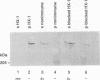
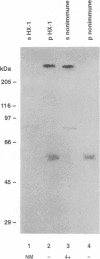
Abstract
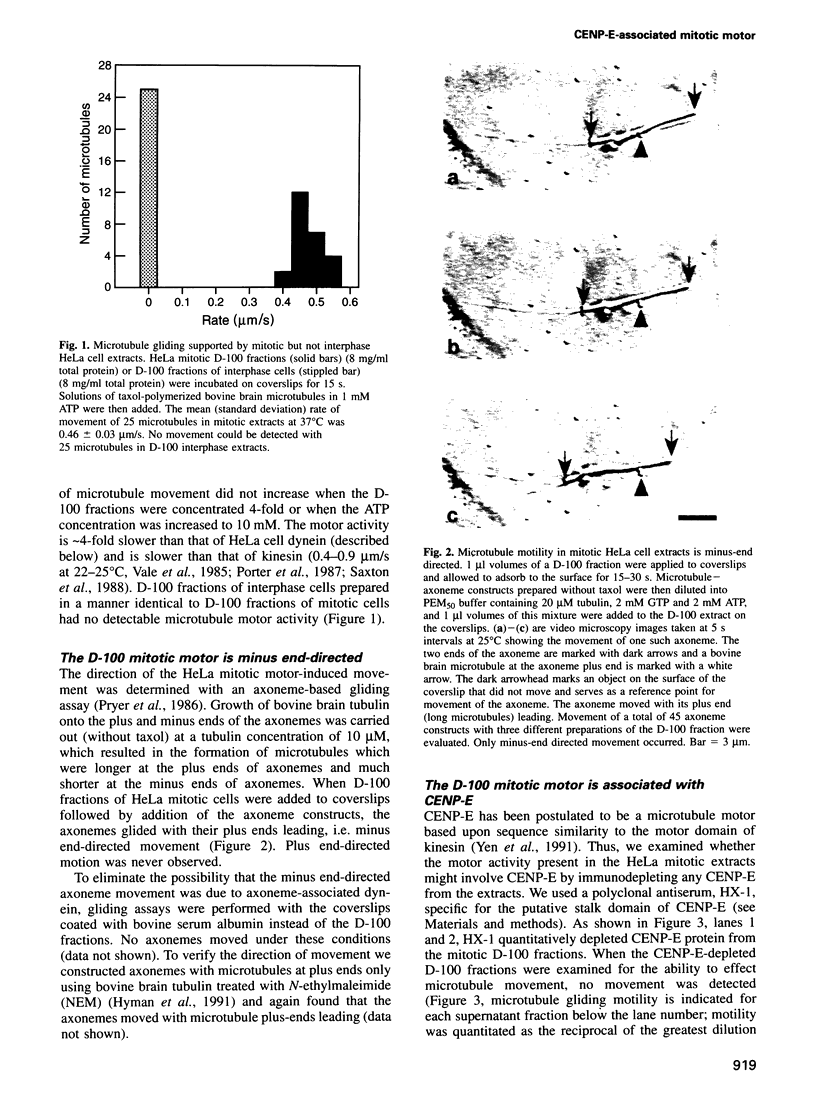
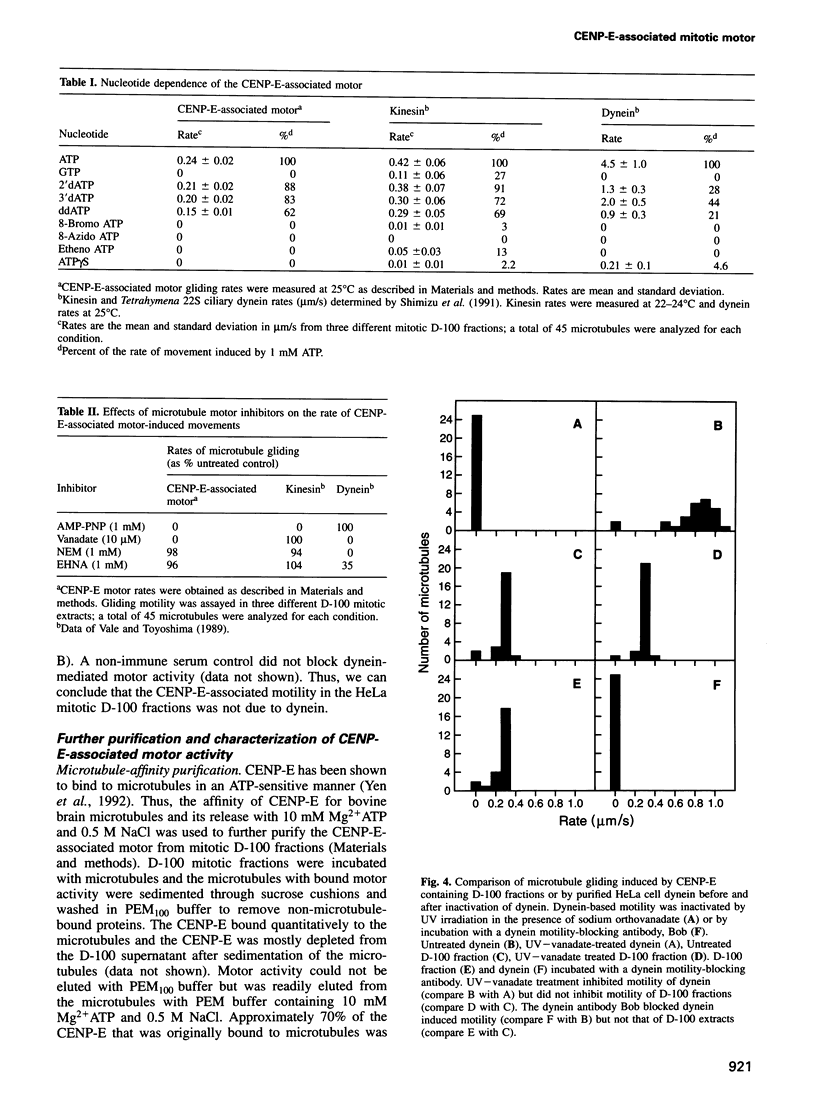
A minus end-directed microtubule motor activity from extracts of HeLa cells blocked at prometaphase/metaphase of mitosis with vinblastine has been partially purified and characterized. The motor activity was eliminated by immunodepletion of Centromere binding protein E (CENP-E). The CENP-E-associated motor activity, which was not detectable in interphase cells, moved microtubules at mean rates of 0.46 micron/s at 37 degrees C and 0.24 micron/s at 25 degrees C. The motor activity co-purified with CENP-E through several purification procedures. Motor activity was clearly not due to dynein or to kinesin. The microtubule gliding rates of the CENP-E-associated motor were different from those of dynein and kinesin. In addition, the pattern of nucleotide substrate utilization by the CENP-E-associated motor and the sensitivity to inhibitors were different from those of dynein and kinesin. The CENP-E-associated motor had an apparent native molecular weight of 874,000 Da and estimated dimensions of 2 nm x 80 nm. This is the first demonstration of motor activity associated with CENP-E, strongly supporting the hypothesis that CENP-E may act as a minus end-directed microtubule motor during mitosis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan V. J., Vale R. D. Cell cycle control of microtubule-based membrane transport and tubule formation in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(2):347–359. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.2.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Wagner M. C., Pfister K. K., Brady S. T. Native structure and physical properties of bovine brain kinesin and identification of the ATP-binding subunit polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3409–3416. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Coulson R. M., Yen T. J., Cleveland D. W. Cyclin-like accumulation and loss of the putative kinetochore motor CENP-E results from coupling continuous synthesis with specific degradation at the end of mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(6):1303–1312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.6.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Henikoff S., Soler-Niedziela L. Mediation of meiotic and early mitotic chromosome segregation in Drosophila by a protein related to kinesin. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):81–83. doi: 10.1038/345081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Kang S. J., Satterwhite L. L., Rose M. D., Skeen V. P., Salmon E. D. Yeast Kar3 is a minus-end microtubule motor protein that destabilizes microtubules preferentially at the minus ends. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2708–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Lee-Eiford A., Mocz G., Phillipson C. A., Tang W. J., Gibbons B. H. Photosensitized cleavage of dynein heavy chains. Cleavage at the "V1 site" by irradiation at 365 nm in the presence of ATP and vanadate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2780–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliksman N. R., Salmon E. D. Microtubule-associated motility in cytoplasmic extracts of sea urchin eggs. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;24(3):167–178. doi: 10.1002/cm.970240304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. S. With apologies to scheherazade: tails of 1001 kinesin motors. Annu Rev Genet. 1993;27:319–351. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.27.120193.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden J. H., Bowser S. S., Rieder C. L. Kinetochores capture astral microtubules during chromosome attachment to the mitotic spindle: direct visualization in live newt lung cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga S., Murofushi H., Okuhara K., Sato R., Masuda Y., Sakai H., Hirokawa N. The molecular structure of adrenal medulla kinesin. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;12(4):264–272. doi: 10.1002/cm.970120407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman A. A., Mitchison T. J. Two different microtubule-based motor activities with opposite polarities in kinetochores. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):206–211. doi: 10.1038/351206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman A., Drechsel D., Kellogg D., Salser S., Sawin K., Steffen P., Wordeman L., Mitchison T. Preparation of modified tubulins. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:478–485. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96041-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Thrower D., Wilson L. Mechanism of inhibition of cell proliferation by Vinca alkaloids. Cancer Res. 1991 Apr 15;51(8):2212–2222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Sato-Yoshitake R., Noda Y., Aizawa H., Nakata T., Matsuura Y., Hirokawa N. KIF3A is a new microtubule-based anterograde motor in the nerve axon. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):1095–1107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Y., Yeh E., Hays T., Bloom K. Disruption of mitotic spindle orientation in a yeast dynein mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10096–10100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao H., Li G., Yen T. J. Mitotic regulation of microtubule cross-linking activity of CENP-E kinetochore protein. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):394–398. doi: 10.1126/science.8023161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald H. B., Stewart R. J., Goldstein L. S. The kinesin-like ncd protein of Drosophila is a minus end-directed microtubule motor. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1159–1165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merdes A., De Mey J. The mechanism of kinetochore-spindle attachment and polewards movement analyzed in PtK2 cells at the prophase-prometaphase transition. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;53(2):313–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. R., Warner F. D. Binding of dynein 21 S ATPase to microtubules. Effects of ionic conditions and substrate analogs. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12535–12544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nislow C., Lombillo V. A., Kuriyama R., McIntosh J. R. A plus-end-directed motor enzyme that moves antiparallel microtubules in vitro localizes to the interzone of mitotic spindles. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):543–547. doi: 10.1038/359543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nislow C., Sellitto C., Kuriyama R., McIntosh J. R. A monoclonal antibody to a mitotic microtubule-associated protein blocks mitotic progression. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):511–522. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfarr C. M., Coue M., Grissom P. M., Hays T. S., Porter M. E., McIntosh J. R. Cytoplasmic dynein is localized to kinetochores during mitosis. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):263–265. doi: 10.1038/345263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Scholey J. M., Stemple D. L., Vigers G. P., Vale R. D., Sheetz M. P., McIntosh J. R. Characterization of the microtubule movement produced by sea urchin egg kinesin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2794–2802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryer N. K., Wadsworth P., Salmon E. D. Polarized microtubule gliding and particle saltations produced by soluble factors from sea urchin eggs and embryos. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1986;6(6):537–548. doi: 10.1002/cm.970060602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Alexander S. P. Kinetochores are transported poleward along a single astral microtubule during chromosome attachment to the spindle in newt lung cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):81–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodionov V. I., Gelfand V. I., Borisy G. G. Kinesin-like molecules involved in spindle formation. J Cell Sci. 1993 Dec;106(Pt 4):1179–1188. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.4.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos U. P. Light and electron microscopy of rat kangaroo cells in mitosis. III. Patterns of chromosome behavior during prometaphase. Chromosoma. 1976 Mar 10;54(4):363–385. doi: 10.1007/BF00292816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawin K. E., Mitchison T. J., Wordeman L. G. Evidence for kinesin-related proteins in the mitotic apparatus using peptide antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1992 Feb;101(Pt 2):303–313. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton W. M., Porter M. E., Cohn S. A., Scholey J. M., Raff E. C., McIntosh J. R. Drosophila kinesin: characterization of microtubule motility and ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1109–1113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer T. A., Steuer E. R., Sheetz M. P. Cytoplasmic dynein is a minus end-directed motor for membranous organelles. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):937–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90627-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Furusawa K., Ohashi S., Toyoshima Y. Y., Okuno M., Malik F., Vale R. D. Nucleotide specificity of the enzymatic and motile activities of dynein, kinesin, and heavy meromyosin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1189–1197. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skibbens R. V., Skeen V. P., Salmon E. D. Directional instability of kinetochore motility during chromosome congression and segregation in mitotic newt lung cells: a push-pull mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):859–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. J., Thaler J. P., Goldstein L. S. Direction of microtubule movement is an intrinsic property of the motor domains of kinesin heavy chain and Drosophila ncd protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5209–5213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrower D., Jordan M. A., Wilson L. Quantitation of cellular tubulin in microtubules and tubulin pools by a competitive ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jan 24;136(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90248-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toso R. J., Jordan M. A., Farrell K. W., Matsumoto B., Wilson L. Kinetic stabilization of microtubule dynamic instability in vitro by vinblastine. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 9;32(5):1285–1293. doi: 10.1021/bi00056a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaisberg E. A., Koonce M. P., McIntosh J. R. Cytoplasmic dynein plays a role in mammalian mitotic spindle formation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):849–858. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80099-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., Salmon E. D., Endow S. A. The Drosophila claret segregation protein is a minus-end directed motor molecule. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):780–782. doi: 10.1038/347780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. J., Compton D. A., Wise D., Zinkowski R. P., Brinkley B. R., Earnshaw W. C., Cleveland D. W. CENP-E, a novel human centromere-associated protein required for progression from metaphase to anaphase. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1245–1254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. J., Li G., Schaar B. T., Szilak I., Cleveland D. W. CENP-E is a putative kinetochore motor that accumulates just before mitosis. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):536–539. doi: 10.1038/359536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]