Abstract
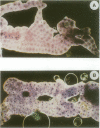
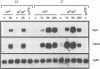
In addition to its function in embryonic development, the NF-kappa B/rel-related gene dorsal (dl) of Drosophila is expressed in larval and adult fat body where its RNA expression is enhanced upon injury. Injury also leads to a rapid nuclear translocation of dl from the cytoplasm in fat body cells. Here we present data which strongly suggest that the nuclear localization of dl during the immune response is controlled by the Toll signaling pathway, comprising gene products that participate in the intracellular part of the embryonic dorsoventral pathway. We also report that in mutants such as Toll or cactus, which exhibit melanotic tumor phenotypes, dl is constitutively nuclear. Together, these results point to a potential link between the Toll signaling pathway and melanotic tumor induction. Although dl has been shown previously to bind to kappa B-related motifs within the promoter of the antibacterial peptide coding gene diptericin, we find that injury-induced expression of diptericin can occur in the absence of dl. Furthermore, the melanotic tumor phenotype of Toll and cactus is not dl dependent. These data underline the complexity of the Drosophila immune response. Finally, we observed that like other rel proteins, dl can control the level of its own transcription.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. V., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Information for the dorsal--ventral pattern of the Drosophila embryo is stored as maternal mRNA. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):223–227. doi: 10.1038/311223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnerot C., Nicolas J. F. Clonal analysis in the intact mouse embryo by intragenic homologous recombination. C R Acad Sci III. 1993 Oct;316(10):1207–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasan R., Jin Y., Anderson K. V. Activation of the easter zymogen is regulated by five other genes to define dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1992 Jun;115(2):607–616. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cociancich S., Bulet P., Hetru C., Hoffmann J. A. The inducible antibacterial peptides of insects. Parasitol Today. 1994 Apr;10(4):132–139. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(94)90260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogswell P. C., Scheinman R. I., Baldwin A. S., Jr Promoter of the human NF-kappa B p50/p105 gene. Regulation by NF-kappa B subunits and by c-REL. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 1;150(7):2794–2804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V., Pellicer A., Axel R., Meselson M. Integration, transcription, and control of a Drosophila heat shock gene in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7038–7042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimarcq J. L., Hoffmann D., Meister M., Bulet P., Lanot R., Reichhart J. M., Hoffmann J. A. Characterization and transcriptional profiles of a Drosophila gene encoding an insect defensin. A study in insect immunity. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Apr 1;221(1):201–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström Y., Kadalayil L., Sun S. C., Samakovlis C., Hultmark D., Faye I. kappa B-like motifs regulate the induction of immune genes in Drosophila. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):327–333. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson E. L., Anderson K. V. Dorsal-ventral pattern formation in the Drosophila embryo: the role of zygotically active genes. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1991;25:17–43. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60410-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garzino V., Pereira A., Laurenti P., Graba Y., Levis R. W., Le Parco Y., Pradel J. Cell lineage-specific expression of modulo, a dose-dependent modifier of variegation in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4471–4479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05548.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gateff E. Malignant neoplasms of genetic origin in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1978 Jun 30;200(4349):1448–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.96525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Keith F. J. Drosophila Toll and IL-1 receptor. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):355–356. doi: 10.1038/351355b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler R., Bergmann A., Hiromi Y., Nüsslein-Volhard C. cactus, a gene involved in dorsoventral pattern formation of Drosophila, is related to the I kappa B gene family of vertebrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):613–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgel P., Meister M., Kappler C., Lemaitre B., Reichhart J. M., Hoffmann J. A. Insect immunity: the diptericin promoter contains multiple functional regulatory sequences homologous to mammalian acute-phase response elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 15;197(2):508–517. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerttula S., Jin Y. S., Anderson K. V. Zygotic expression and activity of the Drosophila Toll gene, a gene required maternally for embryonic dorsal-ventral pattern formation. Genetics. 1988 May;119(1):123–133. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govind S., Steward R. Dorsoventral pattern formation in Drosophila: signal transduction and nuclear targeting. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90456-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govind S., Whalen A. M., Steward R. In vivo self-association of the Drosophila rel-protein dorsal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7861–7865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Temin H. M. Structure and autoregulation of the c-rel promoter. Oncogene. 1990 Dec;5(12):1843–1850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Gerttula S., Anderson K. V. Plasma membrane localization of the Toll protein in the syncytial Drosophila embryo: importance of transmembrane signaling for dorsal-ventral pattern formation. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1021–1028. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Hudson K. L., Anderson K. V. The Toll gene of Drosophila, required for dorsal-ventral embryonic polarity, appears to encode a transmembrane protein. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90516-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht P. M., Anderson K. V. Genetic characterization of tube and pelle, genes required for signaling between Toll and dorsal in the specification of the dorsal-ventral pattern of the Drosophila embryo. Genetics. 1993 Oct;135(2):405–417. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. Control elements of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann J. A., Hetru C., Reichhart J. M. The humoral antibacterial response of Drosophila. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 28;325(1-2):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81414-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D. Immune reactions in Drosophila and other insects: a model for innate immunity. Trends Genet. 1993 May;9(5):178–183. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90165-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Reach M., Engstrom Y., Kadalayil L., Cai H., González-Crespo S., Tatei K., Levine M. Dif, a dorsal-related gene that mediates an immune response in Drosophila. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90495-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isoda K., Roth S., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The functional domains of the Drosophila morphogen dorsal: evidence from the analysis of mutants. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):619–630. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isshiki H., Akira S., Sugita T., Nishio Y., Hashimoto S., Pawlowski T., Suematsu S., Kishimoto T. Reciprocal expression of NF-IL6 and C/EBP in hepatocytes: possible involvement of NF-IL6 in acute phase protein gene expression. New Biol. 1991 Jan;3(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Levine M. Binding affinities and cooperative interactions with bHLH activators delimit threshold responses to the dorsal gradient morphogen. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90402-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler C., Meister M., Lagueux M., Gateff E., Hoffmann J. A., Reichhart J. M. Insect immunity. Two 17 bp repeats nesting a kappa B-related sequence confer inducibility to the diptericin gene and bind a polypeptide in bacteria-challenged Drosophila. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1561–1568. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Inoue J., Davis N., Link E., Baeuerle P. A., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. The rel-associated pp40 protein prevents DNA binding of Rel and NF-kappa B: relationship with I kappa B beta and regulation by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1464–1476. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S. Characterization of the Drosophila cactus locus and analysis of interactions between cactus and dorsal proteins. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):623–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90596-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kylsten P., Samakovlis C., Hultmark D. The cecropin locus in Drosophila; a compact gene cluster involved in the response to infection. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):217–224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08098.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letsou A., Alexander S., Orth K., Wasserman S. A. Genetic and molecular characterization of tube, a Drosophila gene maternally required for embryonic dorsoventral polarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):810–814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald N. J., Kuhl D., Maguire D., Näf D., Gallant P., Goswamy A., Hug H., Büeler H., Chaturvedi M., de la Fuente J. Different pathways mediate virus inducibility of the human IFN-alpha 1 and IFN-beta genes. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90091-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D., Anderson K. V. The spätzle gene encodes a component of the extracellular signaling pathway establishing the dorsal-ventral pattern of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):677–688. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90507-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichhart J. M., Essrich M., Dimarcq J. L., Hoffmann D., Hoffmann J. A., Lagueux M. Insect immunity. Isolation of cDNA clones corresponding to diptericin, an inducible antibacterial peptide from Phormia terranovae (Diptera). Transcriptional profiles during immunization. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 15;182(2):423–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichhart J. M., Meister M., Dimarcq J. L., Zachary D., Hoffmann D., Ruiz C., Richards G., Hoffmann J. A. Insect immunity: developmental and inducible activity of the Drosophila diptericin promoter. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1469–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05191.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G., Cassab A., Bourouis M., Jarry B., Dissous C. The normal developmental regulation of a cloned sgs3 'glue' gene chromosomally integrated in Drosophila melanogaster by P element transformation. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2137–2142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizki T. M., Rizki R. M. Lamellocyte differentiation in Drosophila larvae parasitized by Leptopilina. Dev Comp Immunol. 1992 Mar-Jun;16(2-3):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(92)90011-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Hiromi Y., Godt D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. cactus, a maternal gene required for proper formation of the dorsoventral morphogen gradient in Drosophila embryos. Development. 1991 Jun;112(2):371–388. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.2.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of nuclear localization of the dorsal protein determines dorsoventral pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruohola-Baker H., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. The role of gene cassettes in axis formation during Drosophila oogenesis. Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Han K., Manley J. L., Levine M. The graded distribution of the dorsal morphogen is initiated by selective nuclear transport in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1165–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Henkel T., Baeuerle P. A. Proteins controlling the nuclear uptake of NF-kappa B, Rel and dorsal. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;1(5):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90118-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. S., Hudson K. L., Lin T. Y., Anderson K. V. Dominant and recessive mutations define functional domains of Toll, a transmembrane protein required for dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):797–807. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. S., Jin Y., Morisato D., Anderson K. V. A processed form of the Spätzle protein defines dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1994 May;120(5):1243–1250. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.5.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüpbach T., Wieschaus E. Female sterile mutations on the second chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Maternal effect mutations. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):101–117. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton C. A., Wasserman S. A. pelle encodes a protein kinase required to establish dorsoventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):515–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90071-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Mizel S. B. In vitro activation and nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B catalyzed by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2424–2430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., DeLotto R. Ventralizing signal determined by protease activation in Drosophila embryogenesis. Nature. 1994 Apr 7;368(6471):548–551. doi: 10.1038/368548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Multiple extracellular activities in Drosophila egg perivitelline fluid are required for establishment of embryonic dorsal-ventral polarity. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90181-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D., Roth S., Vogelsang E., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The polarity of the dorsoventral axis in the Drosophila embryo is defined by an extracellular signal. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90381-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R., Govind S. Dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Aug;3(4):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90090-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R., McNally F. J., Schedl P. Isolation of the dorsal locus of Drosophila. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):262–265. doi: 10.1038/311262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Relocalization of the dorsal protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus correlates with its function. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90773-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Lindström I., Lee J. Y., Faye I. Structure and expression of the attacin genes in Hyalophora cecropia. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Feb 26;196(1):247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabad J., Erdélyi M., Hoffmann G., Szidonya J., Wright T. R. Isolation and characterization of dominant female sterile mutations of Drosophila melanogaster. II. Mutations on the second chromosome. Genetics. 1989 Aug;122(4):823–835. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ten R. M., Paya C. V., Israël N., Le Bail O., Mattei M. G., Virelizier J. L., Kourilsky P., Israël A. The characterization of the promoter of the gene encoding the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B indicates that it participates in its own regulation. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):195–203. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryselius Y., Samakovlis C., Kimbrell D. A., Hultmark D. CecC, a cecropin gene expressed during metamorphosis in Drosophila pupae. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. A. A conserved signal transduction pathway regulating the activity of the rel-like proteins dorsal and NF-kappa B. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Aug;4(8):767–771. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.8.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. L., Johnson T. K., Denell R. E. Lethal(1) aberrant immune response mutations leading to melanotic tumor formation in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Genet. 1991;12(3):173–187. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020120302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen A. M., Steward R. Dissociation of the dorsal-cactus complex and phosphorylation of the dorsal protein correlate with the nuclear localization of dorsal. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(3):523–534. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicker C., Reichhart J. M., Hoffmann D., Hultmark D., Samakovlis C., Hoffmann J. A. Insect immunity. Characterization of a Drosophila cDNA encoding a novel member of the diptericin family of immune peptides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22493–22498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. R., Hodgetts R. B., Sherald A. F. The genetics of dopa decarboxylase in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Isolation and characterization of deficiencies that delete the dopa-decarboxylase-dosage-sensitive region and the alpha-methyl-dopa-hypersensitive locus. Genetics. 1976 Oct;84(2):267–285. doi: 10.1093/genetics/84.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]