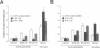Abstract
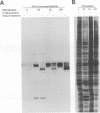
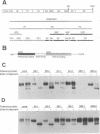
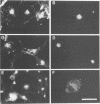
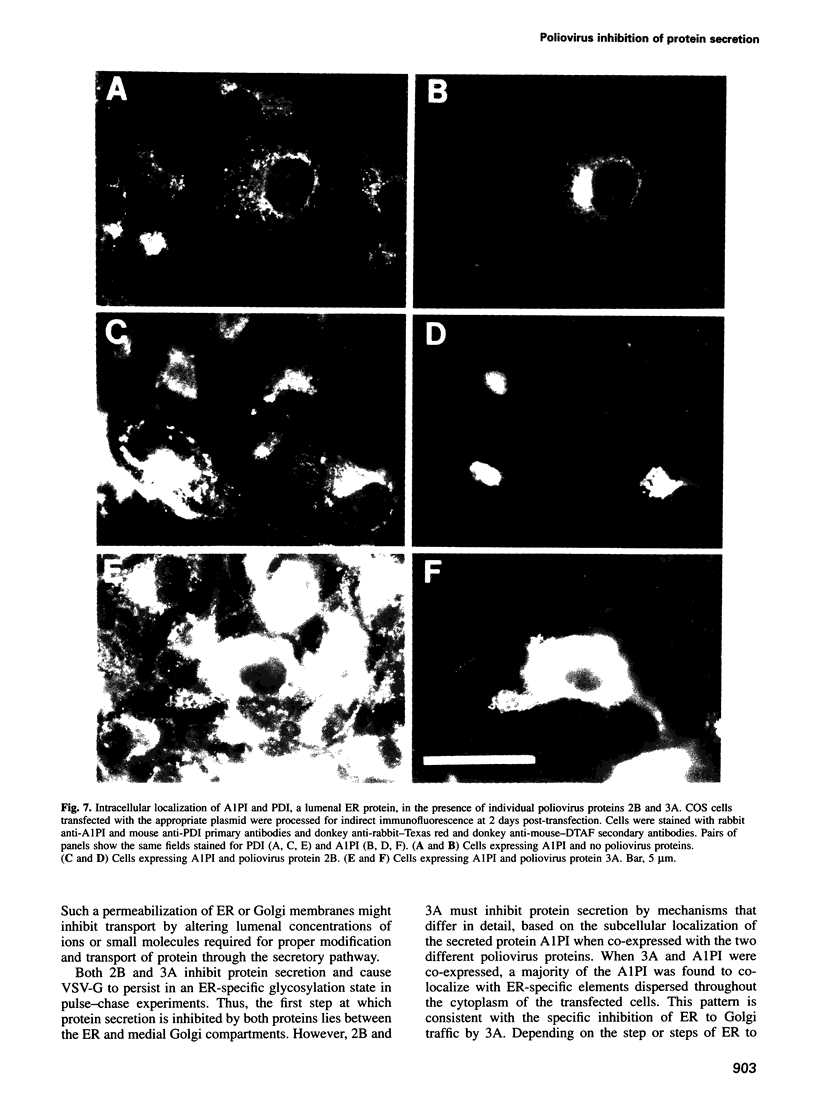
Poliovirus RNA replication occurs on the surface of membranous vesicles that proliferate throughout the cytoplasm of the infected cell. Since at least some of these vesicles are thought to originate within the secretory pathway of the host cell, we examined the effect of poliovirus infection on protein transport through the secretory pathway. We found that transport of both plasma membrane and secretory proteins was inhibited by poliovirus infection early in the infectious cycle. Transport inhibition did not require viral RNA replication or the inhibition of host cell translation by poliovirus. The viral proteins 2B and 3A were each sufficient to inhibit transport in the absence of viral infection. The intracellular localization of a secreted protein in the presence of 3A with the endoplasmic reticulum suggested that 3A directly blocks transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Kamer G., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Similarity in gene organization and homology between proteins of animal picornaviruses and a plant comovirus suggest common ancestry of these virus families. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7251–7267. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Pasamontes L. Association of polioviral proteins of the P2 genomic region with the viral replication complex and virus-induced membrane synthesis as visualized by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry and autoradiography. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Rasser Y., Bossart W. Intracellular distribution of poliovirus proteins and the induction of virus-specific cytoplasmic structures. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90531-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Troxler M., Pasamontes L. Structural organization of poliovirus RNA replication is mediated by viral proteins of the P2 genomic region. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1156-1163.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneau A. M., Sonenberg N. Proteolysis of the p220 component of the cap-binding protein complex is not sufficient for complete inhibition of host cell protein synthesis after poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.986-991.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Action of guanidine on the replication of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):408–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho M. W., Teterina N., Egger D., Bienz K., Ehrenfeld E. Membrane rearrangement and vesicle induction by recombinant poliovirus 2C and 2BC in human cells. Virology. 1994 Jul;202(1):129–145. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. E., Hämmerle T., Wimmer E., Dasgupta A. Poliovirus proteinase 3C converts an active form of transcription factor IIIC to an inactive form: a mechanism for inhibition of host cell polymerase III transcription by poliovirus. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2941–2947. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. E., Lieberman P. M., Berk A. J., Dasgupta A. Direct cleavage of human TATA-binding protein by poliovirus protease 3C in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1232–1237. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascher C., Balch W. E. Dominant inhibitory mutants of ARF1 block endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport and trigger disassembly of the Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1437–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta U., Dasgupta A. Expression and subcellular localization of poliovirus VPg-precursor protein 3AB in eukaryotic cells: evidence for glycosylation in vitro. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4468–4477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4468-4477.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doedens J., Maynell L. A., Klymkowsky M. W., Kirkegaard K. Secretory pathway function, but not cytoskeletal integrity, is required in poliovirus infection. Arch Virol Suppl. 1994;9:159–172. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9326-6_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Cassel D., Kahn R. A., Klausner R. D. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding protein, is required for binding of the coatomer protein beta-COP to Golgi membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Finazzi D., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A inhibits Golgi membrane-catalysed exchange of guanine nucleotide onto ARF protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):350–352. doi: 10.1038/360350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franssen H., Leunissen J., Goldbach R., Lomonossoff G., Zimmern D. Homologous sequences in non-structural proteins from cowpea mosaic virus and picornaviruses. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):855–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachetti C., Hwang S. S., Semler B. L. cis-acting lesions targeted to the hydrophobic domain of a poliovirus membrane protein involved in RNA replication. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6045–6057. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6045-6057.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachetti C., Semler B. L. Role of a viral membrane polypeptide in strand-specific initiation of poliovirus RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2647–2654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2647-2654.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Inhibition of DNA-primed RNA synthesis during poliovirus infection of human cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Dec 19;9:556–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambidge S. J., Sarnow P. Translational enhancement of the poliovirus 5' noncoding region mediated by virus-encoded polypeptide 2A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10272–10276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms J. B., Rothman J. E. Inhibition by brefeldin A of a Golgi membrane enzyme that catalyses exchange of guanine nucleotide bound to ARF. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):352–354. doi: 10.1038/360352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu V. W., Shah N., Klausner R. D. A brefeldin A-like phenotype is induced by the overexpression of a human ERD-2-like protein, ELP-1. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):625–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90226-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irurzun A., Perez L., Carrasco L. Involvement of membrane traffic in the replication of poliovirus genomes: effects of brefeldin A. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):166–175. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90178-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J., Wimmer E. Initiation of protein synthesis by internal entry of ribosomes into the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1651–1660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1651-1660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. L., Sarnow P. Three poliovirus 2B mutants exhibit noncomplementable defects in viral RNA amplification and display dosage-dependent dominance over wild-type poliovirus. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4341–4349. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4341-4349.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R. Construction and characterization of poliovirus subgenomic replicons. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1687–1696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1687-1696.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lama J., Carrasco L. Expression of poliovirus nonstructural proteins in Escherichia coli cells. Modification of membrane permeability induced by 2B and 3A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15932–15937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lama J., Paul A. V., Harris K. S., Wimmer E. Properties of purified recombinant poliovirus protein 3aB as substrate for viral proteinases and as co-factor for RNA polymerase 3Dpol. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):66–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancios L., Lyles D. S. The interactionof antiody with the major surface glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Analysis of neutralizing epitopes with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1982 Aug;121(1):157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenk R., Penman S. The cytoskeletal framework and poliovirus metabolism. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., Baltimore D. Isolation of poliovirus 2C mutants defective in viral RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4016–4021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4016-4021.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Rivas A., Castrillo J. L., Carrasco L. Cation content in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):335–342. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynell L. A., Kirkegaard K., Klymkowsky M. W. Inhibition of poliovirus RNA synthesis by brefeldin A. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1985–1994. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1985-1994.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken A. A., Kruse K. B., Brown J. L. Molecular basis for defective secretion of the Z variant of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor: secretion of variants having altered potential for salt bridge formation between amino acids 290 and 342. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1406–1414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Misumi Y., Miki K., Takatsuki A., Tamura G., Ikehara Y. Novel blockade by brefeldin A of intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser A. G., Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Incorporation of lipid precursors into cytoplasmic membranes of poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz A., Carrasco L. Effect of interferon treatment on blockade of protein synthesis induced by poliovirus infection. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 15;137(3):623–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. K., Sarnow P. Gene regulation: translational initiation by internal ribosome binding. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0959-437X(93)90037-P. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. E., Wimmer E. Production of guanidine-resistant and -dependent poliovirus mutants from cloned cDNA: mutations in polypeptide 2C are directly responsible for altered guanidine sensitivity. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):793–796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.793-796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Expression from cloned cDNA of cell-surface secreted forms of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lodish H. F. Synchronised transmembrane insertion and glycosylation of a nascent membrane protein. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):775–780. doi: 10.1038/269775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein S. J., Hammerle T., Wimmer E., Dasgupta A. Infection of HeLa cells with poliovirus results in modification of a complex that binds to the rRNA promoter. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3062–3068. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3062-3068.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Hanecak R., Dorner L. F., Wimmer E. A membrane-associated precursor to poliovirus VPg identified by immunoprecipitation with antibodies directed against a synthetic heptapeptide. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda N., Kuhn R. J., Yang C. F., Takegami T., Wimmer E. Initiation of poliovirus plus-strand RNA synthesis in a membrane complex of infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):43–53. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.43-53.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Kuhn R. J., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane-dependent uridylylation of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M., Vassalli P. Lectin-binding sites as markers of Golgi subcompartments: proximal-to-distal maturation of oligosaccharides. J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1243–1248. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teal S. B., Hsu V. W., Peters P. J., Klausner R. D., Donaldson J. G. An activating mutation in ARF1 stabilizes coatomer binding to Golgi membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3135–3138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale E. J., Bourne J. R., Khosravi-Far R., Der C. J., Balch W. E. GTP-binding mutants of rab1 and rab2 are potent inhibitors of vesicular transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):749–761. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler M., Egger D., Pfister T., Bienz K. Intracellular localization of poliovirus RNA by in situ hybridization at the ultrastructural level using single-stranded riboprobes. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):687–697. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90244-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomikoski T., Felix M. A., Dorée M., Gruenberg J. Inhibition of endocytic vesicle fusion in vitro by the cell-cycle control protein kinase cdc2. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):942–945. doi: 10.1038/342942a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. W., Bobak D. A., Tsai S. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. GTP but not GDP analogues promote association of ADP-ribosylation factors, 20-kDa protein activators of cholera toxin, with phospholipids and PC-12 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3230–3235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. B., Murphy R. F. Flow-cytometric analysis of endocytic compartments. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:293–317. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61616-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E., Hellen C. U., Cao X. Genetics of poliovirus. Annu Rev Genet. 1993;27:353–436. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.27.120193.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff E. E., Hershey J. W., Ehrenfeld E. Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 is required for poliovirus 2A protease-induced cleavage of the p220 component of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9529–9533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN E. F., HEETER M., DARNELL J. E. RNA synthesis in poliovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:400–408. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bokhoven H., van Lent J. W., Custers R., Vlak J. M., Wellink J., van Kammen A. Synthesis of the complete 200K polyprotein encoded by cowpea mosaic virus B-RNA in insect cells. J Gen Virol. 1992 Nov;73(Pt 11):2775–2784. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-11-2775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]