Abstract
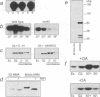
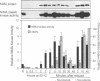
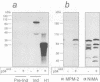
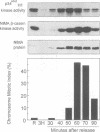
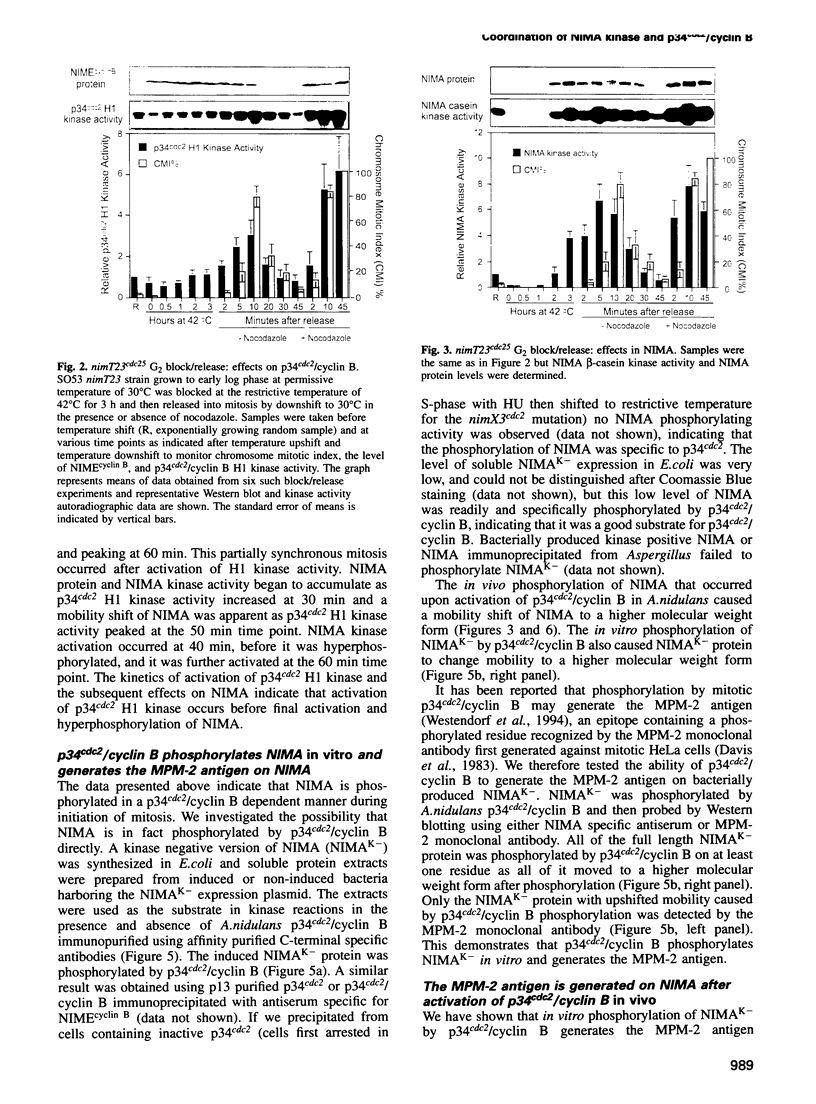
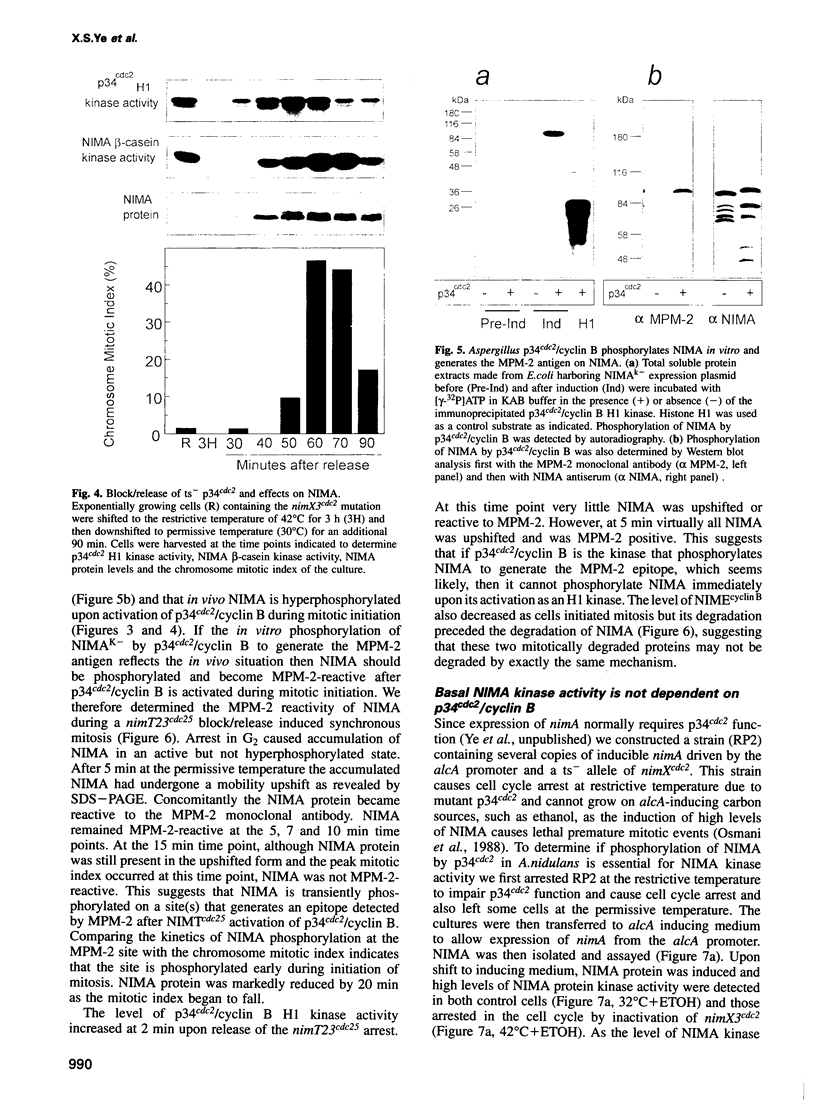
Initiation of mitosis in Aspergillus nidulans requires activation of two protein kinases, p34cdc2/cyclin B and NIMA. Forced expression of NIMA, even when p34cdc2 was inactivated, promoted chromatin condensation. NIMA may therefore directly cause mitotic chromosome condensation. However, the mitosis-promoting function of NIMA is normally under control of p34cdc2/cyclin B as the active G2 form of NIMA is hyperphosphorylated and further activated by p34cdc2/cyclin B when cells initiate mitosis. To see the p34cdc2/cyclin B dependent activation of NIMA, okadaic acid had to be added to isolation buffers to prevent dephosphorylation of NIMA during isolation. Hyperphosphorylated NIMA contained the MPM-2 epitope and, in vitro, phosphorylation of NIMA by p34cdc2/cyclin B generated the MPM-2 epitope, suggesting that NIMA is phosphorylated directly by p34cdc2/cyclin B during mitotic initiation. These two kinases, which are both essential for mitotic initiation, are therefore independently activated as protein kinases during G2. Then, to initiate mitosis, we suggest that each activates the other's mitosis-promoting functions. This ensures that cells coordinately activate p34cdc2/cyclin B and NIMA to initiate mitosis only upon completion of all interphase events. Finally, we show that NIMA is regulated through the cell cycle like cyclin B, as it accumulates during G2 and is degraded only when cells traverse mitosis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booher R. N., Alfa C. E., Hyams J. S., Beach D. H. The fission yeast cdc2/cdc13/suc1 protein kinase: regulation of catalytic activity and nuclear localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):485–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis F. M., Tsao T. Y., Fowler S. K., Rao P. N. Monoclonal antibodies to mitotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2926–2930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G. Cell cycle control in eukaryotes: molecular mechanisms of cdc2 activation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Piwnica-Worms H., Morrison D., Druker B., Roberts T., Beach D. Human cdc2 protein kinase is a major cell-cycle regulated tyrosine kinase substrate. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):738–744. doi: 10.1038/336738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbers D. L., Koesling D., Schultz G. Guanylyl cyclase receptors. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jan;5(1):1–5. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Weinert T. A. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):629–634. doi: 10.1126/science.2683079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. G., Rosamond J. Isolation of a novel protein kinase-encoding gene from yeast by oligodeoxyribonucleotide probing. Gene. 1990 May 31;90(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90442-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuang J., Penkala J. E., Ashorn C. L., Wright D. A., Saunders G. F., Rao P. N. Multiple forms of maturation-promoting factor in unfertilized Xenopus eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11530–11534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuang J., Zhao J., Wright D. A., Saunders G. F., Rao P. N. Mitosis-specific monoclonal antibody MPM-2 inhibits Xenopus oocyte maturation and depletes maturation-promoting activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4982–4986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letwin K., Mizzen L., Motro B., Ben-David Y., Bernstein A., Pawson T. A mammalian dual specificity protein kinase, Nek1, is related to the NIMA cell cycle regulator and highly expressed in meiotic germ cells. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3521–3531. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05435.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorca T., Labbé J. C., Devault A., Fesquet D., Capony J. P., Cavadore J. C., Le Bouffant F., Dorée M. Dephosphorylation of cdc2 on threonine 161 is required for cdc2 kinase inactivation and normal anaphase. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2381–2390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05302.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu K. P., Osmani S. A., Means A. R. Properties and regulation of the cell cycle-specific NIMA protein kinase of Aspergillus nidulans. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8769–8776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Walworth N., Booher R., Dembski M., Kirschner M., Beach D. mik1 and wee1 cooperate in the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1111–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Nurse P. Substrates for p34cdc2: in vivo veritas? Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):549–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90463-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Dominoes and clocks: the union of two views of the cell cycle. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):614–621. doi: 10.1126/science.2683077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A. The substrates of the cdc2 kinase. Semin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;2(4):261–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell M. J., Norbury C., Nurse P. Premature chromatin condensation upon accumulation of NIMA. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4926–4937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06820.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell M. J., Osmani A. H., Morris N. R., Osmani S. A. An extra copy of nimEcyclinB elevates pre-MPF levels and partially suppresses mutation of nimTcdc25 in Aspergillus nidulans. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2139–2149. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dorisio M. S., Chen F., O'Dorisio T. M., Wray D., Qualman S. J. Characterization of somatostatin receptors on human neuroblastoma tumors. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Jan;5(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Morris N. R. A mutation in Aspergillus nidulans that blocks the transition from interphase to prophase. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):1155–1158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani A. H., McGuire S. L., Osmani S. A. Parallel activation of the NIMA and p34cdc2 cell cycle-regulated protein kinases is required to initiate mitosis in A. nidulans. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani A. H., O'Donnell K., Pu R. T., Osmani S. A. Activation of the nimA protein kinase plays a unique role during mitosis that cannot be bypassed by absence of the bimE checkpoint. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2669–2679. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani A. H., van Peij N., Mischke M., O'Connell M. J., Osmani S. A. A single p34cdc2 protein kinase (encoded by nimXcdc2) is required at G1 and G2 in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jun;107(Pt 6):1519–1528. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.6.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani S. A., May G. S., Morris N. R. Regulation of the mRNA levels of nimA, a gene required for the G2-M transition in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1495–1504. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani S. A., Pu R. T., Morris N. R. Mitotic induction and maintenance by overexpression of a G2-specific gene that encodes a potential protein kinase. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Yamashita K., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., Shuttleworth J. The cdc2-related protein p40MO15 is the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that can activate p33cdk2 and p34cdc2. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3123–3132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pu R. T., Osmani S. A. Mitotic destruction of the cell cycle regulated NIMA protein kinase of Aspergillus nidulans is required for mitotic exit. EMBO J. 1995 Mar 1;14(5):995–1003. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07080.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. J., Nigg E. A. Identification of 21 novel human protein kinases, including 3 members of a family related to the cell cycle regulator nimA of Aspergillus nidulans. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Oct;4(10):821–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Harper J. W., Shuttleworth J. CAK, the p34cdc2 activating kinase, contains a protein identical or closely related to p40MO15. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westendorf J. M., Rao P. N., Gerace L. Cloning of cDNAs for M-phase phosphoproteins recognized by the MPM2 monoclonal antibody and determination of the phosphorylated epitope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):714–718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]