Abstract
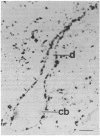
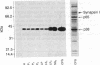
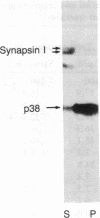
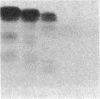
A protein with an apparent molecular mass of 38,000 daltons designated p38 was found in synaptic vesicles from rat brain. The subcellular distribution of p38 and some of its properties were determined with the aid of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. The subcellular distribution of p38 was similar to that of synapsin I, a synaptic-vesicle specific phosphoprotein. p38 in the synaptic vesicle fraction purified by controlled-pore glass bead chromatography showed an enrichment of more than 20-fold over the crude homogenate. Immunostaining of sections through various brain regions revealed an intense labeling of most, and possibly all, nerve terminals. Only faint reaction in the region of the Golgi apparatus and no detectable labeling of axons and dendrites was observed. Two-dimensional electrophoresis revealed that p38 has an acidic pI. Solubilization experiments, as well as phase separation experiments using Triton X-114, indicated that p38 is an integral membrane protein. Binding of antibodies to intact synaptic vesicles, as well as controlled proteolytic digestion of intact and detergent-treated vesicles, revealed that p38 has a domain exposed on the cytoplasmic surface.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson S. S., Kelly R. B. A highly antigenic proteoglycan-like component of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11082–11091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Cameron R., Greengard P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. I. Its general distribution in synapses of the central and peripheral nervous system demonstrated by immunofluorescence in frozen and plastic sections. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Harris S. M., Jr, Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Synapsin I (Protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. II. Its specific association with synaptic vesicles demonstrated by immunocytochemistry in agarose-embedded synaptosomes. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1355–1373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R. C., Dahmus M. E. Rapid visualization of protein bands in preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogenraad N., Helman T., Hoogenraad J. The effect of pre-injection of mice with pristane on ascites tumour formation and monoclonal antibody production. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jul 29;61(3):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90225-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Greengard P. A quantitative dot-immunobinding assay for proteins using nitrocellulose membrane filters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1684–1687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March P. E., Thornton E. R. Binding of concanavalin A to calf brain synaptic vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 10;110(3):804–810. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew W. D., Tsavaler L., Reichardt L. F. Identification of a synaptic vesicle-specific membrane protein with a wide distribution in neuronal and neurosecretory tissue. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):257–269. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugnaini E., Dahl A. L. Zinc-aldehyde fixation for light-microscopic immunocytochemistry of nervous tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Dec;31(12):1435–1438. doi: 10.1177/31.12.6355290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy A., Baker R. R., Morris S. J., Whittaker V. P. The preparation and characterization of synaptic vesicles of high purity. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 11;109(2):285–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90531-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy A., Bock E. Synaptin in acetylcholine- and catecholamine-containing synaptic vesicle fractions from brain cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 16;600(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90415-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy A., Várady G., Joó F., Rakonczay Z., Pilc A. Separation of acetylcholine and catecholamine containing synaptic vesicles from brain cortex. J Neurochem. 1977 Sep;29(3):449–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I in nerve terminals: selective association with small synaptic vesicles. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1209–1211. doi: 10.1126/science.6438799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L. F., Kelly R. B. A molecular description of nerve terminal function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:871–926. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renfroe J. B., Chronister R. B., Haycock J. W., Waymire J. C. The localization of tyrosine hydroxylase-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system: methodological considerations. Brain Res Bull. 1984 Jul;13(1):109–126. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(84)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rye D. B., Saper C. B., Wainer B. H. Stabilization of the tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) reaction product: application for retrograde and anterograde tracing, and combination with immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Nov;32(11):1145–1153. doi: 10.1177/32.11.6548485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. P., Loh H. H. Organization of brain synaptic vesicle proteins. J Neurochem. 1981 May;36(5):1749–1757. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Tashiro T. Isolation of synaptosomal plasma membranes from cholinergic nerve terminals and a comparison of their proteins with those of synaptic vesicles. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;101(1):171–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro T., Stadler H. Chemical composition of cholinergic synaptic vesicles from Torpedo marmorata based on improved purification. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):479–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. A., Kelly R. B. Topological organization of proteins in an intracellular secretory organelle: the synaptic vesicle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4126–4130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. H., Obrocki J., Zimmermann C. W. Identification of a proteoglycan antigen characteristic of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. J Neurochem. 1983 Jul;41(1):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. The structure and function of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. The Third Thudichum Lecture. Biochem Soc Trans. 1984 Aug;12(4):561–576. doi: 10.1042/bst0120561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetta J. P., Reeber A., Vincendon G. Glycoproteins from adult rat brain synaptic vesicles. Fractionation on four immobilized lectins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 28;670(3):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zisapel N. Cross-linking of synaptic vesicle proteins. Effect of ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 5;707(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zisapel N., Zurgil N. Studies on synaptic vesicles in mammalian brain characterization of highly purified synaptic vesicles from bovine cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 14;178(2-3):297–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90695-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]