Abstract
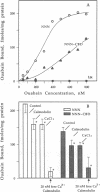
The C-terminal 165 amino acids of the rat brain plasma membrane (PM) Ca(2+)-ATPase II containing the calmodulin binding auto-inhibitory domain was connected to the C-terminus of the ouabain sensitive chicken Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit. Expression of this chimeric molecule in ouabain resistant mouse L cells was assured by the high-affinity binding of [3H]ouabain. In the presence of Ca2+/calmodulin, this chimeric molecule exhibited ouabain inhibitable Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity; the putative chimeric ATPase activity was absent in the absence of Ca2+/calmodulin and activated by Ca2+/calmodulin in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, this chimeric molecule could bind monoclonal IgG 5 specific to the chicken Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit only in the presence of Ca2+/calmodulin, suggesting that the epitope for IgG 5 in this chimera is masked in the absence of Ca2+/calmodulin and uncovered in their presence. These results propose a direct interaction between the calmodulin binding auto-inhibitory domain of the PM Ca(2+)-ATPase and the specific regions of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit that are structurally homologous to the PM Ca(2+)-ATPase. A comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences revealed several possible regions within the Na+,K(+)-ATPase that might interact with the auto-inhibitory domain of the PM Ca(2+)-ATPase.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askari A., Huang W. H., McCormick P. W. (Na+ + K+)-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. Regulation of inorganic phosphate, magnesium ion, and calcium ion interactions with the enzyme by ouabain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3453–3460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Green N. M., Korczak B., MacLennan D. H. Two Ca2+ ATPase genes: homologies and mechanistic implications of deduced amino acid sequences. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Kessler F., Falchetto R., Heim R., Quadroni M., Krebs J., Strehler E. E., Vorherr T. The molecular basis of the modulation of the plasma membrane calcium pump by calmodulin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Nov 30;671:58–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb43784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. The Ca2+ pump of the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2115–2118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chibalin A. V., Vasilets L. A., Hennekes H., Pralong D., Geering K. Phosphorylation of Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunits in microsomes and in homogenates of Xenopus oocytes resulting from the stimulation of protein kinase A and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22378–22384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakle K. A., Kim K. S., Kabalin M. A., Farley R. A. High-affinity ouabain binding by yeast cells expressing Na+, K(+)-ATPase alpha subunits and the gastric H+, K(+)-ATPase beta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerick M. C., Fambrough D. M. Intramolecular fusion of Na pump subunits assures exclusive assembly of the fused alpha and beta subunit domains into a functional enzyme in cells also expressing endogenous Na pump subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23455–23459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi A., Penniston J. T. Autoinhibitory domains of various Ca2+ transporters cross-react. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17120–17125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi A., Vorherr T., James P., McCormick D. J., Filoteo A. G., Carafoli E., Penniston J. T. The calmodulin binding domain of the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump interacts both with calmodulin and with another part of the pump. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12313–12321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchetto R., Vorherr T., Brunner J., Carafoli E. The plasma membrane Ca2+ pump contains a site that interacts with its calmodulin-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2930–2936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Bayne E. K. Multiple forms of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in the chicken. Selective detection of the major nerve, skeletal muscle, and kidney form by a monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3926–3935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley R. A., Tran C. M., Carilli C. T., Hawke D., Shively J. E. The amino acid sequence of a fluorescein-labeled peptide from the active site of (Na,K)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9532–9535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filoteo A. G., Enyedi A., Penniston J. T. The lipid-binding peptide from the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump binds calmodulin, and the primary calmodulin-binding domain interacts with lipid. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11800–11805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greeb J., Shull G. E. Molecular cloning of a third isoform of the calmodulin-sensitive plasma membrane Ca2+-transporting ATPase that is expressed predominantly in brain and skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18569–18576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O. Interaction of cardiac glycosides with (Na+ + K+)-activated ATPase. A biochemical link to digitalis-induced inotropy. Pharmacol Rev. 1984 Sep;36(3):143–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi A., Takeyasu K., Mouradian M. M., Jose P. A., Felder R. A. D1A dopamine receptor stimulation inhibits Na+/K(+)-ATPase activity through protein kinase A. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;43(2):281–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuti K. Some properties of the contractile system and sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned slow fibres from Xenopus muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:1–23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii T., Takeyasu K. The amino-terminal 200 amino acids of the plasma membrane Na+,K+-ATPase alpha subunit confer ouabain sensitivity on the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8881–8885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaisser F., Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Primary sequence and functional expression of a novel ouabain-resistant Na,K-ATPase. The beta subunit modulates potassium activation of the Na,K-pump. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16895–16903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Vorherr T., Krebs J., Morelli A., Castello G., McCormick D. J., Penniston J. T., De Flora A., Carafoli E. Modulation of erythrocyte Ca2+-ATPase by selective calpain cleavage of the calmodulin-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8289–8296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S., Remtulla M. A. Phosphodiesterase protein activator stimulates calcium transport in cardiac microsomal preparations enriched in sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1373–1379. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91373-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Kobayashi S., Horiuti K., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Receptor-coupled, permeabilized smooth muscle. Role of the phosphatidylinositol cascade, G-proteins, and modulation of the contractile response to Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5339–5342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemas M. V., Hamrick M., Takeyasu K., Fambrough D. M. 26 amino acids of an extracellular domain of the Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunit are sufficient for assembly with the Na,K-ATPase beta-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):8255–8259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemas M. V., Takeyasu K., Fambrough D. M. The carboxyl-terminal 161 amino acids of the Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunit are sufficient for assembly with the beta-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20987–20991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi P. A., Sweadner K. J. Postnatal changes in Na,K-ATPase isoform expression in rat cardiac ventricle. Conservation of biphasic ouabain affinity. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9327–9331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckie D. B., Lemas V., Boyd K. L., Fambrough D. M., Takeyasu K. Molecular dissection of functional domains of the E1E2-ATPase using sodium and calcium pump chimeric molecules. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):220–227. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81807-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J., Westlin M., Hanley M. R. Thapsigargin inhibits the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase family of calcium pumps. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17067–17071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Adunyah E. S., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Purified (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase of the erythrocyte membrane. Reconstitution and effect of calmodulin and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):395–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Nagano K., Yoshida M. The active site structure of Na+/K+-transporting ATPase: location of the 5'-(p-fluorosulfonyl)benzoyladenosine binding site and soluble peptides released by trypsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2071–2075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price E. M., Lingrel J. B. Structure-function relationships in the Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit: site-directed mutagenesis of glutamine-111 to arginine and asparagine-122 to aspartic acid generates a ouabain-resistant enzyme. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8400–8408. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Cohen H. T., Katz A. I. Intracellular signaling in the regulation of renal Na-K-ATPase. I. Role of cyclic AMP and phospholipase A2. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1496–1500. doi: 10.1172/JCI115740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultheis P. J., Wallick E. T., Lingrel J. B. Kinetic analysis of ouabain binding to native and mutated forms of Na,K-ATPase and identification of a new region involved in cardiac glycoside interactions. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22686–22694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J., Lingrel J. B. Molecular cloning of three distinct forms of the Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8125–8132. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J. Molecular cloning of two isoforms of the plasma membrane Ca2+-transporting ATPase from rat brain. Structural and functional domains exhibit similarity to Na+,K+- and other cation transport ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8646–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stults N. L., Asta L. M., Lee Y. C. Immobilization of proteins on oxidized crosslinked Sepharose preparations by reductive amination. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jul;180(1):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumbilla C., Lu L., Lewis D. E., Inesi G., Ishii T., Takeyasu K., Feng Y., Fambrough D. M. Ca(2+)-dependent and thapsigargin-inhibited phosphorylation of Na+,K(+)-ATPase catalytic domain following chimeric recombination with Ca(2+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21185–21192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Kadoma M., Inui M., Fujii J. Regulation of Ca2+-pump from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:107–154. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Lemas V., Fambrough D. M. Stability of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha-subunit isoforms in evolution. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):C619–C630. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.4.C619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Tamkun M. M., Renaud K. J., Fambrough D. M. Ouabain-sensitive (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity expressed in mouse L cells by transfection with DNA encoding the alpha-subunit of an avian sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4347–4354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Tamkun M. M., Siegel N. R., Fambrough D. M. Expression of hybrid (Na+ + K+)-ATPase molecules after transfection of mouse Ltk-cells with DNA encoding the beta-subunit of an avian brain sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10733–10740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun M. M., Fambrough D. M. The (Na+ + K+)-ATPase of chick sensory neurons. Studies on biosynthesis and intracellular transport. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1009–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin T., Akera T., Baskin S. I., Brody T. M. Calcium ion and sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase: its mechanism of inhibition and identification of the E 1 -P intermediate. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 May;9(3):336–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorherr T., James P., Krebs J., Enyedi A., McCormick D. J., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Interaction of calmodulin with the calmodulin binding domain of the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):355–365. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu A., Hawkins C., Narayanan N. Phosphorylation and activation of the Ca(2+)-pumping ATPase of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8394–8397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]