Abstract
The steroid hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone controls both induction and repression of the Drosophila 'intermolt gene' Sgs-4. We show here that the ecdysone receptor binds to two sites, element I and element II, in the regulatory region of Sgs-4. A functional analysis revealed that element II appears to be of no importance for Sgs-4 expression, while element I proved to be an ecdysone response element that is necessary, but not sufficient, for induction of Sgs-4 expression. Our results provide no evidence that repression of Sgs-4 expression is mediated by one of the two receptor binding sites. In the close vicinity of elements I and II, we detected two binding sites of secretion enhancer binding protein 3 (SEBP 3). Like receptor element I, one of these sites also proved to be necessary, but not sufficient, for expression of Sgs-4. Therefore, induction of Sgs-4 requires binding of both ecdysone receptor and SEBP 3 to a complex hormone response unit, which also contains binding sites for a third factor, SEBP 2. The SEBP 2 sites coincide with binding sites of products of the Broad-Complex locus, which has been implicated recently with transduction of the hormonal signal. Thus, the available data suggest that induction of Sgs-4, and possibly other 'intermolt genes', is a combination of a primary and a secondary response to the hormone.
Full text
PDF



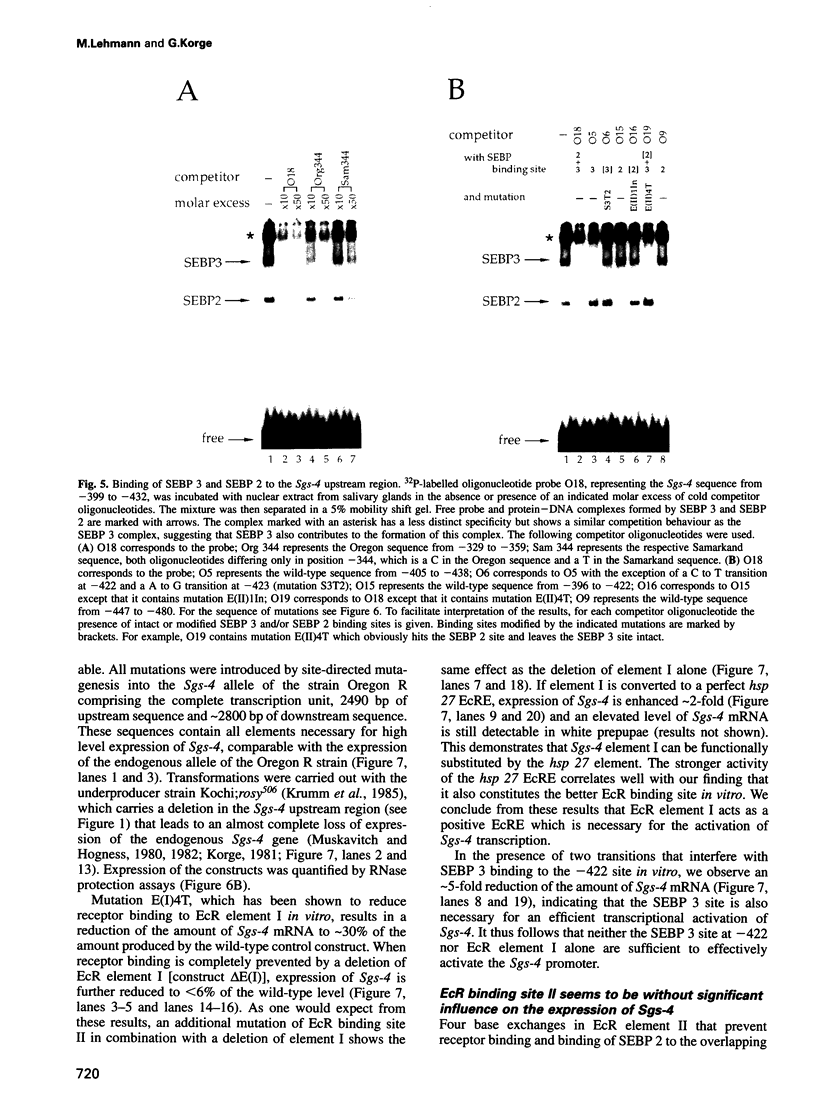






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres A. J., Fletcher J. C., Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular analysis of the initiation of insect metamorphosis: a comparative study of Drosophila ecdysteroid-regulated transcription. Dev Biol. 1993 Dec;160(2):388–404. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres A. J., Thummel C. S. Hormones, puffs and flies: the molecular control of metamorphosis by ecdysone. Trends Genet. 1992 Apr;8(4):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90371-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniewski C., Laval M., Dahan A., Lepesant J. A. The ecdysone response enhancer of the Fbp1 gene of Drosophila melanogaster is a direct target for the EcR/USP nuclear receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4465–4474. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniewski C., Laval M., Lepesant J. A. Structural features critical to the activity of an ecdysone receptor binding site. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;23(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(93)90088-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. VI. Induction by ecdysone in salivary glands of D. melanogaster cultured in vitro. Chromosoma. 1972;38(3):255–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00290925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Dependence upon ecdysone concentration. Dev Biol. 1973 Nov;35(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. II. The effects of inhibitors of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1974 Jul;39(1):141–157. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(74)80016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckendorf S. K., Kafatos F. C. Differentiation in the salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: characterization of the glue proteins and their developmental appearance. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belyaeva E. S., Vlassova I. E., Biyasheva Z. M., Kakpakov V. T., Richards G., Zhimulev I. F. Cytogenetic analysis of the 2B3-4-2B11 region of the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. II. Changes in 20-OH ecdysone puffing caused by genetic defects of puff 2B5. Chromosoma. 1981;84(2):207–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00399132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEVER U. ACTINOMYCIN AND PUROMYCIN: EFFECTS ON SEQUENTIAL GENE ACTIVATION BY ECDYSONE. Science. 1964 Nov 6;146(3645):794–795. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3645.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEVER U., KARLSON P. [Induction of puff changes in the salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus tentans by ecdysone]. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Sep;20:623–626. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherbas L., Lee K., Cherbas P. Identification of ecdysone response elements by analysis of the Drosophila Eip28/29 gene. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):120–131. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson A. M., King D. L., Hatzivassiliou E., Casas J. E., Hallenbeck P. L., Nikodem V. M., Mitsialis S. A., Kafatos F. C. DNA binding and heteromerization of the Drosophila transcription factor chorion factor 1/ultraspiracle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11503–11507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corthésy B., Cardinaux J. R., Claret F. X., Wahli W. A nuclear factor I-like activity and a liver-specific repressor govern estrogen-regulated in vitro transcription from the Xenopus laevis vitellogenin B1 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5548–5562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley T. E., Mathers P. H., Meyerowitz E. M. A trans-acting regulatory product necessary for expression of the Drosophila melanogaster 68C glue gene cluster. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley T. E., Meyerowitz E. M. Steroid regulation of RNAs transcribed from the Drosophila 68c polytene chromosome puff. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):110–121. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBello P. R., Withers D. A., Bayer C. A., Fristrom J. W., Guild G. M. The Drosophila Broad-Complex encodes a family of related proteins containing zinc fingers. Genetics. 1991 Oct;129(2):385–397. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel M. D., Pruitt R. E., Meyerowitz E. M. DNA sequences, gene regulation and modular protein evolution in the Drosophila 68C glue gene cluster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):765–789. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgel P., Dretzen G., Jagla K., Bellard F., Dubrovsky E., Calco V., Bellard M. GEBF-I activates the Drosophila Sgs3 gene enhancer by altering a positioned nucleosomal core particle. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 20;234(2):319–330. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgel P., Ramain P., Giangrande A., Dretzen G., Richards G., Bellard M. Sgs-3 chromatin structure and trans-activators: developmental and ecdysone induction of a glue enhancer-binding factor, GEBF-I, in Drosophila larvae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):523–532. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay P. S., Guild G. M. The ecdysone-induced puffing cascade in Drosophila salivary glands: a Broad-Complex early gene regulates intermolt and late gene transcription. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):169–175. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson L., Lambertsson A. Steroid regulation of glue protein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Hereditas. 1989;110(1):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1989.tb00418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich V. C., Sliter T. J., Lubahn D. B., MacIntyre A., Gilbert L. I. A steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily member in Drosophila melanogaster that shares extensive sequence similarity with a mammalian homologue. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4143–4148. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A., Keinhorst A., Krumm A., Korge G. Regulatory sequences of the Sgs-4 gene of Drosophila melanogaster analysed by P element-mediated transformation. Chromosoma. 1987;96(1):8–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00285877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A., Korge G. Upstream sequences of dosage-compensated and non-compensated alleles of the larval secretion protein gene Sgs-4 in Drosophila. Chromosoma. 1987;96(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00285876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongens T. A., Fowler T., Shermoen A. W., Beckendorf S. K. Functional redundancy in the tissue-specific enhancer of the Drosophila Sgs-4 gene. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2559–2567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Guild G. M., Thummel C. S. The Drosophila Broad-Complex plays a key role in controlling ecdysone-regulated gene expression at the onset of metamorphosis. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):977–988. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelle M. R., Talbot W. S., Segraves W. A., Bender M. T., Cherbas P., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila EcR gene encodes an ecdysone receptor, a new member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):59–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90572-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Chromosome puff activity and protein synthesis in larval salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4550–4554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Genetic analysis of the larval secretion gene Sgs-4 and its regulatory chromosome sites in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1981;84(3):373–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00286027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Larval saliva in Drosophila melanogaster: production, composition, and relationship to chromosome puffs. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):339–355. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Polytene chromosomes. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1987;14:27–58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-47783-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan V., Wang X., Safe S. Estrogen receptor-Sp1 complexes mediate estrogen-induced cathepsin D gene expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15912–15917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumm A., Roth G. E., Korge G. Transformation of salivary gland secretion protein gene Sgs-4 in Drosophila: stage- and tissue-specific regulation, dosage compensation, and position effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5055–5059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laval M., Pourrain F., Deutsch J., Lepesant J. A. In vivo functional characterization of an ecdysone response enhancer in the proximal upstream region of the Fbp1 gene of D. melanogaster. Mech Dev. 1993 Dec;44(2-3):123–138. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas P. C., Granner D. K. Hormone response domains in gene transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1131–1173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Amin J., Voellmy R. Ecdysterone receptor is a sequence-specific transcription factor involved in the developmental regulation of heat shock genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3660–3675. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Givel F., Wahli W. A common ancestor DNA motif for invertebrate and vertebrate hormone response elements. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):263–268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger D., White J. H., Chambon P. The human oestrogen receptor functions in yeast. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):31–36. doi: 10.1038/334031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougneau E., von Seggern D., Fowler T., Rosenblatt J., Jongens T., Rogers B., Gietzen D., Beckendorf S. K. A transcriptional switch between the Pig-1 and Sgs-4 genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):184–195. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. An expandable gene that encodes a Drosophila glue protein is not expressed in variants lacking remote upstream sequences. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1041–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. Molecular analysis of a gene in a developmentally regulated puff of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7362–7366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Relationship between the product of the Drosophila ultraspiracle locus and the vertebrate retinoid X receptor. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):298–301. doi: 10.1038/347298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Nucleic acid hybridization to the DNA of cytological preparations. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;10:1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60727-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R. Repression mechanisms of v-ERBA and other members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 11;684:1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb32266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. The radioimmune assay of ecdysteroid titres in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Mar;21(3):181–197. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. Activation of the Drosophila hsp27 promoter by heat shock and by ecdysone involves independent and remote regulatory sequences. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1653–1658. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. An ecdysone response element in the Drosophila hsp27 promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3729–3734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saumweber H., Frasch M., Korge G. Two puff-specific proteins bind within the 2.5 kb upstream region of the Drosophila melanogaster Sgs-4 gene. Chromosoma. 1990 Apr;99(1):52–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01737289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Kaltschmidt C., Renkawitz R. Many transcription factors interact synergistically with steroid receptors. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.3201230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Otsuka-Murakami H., Renkawitz R. Cooperativity of the glucocorticoid receptor and the CACCC-box binding factor. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):87–90. doi: 10.1038/332087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. The E75 ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):204–219. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea M. J., King D. L., Conboy M. J., Mariani B. D., Kafatos F. C. Proteins that bind to Drosophila chorion cis-regulatory elements: a new C2H2 zinc finger protein and a C2C2 steroid receptor-like component. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1128–1140. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shermoen A. W., Jongens J., Barnett S. W., Flynn K., Beckendorf S. K. Developmental regulation by an enhancer from the Sgs-4 gene of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04740.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeller W. C., Poole S. J., Kornberg T. In vitro transcription of the Drosophila engrailed gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):68–81. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot W. S., Swyryd E. A., Hogness D. S. Drosophila tissues with different metamorphic responses to ecdysone express different ecdysone receptor isoforms. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1323–1337. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. E., Stunnenberg H. G., Stewart A. F. Heterodimerization of the Drosophila ecdysone receptor with retinoid X receptor and ultraspiracle. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):471–475. doi: 10.1038/362471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truss M., Beato M. Steroid hormone receptors: interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid and transcription factors. Endocr Rev. 1993 Aug;14(4):459–479. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truss M., Chalepakis G., Slater E. P., Mader S., Beato M. Functional interaction of hybrid response elements with wild-type and mutant steroid hormone receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3247–3258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T. P., Forman B. M., Jiang Z., Cherbas L., Chen J. D., McKeown M., Cherbas P., Evans R. M. Functional ecdysone receptor is the product of EcR and Ultraspiracle genes. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):476–479. doi: 10.1038/366476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T. P., Segraves W. A., Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Drosophila ultraspiracle modulates ecdysone receptor function via heterodimer formation. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90266-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhimulev I. F., Vlassova I. E., Belyaeva E. S. Cytogenetic analysis of the 2B3-4--2B11 region of the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. III. Puffing disturbance in salivary gland chromosomes of homozygotes for mutation l(1)pp1t10. Chromosoma. 1982;85(5):659–672. doi: 10.1007/BF00330779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kalm L., Crossgrove K., Von Seggern D., Guild G. M., Beckendorf S. K. The Broad-Complex directly controls a tissue-specific response to the steroid hormone ecdysone at the onset of Drosophila metamorphosis. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3505–3516. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06657.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]