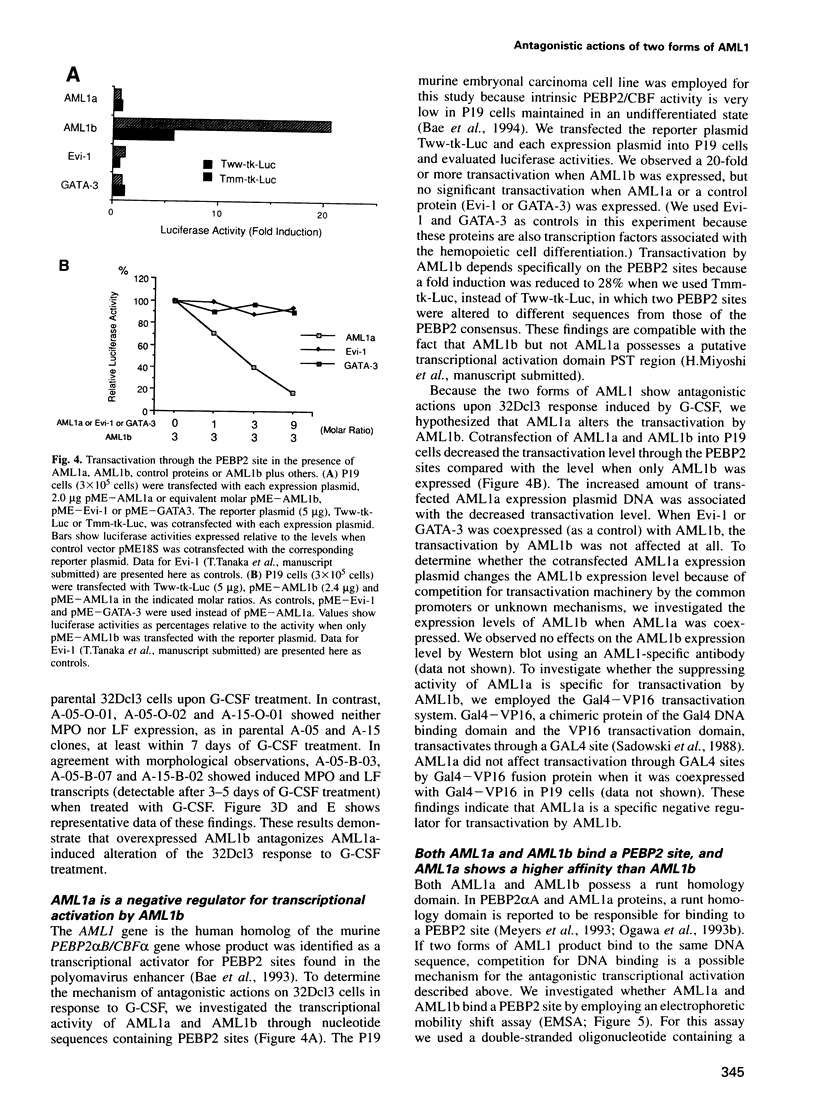
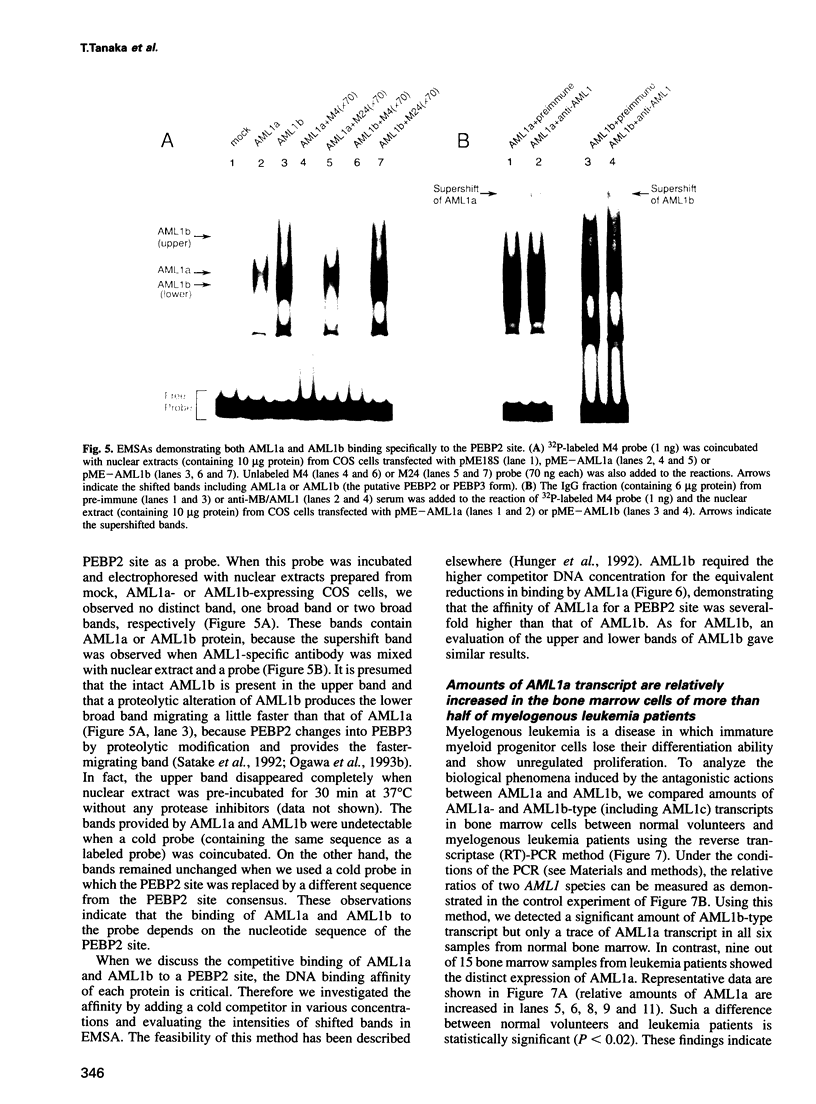
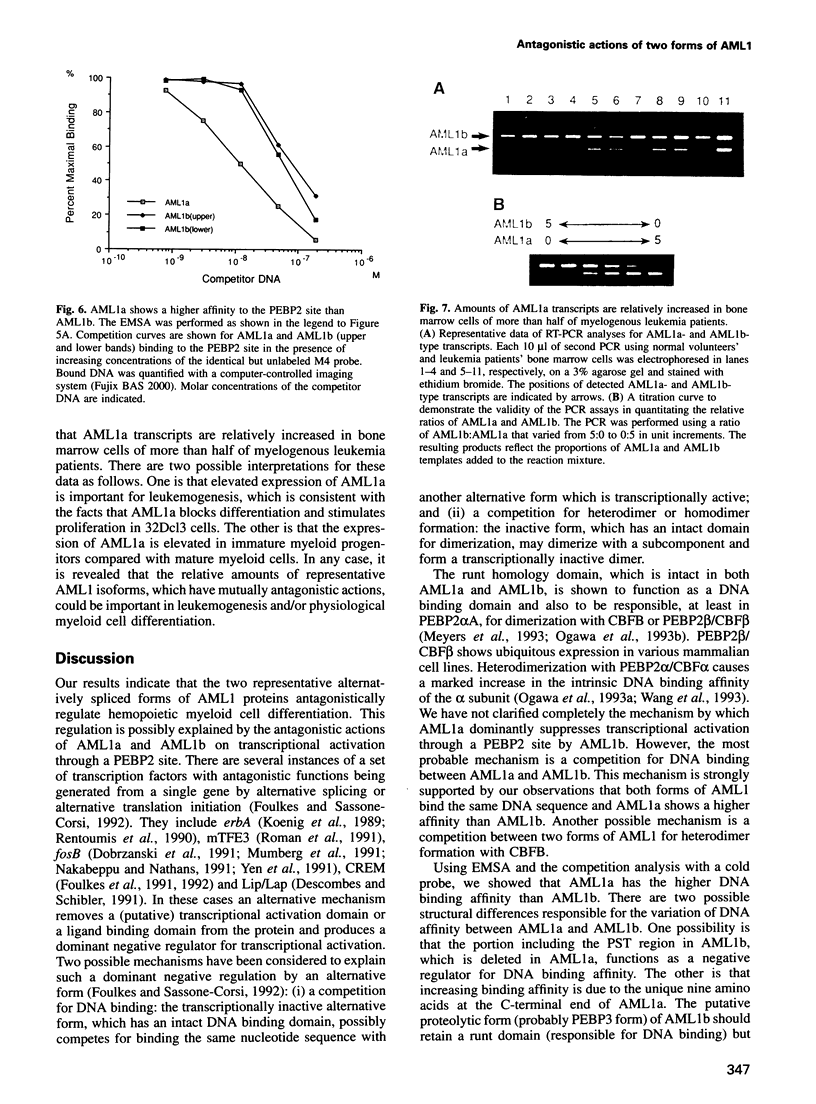
Abstract
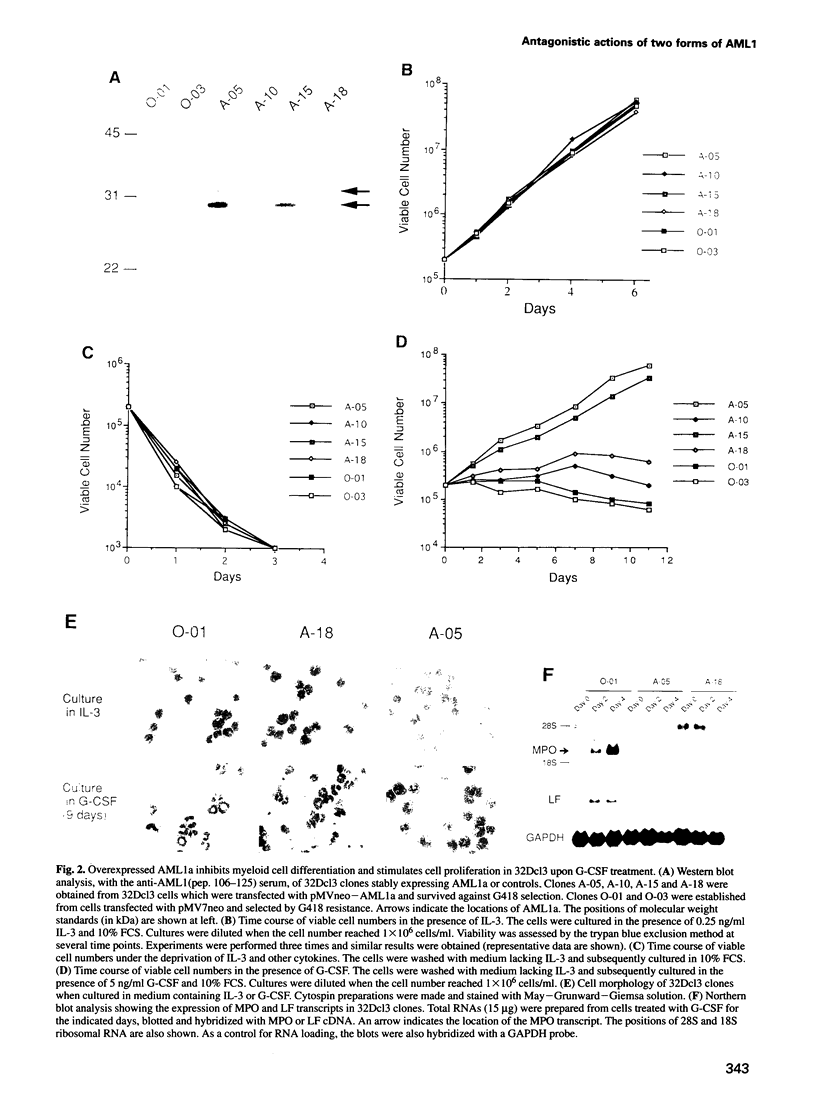
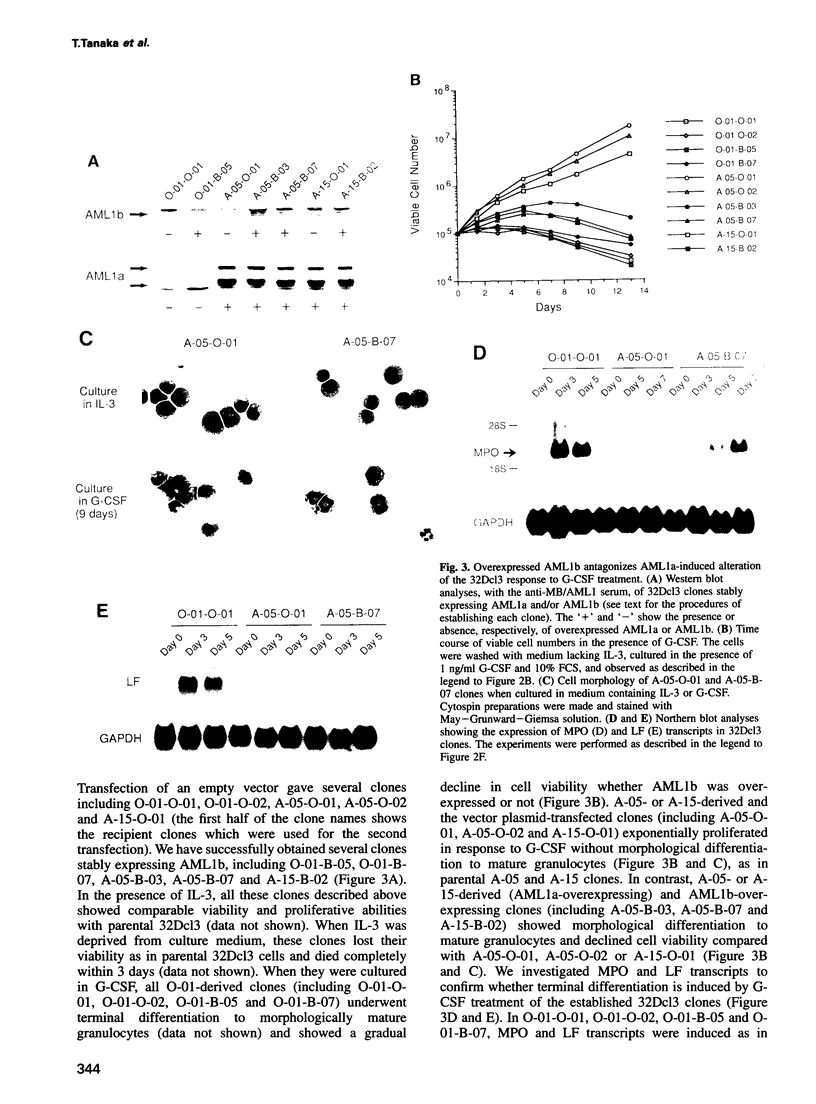
The AML1 gene on chromosome 21 is disrupted in the (8;21)(q22;q22) and (3;21)(q26;q22) translocations associated with myelogenous leukemias and encodes a DNA binding protein. From the AML1 gene, two representative forms of proteins, AML1a and AML1b, are produced by alternative splicing. Both forms have a DNA binding domain but, unlike AML1b, AML1a lacks a putative transcriptional activation domain. Here we demonstrate that overexpressed AML1a totally suppresses granulocytic differentiation and stimulates cell proliferation in 32Dcl3 murine myeloid cells treated with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. These effects of AML1a were canceled by the concomitant overexpression of AML1b. Such biological phenomena could be explained by our observations that (i) AML1a, which on its own has no effects as a transcriptional regulator, dominantly suppresses transcriptional activation by AML1b, and (ii) AML1a exhibits the higher affinity for DNA binding compared with AML1b. These antagonistic actions could be important in leukemogenesis and/or myeloid cell differentiation because more than half of myelogenous leukemia patients showed an increase in the relative amounts of AML1a.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews N. C., Faller D. V. A rapid micropreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from limiting numbers of mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2499–2499. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askew D. S., Ashmun R. A., Simmons B. C., Cleveland J. L. Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae S. C., Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Oka H., Satake M., Shigesada K., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Copeland N. G., Ito Y. PEBP2 alpha B/mouse AML1 consists of multiple isoforms that possess differential transactivation potentials. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3242–3252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae S. C., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Inuzuka M., Kagoshima H., Shigesada K., Satake M., Ito Y. Isolation of PEBP2 alpha B cDNA representing the mouse homolog of human acute myeloid leukemia gene, AML1. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):809–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boral A. L., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J. Identification of the SL3-3 virus enhancer core as a T-lymphoma cell-specific element. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):76–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.76-84.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daga A., Tighe J. E., Calabi F. Leukaemia/Drosophila homology. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):484–484. doi: 10.1038/356484b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrazanski P., Noguchi T., Kovary K., Rizzo C. A., Lazo P. S., Bravo R. Both products of the fosB gene, FosB and its short form, FosB/SF, are transcriptional activators in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5470–5478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson P., Gao J., Chang K. S., Look T., Whisenant E., Raimondi S., Lasher R., Trujillo J., Rowley J., Drabkin H. Identification of breakpoints in t(8;21) acute myelogenous leukemia and isolation of a fusion transcript, AML1/ETO, with similarity to Drosophila segmentation gene, runt. Blood. 1992 Oct 1;80(7):1825–1831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Mellström B., Benusiglio E., Sassone-Corsi P. Developmental switch of CREM function during spermatogenesis: from antagonist to activator. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):80–84. doi: 10.1038/355080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Krieder B. L., Venturelli D., Rovera G. Transcriptional regulation of two myeloid-specific genes, myeloperoxidase and lactoferrin, during differentiation of the murine cell line 32D C13. Blood. 1991 Nov 1;78(9):2426–2432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga R., Ishizaka-Ikeda E., Nagata S. Growth and differentiation signals mediated by different regions in the cytoplasmic domain of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1079–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90729-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Yamaguchi Y., Ogawa E., Shigesada K., Satake M., Ito Y. A ubiquitous repressor interacting with an F9 cell-specific silencer and its functional suppression by differentiated cell-specific positive factors. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Mar;1(3):135–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Butler B. A. Isolation of the Drosophila segmentation gene runt and analysis of its expression during embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1179–1193. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunger S. P., Ohyashiki K., Toyama K., Cleary M. L. Hlf, a novel hepatic bZIP protein, shows altered DNA-binding properties following fusion to E2A in t(17;19) acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1608–1620. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi M., Miyazawa H., Kamakura T., Yamaguchi I., Endo T., Hanaoka F. Blasticidin S-resistance gene (bsr): a novel selectable marker for mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Dec;197(2):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90427-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamachi Y., Ogawa E., Asano M., Ishida S., Murakami Y., Satake M., Ito Y., Shigesada K. Purification of a mouse nuclear factor that binds to both the A and B cores of the polyomavirus enhancer. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4808–4819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4808-4819.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kania M. A., Bonner A. S., Duffy J. B., Gergen J. P. The Drosophila segmentation gene runt encodes a novel nuclear regulatory protein that is also expressed in the developing nervous system. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1701–1713. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko L. J., Yamamoto M., Leonard M. W., George K. M., Ting P., Engel J. D. Murine and human T-lymphocyte GATA-3 factors mediate transcription through a cis-regulatory element within the human T-cell receptor delta gene enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2778–2784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Brent G. A., Larsen P. R., Chin W. W., Moore D. D. Inhibition of thyroid hormone action by a non-hormone binding c-erbA protein generated by alternative mRNA splicing. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):659–661. doi: 10.1038/337659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Tarlé S. A., Hajra A., Claxton D. F., Marlton P., Freedman M., Siciliano M. J., Collins F. S. Fusion between transcription factor CBF beta/PEBP2 beta and a myosin heavy chain in acute myeloid leukemia. Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1041–1044. doi: 10.1126/science.8351518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavilio F., Kreider B. L., Valtieri M., Naso G., Shirsat N., Venturelli D., Reddy E. P., Rovera G. Alteration of growth and differentiation factors response by Kirsten and Harvey sarcoma viruses in the IL-3-dependent murine hematopoietic cell line 32D C13(G). Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers S., Downing J. R., Hiebert S. W. Identification of AML-1 and the (8;21) translocation protein (AML-1/ETO) as sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins: the runt homology domain is required for DNA binding and protein-protein interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6336–6345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliaccio G., Migliaccio A. R., Kreider B. L., Rovera G., Adamson J. W. Selection of lineage-restricted cell lines immortalized at different stages of hematopoietic differentiation from the murine cell line 32D. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):833–841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitani K., Ogawa S., Tanaka T., Miyoshi H., Kurokawa M., Mano H., Yazaki Y., Ohki M., Hirai H. Generation of the AML1-EVI-1 fusion gene in the t(3;21)(q26;q22) causes blastic crisis in chronic myelocytic leukemia. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):504–510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi H., Kozu T., Shimizu K., Enomoto K., Maseki N., Kaneko Y., Kamada N., Ohki M. The t(8;21) translocation in acute myeloid leukemia results in production of an AML1-MTG8 fusion transcript. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2715–2721. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi H., Shimizu K., Kozu T., Maseki N., Kaneko Y., Ohki M. t(8;21) breakpoints on chromosome 21 in acute myeloid leukemia are clustered within a limited region of a single gene, AML1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10431–10434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumberg D., Lucibello F. C., Schuermann M., Müller R. Alternative splicing of fosB transcripts results in differentially expressed mRNAs encoding functionally antagonistic proteins. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1212–1223. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Nathans D. A naturally occurring truncated form of FosB that inhibits Fos/Jun transcriptional activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):751–759. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90504-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nucifora G., Begy C. R., Erickson P., Drabkin H. A., Rowley J. D. The 3;21 translocation in myelodysplasia results in a fusion transcript between the AML1 gene and the gene for EAP, a highly conserved protein associated with the Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7784–7788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nucifora G., Begy C. R., Kobayashi H., Roulston D., Claxton D., Pedersen-Bjergaard J., Parganas E., Ihle J. N., Rowley J. D. Consistent intergenic splicing and production of multiple transcripts between AML1 at 21q22 and unrelated genes at 3q26 in (3;21)(q26;q22) translocations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):4004–4008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.4004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nucifora G., Birn D. J., Espinosa R., 3rd, Erickson P., LeBeau M. M., Roulston D., McKeithan T. W., Drabkin H., Rowley J. D. Involvement of the AML1 gene in the t(3;21) in therapy-related leukemia and in chronic myeloid leukemia in blast crisis. Blood. 1993 May 15;81(10):2728–2734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa E., Inuzuka M., Maruyama M., Satake M., Naito-Fujimoto M., Ito Y., Shigesada K. Molecular cloning and characterization of PEBP2 beta, the heterodimeric partner of a novel Drosophila runt-related DNA binding protein PEBP2 alpha. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):314–331. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Kagoshima H., Inuzuka M., Lu J., Satake M., Shigesada K., Ito Y. PEBP2/PEA2 represents a family of transcription factors homologous to the products of the Drosophila runt gene and the human AML1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6859–6863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Yaniv M. Two different factors bind to the alpha-domain of the polyoma virus enhancer, one of which also interacts with the SV40 and c-fos enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1331–1337. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redondo J. M., Pfohl J. L., Hernandez-Munain C., Wang S., Speck N. A., Krangel M. S. Indistinguishable nuclear factor binding to functional core sites of the T-cell receptor delta and murine leukemia virus enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4817–4823. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentoumis A., Chatterjee V. K., Madison L. D., Datta S., Gallagher G. D., Degroot L. J., Jameson J. L. Negative and positive transcriptional regulation by thyroid hormone receptor isoforms. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1522–1531. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-10-1522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Cohn L., Calame K. A dominant negative form of transcription activator mTFE3 created by differential splicing. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):94–97. doi: 10.1126/science.1840705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Valtieri M., Mavilio F., Reddy E. P. Effect of Abelson murine leukemia virus on granulocytic differentiation and interleukin-3 dependence of a murine progenitor cell line. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Inuzuka M., Shigesada K., Oikawa T., Ito Y. Differential expression of subspecies of polyomavirus and murine leukemia virus enhancer core binding protein, PEBP2, in various hematopoietic cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Jul;83(7):714–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb01971.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Toyoshima H., Sakai R., Miyagawa K., Hagiwara K., Hirai H., Ishikawa F., Takaku F. Mutations of the p53 gene in lymphoid leukemia. Blood. 1991 Mar 15;77(6):1153–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzow J., Friedman A. D. The murine myeloperoxidase promoter contains several functional elements, one of which binds a cell type-restricted transcription factor, myeloid nuclear factor 1 (MyNF1). Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2141–2151. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Nishida J., Mitani K., Ogawa S., Yazaki Y., Hirai H. Evi-1 raises AP-1 activity and stimulates c-fos promoter transactivation with dependence on the second zinc finger domain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24020–24026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Shibasaki F., Ishikawa M., Hirano N., Sakai R., Nishida J., Takenawa T., Hirai H. Molecular cloning of bovine actin-like protein, actin2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):1022–1028. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. W., Speck N. A. Purification of core-binding factor, a protein that binds the conserved core site in murine leukemia virus enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):89–102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S., Wang Q., Crute B. E., Melnikova I. N., Keller S. R., Speck N. A. Cloning and characterization of subunits of the T-cell receptor and murine leukemia virus enhancer core-binding factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3324–3339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen J., Wisdom R. M., Tratner I., Verma I. M. An alternative spliced form of FosB is a negative regulator of transcriptional activation and transformation by Fos proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5077–5081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]