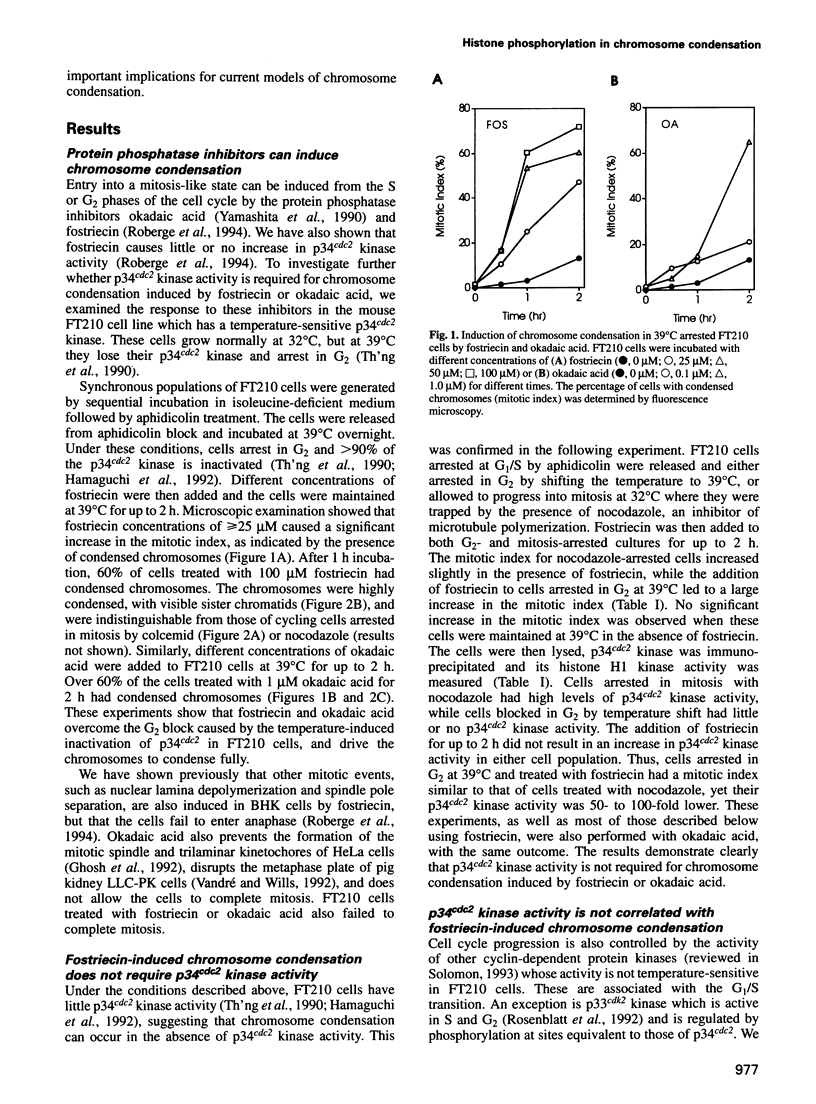
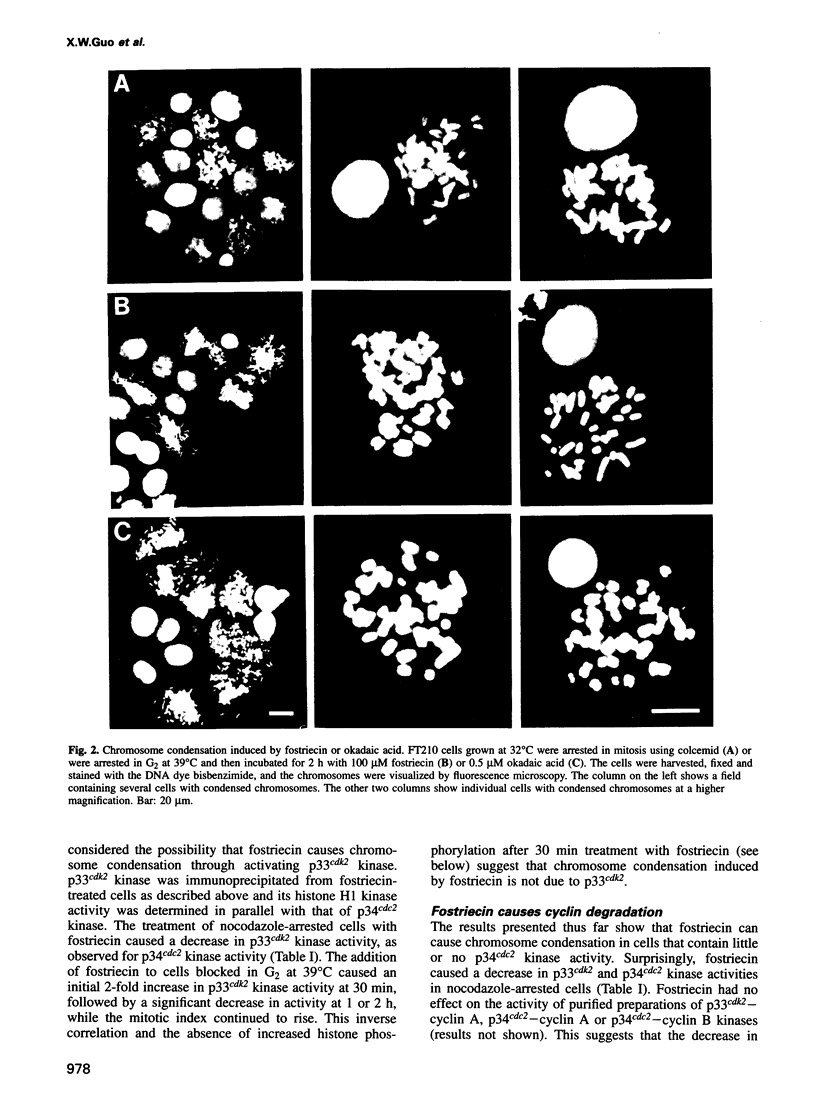
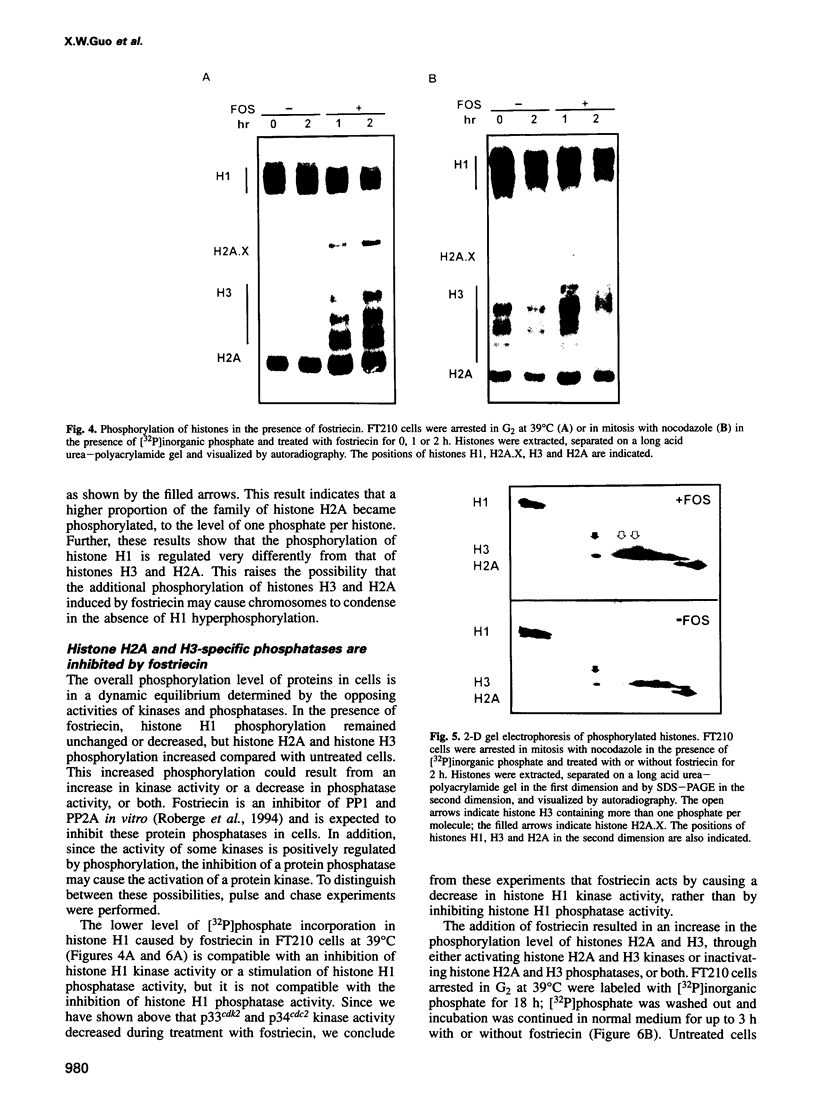
Abstract
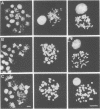
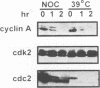
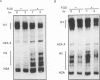
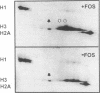
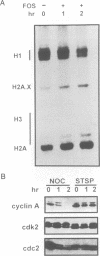
Chromosome condensation at mitosis correlates with the activation of p34cdc2 kinase, the hyperphosphorylation of histone H1 and the phosphorylation of histone H3. Chromosome condensation can also be induced by treating interphase cells with the protein phosphatase 1 and 2A inhibitors okadaic acid and fostriecin. Mouse mammary tumour FT210 cells grow normally at 32 degrees C, but at 39 degrees C they lose p34cdc2 kinase activity and arrest in G2 because of a temperature-sensitive lesion in the cdc2 gene. The treatment of these G2-arrested FT210 cells with fostriecin or okadaic acid resulted in full chromosome condensation in the absence of p34cdc2 kinase activity or histone H1 hyperphosphorylation. However, phosphorylation of histones H2A and H3 was strongly stimulated, partly through inhibition of histone H2A and H3 phosphatases, and cyclins A and B were degraded. The cells were unable to complete mitosis and divide. In the presence of the protein kinase inhibitor starosporine, the addition of fostriecin did not induce histone phosphorylation and chromosome condensation. The results show that chromosome condensation can take place without either the histone H1 hyperphosphorylation or the p34cdc2 kinase activity normally associated with mitosis, although it requires a staurosporine-sensitive protein kinase activity. The results further suggest that protein phosphatases 1 and 2A may be important in regulating chromosome condensation by restricting the level of histone phosphorylation during interphase, thereby preventing premature chromosome condensation.
Full text
PDF

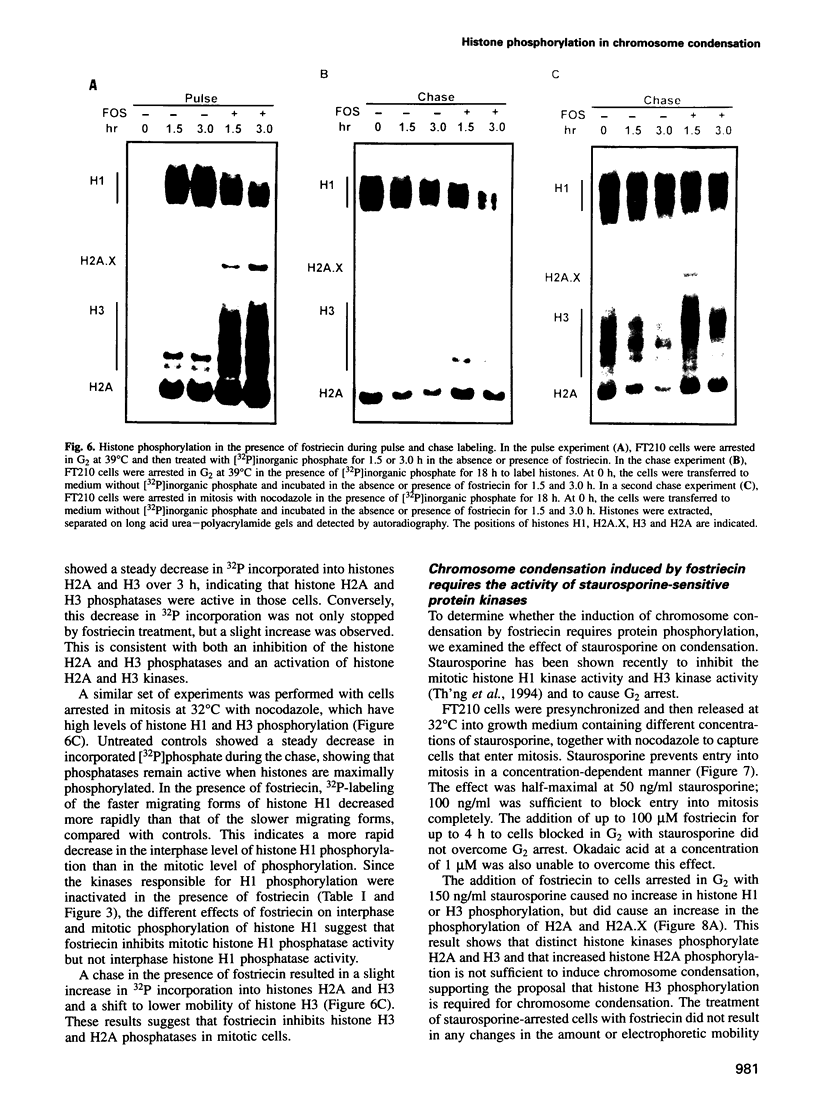
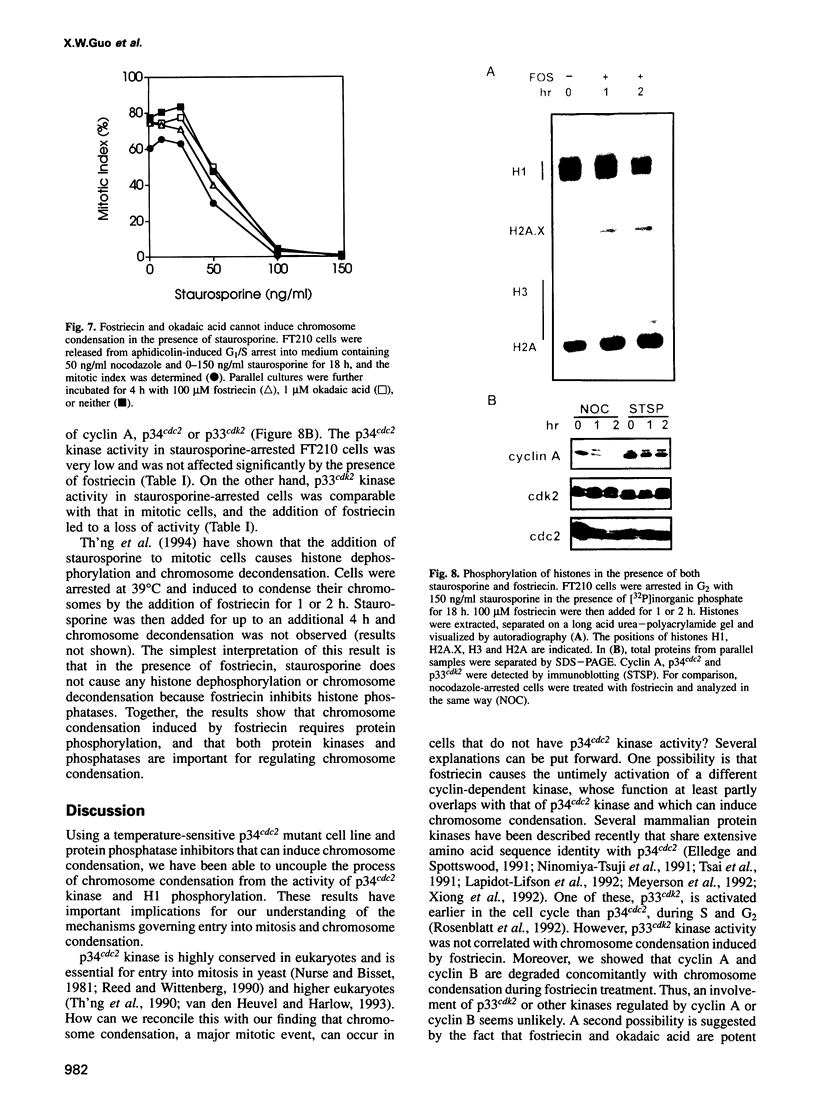



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajiro K., Nishimoto T., Takahashi T. Histone H1 and H3 phosphorylation during premature chromosome condensation in a temperature-sensitive mutant (tsBN2) of baby hamster kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4534–4538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulikas T., Wiseman J. M., Garrard W. T. Points of contact between histone H1 and the histone octamer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):127–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Inglis R. J., Matthews H. R. Control of cell division by very lysine rich histone (F1) phosphorylation. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):257–261. doi: 10.1038/247257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Inglis R. J., Matthews H. R., Langan T. A. Molecular basis of control of mitotic cell division in eukaryotes. Nature. 1974 Jun 7;249(457):553–556. doi: 10.1038/249553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Inglis R. J., Matthews H. R., Sarner N. Phosphorylation of very-lysine-rich histone in Physarum polycephalum. Correlation with chromosome condensation. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):131–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M. Reversible histone modifications and the chromosome cell cycle. Bioessays. 1992 Jan;14(1):9–16. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Sarnecki C., Blenis J. Nuclear localization and regulation of erk- and rsk-encoded protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):915–927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Klumpp S., Schelling D. L. An improved procedure for identifying and quantitating protein phosphatases in mammalian tissues. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):596–600. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80803-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis F. M., Tsao T. Y., Fowler S. K., Rao P. N. Monoclonal antibodies to mitotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2926–2930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Spottswood M. R. A new human p34 protein kinase, CDK2, identified by complementation of a cdc28 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a homolog of Xenopus Eg1. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2653–2659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrigno P., Langan T. A., Cohen P. Protein phosphatase 2A1 is the major enzyme in vertebrate cell extracts that dephosphorylates several physiological substrates for cyclin-dependent protein kinases. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jul;4(7):669–677. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.7.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Félix M. A., Cohen P., Karsenti E. Cdc2 H1 kinase is negatively regulated by a type 2A phosphatase in the Xenopus early embryonic cell cycle: evidence from the effects of okadaic acid. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):675–683. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Paweletz N., Schroeter D. Effects of okadaic acid on mitotic HeLa cells. J Cell Sci. 1992 Sep;103(Pt 1):117–124. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Krebs E. G. Comparison of the substrate specificity of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate- and guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. Kinetic studies using synthetic peptides corresponding to phosphorylation sites in histone H2B. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9728–9738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi J. R., Tobey R. A., Pines J., Crissman H. A., Hunter T., Bradbury E. M. Requirement for p34cdc2 kinase is restricted to mitosis in the mammalian cdc2 mutant FT210. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):1041–1053. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Rodriguez L. V., Rao P. N. Relationship between histone phosphorylation and premature chromosome condensation. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Oct 15;148(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto E., Takeda M., Nishizuka Y., Hamana K., Iwai K. Studies on the sites in histones phosphorylated by adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent and guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6287–6293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Rimmer J. M., Green B. N., Finch J. T., Thomas J. O. Histone-DNA interactions and their modulation by phosphorylation of -Ser-Pro-X-Lys/Arg- motifs. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1939–1948. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharrat A., Derancourt J., Dorée M., Amalric F., Erard M. Synergistic effect of histone H1 and nucleolin on chromatin condensation in mitosis: role of a phosphorylated heteromer. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 22;30(42):10329–10336. doi: 10.1021/bi00106a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Steinbeisser H. DNA-dependent phosphorylation of histone H2A.X during nucleosome assembly in Xenopus laevis oocytes: involvement of protein phosphorylation in nucleosome spacing. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3043–3050. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A. Characterization of highly phosphorylated subcomponents of rat thymus H1 histone. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14835–14846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A., Gautier J., Lohka M., Hollingsworth R., Moreno S., Nurse P., Maller J., Sclafani R. A. Mammalian growth-associated H1 histone kinase: a homolog of cdc2+/CDC28 protein kinases controlling mitotic entry in yeast and frog cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3860–3868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidot-Lifson Y., Patinkin D., Prody C. A., Ehrlich G., Seidman S., Ben-Aziz R., Benseler F., Eckstein F., Zakut H., Soreq H. Cloning and antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibition of a human homolog of cdc2 required in hematopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):579–583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Solomon M. J., Mumby M. C., Kirschner M. W. INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90649-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion C., Martinage A., Tirard A., Roux B., Daune M., Mazen A. Histone phosphorylation in native chromatin induces local structural changes as probed by electric birefringence. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinage A., Mangeat P., Laine B., Couppez M., Sautiere P., Marchis-Mouren G., Biserte G. In vitro phosphorylation of histones H5, H2A, H2B and of the dimer H2A--H2B by a cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from rat pancreas. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 8;118(2):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazen A., Hacques M. F., Marion C. H3 phosphorylation-dependent structural changes in chromatin. Implications for the role of very lysine-rich histones. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):741–745. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerson M., Enders G. H., Wu C. L., Su L. K., Gorka C., Nelson C., Harlow E., Tsai L. H. A family of human cdc2-related protein kinases. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2909–2917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller R. D., Yasuda H., Bradbury E. M. Phosphorylation of histone H1 through the cell cycle of Physarum polycephalum. 24 sites of phosphorylation at metaphase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5081–5086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Nomoto S., Yasuda H., Reed S. I., Matsumoto K. Cloning of a human cDNA encoding a CDC2-related kinase by complementation of a budding yeast cdc28 mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell M. J., Norbury C., Nurse P. Premature chromatin condensation upon accumulation of NIMA. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4926–4937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06820.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. R., Ciesielski W. A., Schram B. R., Mesner P. W. Okadaic acid induces dephosphorylation of histone H1 in metaphase-arrested HeLa cells. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jan;107(Pt 1):267–273. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.1.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. R., Taylor S. S. Phosphorylation of histones 1 and 3 and nonhistone high mobility group 14 by an endogenous kinase in HeLa metaphase chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6064–6072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Wittenberg C. Mitotic role for the Cdc28 protein kinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5697–5701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberge M., Tudan C., Hung S. M., Harder K. W., Jirik F. R., Anderson H. Antitumor drug fostriecin inhibits the mitotic entry checkpoint and protein phosphatases 1 and 2A. Cancer Res. 1994 Dec 1;54(23):6115–6121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is activated during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and associates with cyclin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata K., Ajiro K. Cell cycle-dependent suppressive effect of histone H1 on mitosis-specific H3 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18431–18434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker C. B., Chalkley R. H3-specific nucleohistone kinase of bovine thymus chromatin. Purification, characterization, and specificity for threonine residue 3. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):11048–11055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J. Activation of the various cyclin/cdc2 protein kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):180–186. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi F., Hashimoto E., Yamamura H. Phosphorylation of histone H2A by protein kinase C and identification of the phosphorylation site. J Biochem. 1992 Jun;111(6):788–792. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S. The in vitro phosphorylation of chromatin by the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6056–6063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Th'ng J. P., Guo X. W., Swank R. A., Crissman H. A., Bradbury E. M. Inhibition of histone phosphorylation by staurosporine leads to chromosome decondensation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9568–9573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Th'ng J. P., Wright P. S., Hamaguchi J., Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Nurse P., Bradbury E. M. The FT210 cell line is a mouse G2 phase mutant with a temperature-sensitive CDC2 gene product. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90164-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosuji H., Mabuchi I., Fusetani N., Nakazawa T. Calyculin A induces contractile ring-like apparatus formation and condensation of chromosomes in unfertilized sea urchin eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10613–10617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usachenko S. I., Bavykin S. G., Gavin I. M., Bradbury E. M. Rearrangement of the histone H2A C-terminal domain in the nucleosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6845–6849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandré D. D., Wills V. L. Inhibition of mitosis by okadaic acid: possible involvement of a protein phosphatase 2A in the transition from metaphase to anaphase. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):79–91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. D type cyclins associate with multiple protein kinases and the DNA replication and repair factor PCNA. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90518-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Yasuda H., Pines J., Yasumoto K., Nishitani H., Ohtsubo M., Hunter T., Sugimura T., Nishimoto T. Okadaic acid, a potent inhibitor of type 1 and type 2A protein phosphatases, activates cdc2/H1 kinase and transiently induces a premature mitosis-like state in BHK21 cells. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4331–4338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07882.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel S., Harlow E. Distinct roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in cell cycle control. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2050–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8266103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]