Abstract
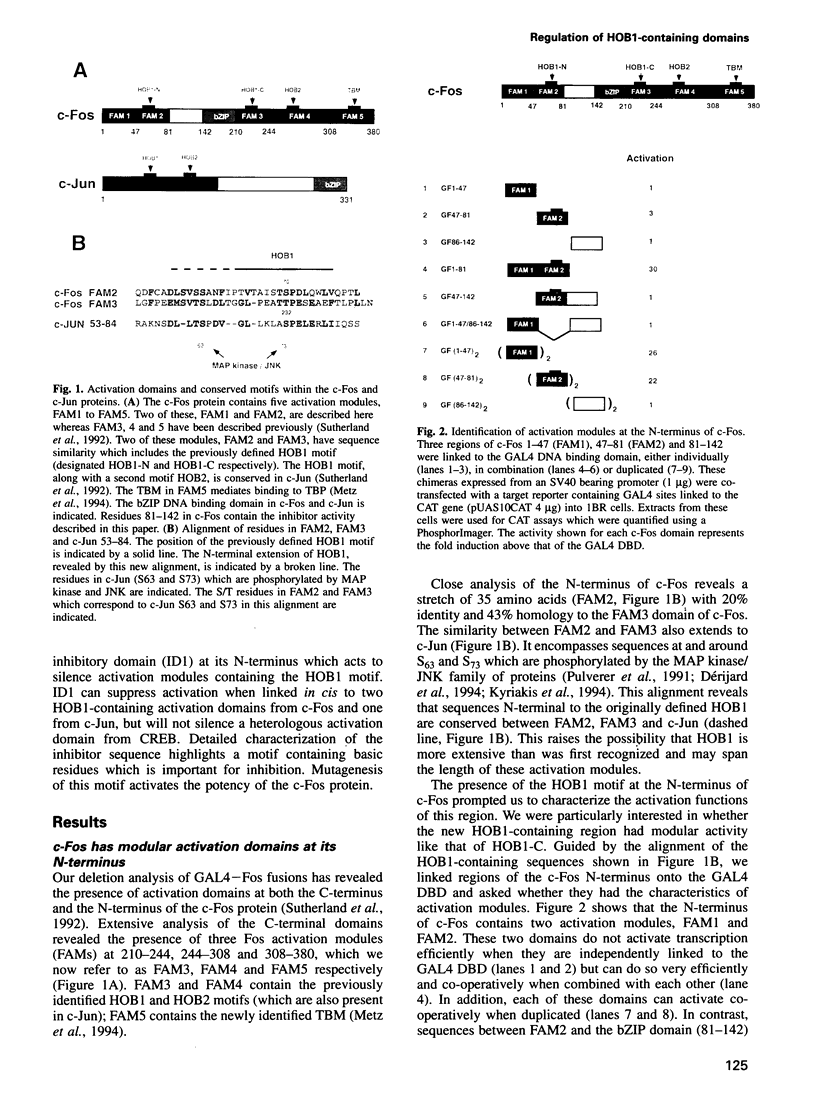
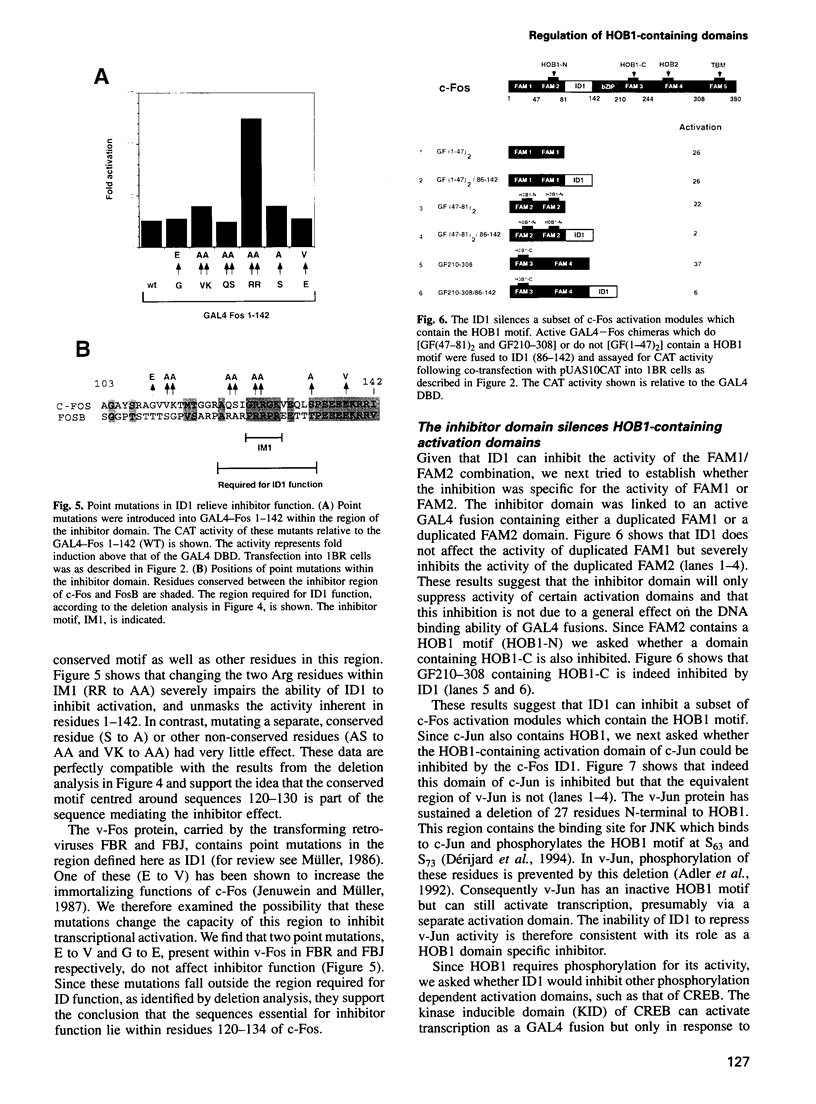
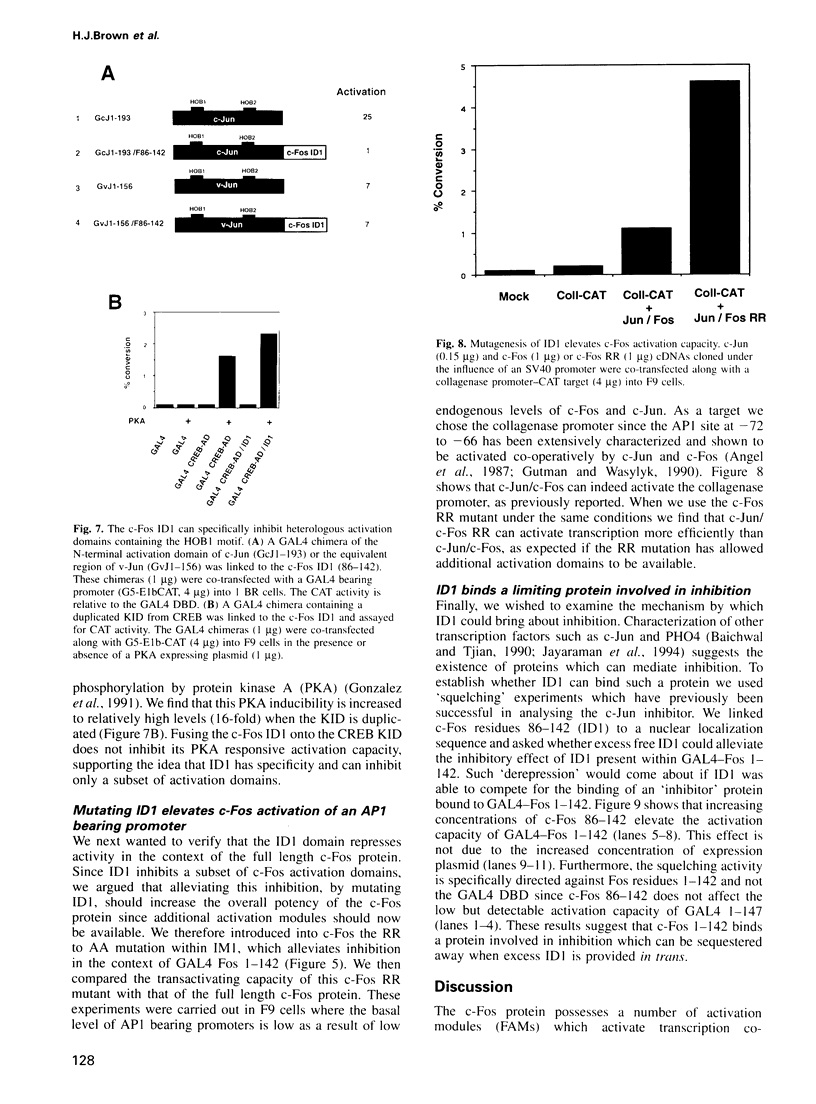
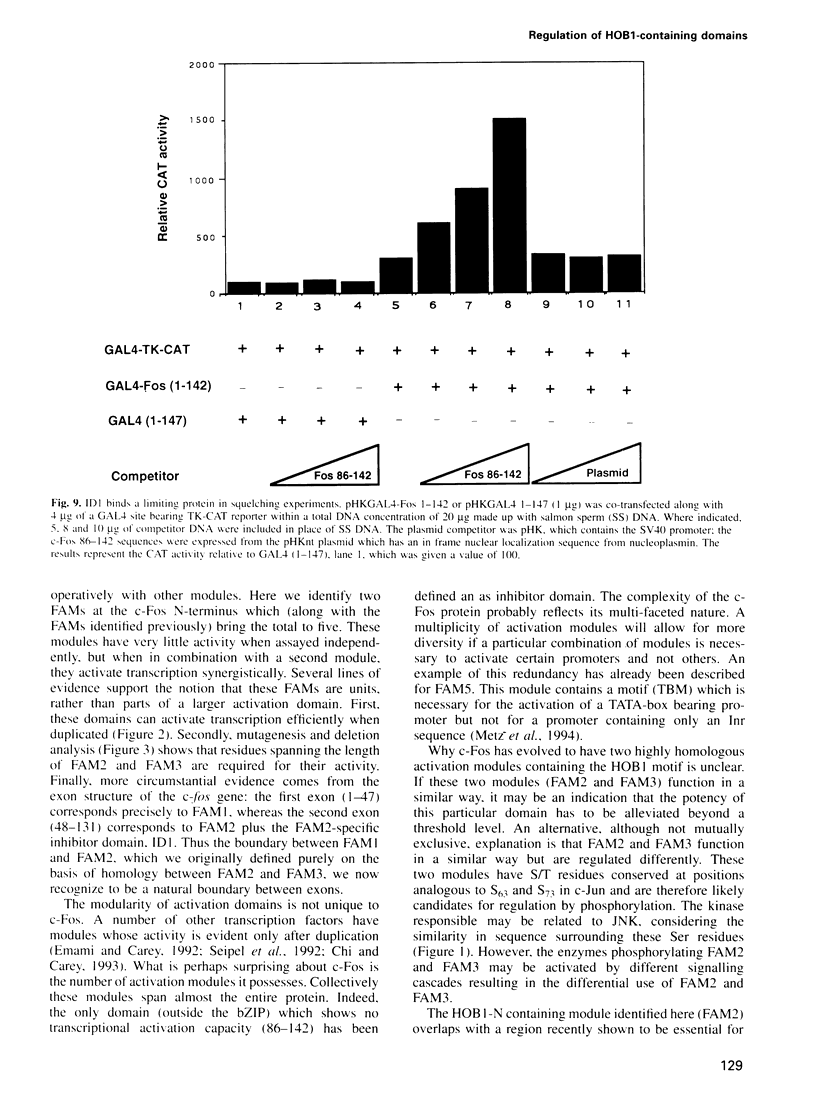
The c-Fos protein has three activation modules at its C-terminus, two of which contain motifs (HOB1 and HOB2) which are also present in the activation domains of c-Jun. Here we show the existence of two additional activation modules at the N-terminus of c-Fos, one of which contains a second HOB1 motif (HOB1-N). The N-terminus also contains an inhibitor domain (ID1) which silences HOB1 activity. GAL4 fusion experiments showed that ID1 can specifically silence HOB1-containing activation domains from c-Fos or c-Jun when linked in cis, but will not affect other distinct activation domains. The c-Fos related protein, FosB, also contains an inhibitor domain. Mutagenic and deletion analyses identify an inhibitor motif (IM1) conserved between c-Fos and FosB, which is required for inhibitor function. Mutagenesis of IM1 enhances the ability of c-Fos to activate an AP1 bearing promoter. Finally, squelching experiments suggest that c-Fos ID1 binds a limiting protein involved in inhibition. These results demonstrate the existence of a new class of inhibitor domain within transcriptional activators, which acts in a sequence specific manner to inhibit a subset of activation domains.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Luk D., Curran T. Transcriptional regulation by Fos and Jun in vitro: interaction among multiple activator and regulatory domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3624–3632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler V., Franklin C. C., Kraft A. S. Phorbol esters stimulate the phosphorylation of c-Jun but not v-Jun: regulation by the N-terminal delta domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5341–5345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Smeal T., Meek J., Karin M. Jun and v-jun contain multiple regions that participate in transcriptional activation in an interdependent manner. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Tjian R. Control of c-Jun activity by interaction of a cell-specific inhibitor with regulatory domain delta: differences between v- and c-Jun. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binétruy B., Smeal T., Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):122–127. doi: 10.1038/351122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Tjian R. Biochemical analysis of transcriptional activation by Jun: differential activity of c- and v-Jun. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi T., Carey M. The ZEBRA activation domain: modular organization and mechanism of action. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7045–7055. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell I. G., Hurst H. C. Transcriptional repression by the human bZIP factor E4BP4: definition of a minimal repression domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jan 11;22(1):59–65. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubendorff J. W., Whittaker L. J., Eltman J. T., Lipsick J. S. Carboxy-terminal elements of c-Myb negatively regulate transcriptional activation in cis and in trans. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2524–2535. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emami K. H., Carey M. A synergistic increase in potency of a multimerized VP16 transcriptional activation domain. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5005–5012. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Menzel P., Leonard J., Fischer W. H., Montminy M. R. Characterization of motifs which are critical for activity of the cyclic AMP-responsive transcription factor CREB. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1306–1312. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. The collagenase gene promoter contains a TPA and oncogene-responsive unit encompassing the PEA3 and AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2241–2246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Georgopoulos K., Greenberg M. E., Leder P. c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression by the Drosophila even-skipped protein: definition of a minimal repression domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):491–503. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Lin A., Smeal T., Minden A., Karin M. Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2135–2148. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman P. S., Hirst K., Goding C. R. The activation domain of a basic helix-loop-helix protein is masked by repressor interaction with domains distinct from that required for transcription regulation. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2192–2199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenuwein T., Müller R. Structure-function analysis of fos protein: a single amino acid change activates the immortalizing potential of v-fos. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):647–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jooss K. U., Funk M., Müller R. An autonomous N-terminal transactivation domain in Fos protein plays a crucial role in transformation. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1467–1475. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaffman A., Herskowitz I., Tjian R., O'Shea E. K. Phosphorylation of the transcription factor PHO4 by a cyclin-CDK complex, PHO80-PHO85. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1153–1156. doi: 10.1126/science.8108735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. Behind the Fos and Jun leucine zipper. Cancer Cells. 1989 Nov;1(3):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. Leucine zippers of fos, jun and GCN4 dictate dimerization specificity and thereby control DNA binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):568–571. doi: 10.1038/340568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Grossel M. J., Figge J., Hansen U. M. Drosophila Krüppel protein is a transcriptional repressor. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):76–79. doi: 10.1038/346076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolin J. F., Friedman J. R., Meyer W. K., Vissing H., Thiesen H. J., Rauscher F. J., 3rd Krüppel-associated boxes are potent transcriptional repression domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkens A. E., Cashmore A. R. Isolation and characterization of a fourth Arabidopsis thaliana G-box-binding factor, which has similarities to Fos oncoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2522–2526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Bannister A. J., Sutherland J. A., Hagemeier C., O'Rourke E. C., Cook A., Bravo R., Kouzarides T. c-Fos-induced activation of a TATA-box-containing promoter involves direct contact with TATA-box-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):6021–6029. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.6021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R. Cellular and viral fos genes: structure, regulation of expression and biological properties of their encoded products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;823(3):207–225. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(86)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerlov C., Ziff E. B. Three levels of functional interaction determine the activity of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-alpha on the serum albumin promoter. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 1;8(3):350–362. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.3.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha S., Brickman J. M., Lehming N., Ptashne M. New eukaryotic transcriptional repressors. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):648–652. doi: 10.1038/363648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Ransone L. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M. Direct interaction between fos and jun nuclear oncoproteins: role of the 'leucine zipper' domain. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):692–695. doi: 10.1038/336692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuermann M., Neuberg M., Hunter J. B., Jenuwein T., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Müller R. The leucine repeat motif in Fos protein mediates complex formation with Jun/AP-1 and is required for transformation. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W. Different activation domains stimulate transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4961–4968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D. A., Birrer M., Karin M. Oncogenic and transcriptional cooperation with Ha-Ras requires phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):494–496. doi: 10.1038/354494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D., Grover-Bardwick A., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R., Karin M. Oncoprotein-mediated signalling cascade stimulates c-Jun activity by phosphorylation of serines 63 and 73. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3507–3513. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland J. A., Cook A., Bannister A. J., Kouzarides T. Conserved motifs in Fos and Jun define a new class of activation domain. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1810–1819. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzgall R., O'Leary E., Leaf A., Onaldi D., Bonventre J. V. The Krüppel-associated box-A (KRAB-A) domain of zinc finger proteins mediates transcriptional repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4514–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]