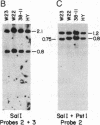
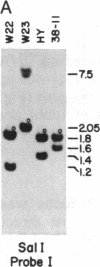
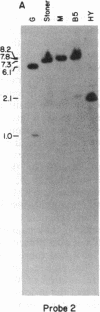
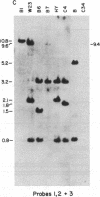
Abstract
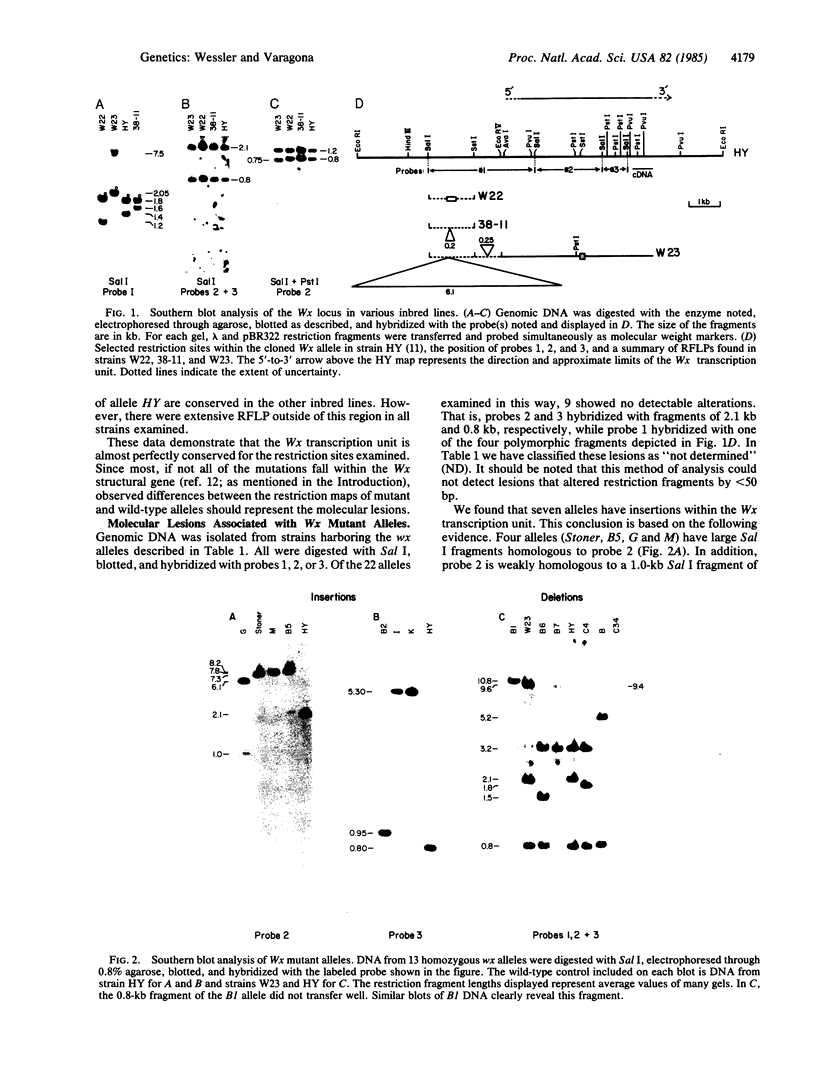
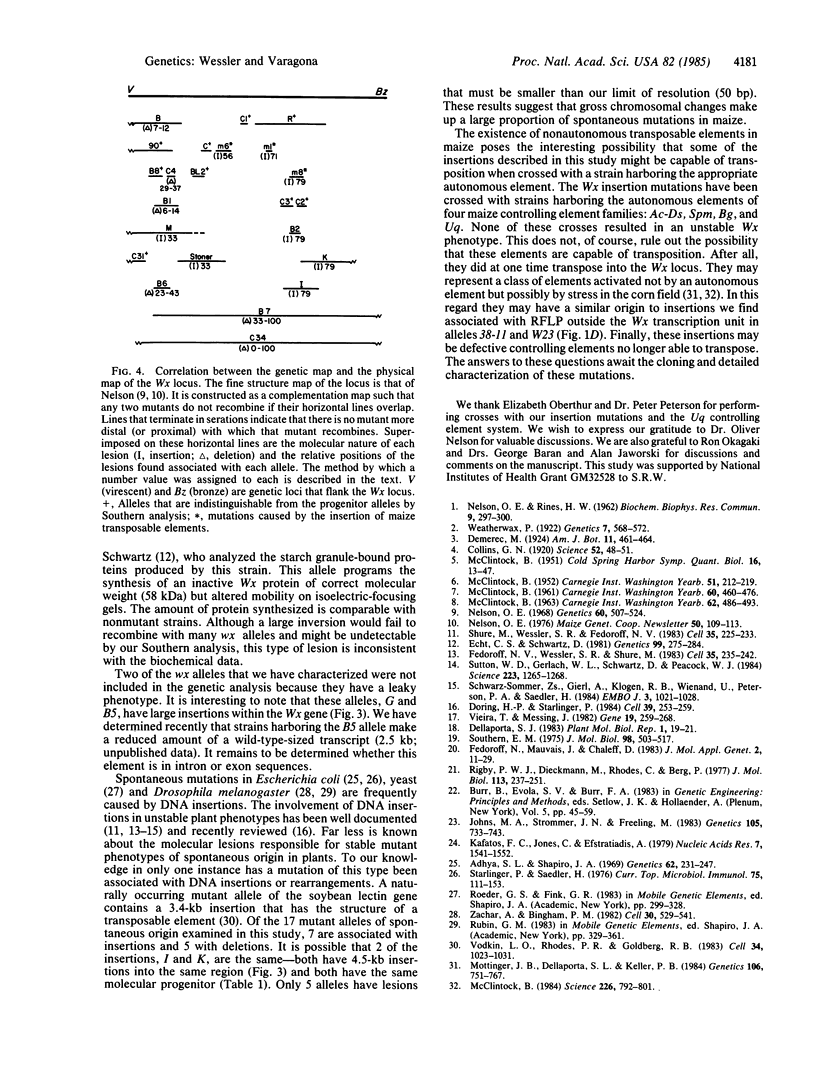
More than 40 mutant alleles of the waxy (Wx) locus of maize are available for molecular analysis. Previous studies have examined the nature of phenotypically unstable Wx mutant alleles caused by insertion of the maize transposable activator (Ac) and dissociation (Ds) elements. In this study we have used Southern blot analysis to characterize the locus in 22 strains harboring wx alleles with stable mutant phenotypes. Of these mutations, 17 are of spontaneous origin, 4 were induced by gamma rays, and 1 was induced by ethyl methanesulfonate. Of these 22 alleles, we find that 13 have either insertions or deletions within the Wx transcription unit. The insertions range in size from 150 base pairs to 6.1 kilobases. For 4 of the 6 deletions identified, the two breakpoints are within the Wx gene. For 9 other alleles we can detect no obvious lesions within or around the transcription unit. Evidence is presented that the insertions and deletions result in the mutant phenotype and are not polymorphisms. This conclusion is based on two findings: (i) a survey of inbred lines revealed only a single instance of polymorphism within the transcription unit, whereas all of the lesions described alter the transcription unit; and (ii) there is an excellent correlation between the position of these lesions on the physical map and their relative position on a fine structure genetic map of the locus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S. L., Shapiro J. A. The galactose operon of E. coli K-12. I. Structural and pleiotropic mutations of the operon. Genetics. 1969 Jun;62(2):231–247. doi: 10.1093/genetics/62.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. N. WAXY MAIZE FROM UPPER BURMA. Science. 1920 Jul 16;52(1333):48–51. doi: 10.1126/science.52.1333.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring H. P., Starlinger P. Barbara McClintock's controlling elements: now at the DNA level. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echt C. S., Schwartz D. Evidence for the Inclusion of Controlling Elements within the Structural Gene at the Waxy Locus in Maize. Genetics. 1981 Oct;99(2):275–284. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Mauvais J., Chaleff D. Molecular studies on mutations at the Shrunken locus in maize caused by the controlling element Ds. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):11–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wessler S., Shure M. Isolation of the transposable maize controlling elements Ac and Ds. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. A., Strommer J. N., Freeling M. Exceptionally High Levels of Restriction Site Polymorphism in DNA near the Maize Adh1 Gene. Genetics. 1983 Nov;105(3):733–743. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.3.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCLINTOCK B. Chromosome organization and genic expression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:13–47. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The significance of responses of the genome to challenge. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):792–801. doi: 10.1126/science.15739260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottinger J. P., Dellaporta S. L., Keller P. B. Stable and unstable mutations in aberrant ratio stocks of maize. Genetics. 1984 Apr;106(4):751–767. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.4.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON O. E., RINES H. W. The enzymatic deficiency in the waxy mutant of maize. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Oct 31;9:297–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson O. E. The WAXY Locus in Maize. II. the Location of the Controlling Element Alleles. Genetics. 1968 Nov;60(3):507–524. doi: 10.1093/genetics/60.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Klösgen R. B., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. The Spm (En) transposable element controls the excision of a 2-kb DNA insert at the wx allele of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1021–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger P., Saedler H. IS-elements in microorganisms. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1976;75:111–152. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66530-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D., Gerlach W. L., Peacock W. J., Schwartz D. Molecular analysis of ds controlling element mutations at the adh1 locus of maize. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1265–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4642.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin L. O., Rhodes P. R., Goldberg R. B. cA lectin gene insertion has the structural features of a transposable element. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1023–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90560-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherwax P. A Rare Carbohydrate in Waxy Maize. Genetics. 1922 Nov;7(6):568–572. doi: 10.1093/genetics/7.6.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Bingham P. M. Regulation of white locus expression: the structure of mutant alleles at the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]