Abstract
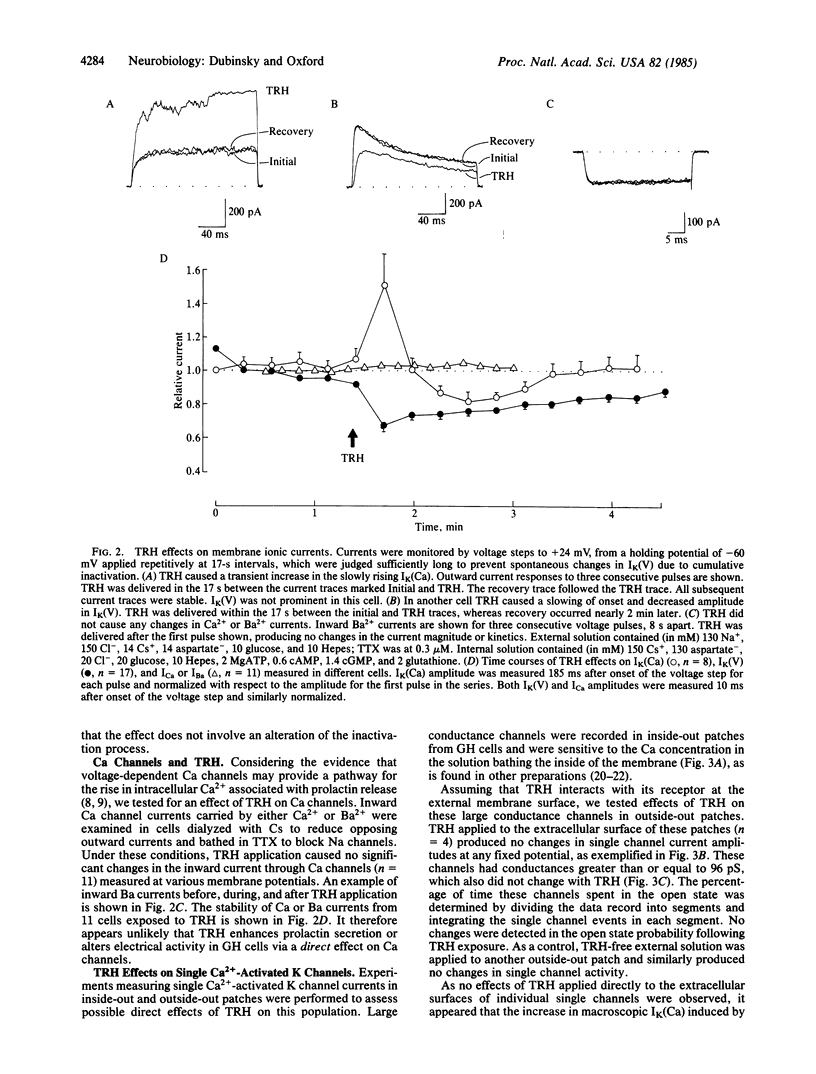
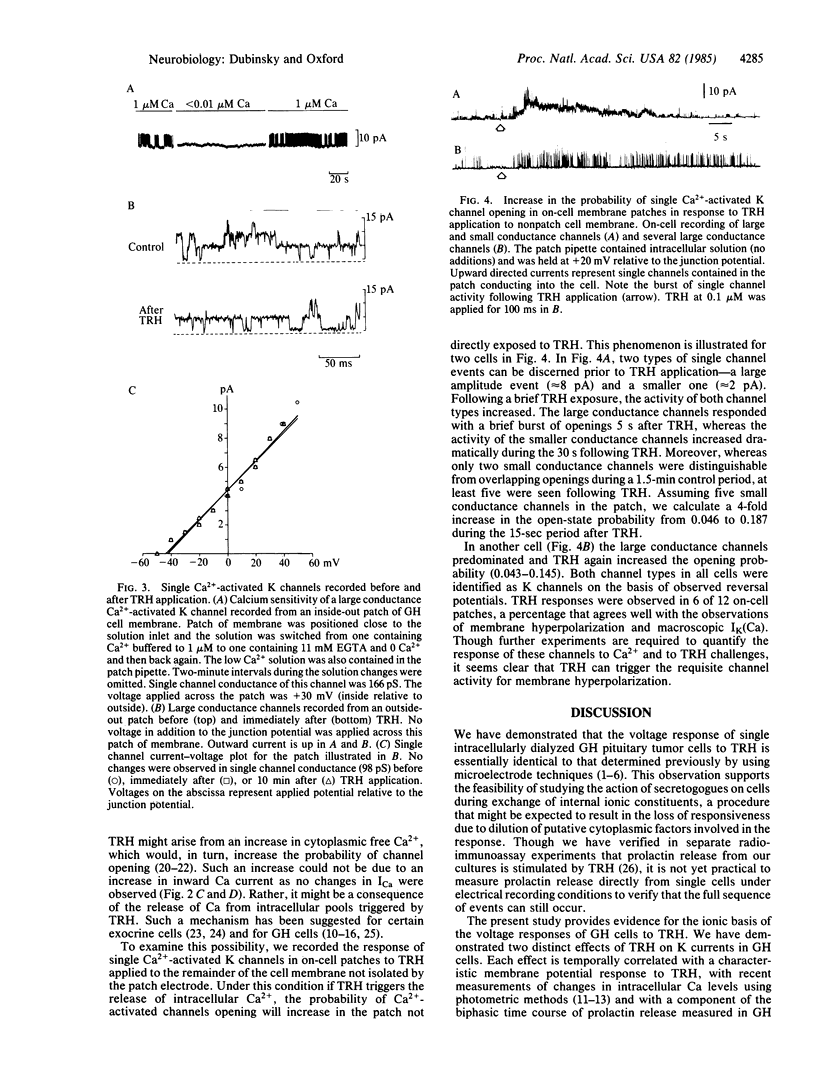
Transmembrane electrical activity in pituitary tumor cells can be altered by substances that either stimulate or inhibit their secretory activity. Using patch recording techniques, we have measured the resting membrane potentials, action potentials, transmembrane macroscopic ionic currents, and single Ca2+-activated K channel currents of GH3 and GH4/C1 rat pituitary tumor cells in response to thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). TRH, which stimulates prolactin secretion, causes a transient hyperpolarization of the membrane potential followed by a period of elevated action potential frequency. In single cells voltage clamped and internally dialyzed with solutions containing K+, TRH application results in a transient increase in Ca2+-activated K currents and a more protracted decrease in voltage-dependent K currents. However, in cells internally dialyzed with K+-free solutions, TRH produces no changes in inward Ca2+ or Ba2+ currents through voltage-dependent Ca channels. The time courses of the effects on Ca2+-activated and voltage-dependent K currents correlate with the phases of hyperpolarization and hyperexcitability, respectively. During application of TRH to whole cells, single Ca2+-activated K channel activity increases in cell-attached patches not directly exposed to TRH. In contrast, TRH applied directly to excised membrane patches produces no change in single Ca2+-activated K channel behavior. We conclude that TRH (i) triggers intracellular Ca2+ release, which opens Ca2+-activated K channels, (ii) depresses voltage-dependent K channels during the hyperexcitable phase, which further elevated intracellular Ca2+, and (iii) does not directly modulate Ca channel activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert P. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced spike and plateau in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentrations in pituitary cells. Relation to prolactin release. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5827–5832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H., Bushfield M., Macphee C. H. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-stimulated [3H]inositol metabolism in GH3 pituitary tumor cells. Studies with lithium. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):201–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubinsky J. M., Oxford G. S. Ionic currents in two strains of rat anterior pituitary tumor cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):309–339. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufy B., Vincent J. D., Fleury H., Du Pasquier P., Gourdji D., Tixier-Vidal A. Dopamine inhibition of action potentials in a prolactin secreting cell line is modulated by oestrogen. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):855–857. doi: 10.1038/282855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufy B., Vincent J. D., Fleury H., Du Pasquier P., Gourdji D., Tixier-Vidal A. Membrane effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone and estrogen shown by intracellular recording from pituitary cells. Science. 1979 May 4;204(4392):509–511. doi: 10.1126/science.107590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C., Thaw C. Calcium influx is not required for TRH to elevate free cytoplasmic calcium in GH3 cells. Endocrinology. 1983 Oct;113(4):1522–1524. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-4-1522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Vandlen R. L., Katz G. M., Reuben J. P. Regulation of excitation-secretion coupling by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH): evidence for TRH receptor-ion channel coupling in cultured pituitary cells. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):109–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01870679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal B. A., Keith C. H., Maxfield F. R. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced changes in intracellular [Ca2+] measured by microspectrofluorometry on individual quin2-loaded cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1167–1172. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macphee C. H., Drummond A. H. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate in GH3 pituitary tumor cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):193–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rapidly activates the phosphodiester hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositides in GH3 pituitary cells. Evidence for the role of a polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14816–14822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Petersen O. H. Control of K+ conductance by cholecystokinin and Ca2+ in single pancreatic acinar cells studied by the patch-clamp technique. J Membr Biol. 1984;79(3):293–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01871068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaman R. E., McKenna D. G., Ono J. K. A pressure system for intracellular and extracellular ejections of picoliter volumes. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 4;136(1):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty C. M., Leuschen M. P. Role of calcium in acute stimulated release of prolactin from neoplastic GH3 cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E705–E711. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa S. Biphasic effect of thyrotropin-releasing hormone on membrane K+ permeability in rat clonal pituitary cells. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 23;209(1):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M. J., Gerry R. H., Gershengorn M. C. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone causes loss of cellular calcium without calcium uptake by rat pituitary cells in culture. Studies using arsenazo III for direct measurement of calcium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2751–2753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronning S. A., Heatley G. A., Martin T. F. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone mobilizes Ca2+ from endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of GH3 pituitary cells: characterization of cellular Ca2+ pools by a method based on digitonin permeabilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6294–6298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sand O., Haug E., Gautvik K. M. Effects of thyroliberin and 4-aminopyridine on action potentials and prolactin release and synthesis in rat pituitary cells in culture. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Mar;108(3):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. N., Tashjian A. H., Jr Voltage-dependent calcium channels in pituitary cells in culture. II. Participation in thyrotropin-releasing hormone action on prolactin release. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):427–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraskevich P. S., Douglas W. W. Electrical behaviour in a line of anterior pituitary cells (GH cells) and the influence of the hypothalamic peptide, thyrotrophin releasing factor. Neuroscience. 1980;5(2):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Lomedico M. E., Maina D. Role of calcium in the thyrotropin-releasing hormone-stimulated release of prolactin from pituitary cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):798–806. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91422-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Yasumura Y., Levine L., Sato G. H., Parker M. L. Establishment of clonal strains of rat pituitary tumor cells that secrete growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):342–352. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann A., Marty A. Activation of Ca-dependent K channels by carbamoylcholine in rat lacrimal glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):611–615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S., Lecar H., Adler M. Single calcium-dependent potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):313–317. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84522-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



