschi E. A., Stossel T. P. Distribution of actin-binding protein and myosin in macrophages during spreading and phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):215–224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Spooner B. S., Ash J. F., Bradley M. O., Luduena M. A., Taylor E. L., Wrenn J. T., Yamada K. Microfilaments in cellular and developmental processes. Science. 1971 Jan 15;171(3967):135–143. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3967.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. R., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I. Stimulation by chemotactic factor of actin association with the cytoskeleton in rabbit neutrophils. Effects of calcium and cytochalasin B. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14041–14047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T., Faulstich H. Amatoxins, phallotoxins, phallolysin, and antamanide: the biologically active components of poisonous Amanita mushrooms. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978 Dec;5(3):185–260. doi: 10.3109/10409237809149870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg G., Stopford C. R., Zimmerman T. P. Antagonism by taxol of effects of microtubule-disrupting agents on lymphocyte cAMP metabolism and cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3496–3500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. P., Iannone M., Wolberg G. 3-Deazaadenosine. S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase-independent mechanism of action in mouse lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1122–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. P., Rideout J. L., Wolberg G., Duncan G. S., Elion G. B. 2-Fluoroadenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. A metabolite of 2-fluoroadenosine in mouse cytotoxic lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6757–6766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. P., Schmitges C. J., Wolberg G., Deeprose R. D., Duncan G. S., Cuatrecasas P., Elion G. B. Modulation of cyclic AMP metabolism by S-adenosylhomocysteine and S-3-deazaadenosylhomocysteine in mouse lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5639–5643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. P., Wolberg G., Duncan G. S. Inhibition of lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis by 3-deazaadenosine: evidence for a methylation reaction essential to cytolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6220–6224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]