Abstract
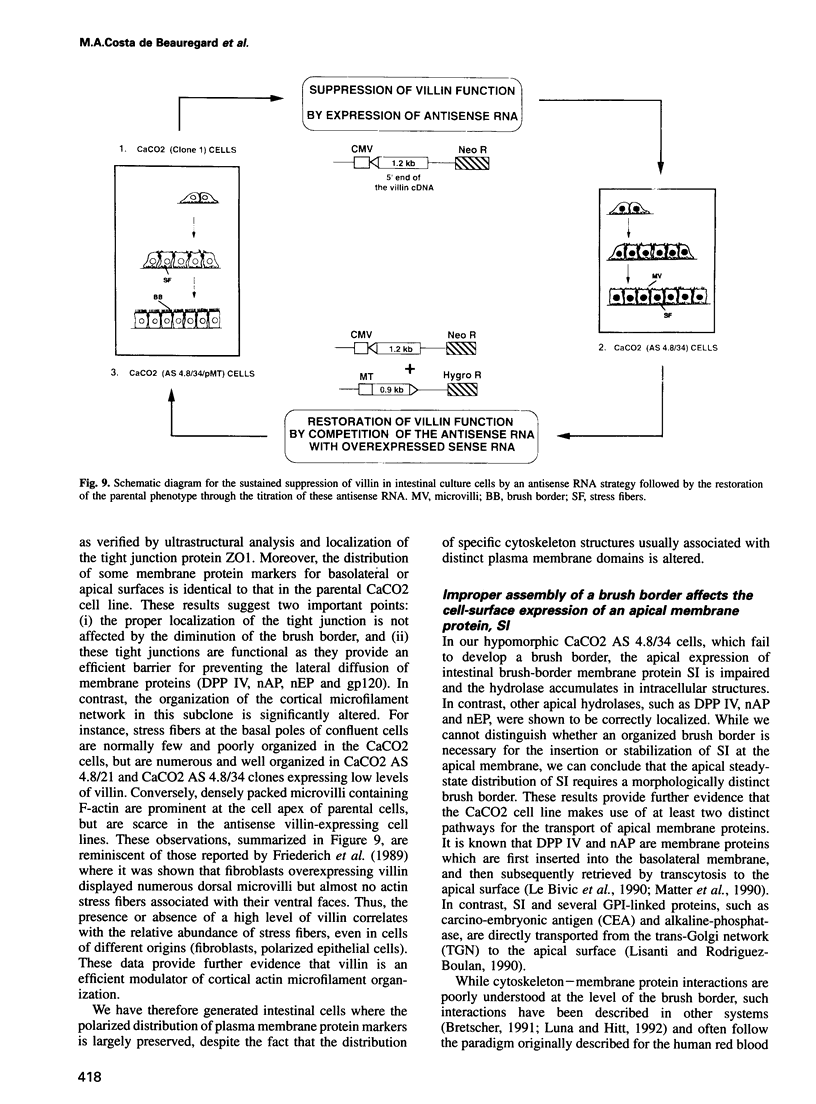
We have used an antisense RNA strategy to investigate the role of the actin-associated protein, villin, in the brush-border morphogenesis of human intestinal CaCO2 cells. Stable expression of a cDNA encoding antisense villin RNA resulted in the permanent down-regulation of the endogenous villin message and dramatically affected brush-border assembly. Ultrastructural and immunolocalization studies revealed that epithelial cell polarity was largely maintained. However, in contrast to brush-border markers such as dipeptidyl-peptidase IV, the apical localization of sucrase-isomaltase was specifically impaired. Retransfection of the villin antisense-expressing cell line with a cDNA encoding a partial sense villin RNA restored both brush-border assembly and sucrase-isomaltase apical expression. The suggestion that brush-border morphogenesis may be important for the trafficking of certain proteins is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
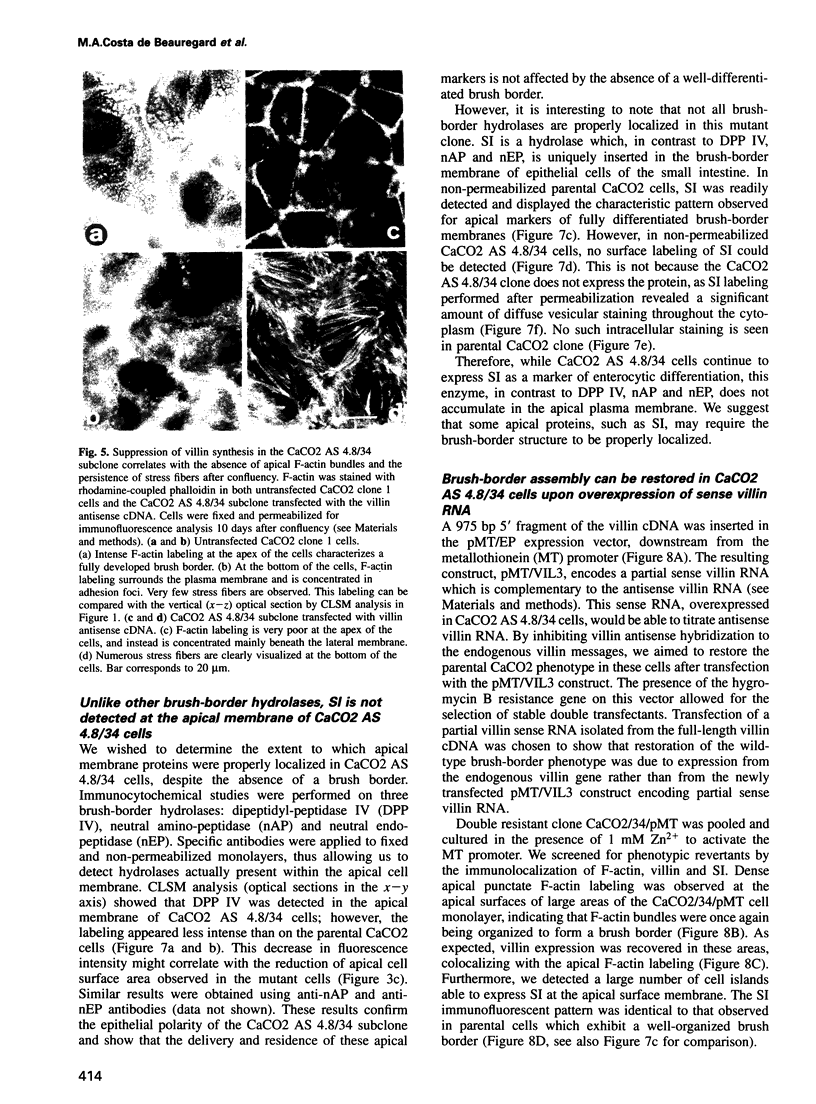
Selected References
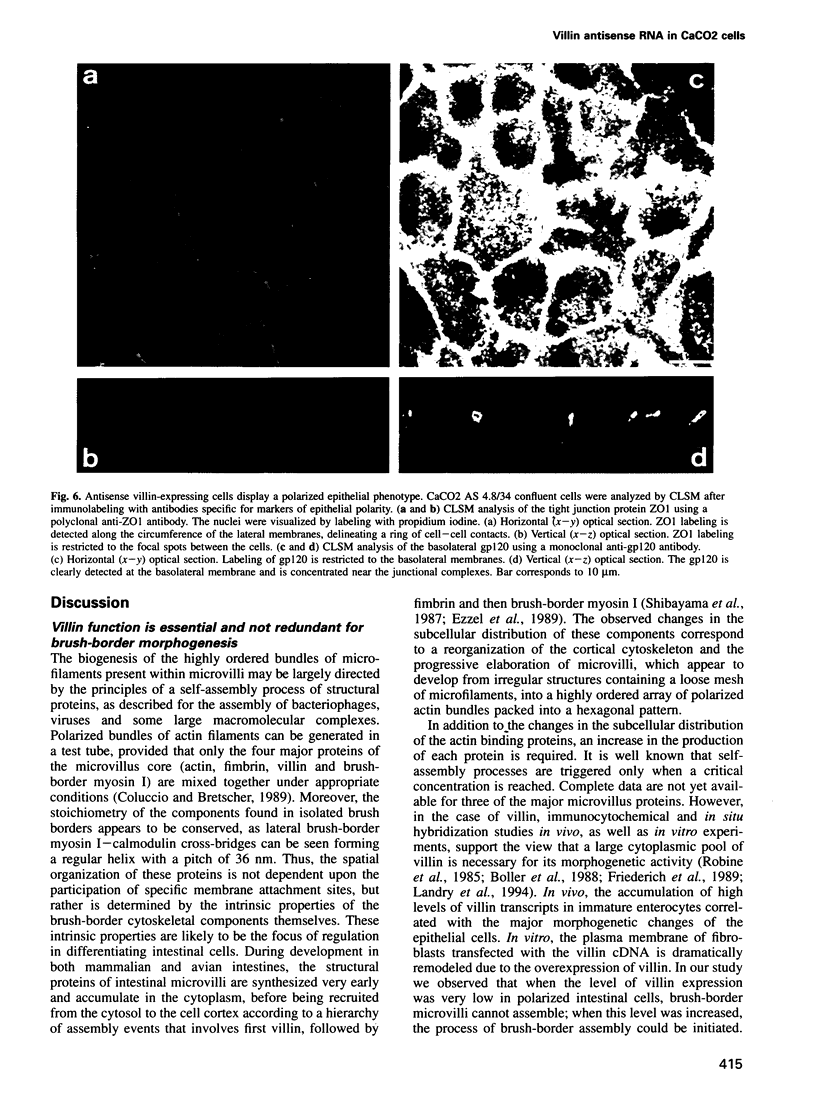
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
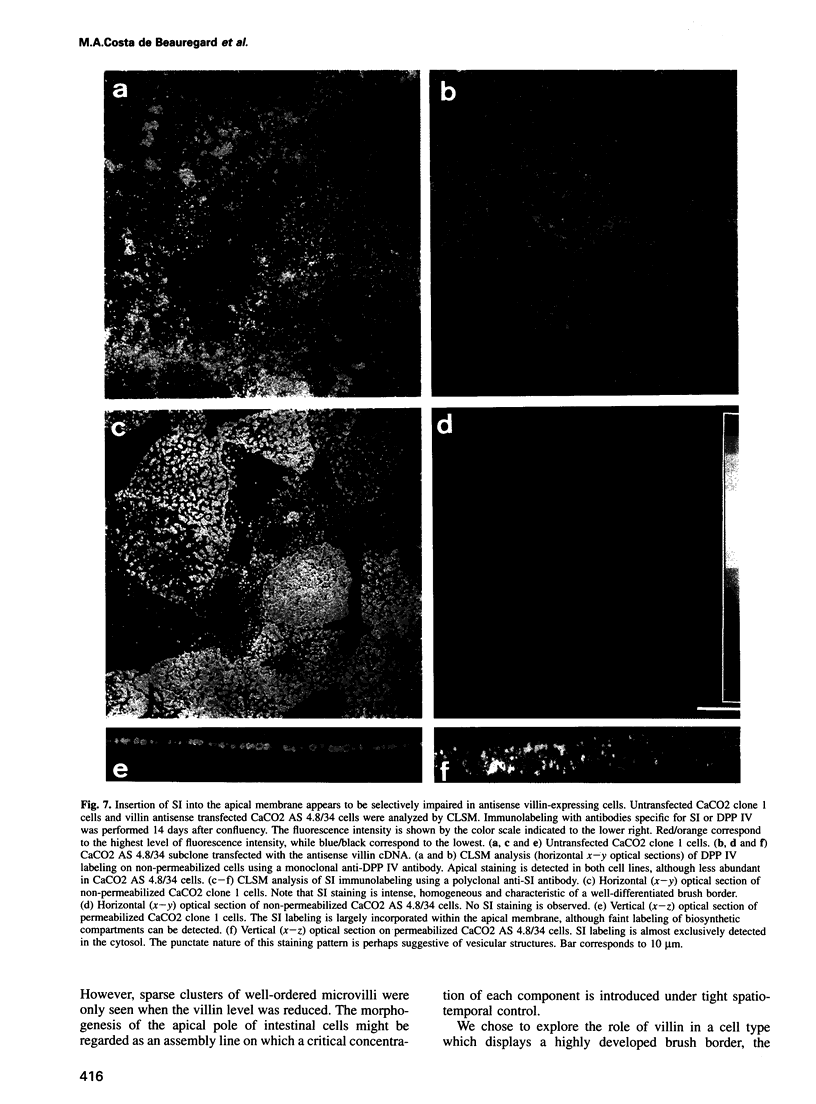
- Anderson J. M., Van Itallie C. M., Peterson M. D., Stevenson B. R., Carew E. A., Mooseker M. S. ZO-1 mRNA and protein expression during tight junction assembly in Caco-2 cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1047–1056. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
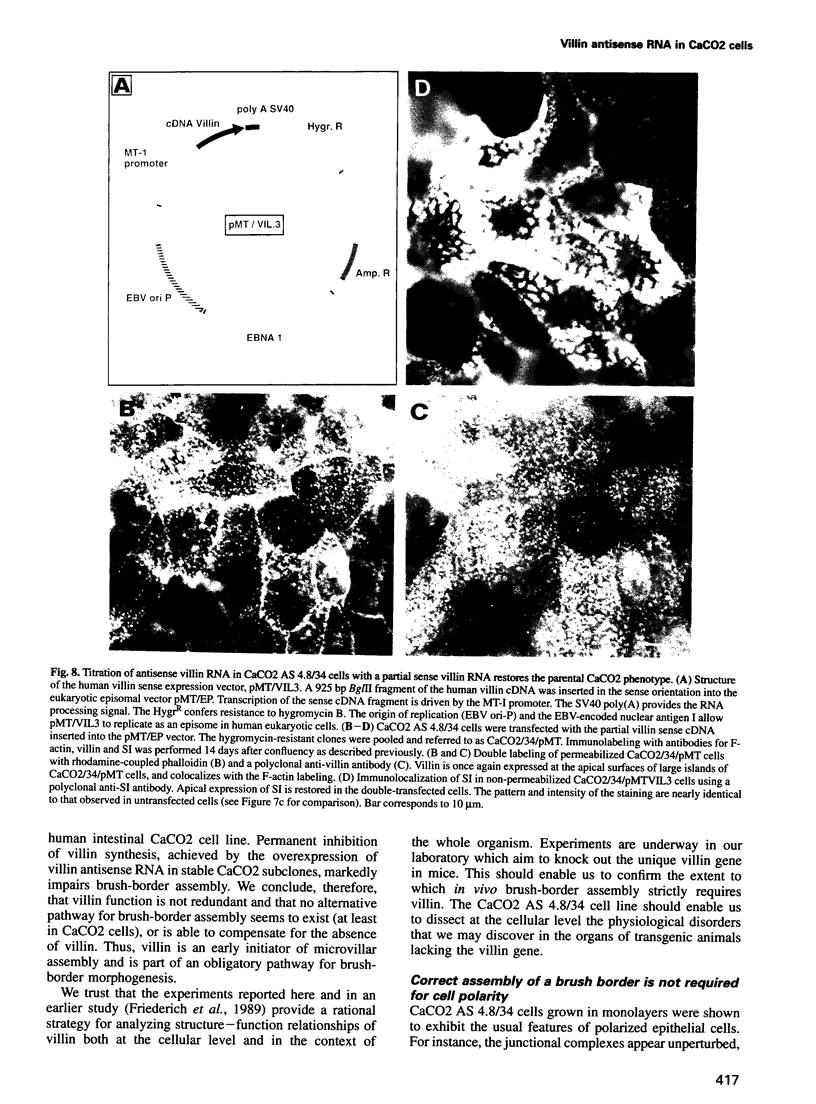
- Arpin M., Pringault E., Finidori J., Garcia A., Jeltsch J. M., Vandekerckhove J., Louvard D. Sequence of human villin: a large duplicated domain homologous with other actin-severing proteins and a unique small carboxy-terminal domain related to villin specificity. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1759–1766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. The spectrin-actin junction of erythrocyte membrane skeletons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boller K., Arpin M., Pringault E., Mangeat P., Reggio H. Differential distribution of villin and villin MRNA in mouse intestinal epithelial cells. Differentiation. 1988 Nov;39(1):51–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Cohen C. M., Tyler J. Interaction of cytoskeletal proteins on the human erythrocyte membrane. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. Microfilament structure and function in the cortical cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:337–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A. Antisense strategies in cell and developmental biology. J Cell Sci. 1990 Nov;97(Pt 3):399–409. doi: 10.1242/jcs.97.3.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coluccio L. M., Bretscher A. Reassociation of microvillar core proteins: making a microvillar core in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):495–502. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coudrier E., Reggio H., Louvard D. Characterization of an integral membrane glycoprotein associated with the microfilaments of pig intestinal microvilli. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):469–475. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudouet B., Robine S., Huet C., Sahuquillo-Merino C., Blair L., Coudrier E., Louvard D. Changes in villin synthesis and subcellular distribution during intestinal differentiation of HT29-18 clones. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):359–369. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers U., Klumperman J., Hauri H. P. Nocodazole, a microtubule-active drug, interferes with apical protein delivery in cultured intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):13–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezzell R. M., Chafel M. M., Matsudaira P. T. Differential localization of villin and fimbrin during development of the mouse visceral endoderm and intestinal epithelium. Development. 1989 Jun;106(2):407–419. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friederich E., Huet C., Arpin M., Louvard D. Villin induces microvilli growth and actin redistribution in transfected fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):461–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friederich E., Vancompernolle K., Huet C., Goethals M., Finidori J., Vandekerckhove J., Louvard D. An actin-binding site containing a conserved motif of charged amino acid residues is essential for the morphogenic effect of villin. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90535-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebelhaus D. H., Eib D. W., Moon R. T. Antisense RNA inhibits expression of membrane skeleton protein 4.1 during embryonic development of Xenopus. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):601–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90576-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Krebs K. E., Whitfield C. F., Riederer B. M., Zagon I. S. Spectrin and related molecules. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(2):171–234. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E., Bienz D., Fransen J. A., Marxer A. Expression and intracellular transport of microvillus membrane hydrolases in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):838–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintzelman M. B., Mooseker M. S. Assembly of the intestinal brush border cytoskeleton. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1992;26:93–122. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Weintraub H. Constitutive and conditional suppression of exogenous and endogenous genes by anti-sense RNA. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):345–352. doi: 10.1126/science.2990048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSEN F. C., GIRARDI A. J., GILDEN R. V., KOPROWSKI H. INFECTION OF HUMAN AND SIMIAN TISSUE CULTURES WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:53–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki M., Sato M., Kimura M., Yokoyama M., Kobayashi K., Nomura T. Conversion of normal behavior to shiverer by myelin basic protein antisense cDNA in transgenic mice. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):593–595. doi: 10.1126/science.2456614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Wold B. J. Stable reduction of thymidine kinase activity in cells expressing high levels of anti-sense RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Loomis W. F. Antisense RNA inactivation of myosin heavy chain gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1081–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.3576221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry C., Huet C., Mangeat P., Sahuquet A., Louvard D., Crine P. Comparative analysis of neutral endopeptidase (NEP) and villin gene expression during mouse embryogenesis and enterocyte maturation. Differentiation. 1994 Apr;56(1-2):55–65. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.1994.56120055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bivic A., Quaroni A., Nichols B., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Biogenetic pathways of plasma membrane proteins in Caco-2, a human intestinal epithelial cell line. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1351–1361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Glycophospholipid membrane anchoring provides clues to the mechanism of protein sorting in polarized epithelial cells. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90195-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd M. L., Olsen W. A. A study of the molecular pathology of sucrase-isomaltase deficiency. A defect in the intracellular processing of the enzyme. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 19;316(8):438–442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702193160804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D. Apical membrane aminopeptidase appears at site of cell-cell contact in cultured kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4132–4136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., Hitt A. L. Cytoskeleton--plasma membrane interactions. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):955–964. doi: 10.1126/science.1439807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamajiwalla S. N., Fath K. R., Burgess D. R. Development of the chicken intestinal epithelium. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1992;26:123–143. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Brauchbar M., Bucher K., Hauri H. P. Sorting of endogenous plasma membrane proteins occurs from two sites in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeill H., Ozawa M., Kemler R., Nelson W. J. Novel function of the cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin as an inducer of cell surface polarity. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90368-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naim H. Y., Roth J., Sterchi E. E., Lentze M., Milla P., Schmitz J., Hauri H. P. Sucrase-isomaltase deficiency in humans. Different mutations disrupt intracellular transport, processing, and function of an intestinal brush border enzyme. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):667–679. doi: 10.1172/JCI113646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palek J., Sahr K. E. Mutations of the red blood cell membrane proteins: from clinical evaluation to detection of the underlying genetic defect. Blood. 1992 Jul 15;80(2):308–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. D., Bement W. M., Mooseker M. S. An in vitro model for the analysis of intestinal brush border assembly. II. Changes in expression and localization of brush border proteins during cell contact-induced brush border assembly in Caco-2BBe cells. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jun;105(Pt 2):461–472. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.2.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. D., Mooseker M. S. An in vitro model for the analysis of intestinal brush border assembly. I. Ultrastructural analysis of cell contact-induced brush border assembly in Caco-2BBe cells. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jun;105(Pt 2):445–460. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.2.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. D., Mooseker M. S. Characterization of the enterocyte-like brush border cytoskeleton of the C2BBe clones of the human intestinal cell line, Caco-2. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jul;102(Pt 3):581–600. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. D., Jenkins P., Raafat F., Walker-Smith J. A. Congenital microvillous atrophy: specific diagnostic features. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Feb;60(2):135–140. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollenz R. S., Chen T. L., Trivinos-Lagos L., Chisholm R. L. The Dictyostelium essential light chain is required for myosin function. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):951–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90614-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringault E., Arpin M., Garcia A., Finidori J., Louvard D. A human villin cDNA clone to investigate the differentiation of intestinal and kidney cells in vivo and in culture. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3119–3124. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringault E., Robine S., Louvard D. Structure of the human villin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10811–10815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reggio H., Webster P., Louvard D. Use of immunocytochemical techniques in studying the biogenesis of cell surfaces in polarized epithelia. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:379–395. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robine S., Huet C., Moll R., Sahuquillo-Merino C., Coudrier E., Zweibaum A., Louvard D. Can villin be used to identify malignant and undifferentiated normal digestive epithelial cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8488–8492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robine S., Sahuquillo-Merino C., Louvard D., Pringault E. Regulatory sequences on the human villin gene trigger the expression of a reporter gene in a differentiating HT29 intestinal cell line. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11426–11434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez Fernández J. L., Geiger B., Salomon D., Ben-Ze'ev A. Suppression of vinculin expression by antisense transfection confers changes in cell morphology, motility, and anchorage-dependent growth of 3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(6):1285–1294. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.6.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibayama T., Carboni J. M., Mooseker M. S. Assembly of the intestinal brush border: appearance and redistribution of microvillar core proteins in developing chick enterocytes. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):335–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. A 12-base-pair DNA motif that is repeated several times in metallothionein gene promoters confers metal regulation to a heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7318–7322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojan J., Blossey B. K., Johnson T. R., Rudin S. D., Tykocinski M., Ilan J., Ilan J. Loss of tumorigenicity of rat glioblastoma directed by episome-based antisense cDNA transcription of insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4874–4878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. E., Shelanski M. L., Liem R. K. Suppression by antisense mRNA demonstrates a requirement for the glial fibrillary acidic protein in the formation of stable astrocytic processes in response to neurons. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1205–1213. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]