Abstract
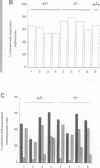
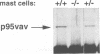
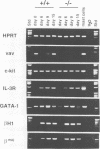
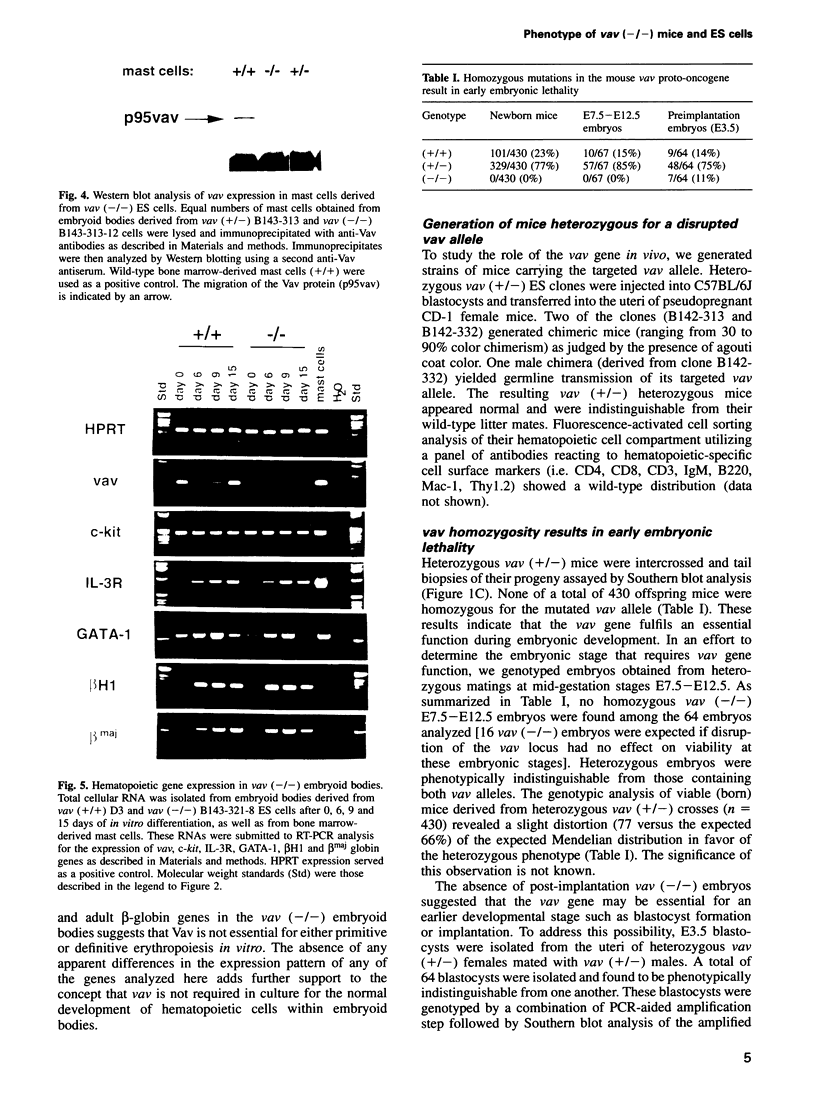
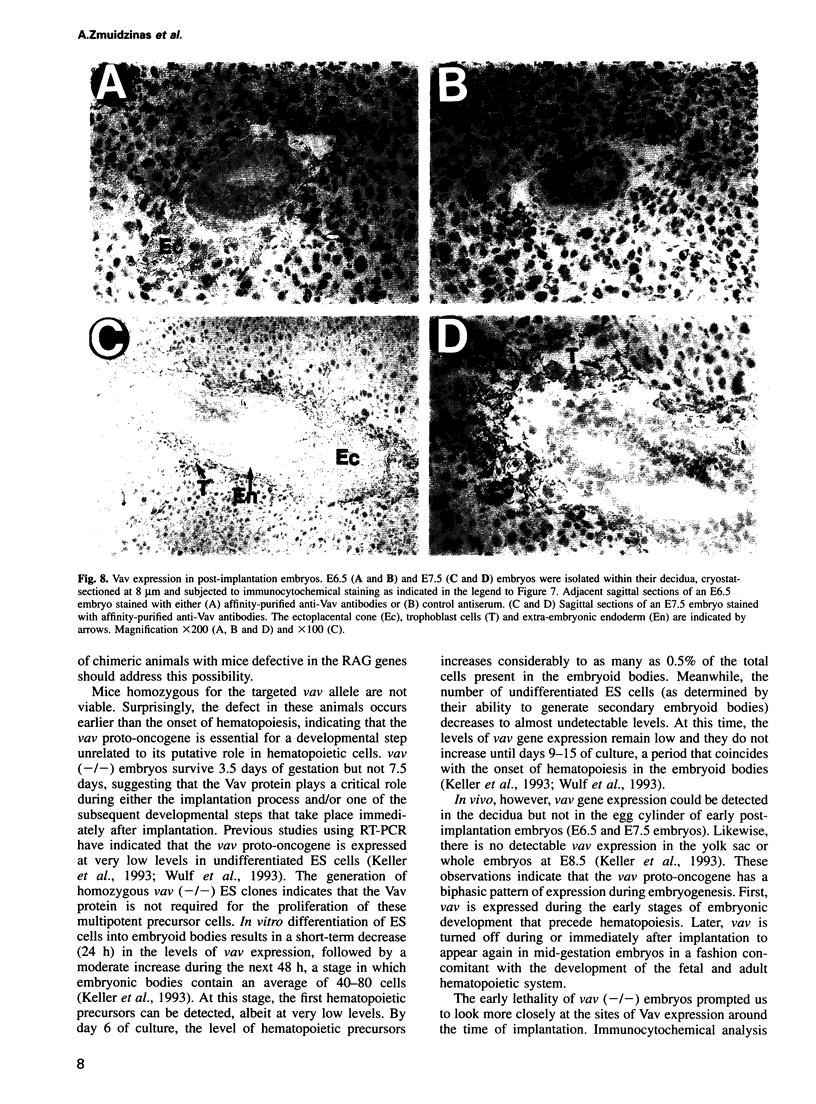
Previous studies have suggested that the vav protooncogene plays an important role in hematopoiesis. To study this further, we have ablated the vav protooncogene by homologous recombination in embryonic stem (ES) cells. Homozygous vav (-/-) ES clones differentiate normally in culture and generate cells of erythroid, myeloid and mast cell lineages. Mice heterozygous for the targeted vav allele do not display any obvious abnormalities. However, homozygous embryos die very early during development. Crosses of vav (+/-) heterozygous mice yield apparently normal vav (-/-) E3.5 embryos but not post-implantation embryos (> or = E7.5). Furthermore, homozygous vav (-/-) blastocysts do not hatch in vitro. These results indicate that vav is essential for an early developmental step(s) that precedes the onset of hematopoiesis. Consistent with the phenotypic analysis of vav (-/-) embryos, we have identified Vav immunoreactivity in the extra-embryonic trophoblastic cell layer but not in the inner embryonic cell mass of E3.5 preimplantation embryos or in the egg cylinder of E6.5 and E7.5 post-implantation embryos. These results suggest that the vav gene is essential for normal trophoblast development and for implantation of the developing embryo.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Houston H., Allen J., Lints T., Harvey R. The hematopoietically expressed vav proto-oncogene shares homology with the dbl GDP-GTP exchange factor, the bcr gene and a yeast gene (CDC24) involved in cytoskeletal organization. Oncogene. 1992 Apr;7(4):611–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adra C. N., Boer P. H., McBurney M. W. Cloning and expression of the mouse pgk-1 gene and the nucleotide sequence of its promoter. Gene. 1987;60(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alai M., Mui A. L., Cutler R. L., Bustelo X. R., Barbacid M., Krystal G. Steel factor stimulates the tyrosine phosphorylation of the proto-oncogene product, p95vav, in human hemopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18021–18025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustelo X. R., Barbacid M. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the vav proto-oncogene product in activated B cells. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1196–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustelo X. R., Ledbetter J. A., Barbacid M. Product of vav proto-oncogene defines a new class of tyrosine protein kinase substrates. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):68–71. doi: 10.1038/356068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustelo X. R., Rubin S. D., Suen K. L., Carrasco D., Barbacid M. Developmental expression of the vav protooncogene. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Apr;4(4):297–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustelo X. R., Suen K. L., Leftheris K., Meyers C. A., Barbacid M. Vav cooperates with Ras to transform rodent fibroblasts but is not a Ras GDP/GTP exchange factor. Oncogene. 1994 Aug;9(8):2405–2413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copp A. J. Interaction between inner cell mass and trophectoderm of the mouse blastocyst. I. A study of cellular proliferation. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1978 Dec;48:109–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J., Bryant S., Koda T., Conway D., Barbacid M. Mechanism of activation of the vav protooncogene. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Feb;2(2):95–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T., Gregg R. G., Maeda N., Hooper M. L., Melton D. W., Thompson S., Smithies O. Targetted correction of a mutant HPRT gene in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):576–578. doi: 10.1038/330576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosil M., Wang S., Lemischka I. R. Mitogenic signalling and substrate specificity of the Flk2/Flt3 receptor tyrosine kinase in fibroblasts and interleukin 3-dependent hematopoietic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6572–6585. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Howard O. M., Erwin R., Farrar W. L. Interleukin-2 induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the vav proto-oncogene product in human T cells: lack of requirement for the tyrosine kinase lck. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 1;294(Pt 2):339–342. doi: 10.1042/bj2940339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. L., Papaioannou V. E., Barton S. C. Origin of the ectoplacental cone and secondary giant cells in mouse blastocysts reconstituted from isolated trophoblast and inner cell mass. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1973 Dec;30(3):561–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbins E., Coggeshall K. M., Baier G., Katzav S., Burn P., Altman A. Tyrosine kinase-stimulated guanine nucleotide exchange activity of Vav in T cell activation. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):822–825. doi: 10.1126/science.8484124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbins E., Coggeshall K. M., Baier G., Telford D., Langlet C., Baier-Bitterlich G., Bonnefoy-Berard N., Burn P., Wittinghofer A., Altman A. Direct stimulation of Vav guanine nucleotide exchange activity for Ras by phorbol esters and diglycerides. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4749–4758. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbins E., Coggeshall K. M., Langlet C., Baier G., Bonnefoy-Berard N., Burn P., Wittinghofer A., Katzav S., Altman A. Activation of Ras in vitro and in intact fibroblasts by the Vav guanine nucleotide exchange protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):906–913. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbins E., Langlet C., Baier G., Bonnefoy-Berard N., Herbert E., Altman A., Coggeshall K. M. Tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of Vav GTP/GDP exchange activity in antigen receptor-triggered B cells. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 1;152(5):2123–2129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobert O., Jallal B., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Novel signaling pathway suggested by SH3 domain-mediated p95vav/heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein K interaction. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20225–20228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A. L., Skarnes W. C., Rossant J. Production of a mutation in mouse En-2 gene by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):153–156. doi: 10.1038/338153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzav S., Cleveland J. L., Heslop H. E., Pulido D. Loss of the amino-terminal helix-loop-helix domain of the vav proto-oncogene activates its transforming potential. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1912–1920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzav S., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. vav, a novel human oncogene derived from a locus ubiquitously expressed in hematopoietic cells. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2283–2290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
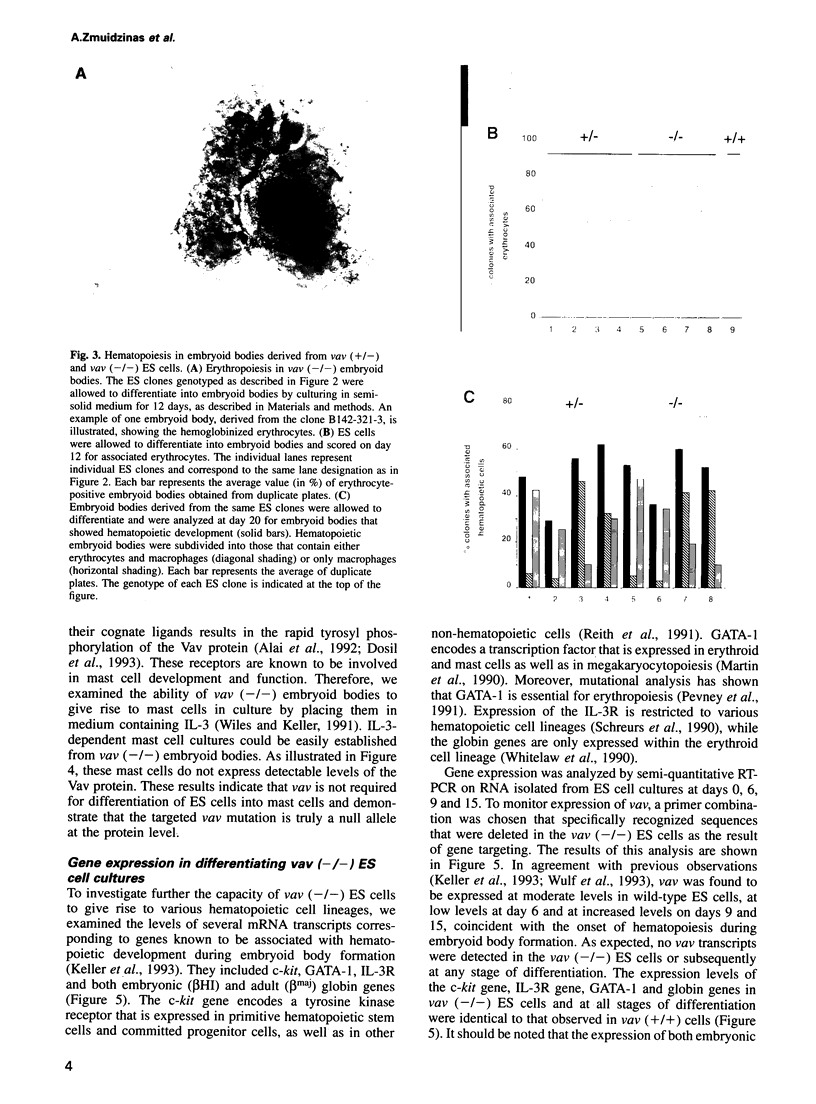
- Keller G., Kennedy M., Papayannopoulou T., Wiles M. V. Hematopoietic commitment during embryonic stem cell differentiation in culture. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):473–486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi-Far R., Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M., Solski P. A., Eva A., Burridge K., Der C. J. Dbl and Vav mediate transformation via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways that are distinct from those activated by oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6848–6857. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Hu P., Katzav S., Li W., Oliver J. M., Ullrich A., Weiss A., Schlessinger J. Tyrosine phosphorylation of vav proto-oncogene product containing SH2 domain and transcription factor motifs. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):71–74. doi: 10.1038/356071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Zon L. I., Mutter G., Orkin S. H. Expression of an erythroid transcription factor in megakaryocytic and mast cell lineages. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):444–447. doi: 10.1038/344444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Sutherland L. C., Adra C. N., Leclair B., Rudnicki M. A., Jardine K. The mouse Pgk-1 gene promoter contains an upstream activator sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5755–5761. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. M., Conner D. A., Chao S., Geisterfer-Lowrance A. A., Seidman J. G. Production of homozygous mutant ES cells with a single targeting construct. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2391–2395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevny L., Simon M. C., Robertson E., Klein W. H., Tsai S. F., D'Agati V., Orkin S. H., Costantini F. Erythroid differentiation in chimaeric mice blocked by a targeted mutation in the gene for transcription factor GATA-1. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):257–260. doi: 10.1038/349257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platanias L. C., Sweet M. E. Interferon alpha induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of the vav proto-oncogene product in hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3143–3146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puil L., Pawson T. Vagaries of vav. Curr Biol. 1992 May;2(5):275–277. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90396-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith A. D., Ellis C., Lyman S. D., Anderson D. M., Williams D. E., Bernstein A., Pawson T. Signal transduction by normal isoforms and W mutant variants of the Kit receptor tyrosine kinase. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2451–2459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreurs J., Arai K., Miyajima A. Evidence for a low-affinity interleukin-3 receptor. Growth Factors. 1990;2(2-3):221–233. doi: 10.3109/08977199009071508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw E., Tsai S. F., Hogben P., Orkin S. H. Regulated expression of globin chains and the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 during erythropoiesis in the developing mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6596–6606. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles M. V., Keller G. Multiple hematopoietic lineages develop from embryonic stem (ES) cells in culture. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):259–267. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulf G. M., Adra C. N., Lim B. Inhibition of hematopoietic development from embryonic stem cells by antisense vav RNA. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5065–5074. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]