Abstract
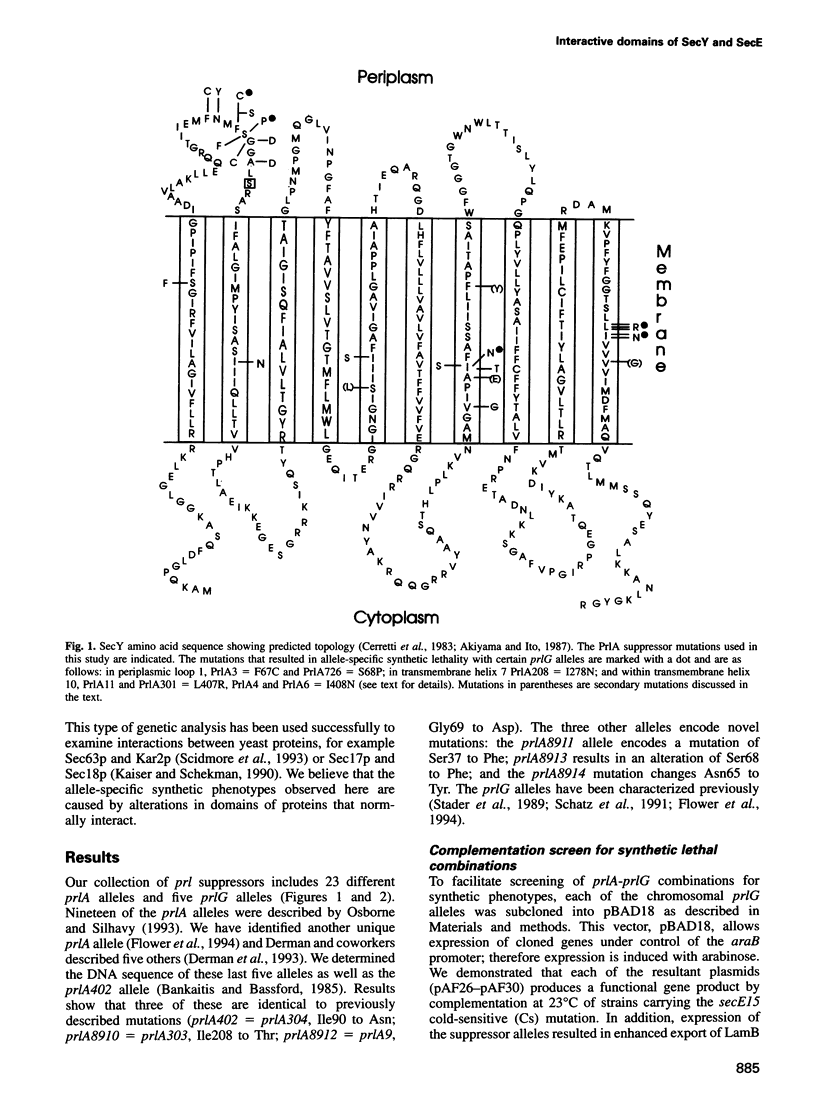
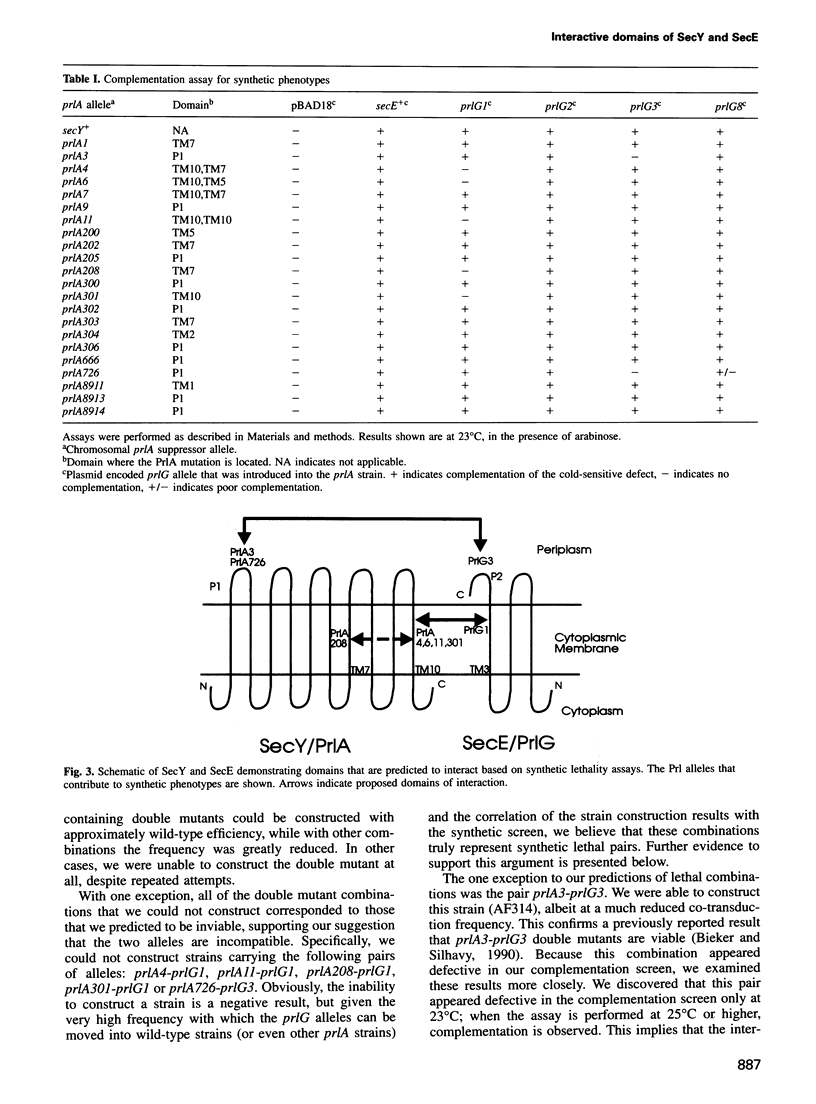
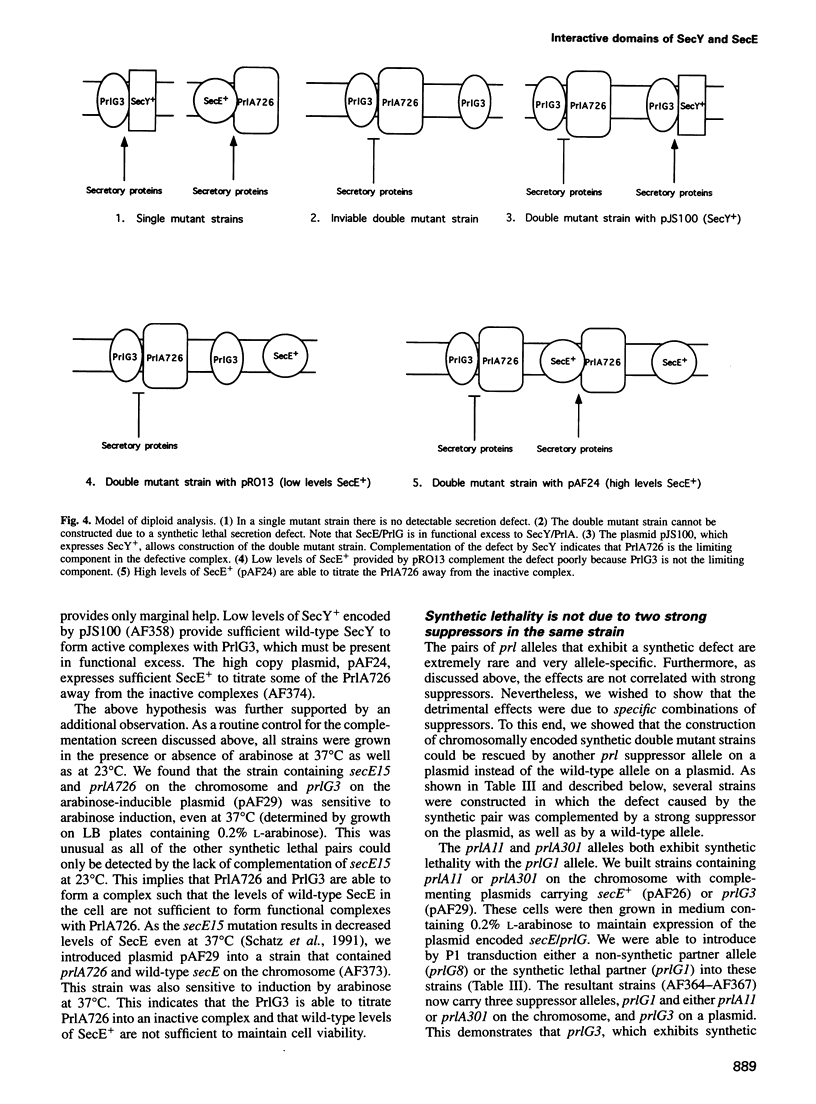
The secretion of proteins from the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli requires the interaction of two integral inner membrane components, SecY and SecE. We have devised a genetic approach to probe the molecular nature of the SecY-SecE interaction. Suppressor alleles of secY and secE, termed prlA and prlG, respectively, were analyzed in pair-wise combinations for synthetic phenotypes. From a total of 115 combinations, we found only seven pairs of alleles that exhibit a synthetic defect when present in combination with one another. The phenotypes observed are not the result of additive defects caused by the prl alleles, nor are they the consequence of multiple suppressors functioning within the same strain. In all cases, the synthetic defect is recessive to wild-type secY or secE provided in trans. The recessive nature argues for a defective interaction between the Prl suppressors. The extreme allele specificity and topological coincidence of the mutations represented by these seven pairs of alleles identify domains of interaction between SecY/PrlA and SecE/PrlG.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Reconstitution of a protein translocation system containing purified SecY, SecE, and SecA from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6545–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama Y., Ito K. Topology analysis of the SecY protein, an integral membrane protein involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3465–3470. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkowitz R. A., Wickner W. SecD and SecF are required for the proton electrochemical gradient stimulation of preprotein translocation. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):954–963. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T., Taura T., Shimoike T., Akiyama Y., Yoshihisa T., Ito K. A cytoplasmic domain is important for the formation of a SecY-SecE translocator complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4539–4543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Proper interaction between at least two components is required for efficient export of proteins to the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):169–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.169-178.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker-Brady K., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor analysis suggests a multistep, cyclic mechanism for protein secretion in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3165–3174. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker K. L., Phillips G. J., Silhavy T. J. The sec and prl genes of Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):291–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00763169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker K. L., Silhavy T. J. PrlA (SecY) and PrlG (SecE) interact directly and function sequentially during protein translocation in E. coli. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):833–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90193-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker K. L., Silhavy T. J. PrlA is important for the translocation of exported proteins across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage L., Fimmel C. J., Mizushima S., Wickner W. SecY, SecE, and band 1 form the membrane-embedded domain of Escherichia coli preprotein translocase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):4166–4170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage L., Hendrick J. P., Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Wickner W. The purified E. coli integral membrane protein SecY/E is sufficient for reconstitution of SecA-dependent precursor protein translocation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90111-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabelli R. J., Chen L., Tai P. C., Oliver D. B. SecA protein is required for secretory protein translocation into E. coli membrane vesicles. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerretti D. P., Dean D., Davis G. R., Bedwell D. M., Nomura M. The spc ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli: sequence and cotranscription of the ribosomal protein genes and a protein export gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2599–2616. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman A. I., Puziss J. W., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. A signal sequence is not required for protein export in prlA mutants of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):879–888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05728.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douville K., Leonard M., Brundage L., Nishiyama K., Tokuda H., Mizushima S., Wickner W. Band 1 subunit of Escherichia coli preportein translocase and integral membrane export factor P12 are the same protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):18705–18707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing W. L., Sullivan S. L., Gottesman M. E., Dennis P. P. Sequence and transcriptional pattern of the essential Escherichia coli secE-nusG operon. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1621–1627. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1621-1627.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esnault Y., Blondel M. O., Deshaies R. J., Scheckman R., Képès F. The yeast SSS1 gene is essential for secretory protein translocation and encodes a conserved protein of the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4083–4093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower A. M., Doebele R. C., Silhavy T. J. PrlA and PrlG suppressors reduce the requirement for signal sequence recognition. J Bacteriol. 1994 Sep;176(18):5607–5614. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.18.5607-5614.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Prehn S., Hartmann E., Kalies K. U., Rapoport T. A. A mammalian homolog of SEC61p and SECYp is associated with ribosomes and nascent polypeptides during translocation. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):489–503. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90517-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Rapoport T. A. Protein translocation into proteoliposomes reconstituted from purified components of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):615–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E., Sommer T., Prehn S., Görlich D., Jentsch S., Rapoport T. A. Evolutionary conservation of components of the protein translocation complex. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):654–657. doi: 10.1038/367654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. C., Leonard M. R., Wickner W. T. Subunit dynamics in Escherichia coli preprotein translocase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4703–4707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Schekman R. Distinct sets of SEC genes govern transport vesicle formation and fusion early in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):723–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90483-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Akimaru J., Mizushima S. SecE-dependent overproduction of SecY in Escherichia coli. Evidence for interaction between two components of the secretory machinery. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 20;269(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81128-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Fujita Y., Mizushima S. SecD is involved in the release of translocated secretory proteins from the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):265–270. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05652.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy C. K., Beckwith J. Residues essential for the function of SecE, a membrane component of the Escherichia coli secretion apparatus, are located in a conserved cytoplasmic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2557–2561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama K., Kabuyama Y., Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. SecY is an indispensable component of the protein secretory machinery of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 31;1065(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90015-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama K., Mizushima S., Tokuda H. A novel membrane protein involved in protein translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3409–3415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama K., Mizushima S., Tokuda H. The carboxyl-terminal region of SecE interacts with SecY and is functional in the reconstitution of protein translocation activity in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7170–7176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne R. S., Silhavy T. J. PrlA suppressor mutations cluster in regions corresponding to three distinct topological domains. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3391–3398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogliano J. A., Beckwith J. SecD and SecF facilitate protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):554–561. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogliano K. J., Beckwith J. Genetic and molecular characterization of the Escherichia coli secD operon and its products. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(3):804–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.3.804-814.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogliano K. J., Beckwith J. The Cs sec mutants of Escherichia coli reflect the cold sensitivity of protein export itself. Genetics. 1993 Apr;133(4):763–773. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.4.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puziss J. W., Strobel S. M., Bassford P. J., Jr Export of maltose-binding protein species with altered charge distribution surrounding the signal peptide hydrophobic core in Escherichia coli cells harboring prl suppressor mutations. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):92–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.92-101.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo F. D., Slauch J. M., Silhavy T. J. Mutations that affect separate functions of OmpR the phosphorylated regulator of porin transcription in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1993 May 20;231(2):261–273. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagara K., Matsuyama S., Mizushima S. SecF stabilizes SecD and SecY, components of the protein translocation machinery of the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jul;176(13):4111–4116. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.13.4111-4116.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sako T., Iino T. Distinct mutation sites in prlA suppressor mutant strains of Escherichia coli respond either to suppression of signal peptide mutations or to blockage of staphylokinase processing. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5389–5391. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5389-5391.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Bieker K. L., Ottemann K. M., Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. One of three transmembrane stretches is sufficient for the functioning of the SecE protein, a membrane component of the E. coli secretion machinery. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1749–1757. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07699.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Riggs P. D., Jacq A., Fath M. J., Beckwith J. The secE gene encodes an integral membrane protein required for protein export in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1035–1044. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scidmore M. A., Okamura H. H., Rose M. D. Genetic interactions between KAR2 and SEC63, encoding eukaryotic homologues of DnaK and DnaJ in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Nov;4(11):1145–1159. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.11.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J., Gansheroff L. J., Silhavy T. J. New suppressors of signal-sequence mutations, prlG, are linked tightly to the secE gene of Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1045–1052. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling C. J., Rothblatt J., Hosobuchi M., Deshaies R., Schekman R. Protein translocation mutants defective in the insertion of integral membrane proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Feb;3(2):129–142. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trun N. J., Silhavy T. J. Characterization and in vivo cloning of prlC, a suppressor of signal sequence mutations in Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1987 Aug;116(4):513–521. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.4.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Blobel G. SecA protein is required for translocation of a model precursor protein into inverted vesicles of Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9011–9015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U. The enzymology of protein translocation across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:101–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


