Abstract
The three-dimensional structure of beta 2-microglobulin, the light chain of the major histocompatibility complex class I antigens, has been determined by x-ray crystallography. An electron density map of the bovine protein was calculated at a nominal resolution of 2.9 A by using the methods of multiple isomorphous replacement and electron density modification refinement. The molecule is approximately 45 X 25 X 20 A in size. Almost half of the amino acid residues participate in two large beta structures, one of four strands and the other of three, linked by a central disulfide bond. The molecule thus strongly resembles Ig constant domains in polypeptide chain folding and overall tertiary structure. Amino acid residues that are the same in the sequences of beta 2-microglobulin and Ig constant domains are predominantly in the interior of the molecule, whereas residues conserved among beta 2-microglobulins from different species are both in the interior and on the molecular surface. In the crystals studied, the molecule is clearly monomeric, consistent with the observation that beta 2-microglobulin, unlike Ig constant domains, apparently does not form dimers in vivo but associates with the heavy chains of major histocompatibility complex antigens. Our results demonstrate that, at the level of detailed three-dimensional structure, the light chain of the major histocompatibility class I antigens belongs to a superfamily of structures related to the Ig constant domains.
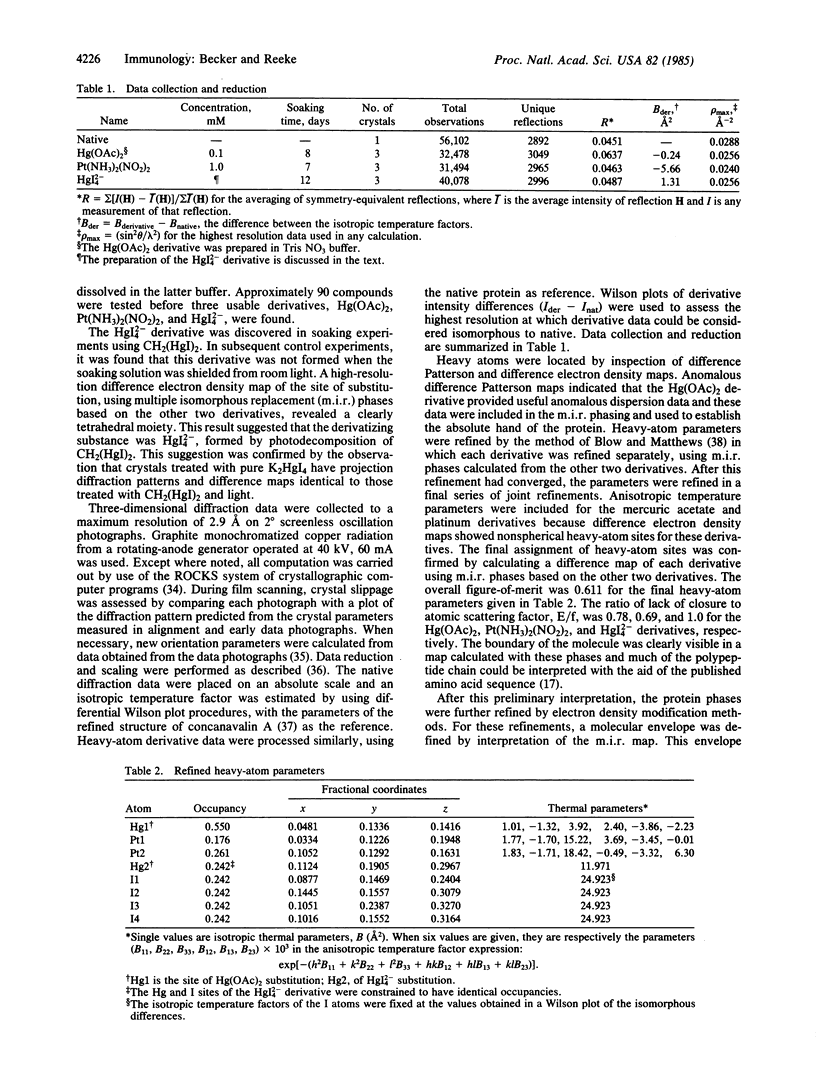
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker J. W., Reeke G. N., Jr, Wang J. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. III. Structure of the monomer and its interactions with metals and saccharides. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1513–1524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J. W., Ziffer J. A., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Crystallographic studies of bovine beta2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3345–3349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggård I., Bearn A. G. Isolation and properties of a low molecular weight beta-2-globulin occurring in human biological fluids. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 10;243(15):4095–4103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. G., Williams A. F., Bayley P. M., Reid K. B. Structural similarities between Thy-1 antigen from rat brain and immunoglobulin. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):341–342. doi: 10.1038/282341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A. Structure and significance of beta2-microglobulin. Fed Proc. 1976 Apr;35(5):1171–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Wang J. L., Berggård I., Peterson P. A. The complete amino acid sequence of beta 2-microglobulin. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4811–4822. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Metzger H. Structural basis of antibody function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:87–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of a human Fc fragment and its complex with fragment B of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus at 2.9- and 2.8-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2361–2370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobberstein B., Kvist S., Roberts L. Structure and biosynthesis of histocompatibility antigens (H-2, HLA). Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 24;300(1099):161–172. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. XI. Functional implications. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 4;9(16):3197–3205. doi: 10.1021/bi00818a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbi M., Acuto O., Smart J. E., Reinherz E. L. Homology of Ti alpha-subunit of a T-cell antigen-MHC receptor with immunoglobulin. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):269–271. doi: 10.1038/312269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROVES M. L., BASCH J. J., GORDON W. G. ISOLATION, CHARACTERIZATION, AND AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF A NEW CRYSTALLINE PROTEIN, LACTOLLIN, FROM MILK. Biochemistry. 1963 Jul-Aug;2:814–817. doi: 10.1021/bi00904a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gates F. T., 3rd, Coligan J. E., Kindt T. J. Complete amino acid sequence of murine beta 2-microglobulin: structural evidence for strain-related polymorphism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):554–558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gates F. T., 3rd, Coligan J. E., Kindt T. J. Complete amino acid sequence of rabbit beta 2-microglobulin. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2267–2272. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Kubo R. T., Colon S. M., Poulik M. D., Cresswell P., Springer T., Turner M., Strominger J. L. The small subunit of HL-A antigens is beta 2-microglobulin. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1608–1612. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. L., Greenberg R. Complete amino acid sequence of bovine beta 2-microglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2619–2626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Kappler J. W., Trowbridge I. S., Marrack P., Freed J. H. Immunoglobulin-like nature of the alpha-chain of a human T-cell antigen/MHC receptor. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):65–67. doi: 10.1038/312065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Cohen D. I., Nielsen E. A., Davis M. M. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding T cell-specific membrane-associated proteins. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):149–153. doi: 10.1038/308149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Nielsen E. A., Kavaler J., Cohen D. I., Davis M. M. Sequence relationships between putative T-cell receptor polypeptides and immunoglobulins. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):153–158. doi: 10.1038/308153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hester R. B., Kubo R. T., Grey H. M. Studies on the cytophilic properties of human beta2-microglobulin. II. The role of histocompatibility antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1979;9(2):125–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb02714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Malissen B. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:529–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Auffray C., Korman A. J., Shackelford D. A., Strominger J. The class II molecules of the human and murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Assembly and maturation of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens in vivo. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):979–991. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90210-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancet D., Parham P., Strominger J. L. Heavy chain of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens is conformationally labile: a possible role for beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3844–3848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesk A. M., Chothia C. Evolution of proteins formed by beta-sheets. II. The core of the immunoglobulin domains. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):325–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lögdberg L., Cigén R., Björck L. Binding of beta 2-microglobulin by heterologous sera. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(3):237–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquart M., Deisenhofer J., Huber R., Palm W. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of the intact immunoglobulin molecule Kol and its antigen-binding fragment at 3.0 A and 1.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 25;141(4):369–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamuro K., Tanigaki N., Pressman D. Multiple common properties of human beta2-microglobulin and the common portion fragment derived from HL-A antigen molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2863–2865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Androlewicz M. J., Holmes N. J., Rothenberg B. E. Arginine 45 is a major part of the antigenic determinant of human beta 2-microglobulin recognized by mouse monoclonal antibody BBM.1. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6179–6186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. C., Strominger J. L. Localization of the sites of iodination of human beta 2-microglobulin: quaternary structure implications for histocompatibility antigens. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1145–1153. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Rask L., Lindblom J. B. Highly purified papain-solubilized HL-A antigens contain beta2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):35–39. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeke G. N., Jr, Becker J. W., Edelman G. M. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. IV. Atomic coordinates, hydrogen bonding, and quaternary structure. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1525–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul F. A., Amzel L. M., Poljak R. J. Preliminary refinement and structural analysis of the Fab fragment from human immunoglobulin new at 2.0 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):585–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W., Festenstein H., Ward P. J., Sanderson A. R. Interspecies exchange of beta 2-microglobulin and associated MHC and differentiation antigens. Immunogenetics. 1981;13(6):483–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00343716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Hood L. Detergent-solubilised H-2 alloantigen is associated with a small molecular weight polypeptide. Nature. 1974 Jun 21;249(459):764–765. doi: 10.1038/249764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Cebra J. J. The primary structure of guinea pig beta 2-microglobulin. Mol Immunol. 1980 Dec;17(12):1493–1505. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi Y., Yoshikai Y., Leggett K., Clark S. P., Aleksander I., Mak T. W. A human T cell-specific cDNA clone encodes a protein having extensive homology to immunoglobulin chains. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):145–149. doi: 10.1038/308145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama K., Nathenson S. G. Intramolecular organization of Class I H-2 MHC antigens; localization of the alloantigenic determinants and the beta 2 m binding site to different regions of the H-2 Kb glycoprotein. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1419–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



