Abstract
Infection of primary B-lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) leads to growth transformation of these B-cells in vitro. EBV nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2), one of the first genes expressed after EBV infection of B-cells, is a transcriptional activator of viral and cellular genes and is essential for the transforming potential of the virus. We generated conditional EBV mutants by expressing EBNA2 as chimeric fusion protein with the hormone binding domain of the estrogen receptor on the genetic background of the virus. Growth transformation of primary normal B-cells by mutant virus resulted in estrogen-dependent lymphoblastoid cell lines expressing the chimeric EBNA2 protein. In the absence of estrogen about half of the cells enter a quiescent non-proliferative state whereas the others die by apoptosis. EBNA2 is thus required not only for initiation but also for maintenance of transformation. Growth arrest occurred at G1 and G2 stages of the cell cycle, indicating that functional EBNA2 is required at different restriction points of the cell cycle. Growth arrest is reversible for G1/G0 cells as indicated by the sequential accumulation and modification of cell cycle regulating proteins. EBV induces the same cell cycle regulating proteins as polyclonal stimuli in primary B-cells. These data suggest that EBV is using a common pathway for B-cell activation bypassing the requirement for antigen, T-cell signals and growth factors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbot S. D., Rowe M., Cadwallader K., Ricksten A., Gordon J., Wang F., Rymo L., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 induces expression of the virus-encoded latent membrane protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2126–2134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2126-2134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama N., Tsuruta H., Sasaki H., Sakamoto H., Hamaguchi M., Ohmura Y., Seto M., Ueda R., Hirai H., Yazaki Y. Messenger RNA levels of five genes located at chromosome 11q13 in B-cell tumors with chromosome translocation t(11;14)(q13;q32). Cancer Res. 1994 Jan 15;54(2):377–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allday M. J., Crawford D. H., Griffin B. E. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B cell immortalization. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jul;70(Pt 7):1755–1764. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-7-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banchereau J., de Paoli P., Vallé A., Garcia E., Rousset F. Long-term human B cell lines dependent on interleukin-4 and antibody to CD40. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1702555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk O., Klempnauer K. H. Estrogen-dependent alterations in differentiation state of myeloid cells caused by a v-myb/estrogen receptor fusion protein. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3713–3719. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04939.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan M. A., Stein L. D., Dosch H. M., Sigal N. H. Heterogeneity of EBV-transformable human B lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):106–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Mannick J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 is a key determinant of lymphocyte transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9558–9562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combriato G., Klobeck H. G. V lambda and J lambda-C lambda gene segments of the human immunoglobulin lambda light chain locus are separated by 14 kb and rearrange by a deletion mechanism. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jun;21(6):1513–1522. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Zimber U., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Banchereau J., Tursz T., Bornkamm G., Lenoir G. M. Stable transfection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2 in lymphoma cells containing the EBV P3HR1 genome induces expression of B-cell activation molecules CD21 and CD23. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1002–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1002-1013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Picard D., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M. Chimaeras of myc oncoprotein and steroid receptors cause hormone-dependent transformation of cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):66–68. doi: 10.1038/340066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwart J. W., Dörmer P. Vitality measurement using spectrum shift in Hoechst 33342 stained cells. Cytometry. 1990;11(2):239–243. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Jansson A., Ricksten A., Sjöblom A., Rymo L. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 2 activates the viral latent membrane protein promoter by modulating the activity of a negative regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7390–7394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):393–397. doi: 10.1038/340393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Lees J. A., Vidal M., Dyson N., Harlow E., Fattaey A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90107-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Ling P. D., Hayward S. D., Peterson M. G. Mediation of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2 transactivation by recombination signal-binding protein J kappa. Science. 1994 Jul 1;265(5168):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8016657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lipp M., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human MYC promoter is mediated by the E2F factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutt-Fletcher L. M. Synergistic activation of cells by Epstein-Barr virus and B-cell growth factor. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):774–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.774-781.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye K. M., Izumi K. M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 is essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9150–9154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C. The level of c-fgr RNA is increased by EBNA-2, an Epstein-Barr virus gene required for B-cell immortalization. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2530–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2530-2536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Staub A., Chambon P. Localisation of the oestradiol-binding and putative DNA-binding domains of the human oestrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2231–2236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling P. D., Rawlins D. R., Hayward S. D. The Epstein-Barr virus immortalizing protein EBNA-2 is targeted to DNA by a cellular enhancer-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9237–9241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunami N., Hamaguchi Y., Yamamoto Y., Kuze K., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Kawaichi M., Honjo T. A protein binding to the J kappa recombination sequence of immunoglobulin genes contains a sequence related to the integrase motif. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):934–937. doi: 10.1038/342934a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Quelle D. E., Shurtleff S. A., Shibuya M., Sherr C. J., Kato J. Y. D-type cyclin-dependent kinase activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2066–2076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Lantzsch N., Lenoir G. M., Sauter M., Takaki K., Béchet J. M., Kuklik-Roos C., Wunderlich D., Bornkamm G. W. Identification of the coding region for a second Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA 2) by transfection of cloned DNA fragments. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1805–1811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod M. G., Collins M. K., Rodriguez-Tarduchy G., Robertson D. Apoptosis in interleukin-3-dependent haemopoietic cells. Quantification by two flow cytometric methods. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Aug 30;153(1-2):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90305-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmero I., Holder A., Sinclair A. J., Dickson C., Peters G. Cyclins D1 and D2 are differentially expressed in human B-lymphoid cell lines. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):1049–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz G. A., Trounstine M. L., Moore K. W. Cloned and expressed human Fc receptor for IgG mediates anti-CD3-dependent lymphoproliferation. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):1891–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng M., Lundgren E. Transient expression of the Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene in human primary B cells induces cellular activation and DNA synthesis. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1775–1782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Salser S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: take your partners. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jun;18(6):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90185-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Gradoville L., Heston L., Miller G. Non-immortalizing P3J-HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus: a deletion mutant of its transforming parent, Jijoye. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):834–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.834-844.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimokh R., Berger F., Delsol G., Charrin C., Berthéas M. F., Ffrench M., Garoscio M., Felman P., Coiffier B., Bryon P. A. Rearrangement and overexpression of the BCL-1/PRAD-1 gene in intermediate lymphocytic lymphomas and in t(11q13)-bearing leukemias. Blood. 1993 Jun 1;81(11):3063–3067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers R. P., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Epstein-Barr virus in B lymphocytes: viral gene expression and function in latency. Adv Cancer Res. 1992;58:1–26. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60288-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Brimmell M., Buschle M., Allan G., Farrell P. J., Kolman J. L. Host cell and EBNA-2 regulation of Epstein-Barr virus latent-cycle promoter activity in B lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):496–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.496-504.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C., Howe J. G., Speck S. H., Miller G. Influence of Burkitt's lymphoma and primary B cells on latent gene expression by the nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1531–1539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1531-1539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
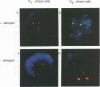
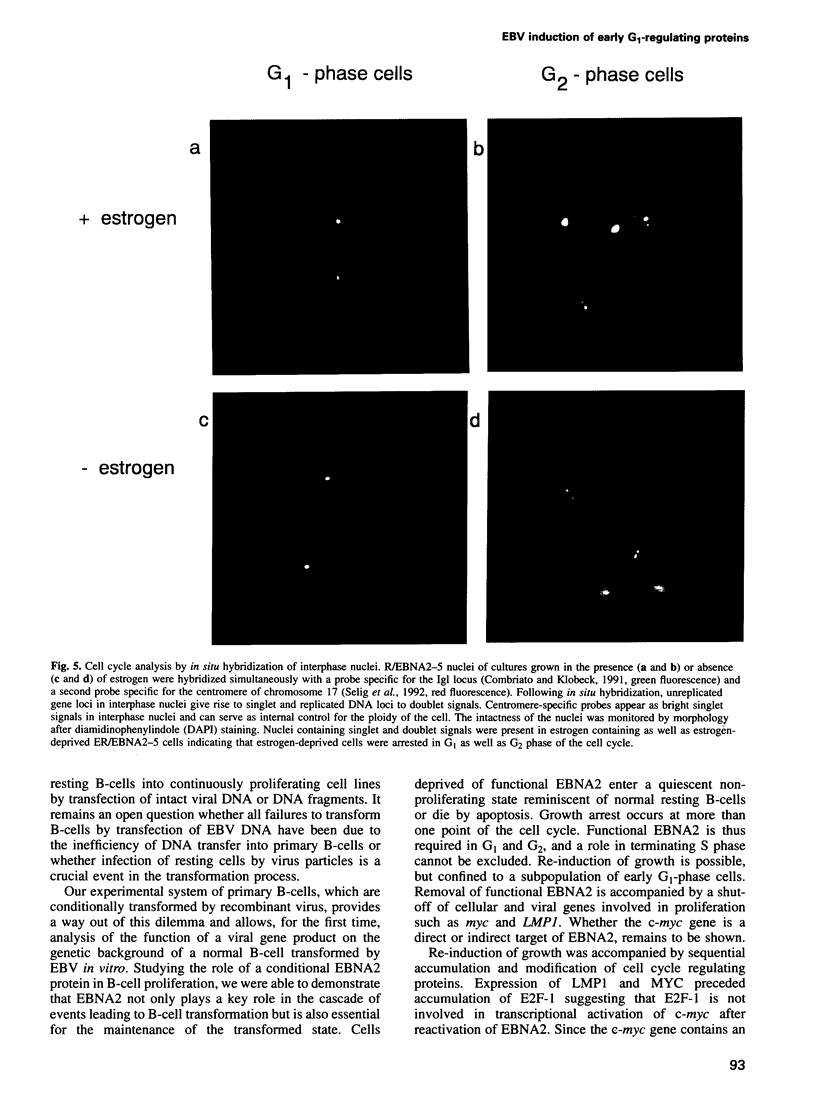
- Selig S., Okumura K., Ward D. C., Cedar H. Delineation of DNA replication time zones by fluorescence in situ hybridization. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1217–1225. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
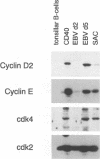
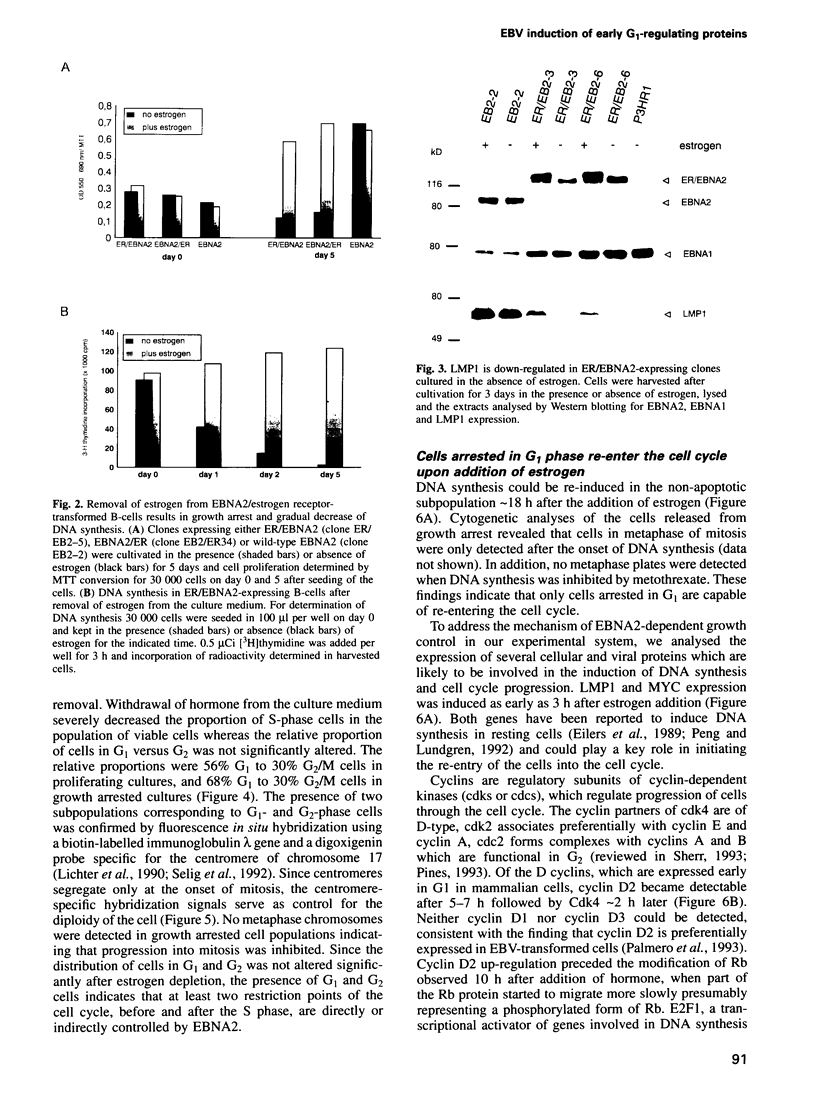
- Sinclair A. J., Palmero I., Peters G., Farrell P. J. EBNA-2 and EBNA-LP cooperate to cause G0 to G1 transition during immortalization of resting human B lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3321–3328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitkovsky D., Steiner P., Lukas J., Lees E., Pagano M., Schulze A., Joswig S., Picard D., Tommasino M., Eilers M. Modulation of cyclin gene expression by adenovirus E1A in a cell line with E1A-dependent conditional proliferation. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2206–2214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2206-2214.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung N. S., Kenney S., Gutsch D., Pagano J. S. EBNA-2 transactivates a lymphoid-specific enhancer in the BamHI C promoter of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2164–2169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2164-2169.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalmeier K., Synovzik H., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L., Lipp M. Nuclear factor E2F mediates basic transcription and trans-activation by E1a of the human MYC promoter. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):527–536. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson B., Robertson E., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins EBNA-3A and EBNA-3C are essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2014–2025. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2014-2025.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber-Strobl U., Kremmer E., Grässer F., Marschall G., Laux G., Bornkamm G. W. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 interacts with an EBNA2 responsive cis-element of the terminal protein 1 gene promoter. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):167–175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05642.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Laux G., Eick D., Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 activates transcription of the terminal protein gene. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):415–423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.415-423.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]