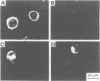
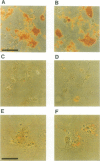
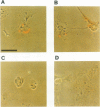
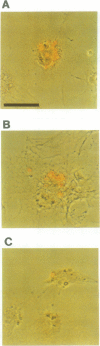
Abstract
Cross-linking of the high affinity receptor for IgG, Fc gamma RI, can result in both endocytosis of immune complexes and phagocytosis of opsonized particles in myeloid cells, although the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor lacks the tyrosine activation motif which has been implicated in signal transduction triggered by cross-linking of other Fc receptors. To identify the structural determinants of Fc gamma RI-mediated ligand internalization, we have expressed Fc gamma RI or truncated versions of Fc gamma RI in COS cells, either alone or in the presence of the Fc epsilon RI gamma subunit (which contains a classical tyrosine activation motif and associates with Fc gamma RI in myeloid cells), and assessed their ability to mediate endocytosis and phagocytosis. We have found that Fc gamma RI alone (in the absence of the gamma subunit) is capable of mediating endocytosis in COS cells and that the process occurs via a novel, tyrosine kinase-independent signalling pathway. Activation of this pathway following cross-linking appears to require only the receptor extracellular domain. In contrast, Fc gamma RI phagocytic function in COS cells is dependent on an interaction between the receptor transmembrane domain and the gamma subunit and is mediated by recruitment of tyrosine kinase activity. Our data therefore indicate that distinct domains of the receptor regulate ligand internalization following receptor cross-linking by either immune complexes (endocytosis) or opsonized particles (phagocytosis) and that these functions are mediated by different intracellular signalling pathways.
Full text
PDF
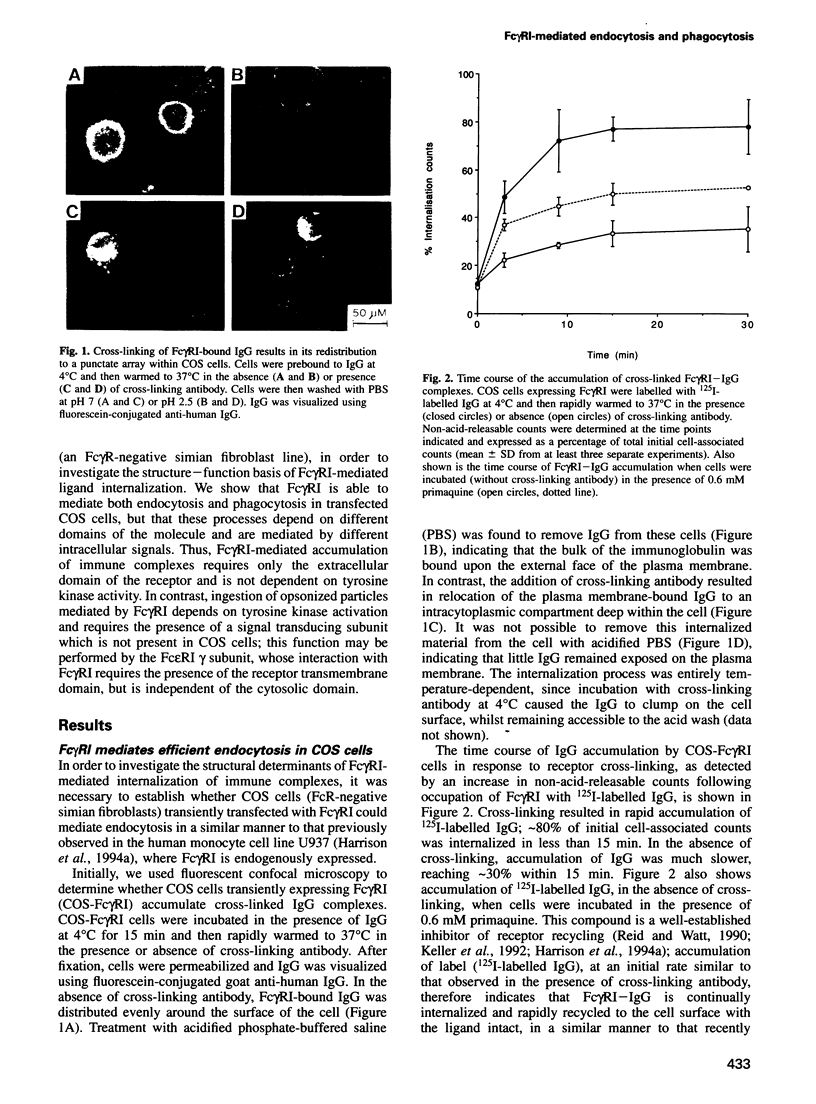
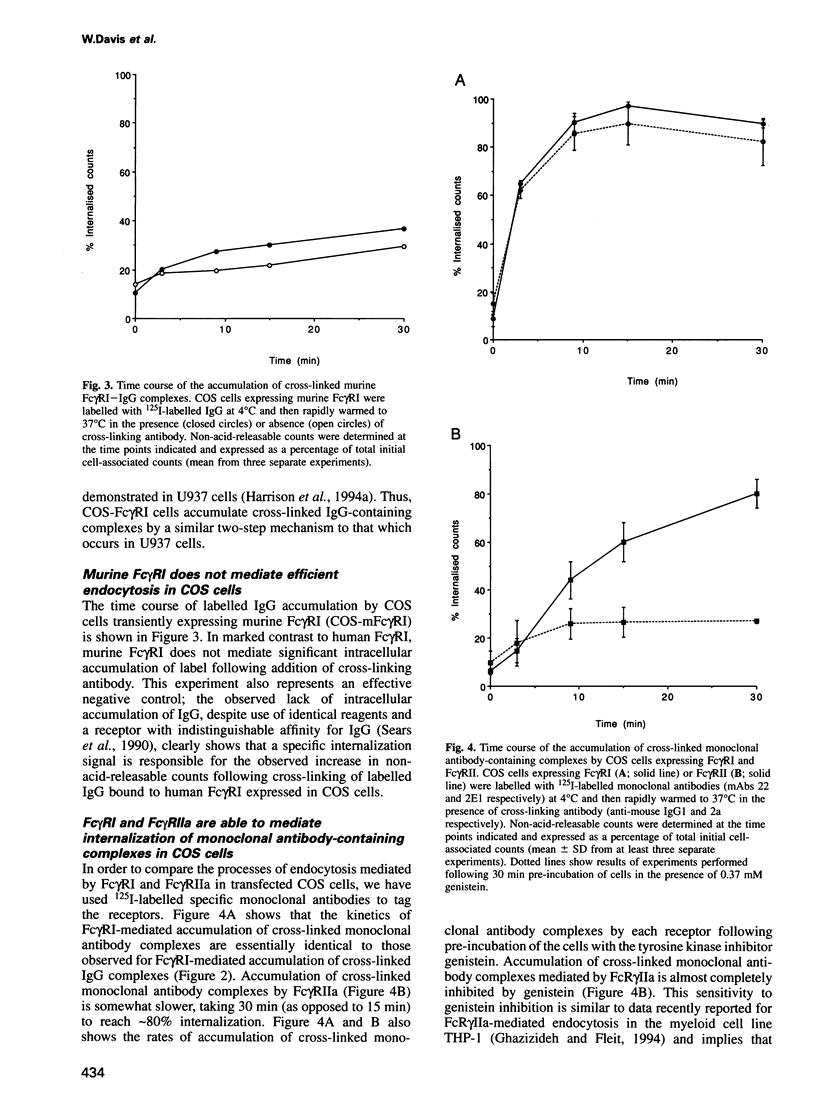
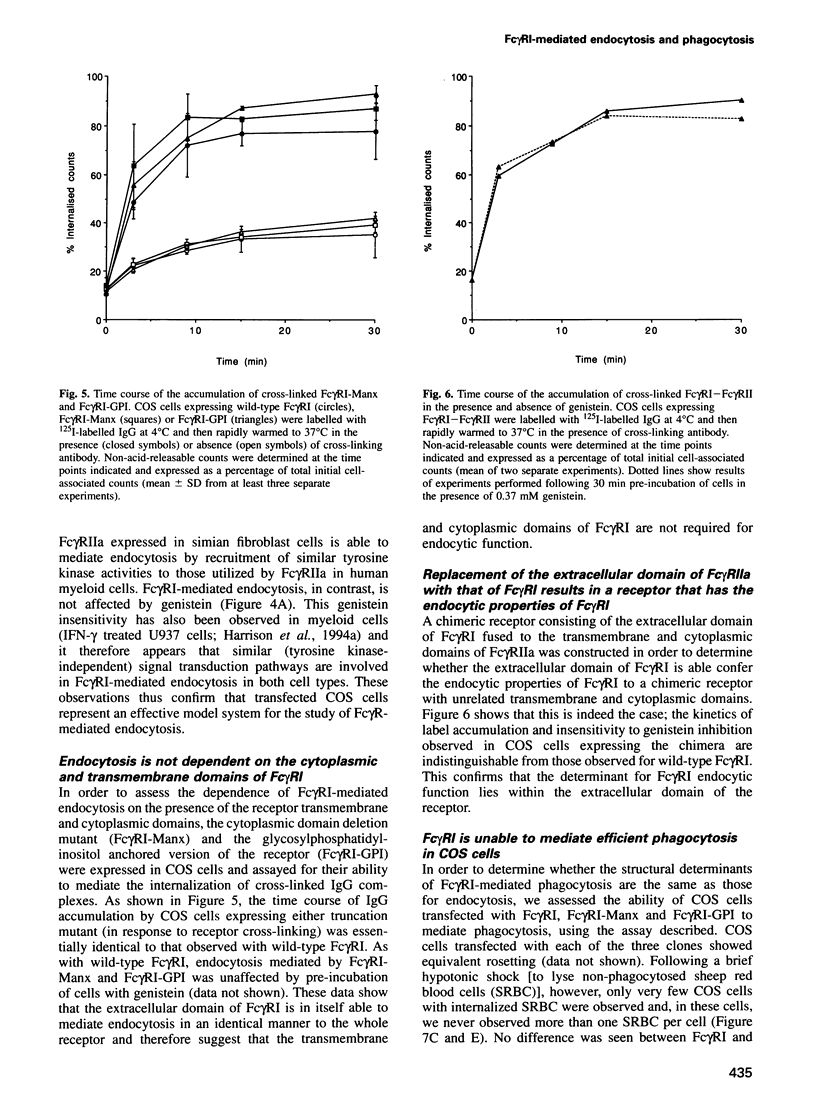
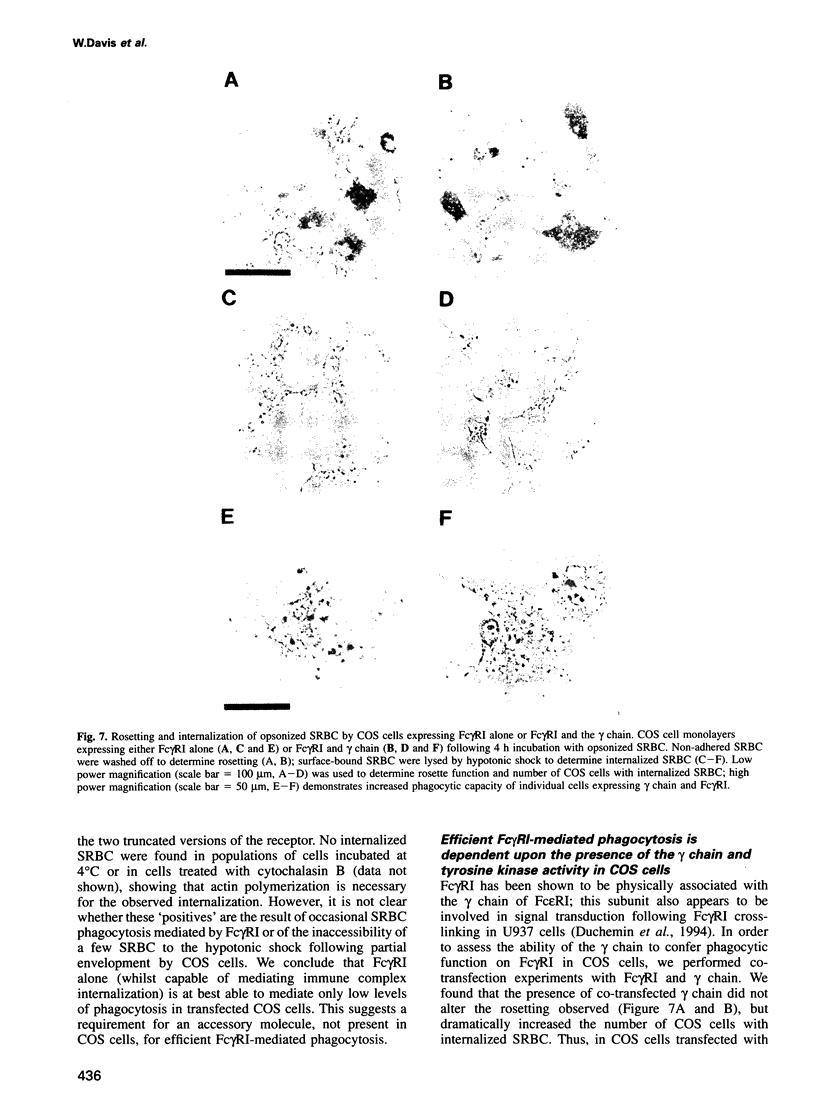




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. M., Seed B. Isolation and expression of functional high-affinity Fc receptor complementary DNAs. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):378–381. doi: 10.1126/science.2911749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amigorena S., Bonnerot C., Drake J. R., Choquet D., Hunziker W., Guillet J. G., Webster P., Sautes C., Mellman I., Fridman W. H. Cytoplasmic domain heterogeneity and functions of IgG Fc receptors in B lymphocytes. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1535455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amigorena S., Salamero J., Davoust J., Fridman W. H., Bonnerot C. Tyrosine-containing motif that transduces cell activation signals also determines internalization and antigen presentation via type III receptors for IgG. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):337–341. doi: 10.1038/358337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. L., Shen L., Eicher D. M., Wewers M. D., Gill J. K. Phagocytosis mediated by three distinct Fc gamma receptor classes on human leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1333–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnerot C., Amigorena S. Murine low-affinity receptors for the Fc portion of IgG. Roles in cell activation and ligand internalization. Receptors Channels. 1993;1(1):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchemin A. M., Ernst L. K., Anderson C. L. Clustering of the high affinity Fc receptor for immunoglobulin G (Fc gamma RI) results in phosphorylation of its associated gamma-chain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):12111–12117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durden D. L., Rosen H., Cooper J. A. Serine/threonine phosphorylation of the gamma-subunit after activation of the high-affinity Fc receptor for immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1994 Apr 15;299(Pt 2):569–577. doi: 10.1042/bj2990569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst L. K., Duchemin A. M., Anderson C. L. Association of the high-affinity receptor for IgG (Fc gamma RI) with the gamma subunit of the IgE receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6023–6027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazizadeh S., Fleit H. B. Tyrosine phosphorylation provides an obligatory early signal for Fc gamma RII-mediated endocytosis in the monocytic cell line THP-1. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 1;152(1):30–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S., Chang P., Silverstein S. C. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the gamma subunit of Fc gamma receptors, p72syk, and paxillin during Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3897–3902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. T., Davis W., Norman J. C., Hockaday A. R., Allen J. M. Binding of monomeric immunoglobulin G triggers Fc gamma RI-mediated endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24396–24402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. T., Hutchinson M. J., Allen J. M. A convenient method for the construction and expression of GPI-anchored proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Sep 11;22(18):3813–3814. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.18.3813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Indik Z., Kelly C., Chien P., Levinson A. I., Schreiber A. D. Human Fc gamma RII, in the absence of other Fc gamma receptors, mediates a phagocytic signal. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1766–1771. doi: 10.1172/JCI115496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. A., Siegel M. W., Caras I. W. Endocytosis of glycophospholipid-anchored and transmembrane forms of CD4 by different endocytic pathways. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):863–874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. T., Shen Z., Boros P., Unkeless J. C. Fc receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Clin Immunol. 1994 Jan;14(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF01541170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen H. M., Matter K., Hunziker W., Rose J. K., Mellman I. Fc receptor endocytosis is controlled by a cytoplasmic domain determinant that actively prevents coated pit localization. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(4):875–888. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.4.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odin J. A., Edberg J. C., Painter C. J., Kimberly R. P., Unkeless J. C. Regulation of phagocytosis and [Ca2+]i flux by distinct regions of an Fc receptor. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1785–1788. doi: 10.1126/science.1837175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P. A., Watts C. Cycling of cell-surface MHC glycoproteins through primaquine-sensitive intracellular compartments. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):655–657. doi: 10.1038/346655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears D. W., Osman N., Tate B., McKenzie I. F., Hogarth P. M. Molecular cloning and expression of the mouse high affinity Fc receptor for IgG. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):371–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Aruffo A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stengelin S., Stamenkovic I., Seed B. Isolation of cDNAs for two distinct human Fc receptors by ligand affinity cloning. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1053–1059. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte M. K., Hardwick S. J., Meagher L. C., Savill J. S., Haslett C. Transient elevations of cytosolic free calcium retard subsequent apoptosis in neutrophils in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):446–455. doi: 10.1172/JCI116587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Capel P. J. Human IgG Fc receptor heterogeneity: molecular aspects and clinical implications. Immunol Today. 1993 May;14(5):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90166-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]