Abstract
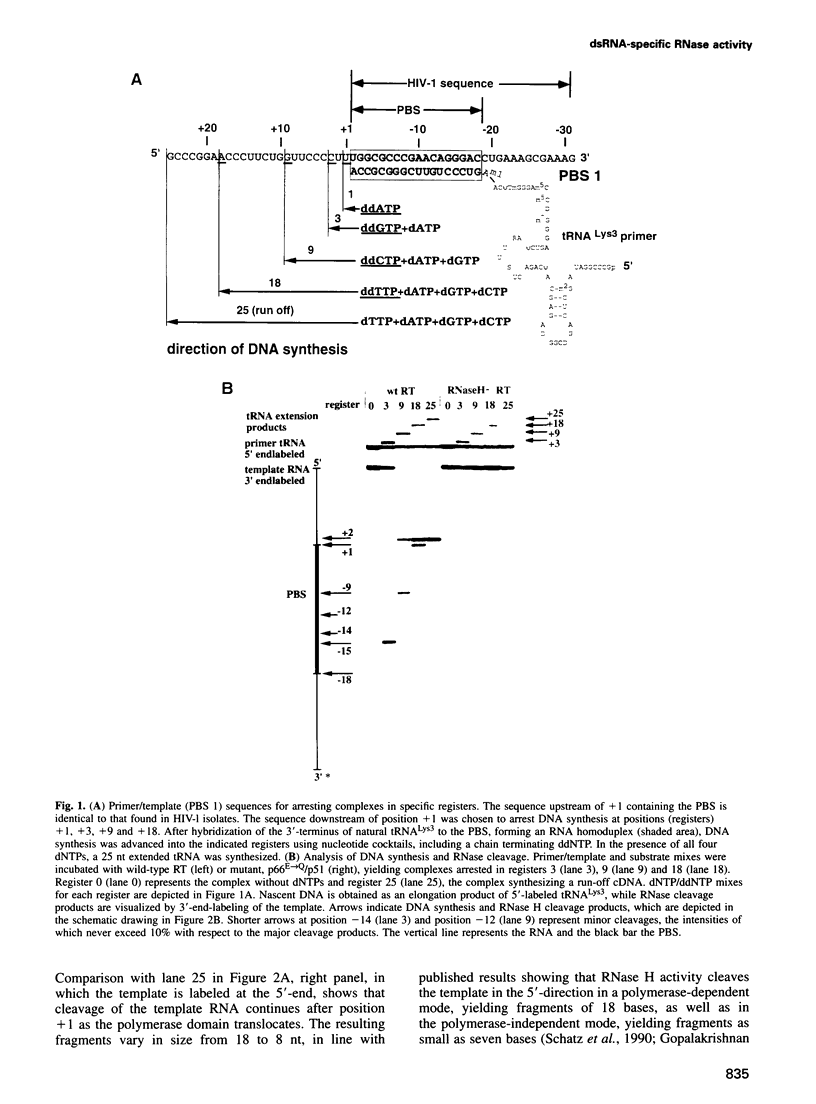
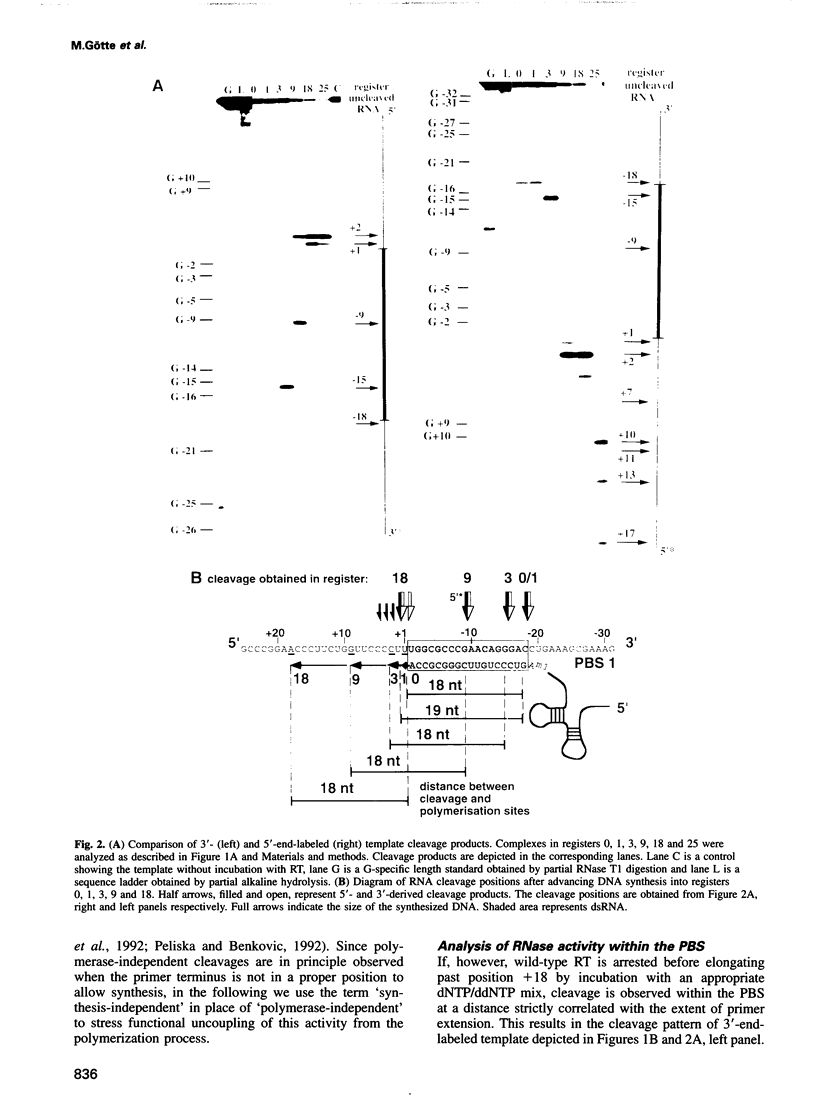
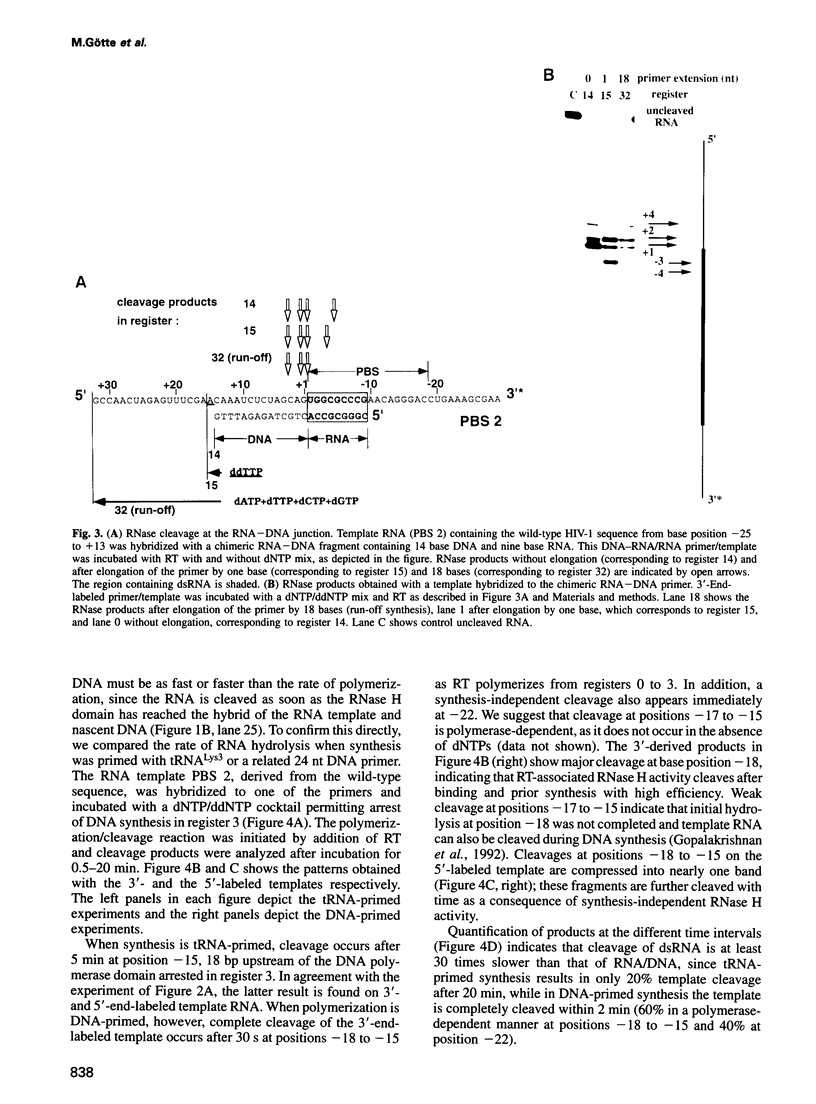
Reverse transcription of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) is primed by tRNA(Lys3), which forms an 18 base pair RNA homoduplex with its 3' terminus and the primer binding site (PBS) of the viral genome. Using an in vitro system mimicking initiation of minus strand DNA synthesis, we analyzed the mechanism by which HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT)-associated ribonuclease H (RNase H) distinguishes between RNA/DNA and RNA/RNA (dsRNA). tRNA(Lys3) was hybridized to a PBS-containing RNA template and extended by addition of deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs). In the presence of all four dNTPs, initial cleavage of the RNA template occurred immediately downstream of the tRNA-DNA junction, reflecting RNase H specificity for RNA in a RNA/DNA hybrid. However, in the absence of DNA synthesis, or limiting this by chain termination, the PBS was cleaved at a constant distance of 18 nucleotides upstream of the nascent primer 3' terminus. The position of cleavage remained in register with the position of DNA synthesis arrest, indicating that hydrolysis of homoduplex RNA is spatialy co-ordinated with DNA synthesis. Kinetic studies comparing cleavage rates of an analogous DNA primer/PBS heteroduplex and the tRNA(Lys3)/PBS homoduplex showed that while the former is cleaved as rapidly as RT polymerizes, the latter proceeds 30-fold slower. Although the RNase H domain hydrolyzes dsRNA when RT is artificially arrested, specificity for RNA/DNA hybrids is maintained when DNA is actively synthesized, since residency of the RNase H domain at a single base position is not long enough to allow significant cleavage on dsRNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Artzi H., Zeelon E., Gorecki M., Panet A. Double-stranded RNA-dependent RNase activity associated with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):927–931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Artzi H., Zeelon E., Le-Grice S. F., Gorecki M., Panet A. Characterization of the double stranded RNA dependent RNase activity associated with recombinant reverse transcriptases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5115–5118. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blain S. W., Goff S. P. Nuclease activities of Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase. Mutants with altered substrate specificities. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23585–23592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Reactions at the termini of tRNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3665–3677. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff OYu, Salazar M., Reid B. R. Structure of a DNA:RNA hybrid duplex. Why RNase H does not cleave pure RNA. J Mol Biol. 1993 Oct 5;233(3):509–523. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furfine E. S., Reardon J. E. Reverse transcriptase.RNase H from the human immunodeficiency virus. Relationship of the DNA polymerase and RNA hydrolysis activities. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):406–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan V., Peliska J. A., Benkovic S. J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase: spatial and temporal relationship between the polymerase and RNase H activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10763–10767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostomsky Z., Hudson G. O., Rahmati S., Hostomska Z. RNase D, a reported new activity associated with HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, displays the same cleavage specificity as Escherichia coli RNase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5819–5824. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostomsky Z., Hughes S. H., Goff S. P., Le Grice S. F. Redesignation of the RNase D activity associated with retroviral reverse transcriptase as RNase H. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1970–1971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1970-1971.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isel C., Marquet R., Keith G., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Modified nucleotides of tRNA(3Lys) modulate primer/template loop-loop interaction in the initiation complex of HIV-1 reverse transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25269–25272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobo-Molina A., Ding J., Nanni R. G., Clark A. D., Jr, Lu X., Tantillo C., Williams R. L., Kamer G., Ferris A. L., Clark P. Crystal structure of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase complexed with double-stranded DNA at 3.0 A resolution shows bent DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6320–6324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kati W. M., Johnson K. A., Jerva L. F., Anderson K. S. Mechanism and fidelity of HIV reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25988–25997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Steitz T. A. Reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus can use either human tRNA(3Lys) or Escherichia coli tRNA(2Gln) as a primer in an in vitro primer-utilization assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9652–9656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Wang J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1377403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grice S. F., Grüninger-Leitch F. Rapid purification of homodimer and heterodimer HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by metal chelate affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 26;187(2):307–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger W., Hermann T., Schatz O., Le Grice S. F., Heumann H. Hydroxyl radical footprint analysis of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase-template.primer complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5909–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakawa G. J., Chen C. H., Kuwabara M. D., Nierlich D. P., Sigman D. S. Scission of RNA by the chemical nuclease of 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: preference for single-stranded loops. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5361–5375. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peliska J. A., Benkovic S. J. Mechanism of DNA strand transfer reactions catalyzed by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1112–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.1279806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raba M., Limburg K., Burghagen M., Katze J. R., Simsek M., Heckman J. E., Rajbhandary U. L., Gross H. J. Nucleotide sequence of three isoaccepting lysine tRNAs from rabbit liver and SV40-transformed mouse fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):305–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz O., Cromme F. V., Grüninger-Leitch F., Le Grice S. F. Point mutations in conserved amino acid residues within the C-terminal domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase specifically repress RNase H function. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81559-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz O., Mous J., Le Grice S. F. HIV-1 RT-associated ribonuclease H displays both endonuclease and 3'----5' exonuclease activity. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1171–1176. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Roth M. J. Purification and characterization of an active human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNase H domain. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4037–4049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4037-4049.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield J. K., Rhim H., Morrow C. D. Minimal sequence requirements of a functional human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primer binding site. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1605–1614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1605-1614.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöhrl B. M., Moelling K. Interaction of HIV-1 ribonuclease H with polypurine tract containing RNA-DNA hybrids. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10141–10147. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







