Abstract
The antigen receptor on T cells (TCR) has been predicted to have a structure similar to a membrane-anchored form of an immunoglobulin F(ab) fragment. Virtually all of the conserved amino acids that are important for inter- and intramolecular interactions in the VH-VL pair are also conserved in the TCR V alpha and V beta chains. A molecular model of the TCR has been constructed by homology and we have used the information from this, as well as the earlier structural predictions of others, to study the basis for specificity. Specifically, regions of a TCR cloned from an antigen-specific T cell were stitched into the corresponding framework of a second TCR. Results indicate that the substitution of amino acid sequences corresponding to the complementarity determining regions (CDRs) of immunoglobulin can convey the specificity for antigen and major histocompatibility complex molecules. These data are consistent with a role, but not an exclusive role, for CDR3 in antigen peptide recognition.
Full text
PDF



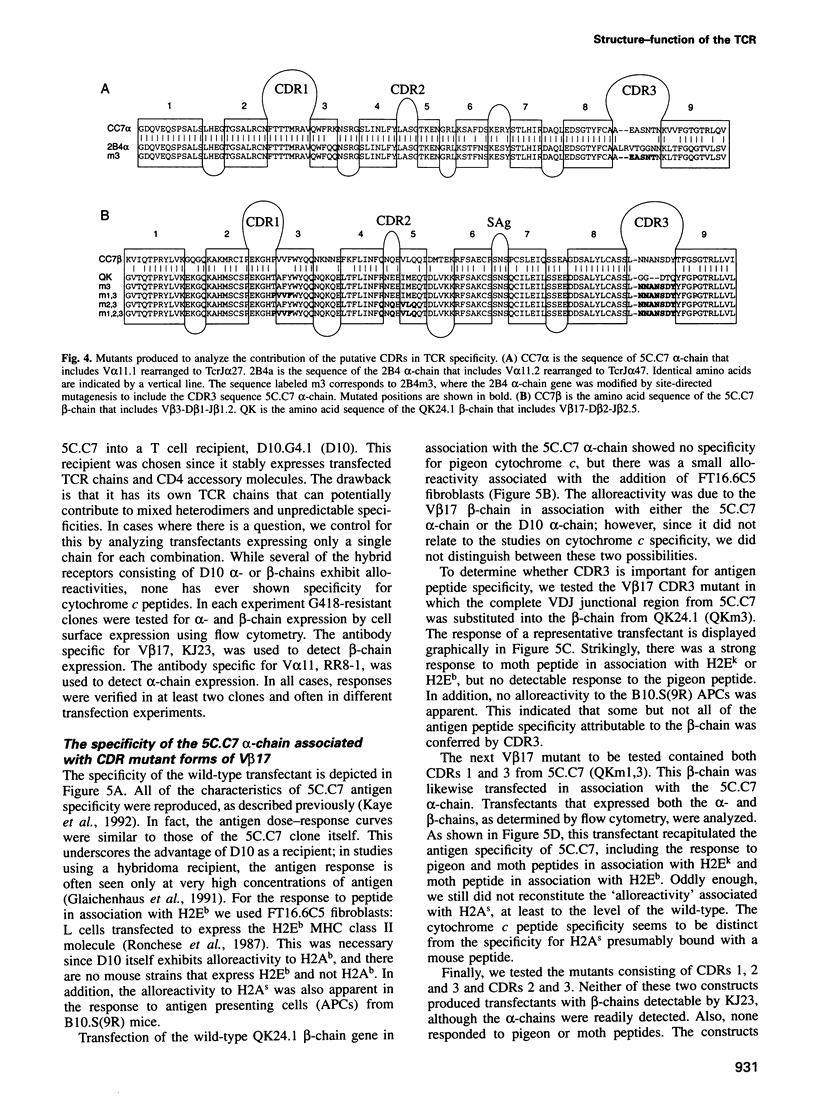
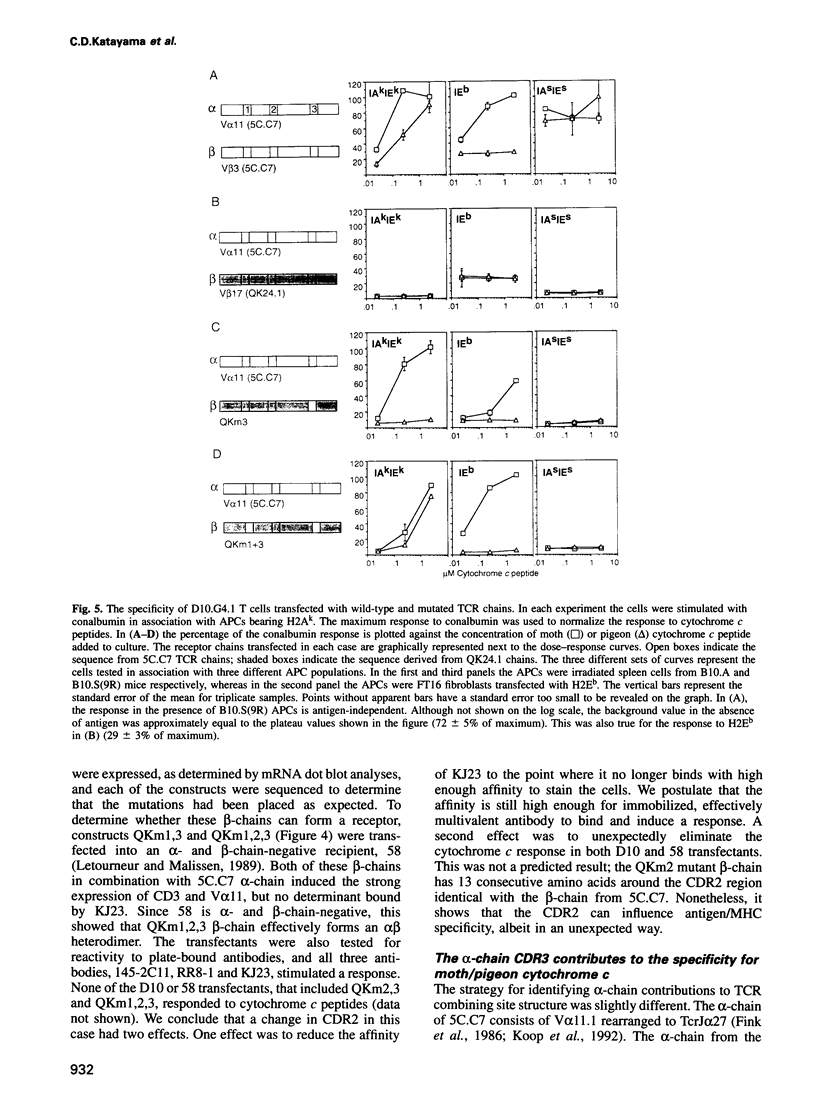






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beale D., Coadwell J. Unusual features of the T-cell receptor C domains are revealed by structural comparisons with other members of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1986;85(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(86)90244-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellio M., Lone Y. C., de la Calle-Martin O., Malissen B., Abastado J. P., Kourilsky P. The V beta complementarity determining region 1 of a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-restricted T cell receptor is involved in the recognition of peptide/MHC I and superantigen/MHC II complex. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1087–1097. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowie J. U., Lüthy R., Eisenberg D. A method to identify protein sequences that fold into a known three-dimensional structure. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):164–170. doi: 10.1126/science.1853201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein N. S., Weber D. A., Wang X. C., Long E. O., Karp D. Sequences in both class II major histocompatibility complex alpha and beta chains contribute to the binding of the superantigen toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1301–1305. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T. S., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Urban R. G., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):33–39. doi: 10.1038/364033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändle D., Bürki K., Wallace V. A., Rohrer U. H., Mak T. W., Malissen B., Hengartner H., Pircher H. Involvement of both T cell receptor V alpha and V beta variable region domains and alpha chain junctional region in viral antigen recognition. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Sep;21(9):2195–2202. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Miles C., Grey H. M. The relation between major histocompatibility complex (MHC) restriction and the capacity of Ia to bind immunogenic peptides. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1353–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.2435001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave P. A., Marche P. N., Jouvin-Marche E., Voegtlé D., Bonhomme F., Bandeira A., Coutinho A. V beta 17 gene polymorphism in wild-derived mouse strains: two amino acid substitutions in the V beta 17 region greatly alter T cell receptor specificity. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y., Becker D. M., Lindsten T., Okamura M., Cohen D. I., Davis M. M. A third type of murine T-cell receptor gene. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):31–35. doi: 10.1038/312031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Herman A., DiGiusto D., Wade T., Marrack P., Kappler J. Residues of the variable region of the T-cell-receptor beta-chain that interact with S. aureus toxin superantigens. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):471–473. doi: 10.1038/346471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Boswell D. R., Lesk A. M. The outline structure of the T-cell alpha beta receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3745–3755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M. Canonical structures for the hypervariable regions of immunoglobulins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):901–917. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M., Prochnicka-Chalufour A., Bougueleret L. Implications of a Fab-like structure for the T-cell receptor. Immunol Today. 1989 Jan;10(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danska J. S., Livingstone A. M., Paragas V., Ishihara T., Fathman C. G. The presumptive CDR3 regions of both T cell receptor alpha and beta chains determine T cell specificity for myoglobin peptides. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):27–33. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrich E. W., Devaux B., Rock E. P., Jorgensen J. L., Davis M. M., Chien Y. H. T cell receptor interaction with peptide/major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and superantigen/MHC ligands is dominated by antigen. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):713–722. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel I., Hedrick S. M. Site-directed mutations in the VDJ junctional region of a T cell receptor beta chain cause changes in antigenic peptide recognition. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Blair M. J., Matis L. A., Hedrick S. M. Molecular analysis of the influences of positive selection, tolerance induction, and antigen presentation on the T cell receptor repertoire. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):139–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Matis L. A., McElligott D. L., Bookman M., Hedrick S. M. Correlations between T-cell specificity and the structure of the antigen receptor. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):219–226. doi: 10.1038/321219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischmann T. O., Bentley G. A., Bhat T. N., Boulot G., Mariuzza R. A., Phillips S. E., Tello D., Poljak R. J. Crystallographic refinement of the three-dimensional structure of the FabD1.3-lysozyme complex at 2.5-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12915–12920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N. MHC-dependent antigen processing and peptide presentation: providing ligands for T lymphocyte activation. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90336-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaichenhaus N., Davis C., Bornschlegel K., Allison J. P., Shastri N. A novel strategy for the generation of T cell lines lacking expression of endogenous alpha- and/or beta-chain T cell receptor genes. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2095–2101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Leavitt J., Muscat G., Ng S. Y., Kedes L. A human beta-actin expression vector system directs high-level accumulation of antisense transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4831–4835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Engel I., McElligott D. L., Fink P. J., Hsu M. L., Hansburg D., Matis L. A. Selection of amino acid sequences in the beta chain of the T cell antigen receptor. Science. 1988 Mar 25;239(4847):1541–1544. doi: 10.1126/science.2832942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Matis L. A., Hecht T. T., Samelson L. E., Longo D. L., Heber-Katz E., Schwartz R. H. The fine specificity of antigen and Ia determinant recognition by T cell hybridoma clones specific for pigeon cytochrome c. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Croteau G., Sekaly R. P., Kappler J., Marrack P. HLA-DR alleles differ in their ability to present staphylococcal enterotoxins to T cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):709–717. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. C., Chelouche A., Lin R. H., Shaywitz D., Braunstein N. S., Glimcher L., Janeway C. A., Jr An MHC interaction site maps to the amino-terminal half of the T cell receptor alpha chain variable domain. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):999–1009. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90618-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin M. J., Hudson K. R., Ames K. T., Fraser J. D., Gascoigne N. R. T-cell receptor beta-chain binding to enterotoxin superantigens. Immunol Rev. 1993 Feb;131:61–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1993.tb01530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Brown J. H., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Urban R. G., Chi Y. I., Stauffacher C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Three-dimensional structure of a human class II histocompatibility molecule complexed with superantigen. Nature. 1994 Apr 21;368(6473):711–718. doi: 10.1038/368711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. L., Esser U., Fazekas de St Groth B., Reay P. A., Davis M. M. Mapping T-cell receptor-peptide contacts by variant peptide immunization of single-chain transgenics. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):224–230. doi: 10.1038/355224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Wade T., White J., Kushnir E., Blackman M., Bill J., Roehm N., Marrack P. A T cell receptor V beta segment that imparts reactivity to a class II major histocompatibility complex product. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90567-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp D. R., Long E. O. Identification of HLA-DR1 beta chain residues critical for binding staphylococcal enterotoxins A and E. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):415–424. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasibhatla S., Nalefski E. A., Rao A. Simultaneous involvement of all six predicted antigen binding loops of the T cell receptor in recognition of the MHC/antigenic peptide complex. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 15;151(6):3140–3151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Hedrick S. M. Analysis of specificity for antigen, Mls, and allogenic MHC by transfer of T-cell receptor alpha- and beta-chain genes. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):580–583. doi: 10.1038/336580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Kersh G., Engel I., Hedrick S. M. Structure and specificity of the T cell antigen receptor. Semin Immunol. 1991 Sep;3(5):269–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Porcelli S., Tite J., Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Both a monoclonal antibody and antisera specific for determinants unique to individual cloned helper T cell lines can substitute for antigen and antigen-presenting cells in the activation of T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):836–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Vasquez N. J., Hedrick S. M. Involvement of the same region of the T cell antigen receptor in thymic selection and foreign peptide recognition. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3342–3353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop B. F., Wilson R. K., Wang K., Vernooij B., Zallwer D., Kuo C. L., Seto D., Toda M., Hood L. Organization, structure, and function of 95 kb of DNA spanning the murine T-cell receptor C alpha/C delta region. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1209–1230. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90039-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Siu G., Hood L. E., Shastri N. The molecular genetics of the T-cell antigen receptor and T-cell antigen recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:529–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. Z., Jang Y. J., Chen L. K., Gefter M. L. Restricted V-(D)-J junctional regions in the T cell response to lambda-repressor. Identification of residues critical for antigen recognition. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4851–4856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesk A. M., Chothia C. Evolution of proteins formed by beta-sheets. II. The core of the immunoglobulin domains. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):325–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Malissen B. Derivation of a T cell hybridoma variant deprived of functional T cell receptor alpha and beta chain transcripts reveals a nonfunctional alpha-mRNA of BW5147 origin. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2269–2274. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A., Longo D. L., Hedrick S. M., Hannum C., Margoliash E., Schwartz R. H. Clonal analysis of the major histocompatibility complex restriction and the fine specificity of antigen recognition in the T cell proliferative response to cytochrome C. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1527–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalefski E. A., Kasibhatla S., Rao A. Functional analysis of the antigen binding site on the T cell receptor alpha chain. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1553–1563. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalefski E. A., Wong J. G., Rao A. Amino acid substitutions in the first complementarity-determining region of a murine T-cell receptor alpha chain affect antigen-major histocompatibility complex recognition. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8842–8846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny J., Ganju R. K., Smiley S. T., Hussey R. E., Luther M. A., Recny M. A., Siliciano R. F., Reinherz E. L. A soluble, single-chain T-cell receptor fragment endowed with antigen-combining properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8646–8650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Tonegawa S., Saito H., Kranz D. M., Eisen H. N. Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of T-cell-specific immunoglobulin-like polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panina-Bordignon P., Fu X. T., Lanzavecchia A., Karr R. W. Identification of HLA-DR alpha chain residues critical for binding of the toxic shock syndrome toxin superantigen. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1779–1784. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patten P. A., Rock E. P., Sonoda T., Fazekas de St Groth B., Jorgensen J. L., Davis M. M. Transfer of putative complementarity-determining region loops of T cell receptor V domains confers toxin reactivity but not peptide/MHC specificity. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2281–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. M., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. The T-cell repertoire is heavily influenced by tolerance to polymorphic self-antigens. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):796–801. doi: 10.1038/335796a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. M., Wade T., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Identification of the region of T cell receptor beta chain that interacts with the self-superantigen MIs-1a. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1365–1374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90700-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronchese F., Schwartz R. H., Germain R. N. Functionally distinct subsites on a class II major histocompatibility complex molecule. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):254–256. doi: 10.1038/329254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D. R., Seaton B. A., Petsko G. A., Novotný J., Margolies M. N., Locke E., Haber E. Crystallization of the Fab fragment of a monoclonal anti-digoxin antibody and its complex with digoxin. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 25;165(1):203–206. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberti G., Paragas V., Kim D., Fathman C. G. Selection for amino acid sequence and J beta element usage in the beta chain of DBA/2V beta b- and DBA/2V beta a-derived myoglobin-specific T cell clones. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6185–6194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudikoff S., Satow Y., Padlan E., Davies D., Potter M. Kappa chain structure from a crystallized murine Fab': role of joining segment in hapten binding. Mol Immunol. 1981 Aug;18(8):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholl P. R., Sekaly R. P., Diez A., Glimcher L. H., Geha R. S. Binding of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 to murine major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Sep;20(9):1911–1916. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellins K. S., Danska J. S., Paragas V., Fathman C. G. Limited T cell receptor beta-chain usage in the sperm whale myoglobin 110-121/E alpha dA beta d response by H-2d congenic mouse strains. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2323–2327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solinger A. M., Ultee M. E., Margoliash E., Schwartz R. H. T-lymphocyte response to cytochrome c. I. Demonstration of a T-cell heteroclitic proliferative response and identification of a topographic antigenic determinant on pigeon cytochrome c whose immune recognition requires two complementing major histocompatibility complex-linked immune response genes. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):830–848. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger S. B., Hedrick S. M., Fink P. J., Bookman M. A., Matis L. A. Generation of diversity in T cell receptor repertoire specific for pigeon cytochrome c. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):279–301. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger S. B., Paterson Y., Fink P. J., Hedrick S. M. T cell receptor junctional regions and the MHC molecule affect the recognition of antigenic peptides by T cell clones. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):1127–1135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., McKenzie D. T., Weinberg A. D., Hancock W. Characterization of T helper 1 and 2 cell subsets in normal mice. Helper T cells responsible for IL-4 and IL-5 production are present as precursors that require priming before they develop into lymphokine-secreting cells. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3445–3455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Pullen A., Choi K., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Antigen recognition properties of mutant V beta 3+ T cell receptors are consistent with an immunoglobulin-like structure for the receptor. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):119–125. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wither J., Pawling J., Phillips L., Delovitch T., Hozumi N. Amino acid residues in the T cell receptor CDR3 determine the antigenic reactivity patterns of insulin-reactive hybridomas. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3513–3522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





