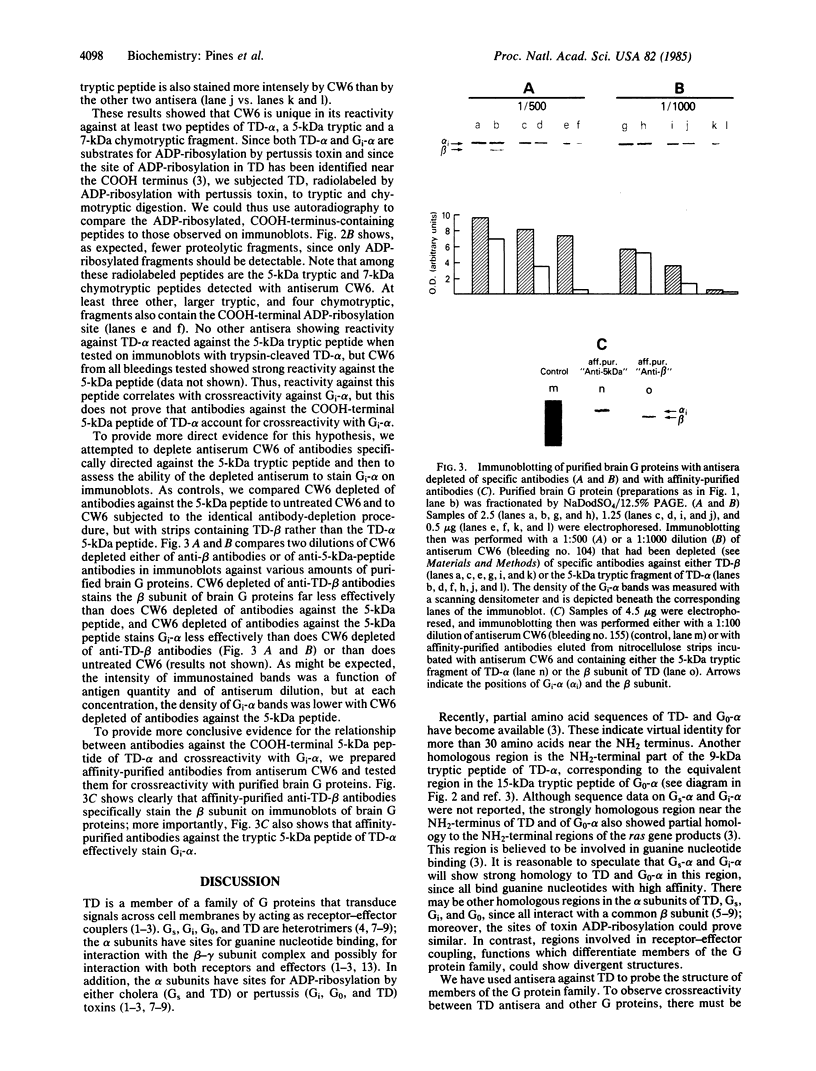
Abstract
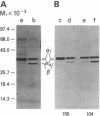
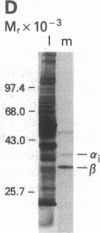
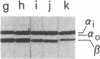
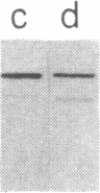
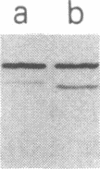
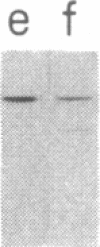
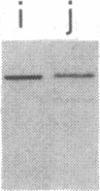
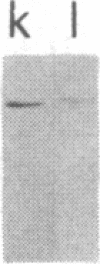
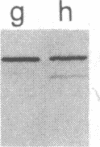
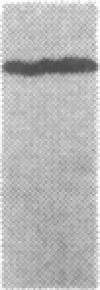
We tested 18 antisera showing reactivity against the alpha subunit of transducin, the guanine nucleotide binding protein from rod outer segment, for crossreactivity against the 40- and 39-kDa guanine nucleotide binding proteins purified from bovine brain. A single antiserum, CW6, showed crossreactivity, and this was predominantly against the 40-kDa protein. Immunoblots of the tryptic fragments of transducin alpha subunit with multiple antisera raised against that subunit showed that only CW6 recognizes a COOH-terminal 5-kDa peptide that includes the site of pertussis toxin ADP-ribosylation. Antibodies against the 5-kDa peptide, affinity-purified from CW6, specifically react with the 40-kDa brain protein on immunoblots. The results show that the 39- and 40-kDa guanine nucleotide binding proteins from brain differ immunochemically and that the COOH-terminal 5-kDa peptide of transducin alpha subunit is homologous to a region in the 40-kDa brain protein. We speculate that this homologous region may be in a domain that confers specificity for receptor interactions of guanine nucleotide binding proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Benovic J. L., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Gierschik P., Somers R., Spiegel A. M., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Specificity of the functional interactions of the beta-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins reconstituted in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1493–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. I. Separation and reconstitution of the subunits. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10495–10502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Codina J., Simons C., Birnbaumer L., Spiegel A. Antisera against a guanine nucleotide binding protein from retina cross-react with the beta subunit of the adenylyl cyclase-associated guanine nucleotide binding proteins, Ns and Ni. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Risinger R., Birnbaumer L. Identification of a gamma subunit associated with the adenylyl cyclase regulatory proteins Ns and Ni. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2039–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Simon M. I., Teplow D. B., Robishaw J. D., Gilman A. G. Homologies between signal transducing G proteins and ras gene products. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.6436980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaho Y., Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Hewlett E. L., Moss J., Vaughan M. Rhodopsin-enhanced GTPase activity of the inhibitory GTP-binding protein of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7378–7381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. ADP ribosylation of the specific membrane protein of C6 cells by islet-activating protein associated with modification of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7210–7216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Rapiejko P. J., Garciá-Sáinz J. A. Pertussis toxin catalyzes the ADP-ribosylation of two distinct peptides, 40 and 41 kDa, in rat fat cell membranes. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. R., Gilman A. G. The regulatory components of adenylate cyclase and transducin. A family of structurally homologous guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7059–7063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Klee W. A. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Ni) purified from bovine brain is a high affinity GTPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2057–2063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekura R. D., Fish F., Manclark C. R., Meade B., Zhang Y. L. Pertussis toxin. Affinity purification of a new ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14647–14651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozawa T., Uchida S., Martin E., Cafiso D., Hubbell W., Bitensky M. Additional component required for activity and reconstitution of light-activated vertebrate photoreceptor GTPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1408–1411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M., Gierschik P., Levine M. A., Downs R. W., Jr Clinical implications of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins as receptor-effector couplers. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 3;312(1):26–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501033120106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taparowsky E., Shimizu K., Goldfarb M., Wigler M. Structure and activation of the human N-ras gene. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]