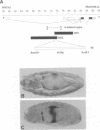
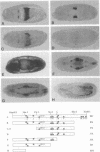
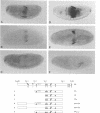
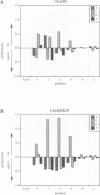
Abstract
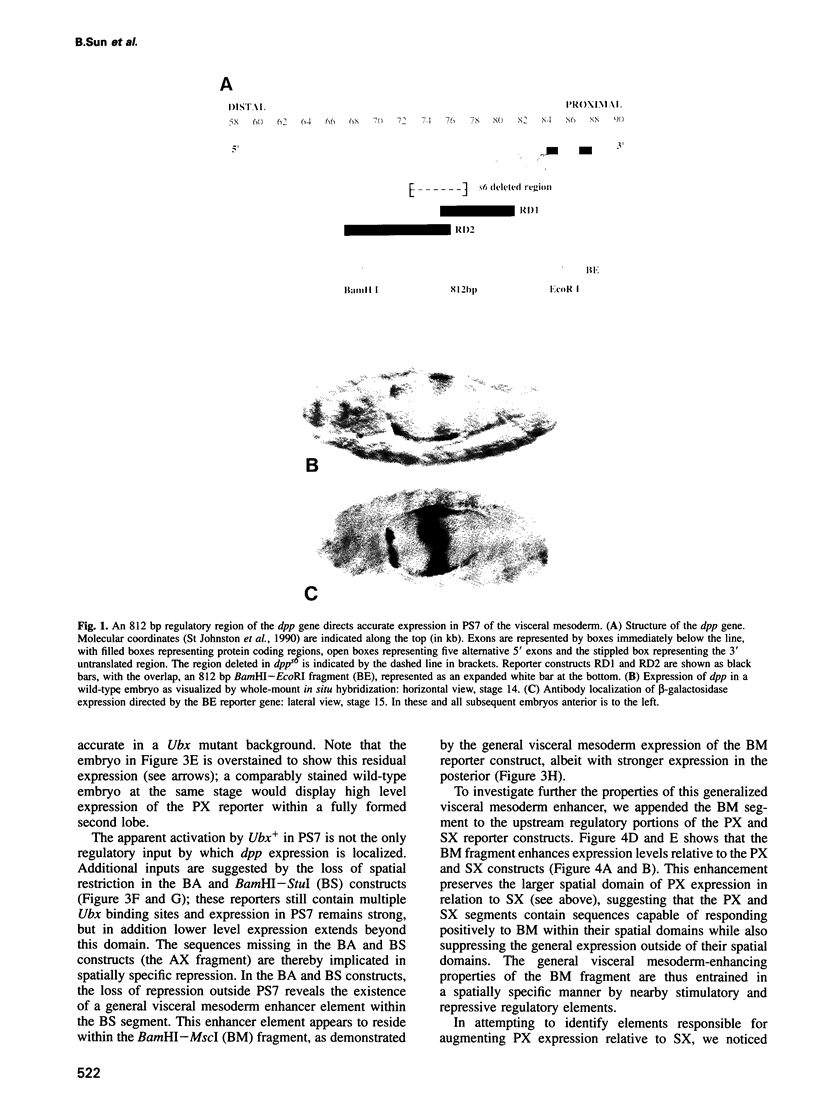
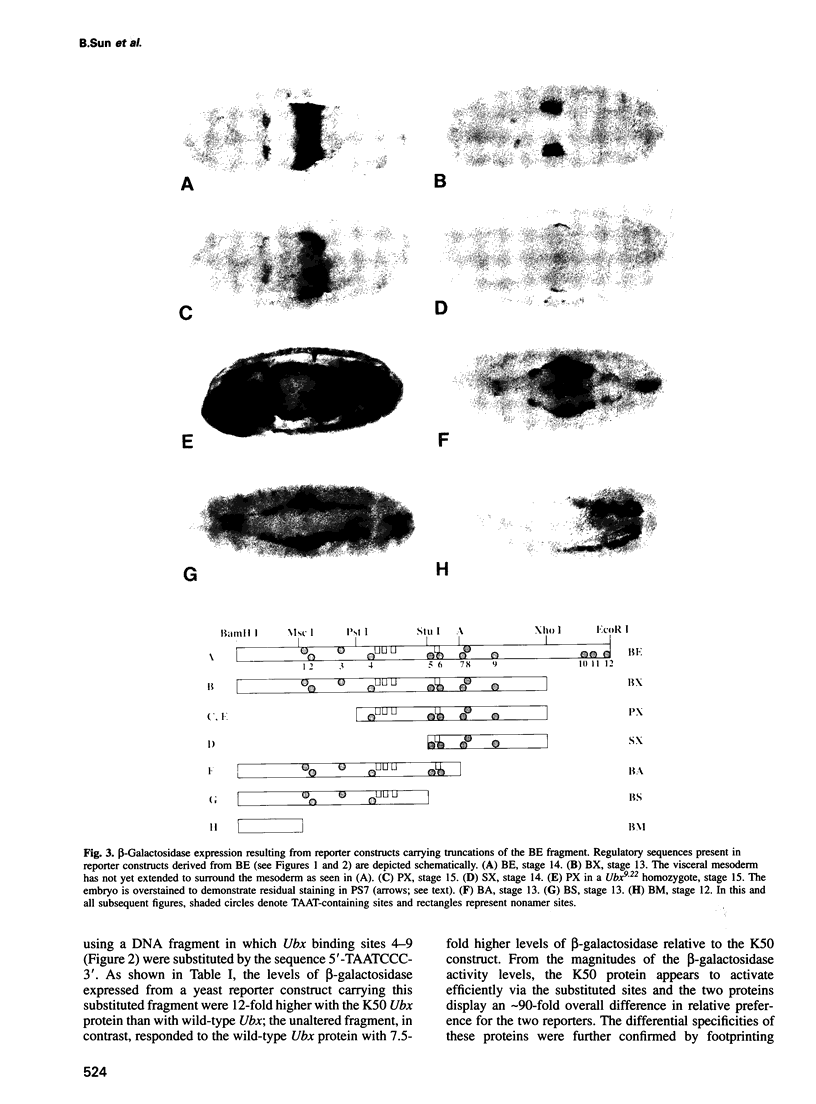
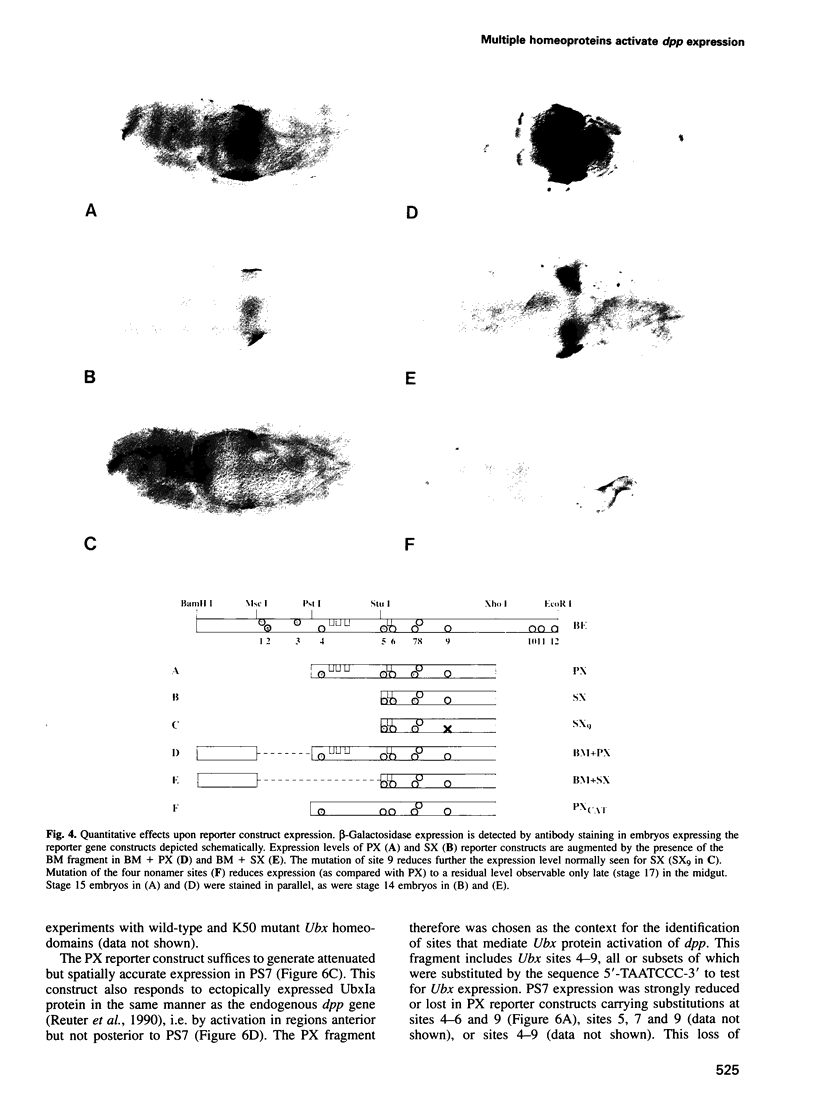
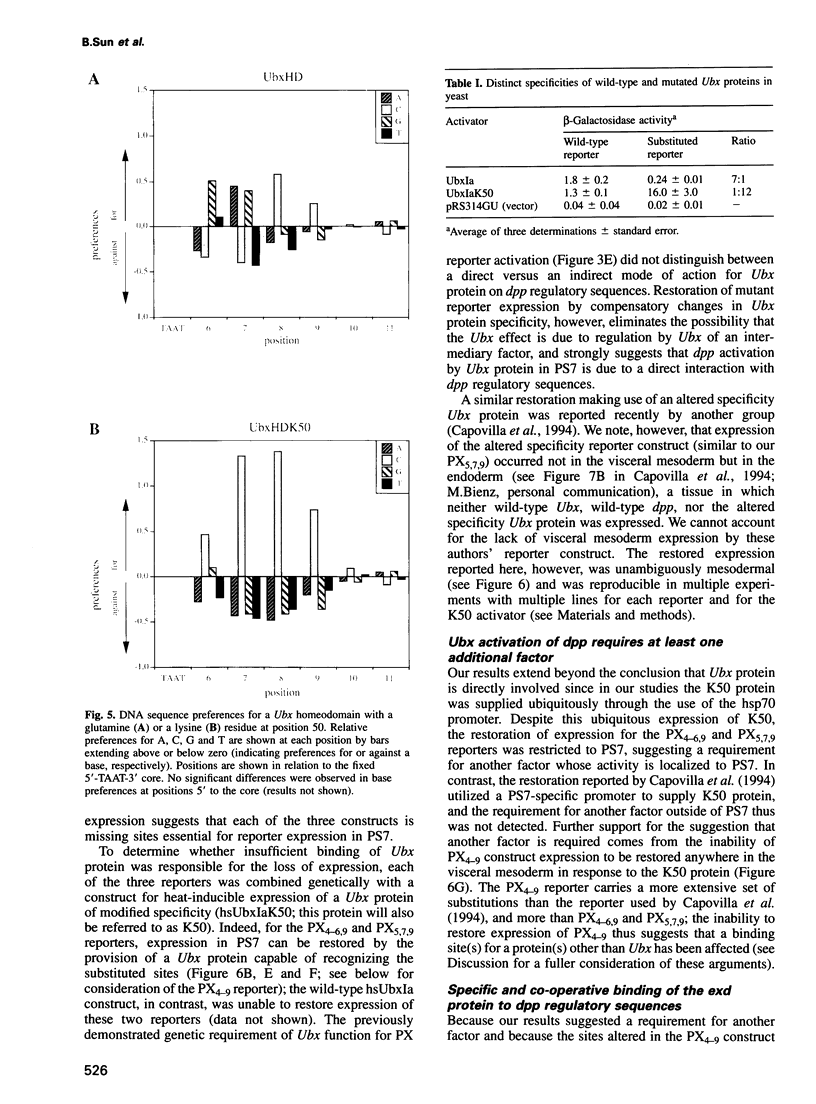
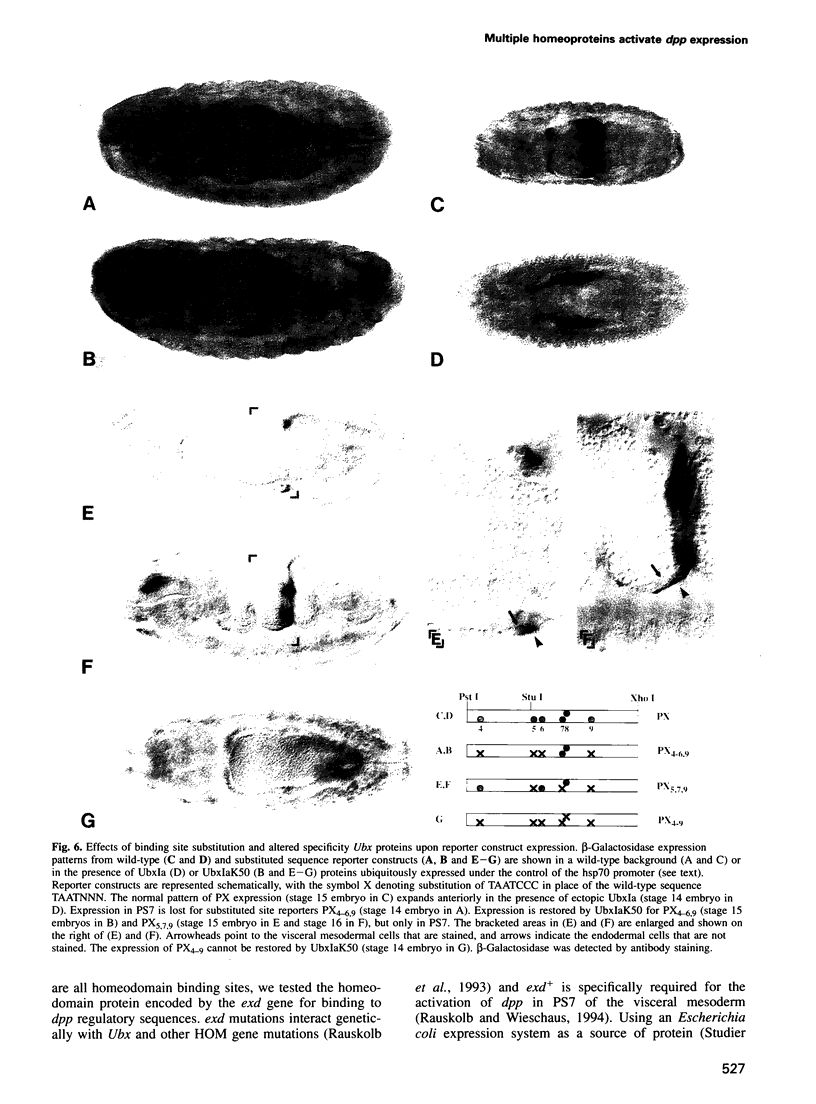
To elucidate the mechanisms by which homeotic selector (HOM) genes specify the unique features of Drosophila segments, we have analyzed the regulation of decapentaplegic (dpp), a transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta superfamily member, and have found that the Ultrabithorax (Ubx) HOM protein directly activates dpp expression in parasegment 7 (PS7) of the embryonic visceral mesoderm. Other factors are also required, including one that appears to act through homeodomain protein binding sites and may be encoded by extradenticle (exd). The exd protein binds in a highly co-operative manner to regulatory sequences mediating PS7-specific dpp expression, consistent with a genetic requirement for exd function in normal visceral mesoderm expression of dpp. A second mechanism contributing to PS7 expression of dpp appears not to require Ubx protein directly, and involves a general visceral mesoderm enhancer coupled to a spatially specific repression element. Thus, even in an apparently simple case where visceral mesoderm expression of the dpp target gene mirrors that of the Ubx HOM protein, full activation by Ubx protein requires at least one additional factor. In addition, a distinct regulatory mode not directly involving Ubx protein also appears to contribute to PS7-specific expression.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel B., Sakonju S. Cell-type-specific mechanisms of transcriptional repression by the homeotic gene products UBX and ABD-A in Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1099–1109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachy P. A., Krasnow M. A., Gavis E. R., Hogness D. S. An Ultrabithorax protein binds sequences near its own and the Antennapedia P1 promoters. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1069–1081. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachy P. A., Varkey J., Young K. E., von Kessler D. P., Sun B. I., Ekker S. C. Cooperative binding of an Ultrabithorax homeodomain protein to nearby and distant DNA sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6941–6956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Akam M., Karch F., Beachy P. A., Peifer M., Spierer P., Lewis E. B., Hogness D. S. Molecular Genetics of the Bithorax Complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):23–29. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4605.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M. Homeotic genes and positional signalling in the Drosophila viscera. Trends Genet. 1994 Jan;10(1):22–26. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Tremml G. Domain of Ultrabithorax expression in Drosophila visceral mesoderm from autoregulation and exclusion. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):576–578. doi: 10.1038/333576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R., Ruvkun G. New motif in PBX genes. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):319–320. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capovilla M., Brandt M., Botas J. Direct regulation of decapentaplegic by Ultrabithorax and its role in Drosophila midgut morphogenesis. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):461–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Jaffe L., Capovilla M., Botas J., Mann R. S. The DNA binding specificity of Ultrabithorax is modulated by cooperative interactions with extradenticle, another homeoprotein. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90525-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Mann R. S. The segment identity functions of Ultrabithorax are contained within its homeo domain and carboxy-terminal sequences. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):796–811. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., Jackson D. G., von Kessler D. P., Sun B. I., Young K. E., Beachy P. A. The degree of variation in DNA sequence recognition among four Drosophila homeotic proteins. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3551–3560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., Young K. E., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Optimal DNA sequence recognition by the Ultrabithorax homeodomain of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Differential DNA sequence recognition is a determinant of specificity in homeotic gene action. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4059–4072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukubo-Tokunaga K., Flister S., Gehring W. J. Functional specificity of the Antennapedia homeodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6360–6364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galang C. K., Hauser C. A. Cooperative DNA binding of the highly conserved human Hox 2.1 homeodomain gene product. New Biol. 1992 May;4(5):558–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Reyes A., Urquia N., Gehring W. J., Struhl G., Morata G. Are cross-regulatory interactions between homoeotic genes functionally significant? Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):78–80. doi: 10.1038/344078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutte C., Johnson A. D. Yeast a1 and alpha 2 homeodomain proteins form a DNA-binding activity with properties distinct from those of either protein. J Mol Biol. 1993 Oct 5;233(3):359–371. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Brent R. A genetic model for interaction of the homeodomain recognition helix with DNA. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):426–430. doi: 10.1126/science.1671176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C. Y., Adamson J. G., Hodges R. S., Smith M. Heterodimerization of the yeast MATa1 and MAT alpha 2 proteins is mediated by two leucine zipper-like coiled-coil motifs. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1403–1413. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursh D. A., Padgett R. W., Gelbart W. M. Cross regulation of decapentaplegic and Ultrabithorax transcription in the embryonic visceral mesoderm of Drosophila. Development. 1993 Apr;117(4):1211–1222. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.4.1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Immerglück K., Lawrence P. A., Bienz M. Induction across germ layers in Drosophila mediated by a genetic cascade. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90364-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Winistorfer S. C. Recombinant circle PCR and recombination PCR for site-specific mutagenesis without PCR product purification. Biotechniques. 1992 Apr;12(4):528-30, 532, 534-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Smeal T. Control of transcription factors by signal transduction pathways: the beginning of the end. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):418–422. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerridge S., Morata G. Developmental effects of some newly induced Ultrabithorax alleles of Drosophila. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1982 Apr;68:211–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. A homeodomain substitution changes the regulatory specificity of the deformed protein in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Altering the regulatory targets of the Deformed protein in Drosophila embryos by substituting the Abdominal-B homeodomain. Mech Dev. 1990 Dec;33(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(90)90137-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masucci J. D., Hoffmann F. M. Identification of two regions from the Drosophila decapentaplegic gene required for embryonic midgut development and larval viability. Dev Biol. 1993 Sep;159(1):276–287. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muro A. F., Pesce C. G., Kornblihtt A. R. DNA sequencing by the chemical method: a 10 minute procedure for the G+A reaction. Trends Genet. 1993 Oct;9(10):337–338. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90025-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban G. E., Reuter R., Scott M. P., Hoffmann F. M. A Drosophila growth factor homolog, decapentaplegic, regulates homeotic gene expression within and across germ layers during midgut morphogenesis. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1041–1050. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban G. E., Reuter R., Scott M. P., Hoffmann F. M. A Drosophila growth factor homolog, decapentaplegic, regulates homeotic gene expression within and across germ layers during midgut morphogenesis. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1041–1050. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J. The interaction with DNA of wild-type and mutant fushi tarazu homeodomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3967–3974. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauskolb C., Peifer M., Wieschaus E. extradenticle, a regulator of homeotic gene activity, is a homolog of the homeobox-containing human proto-oncogene pbx1. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1101–1112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90731-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauskolb C., Wieschaus E. Coordinate regulation of downstream genes by extradenticle and the homeotic selector proteins. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3561–3569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schier A. F., Gehring W. J. Direct homeodomain-DNA interaction in the autoregulation of the fushi tarazu gene. Nature. 1992 Apr 30;356(6372):804–807. doi: 10.1038/356804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schier A. F., Gehring W. J. Functional specificity of the homeodomain protein fushi tarazu: the role of DNA-binding specificity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1450–1454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D., Gelbart W. M. Shortvein, a new component of the decapentaplegic gene complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1985 Jan;109(1):119–143. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston R. D., Gelbart W. M. Decapentaplegic transcripts are localized along the dorsal-ventral axis of the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2785–2791. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston R. D., Hoffmann F. M., Blackman R. K., Segal D., Grimaila R., Padgett R. W., Irick H. A., Gelbart W. M. Molecular organization of the decapentaplegic gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1114–1127. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. R., Johnson A. D. Interaction between two homeodomain proteins is specified by a short C-terminal tail. Nature. 1994 Sep 29;371(6496):429–432. doi: 10.1038/371429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thüringer F., Bienz M. Indirect autoregulation of a homeotic Drosophila gene mediated by extracellular signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3899–3903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thüringer F., Cohen S. M., Bienz M. Dissection of an indirect autoregulatory response of a homeotic Drosophila gene. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2419–2430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Gönczy P., Vashishtha M., Harris E., Desplan C. A single amino acid can determine the DNA binding specificity of homeodomain proteins. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):553–562. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremml G., Bienz M. Homeotic gene expression in the visceral mesoderm of Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2677–2685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk M. A., Voorhoeve P. M., Murre C. Pbx1 is converted into a transcriptional activator upon acquiring the N-terminal region of E2A in pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastoid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6061–6065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vershon A. K., Johnson A. D. A short, disordered protein region mediates interactions between the homeodomain of the yeast alpha 2 protein and the MCM1 protein. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90054-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Kassis J. A., O'Farrell P. H. A synthetic homeodomain binding site acts as a cell type specific, promoter specific enhancer in Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2573–2578. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Admon A., Lüscher B., Tjian R. Cloning and expression of AP-2, a cell-type-specific transcription factor that activates inducible enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1557–1569. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng C., Pinsonneault J., Gellon G., McGinnis N., McGinnis W. Deformed protein binding sites and cofactor binding sites are required for the function of a small segment-specific regulatory element in Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2362–2377. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng W., Andrew D. J., Mathies L. D., Horner M. A., Scott M. P. Ectopic expression and function of the Antp and Scr homeotic genes: the N terminus of the homeodomain is critical to functional specificity. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):339–352. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk M. A., Murre C. extradenticle raises the DNA binding specificity of homeotic selector gene products. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):617–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]