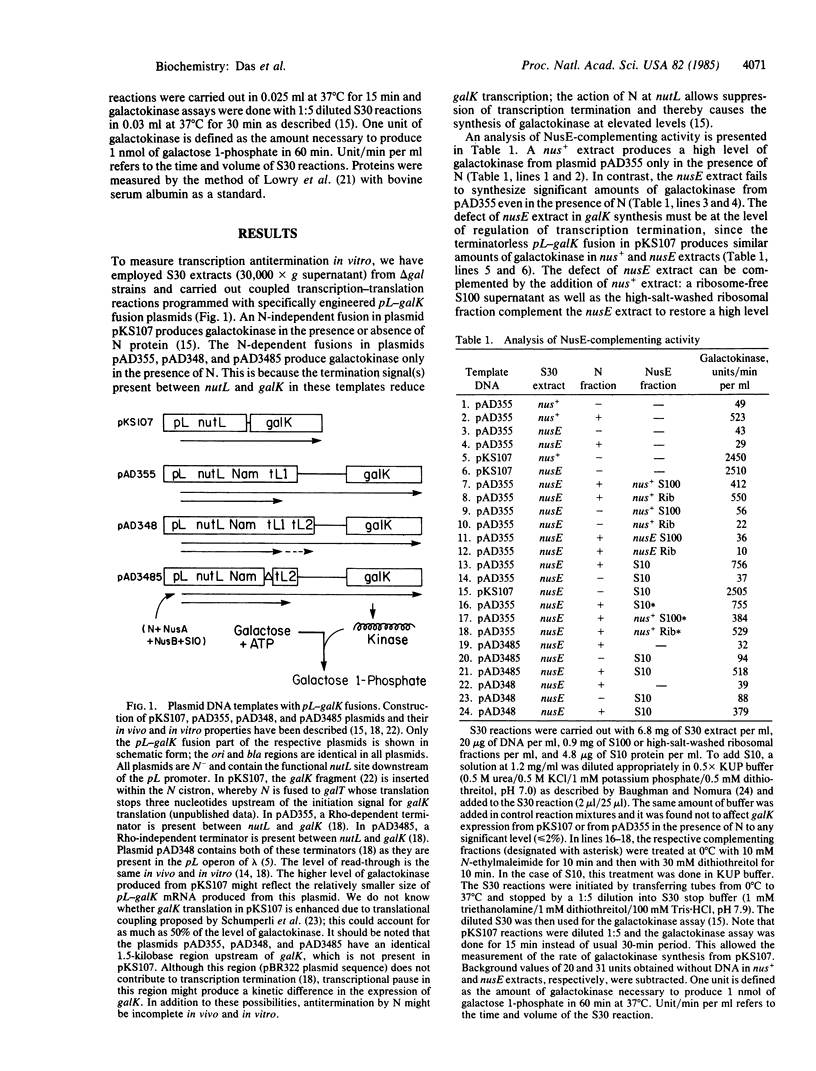
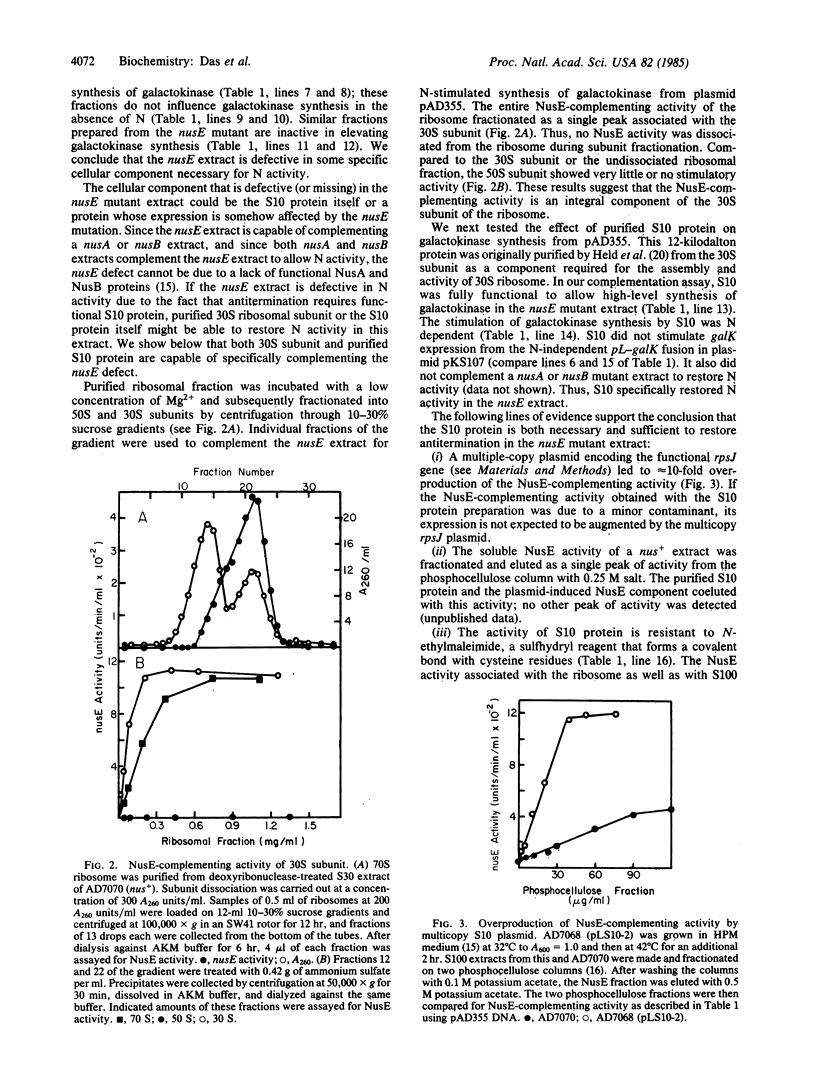
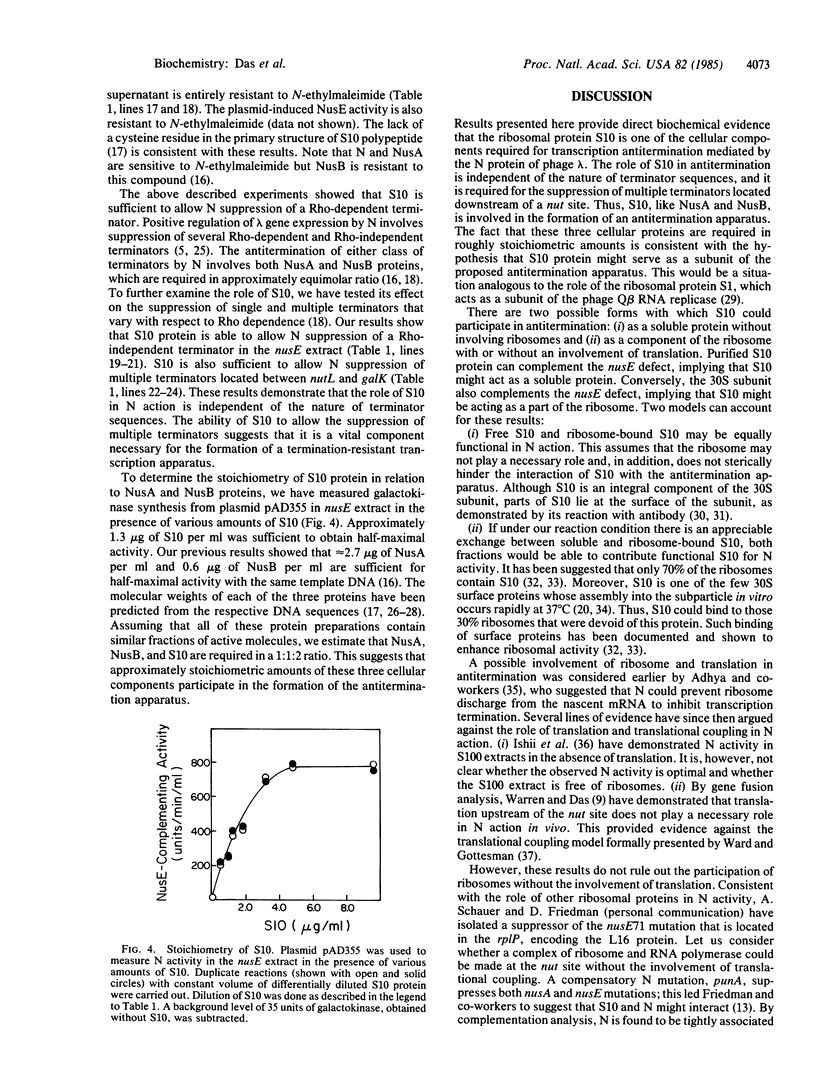
Abstract
Bacteriophage lambda N gene product acts to modify host RNA polymerase allowing the formation of a termination-resistant transcription apparatus. Previous studies have demonstrated that the nusE71 mutation that has altered the ribosomal protein S10 prevents N action in vivo. Using a coupled transcription-translation system, we demonstrate here that purified S10 protein as well as the 30S ribosomal subunit is sufficient to restore N activity in the nusE mutant extract, allowing antitermination of Rho-dependent and Rho-independent terminators. This provides direct biochemical evidence that the S10 protein itself is one of the cellular components necessary for the formation of an antitermination apparatus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M., De Crombrugghe B. Release of polarity in Escherichia coli by gene N of phage lambda: termination and antitermination of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2534–2538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughman G., Nomura M. Localization of the target site for translational regulation of the L11 operon and direct evidence for translational coupling in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):979–988. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90555-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Gottesman M. E., Wardwell J., Trisler P., Gottesman S. lambda mutation in the Escherichia coli rho gene that inhibits the N protein activity of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5530–5534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Wolska K. Transcription antitermination in vitro by lambda N gene product: requirement for a phage nut site and the products of host nusA, nusB, and nusE genes. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90537-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C. Altered reading of genetic signals fused to the N operon of bacteriophage lambda: genetic evidence for modification of polymerase by the protein product of the N gene. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Baumann M., Baron L. S. Cooperative effects of bacterial mutations affecting lambda N gene expression. I. Isolation and characterization of a nusB mutant. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Schauer A. T., Baumann M. R., Baron L. S., Adhya S. L. Evidence that ribosomal protein S10 participates in control of transcription termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1115–1118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Wilgus G. S., Mural R. J. Gene N regulator function of phage lambda immun21: evidence that a site of N action differs from a site of N recognition. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 25;81(4):505–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90519-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B., Das A. nusB: a protein factor necessary for transcription antitermination in vitro by phage lambda N gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6305–6309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Li J. The nusA gene protein of Escherichia coli. Its identification and a demonstration that it interacts with the gene N transcription anti-termination protein of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Reconstitution of Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal subunits from purified molecular components. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5720–5730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Hatada E., Maekawa T., Imamoto F. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the nusB gene of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4987–4995. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Ihara M., Maekawa T., Nakamura Y., Uchida H., Imamoto F. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned nusA gene and its flanking region of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3333–3342. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Salstrom J. S., Sugino Y., Szybalski W., Imamoto F. A biochemical assay for the transcription-antitermination function of the coliphage lambda N gene product. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan L., Winkelmann D. A., Lake J. A. Ribosomal proteins S3, S6, S8 and S10 of Escherichia coli localized on the external surface of the small subunit by immune electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):193–214. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. Structure and function of the bacterial ribosome. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41(10):377–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G., Voynow P., Hardy S. J., Randall L., Lutter L. Physical and functional heterogeneity of E. coli ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:17–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Archer R., Zengel J. M. Transcription of the S10 ribosomal protein operon is regulated by an attenuator in the leader. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins P. O., Nomura M. Regulation of the S10 ribosomal protein operon in E. coli: nucleotide sequence at the start of the operon. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90303-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salstrom J. S., Szybalski W. Coliphage lambdanutL-: a unique class of mutants defective in the site of gene N product utilization for antitermination of leftward transcription. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):195–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salstrom J. S., Szybalski W. Transcription termination sites in the major leftward operon of coliphage lambda. Virology. 1978 Jul 15;88(2):252–262. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90282-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümperli D., McKenney K., Sobieski D. A., Rosenberg M. Translational coupling at an intercistronic boundary of the Escherichia coli galactose operon. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):865–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90291-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa T., Imamoto F. Evidence of read-through at the termination signal for transcription of the trp operon. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swindle J., Ajioka J., Dawson D., Myers R., Carroll D., Georgopoulos C. The nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli K12 nusB (groNB) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4977–4985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahba A. J., Miller M. J., Niveleau A., Landers T. A., Carmichael G. G., Weber K., Hawley D. A., Slobin L. I. Subunit I of G beta replicase and 30 S ribosomal protein S1 of Escherichia coli. Evidence for the identity of the two proteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3314–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. F., DeLong A., Gottesman M. E. Escherichia coli nusB mutations that suppress nusA1 exhibit lambda N specificity. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):73–85. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. F., Gottesman M. E. Suppression of transcription termination by phage lambda. Science. 1982 May 28;216(4549):946–951. doi: 10.1126/science.6281888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren F., Das A. Formation of termination-resistant transcription complex at phage lambda nut locus: effects of altered translation and a ribosomal mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3612–3616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G. Architecture of prokaryotic ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:35–65. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Nomura M. Organization of genes for transcription and translation in the rif region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):584–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.584-594.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Mudryj M., DiLauro R., Gottesman M. Specificity of the bacteriophage lambda N gene product (pN): nut sequences are necessary and sufficient for antitermination by pN. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



