Abstract
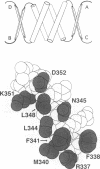
The p53 tumor suppressor forms stable tetramers, whose DNA binding activity is allosterically regulated. The tetramerization domain is contained within the C-terminus (residues 323-355) and its three-dimensional structure exhibits dihedral symmetry, such that a p53 tetramer can be considered a dimer of dimers. Under conditions where monomeric p53 fails to bind DNA, we studied the effects of p53 C-terminal mutations on DNA binding. Residues 322-355 were sufficient to drive DNA binding of p53 as a tetramer. Within this region residues predicted by the three-dimensional structure to stabilize tetramerization, such as Arg337 and Phe341, were critical for DNA binding. Furthermore, substitution of Leu344 caused p53 to dissociate into DNA binding-competent dimers, consistent with the location of this residue at the dimer-dimer interface. The p53 DNA site contains two inverted repeats juxtaposed to a second pair of inverted repeats. Thus, the four repeats exhibit cyclic-translation symmetry and cannot be recognized simultaneously by four dihedrally symmetric p53 DNA binding domains. The discrepancy may be resolved by flexible linkers between the p53 DNA binding and tetramerization domains. When these linkers were deleted p53 exhibited novel DNA binding properties consistent with an inability to recognize four contiguous DNA repeats. Allosteric regulation of p53 DNA binding may involve repositioning the DNA binding domains from a dihedrally symmetric state to a DNA-bound asymmetric state.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti S., Oehler S., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Genetic analysis of the leucine heptad repeats of Lac repressor: evidence for a 4-helical bundle. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3227–3236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05992.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Manfredi J. J., Chen X., Marshak D. R., Prives C. A proteolytic fragment from the central region of p53 has marked sequence-specific DNA-binding activity when generated from wild-type but not from oncogenic mutant p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2565–2574. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Reynisdóttir I., Friedman P. N., Prives C. Site-specific binding of wild-type p53 to cellular DNA is inhibited by SV40 T antigen and mutant p53. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1886–1898. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho Y., Gorina S., Jeffrey P. D., Pavletich N. P. Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):346–355. doi: 10.1126/science.8023157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Omichinski J. G., Sakaguchi K., Zambrano N., Sakamoto H., Appella E., Gronenborn A. M. High-resolution structure of the oligomerization domain of p53 by multidimensional NMR. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):386–391. doi: 10.1126/science.8023159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer G., Bargonetti J., Zhu H., Friedman P., Prywes R., Prives C. Wild-type p53 activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):83–86. doi: 10.1038/358083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. N., Chen X., Bargonetti J., Prives C. The p53 protein is an unusually shaped tetramer that binds directly to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. p53: a glimpse at the puppet behind the shadow play. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):334–335. doi: 10.1126/science.8023155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., Pak D. T., Karas R. H., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. A transcriptionally active DNA-binding site for human p53 protein complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2866–2871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut P., Hall A., Milner J. Analysis of p53 quaternary structure in relation to sequence-specific DNA binding. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):299–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Davis L. J., Kandil A. N. Wild-type p53 adopts a 'mutant'-like conformation when bound to DNA. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1021–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Conformational shifts propagate from the oligomerization domain of p53 to its tetrameric DNA binding domain and restore DNA binding to select p53 mutants. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5057–5064. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4, a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, binds as a dimer to target DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Meek D. W., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. Regulation of the specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90562-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwabuchi K., Li B., Bartel P., Fields S. Use of the two-hybrid system to identify the domain of p53 involved in oligomerization. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1693–1696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraiss S., Quaiser A., Oren M., Montenarh M. Oligomerization of oncoprotein p53. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4737–4744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4737-4744.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Niemöller M., Amouyal M., Revet B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. lac repressor forms loops with linear DNA carrying two suitably spaced lac operators. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1481–1491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J., Chen J., Elenbaas B., Levine A. J. Several hydrophobic amino acids in the p53 amino-terminal domain are required for transcriptional activation, binding to mdm-2 and the adenovirus 5 E1B 55-kD protein. Genes Dev. 1994 May 15;8(10):1235–1246. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.10.1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. Cotranslation of activated mutant p53 with wild type drives the wild-type p53 protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90384-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Chambers K. A., Pabo C. O. The DNA-binding domain of p53 contains the four conserved regions and the major mutation hot spots. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2556–2564. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto H., Lewis M. S., Kodama H., Appella E., Sakaguchi K. Specific sequences from the carboxyl terminus of human p53 gene product form anti-parallel tetramers in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8974–8978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenger J. E., Mayr G. A., Mann K., Tegtmeyer P. Formation of stable p53 homotetramers and multiples of tetramers. Mol Carcinog. 1992;5(2):102–106. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940050204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Brain R., Addison C., Rudge K., Remm M., Grimaldi M., Keenan E., Jenkins J. R. A C-terminal alpha-helix plus basic region motif is the major structural determinant of p53 tetramerization. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1513–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Nau M. M., Segal S., Minna J. D. p53: a transdominant regulator of transcription whose function is ablated by mutations occurring in human cancer. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1383–1390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade-Evans A., Jenkins J. R. Precise epitope mapping of the murine transformation-associated protein, p53. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):699–706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P., Reed M., Wang Y., Mayr G., Stenger J. E., Anderson M. E., Schwedes J. F., Tegtmeyer P. p53 domains: structure, oligomerization, and transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5182–5191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Reed M., Wang P., Stenger J. E., Mayr G., Anderson M. E., Schwedes J. F., Tegtmeyer P. p53 domains: identification and characterization of two autonomous DNA-binding regions. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2575–2586. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Bayle J. H., Olson D., Levine A. J. The p53-mdm-2 autoregulatory feedback loop. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1126–1132. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]