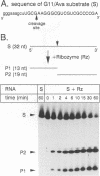
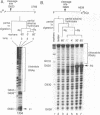
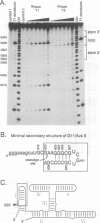
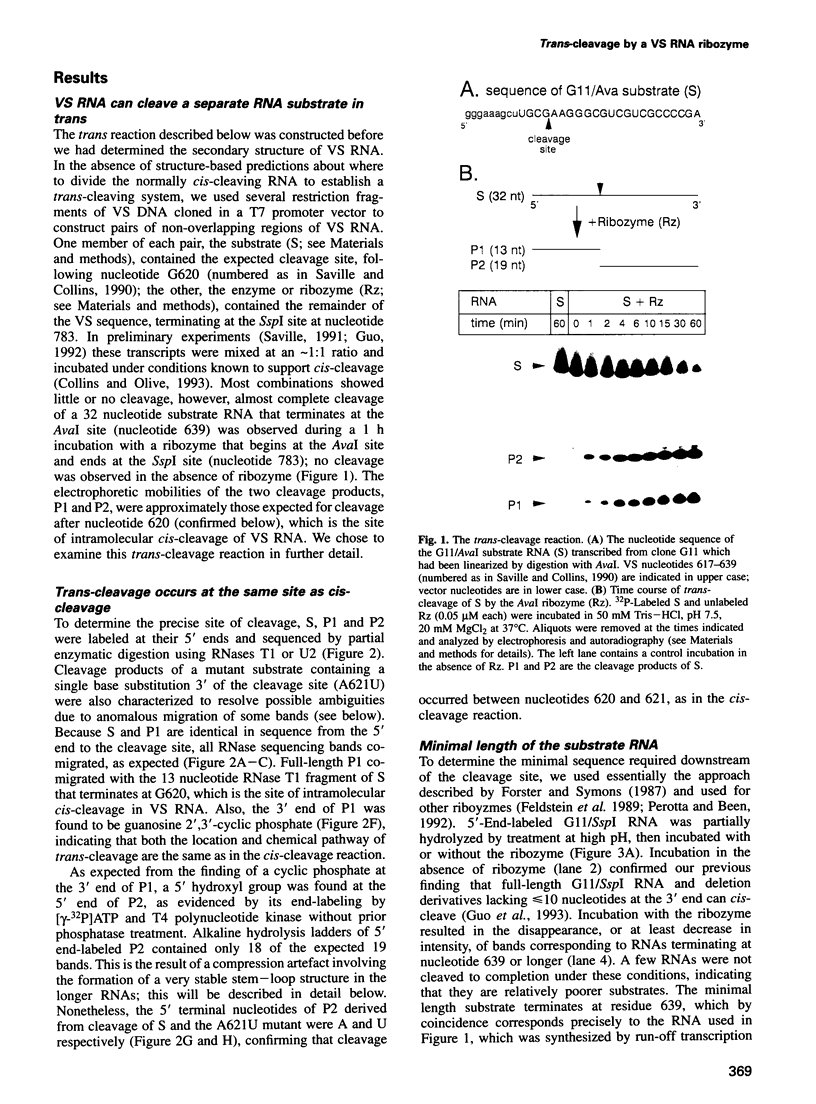
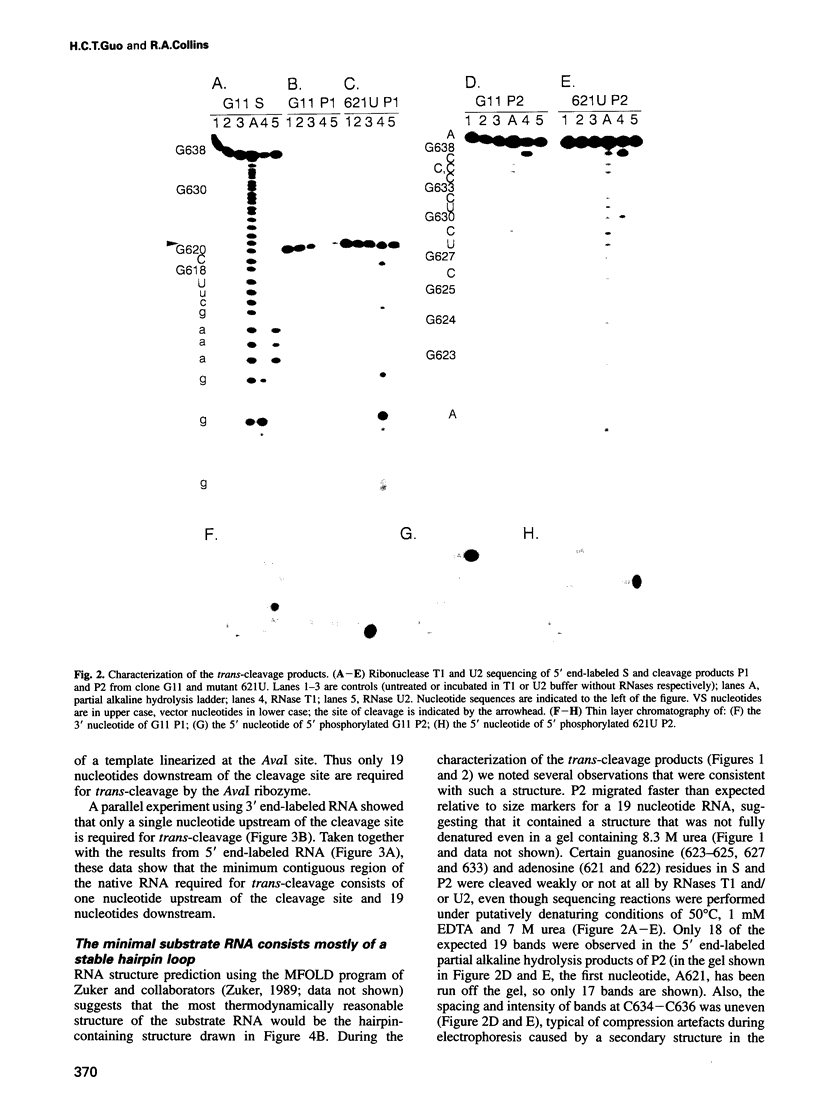
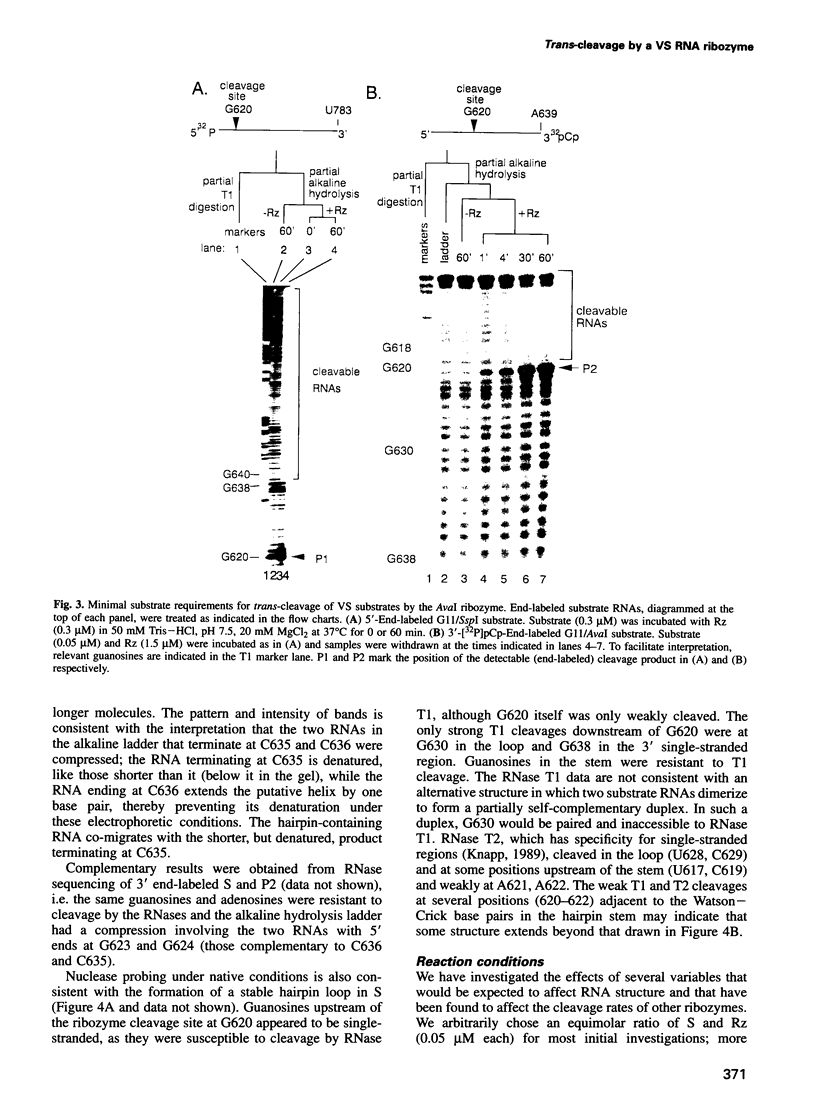
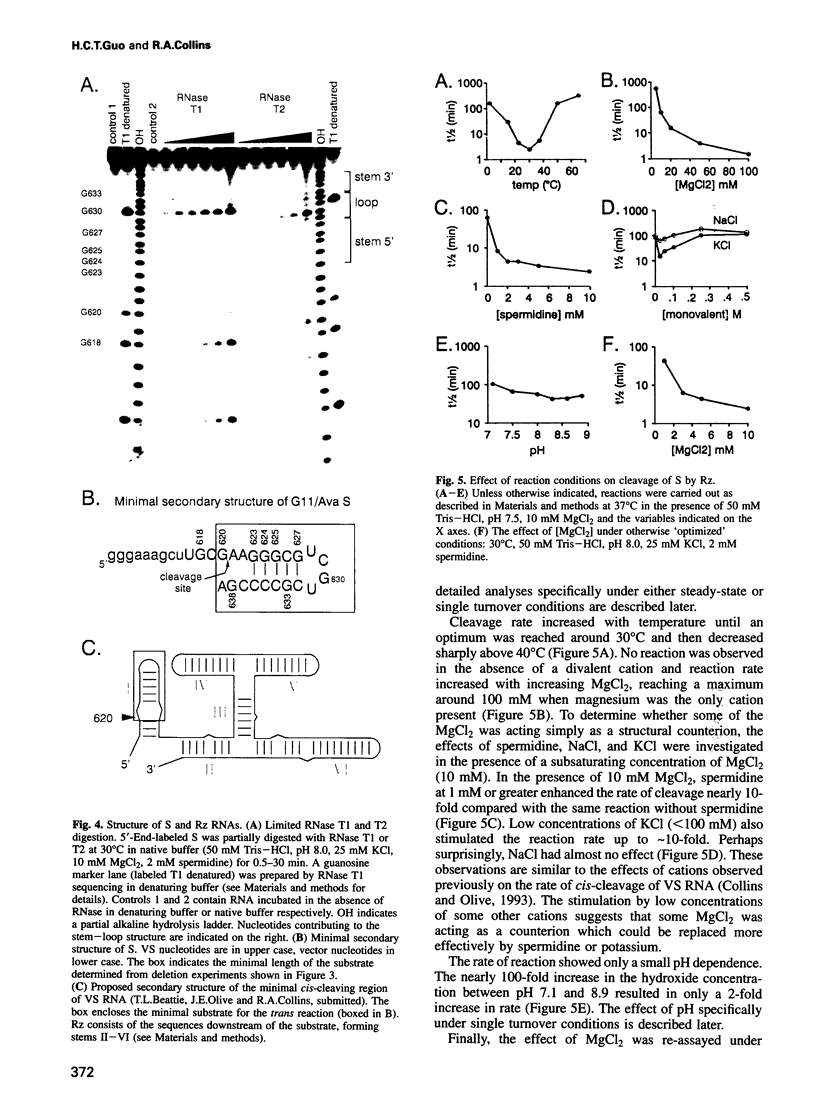
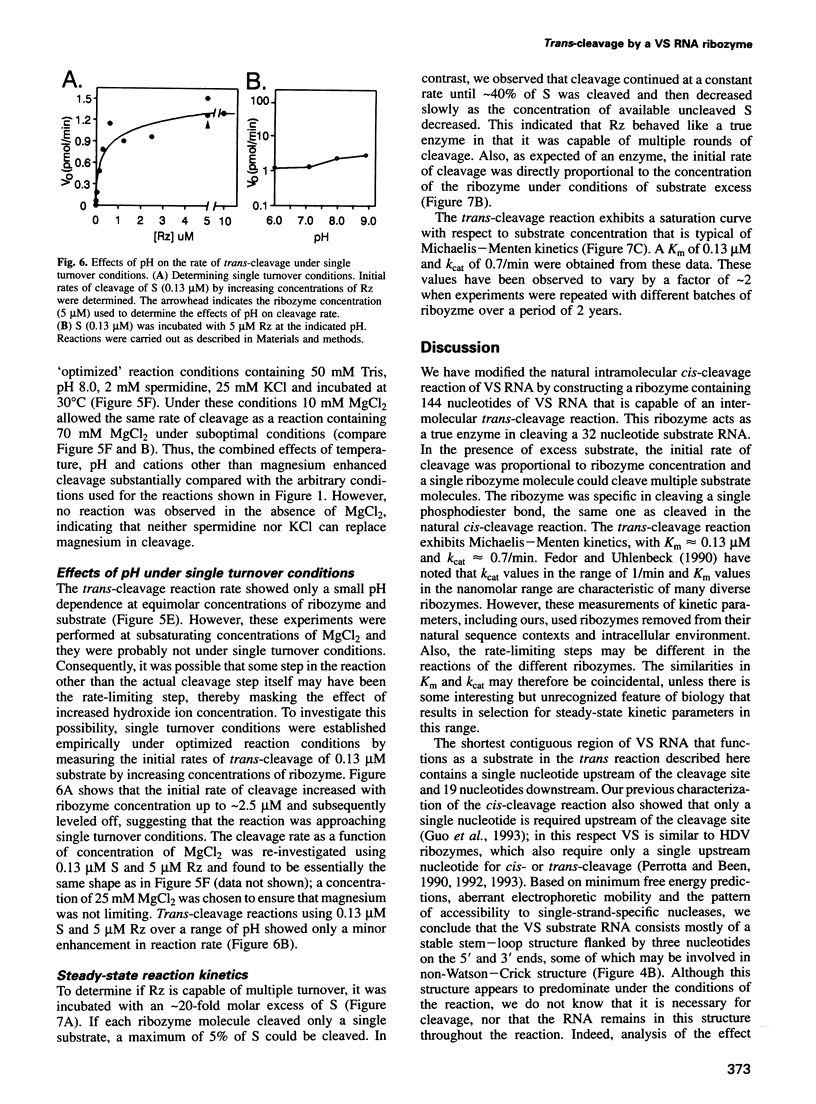
Abstract
We have constructed a ribozyme containing 144 nucleotides of Neurospora VS RNA that can catalyze the cleavage of a separate RNA in a true enzymatic manner (Km approximately 0.13 microM, kcat approximately 0.7/min). Comparison of the rates of cis- and trans-cleavage, as well as the lack of effect of pH on the rate of cleavage, suggest that a rate-limiting step, possibly a conformational change, occurs prior to cleavage. The minimum contiguous substrate sequence required for cleavage consists of one nucleotide upstream and 19 nucleotides downstream of the cleavage site. Unlike most other ribozymes which interact with long single-stranded regions of their substrates, the minimal substrate for the VS ribozyme consists mostly of a stable stem-loop, which would appear to preclude its recognition simply via extensive Watson-Crick base pairing.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beebe J. A., Fierke C. A. A kinetic mechanism for cleavage of precursor tRNA(Asp) catalyzed by the RNA component of Bacillus subtilis ribonuclease P. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 30;33(34):10294–10304. doi: 10.1021/bi00200a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch A. D., Robertson H. D. Efficient trans cleavage and a common structural motif for the ribozymes of the human hepatitis delta agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10163–10167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castanotto D., Rossi J. J., Deshler J. O. Biological and functional aspects of catalytic RNAs. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1992;2(4):331–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins R. A., Olive J. E. Reaction conditions and kinetics of self-cleavage of a ribozyme derived from Neurospora VS RNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 23;32(11):2795–2799. doi: 10.1021/bi00062a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins R. A., Saville B. J. Independent transfer of mitochondrial chromosomes and plasmids during unstable vegetative fusion in Neurospora. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):177–179. doi: 10.1038/345177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahm S. C., Derrick W. B., Uhlenbeck O. C. Evidence for the role of solvated metal hydroxide in the hammerhead cleavage mechanism. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 7;32(48):13040–13045. doi: 10.1021/bi00211a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dib-Hajj S. D., Boulanger S. C., Hebbar S. K., Peebles C. L., Franzen J. S., Perlman P. S. Domain 5 interacts with domain 6 and influences the second transesterification reaction of group II intron self-splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1797–1804. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doudna J. A., Szostak J. W. RNA-catalysed synthesis of complementary-strand RNA. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):519–522. doi: 10.1038/339519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Uhlenbeck O. C. Substrate sequence effects on "hammerhead" RNA catalytic efficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1668–1672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldstein P. A., Bruening G. Catalytically active geometry in the reversible circularization of 'mini-monomer' RNAs derived from the complementary strand of tobacco ringspot virus satellite RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1991–1998. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldstein P. A., Buzayan J. M., Bruening G. Two sequences participating in the autolytic processing of satellite tobacco ringspot virus complementary RNA. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldstein P. A., Buzayan J. M., van Tol H., deBear J., Gough G. R., Gilham P. T., Bruening G. Specific association between an endoribonucleolytic sequence from a satellite RNA and a substrate analogue containing a 2'-5' phosphodiester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2623–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of virusoid RNA is performed by the proposed 55-nucleotide active site. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90657-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. A physical assay for and kinetic analysis of the interactions between M1 RNA and tRNA precursor substrates. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 20;32(28):7152–7161. doi: 10.1021/bi00079a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Haydock K., Allen L., Altman S. Metal ion requirements and other aspects of the reaction catalyzed by M1 RNA, the RNA subunit of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1509–1515. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo H. C., De Abreu D. M., Tillier E. R., Saville B. J., Olive J. E., Collins R. A. Nucleotide sequence requirements for self-cleavage of Neurospora VS RNA. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):351–361. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampel A., Tritz R., Hicks M., Cruz P. 'Hairpin' catalytic RNA model: evidence for helices and sequence requirement for substrate RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):299–304. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D., Eckstein F., Cech T. R. The importance of being ribose at the cleavage site in the Tetrahymena ribozyme reaction. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 17;32(32):8312–8321. doi: 10.1021/bi00083a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D., Khosla M. Comparison of pH dependencies of the Tetrahymena ribozyme reactions with RNA 2'-substituted and phosphorothioate substrates reveals a rate-limiting conformational step. Biochemistry. 1994 May 3;33(17):5291–5297. doi: 10.1021/bi00183a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp G. Enzymatic approaches to probing of RNA secondary and tertiary structure. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:192–212. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. Y., Sharmeen L., Dinter-Gottlieb G., Taylor J. Characterization of self-cleaving RNA sequences on the genome and antigenome of human hepatitis delta virus. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4439–4444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4439-4444.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Umesono K., Ozeki H. Comparative and functional anatomy of group II catalytic introns--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):5–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrotta A. T., Been M. D. A pseudoknot-like structure required for efficient self-cleavage of hepatitis delta virus RNA. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):434–436. doi: 10.1038/350434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrotta A. T., Been M. D. Assessment of disparate structural features in three models of the hepatitis delta virus ribozyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 25;21(17):3959–3965. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.17.3959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrotta A. T., Been M. D. Cleavage of oligoribonucleotides by a ribozyme derived from the hepatitis delta virus RNA sequence. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):16–21. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrotta A. T., Been M. D. The self-cleaving domain from the genomic RNA of hepatitis delta virus: sequence requirements and the effects of denaturant. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6821–6827. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle A. M., Murphy F. L., Cech T. R. RNA substrate binding site in the catalytic core of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):123–128. doi: 10.1038/358123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saville B. J., Collins R. A. A site-specific self-cleavage reaction performed by a novel RNA in Neurospora mitochondria. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90480-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharmeen L., Kuo M. Y., Dinter-Gottlieb G., Taylor J. Antigenomic RNA of human hepatitis delta virus can undergo self-cleavage. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2674–2679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2674-2679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Burgin A. B., Haas E. S., Pace N. R. Influence of metal ions on the ribonuclease P reaction. Distinguishing substrate binding from catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2429–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Pace N. R. Multiple magnesium ions in the ribonuclease P reaction mechanism. Biochemistry. 1993 May 25;32(20):5273–5281. doi: 10.1021/bi00071a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Small catalytic RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:641–671. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W. Enzymatic activity of the conserved core of a group I self-splicing intron. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):83–86. doi: 10.1038/322083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C. A small catalytic oligoribonucleotide. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):596–600. doi: 10.1038/328596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altman S. Three-dimensional working model of M1 RNA, the catalytic RNA subunit of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5133–5137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. N., Wang Y. J., Hung C. F., Lee H. J., Lai M. M. Sequence and structure of the catalytic RNA of hepatitis delta virus genomic RNA. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90728-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. The intervening sequence RNA of Tetrahymena is an enzyme. Science. 1986 Jan 31;231(4737):470–475. doi: 10.1126/science.3941911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]