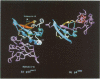
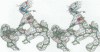Abstract
p13suc1 binds to p34cdc2 kinase and is essential for cell cycle progression in eukaryotic cells. The crystal structure of S.pombe p13suc1 has been solved to 2.7 A resolution using data collected at the ESRF source, Grenoble, from both native crystals and crystals of a seleno-methionine derivative. The starting point for structure solution was the determination of the six selenium sites by direct methods. The structure is dominated by a four-stranded beta-sheet, with four further alpha-helical regions. p13suc1 crystallizes as a dimer in the asymmetric unit stabilized by the binding of two zinc ions. A third zinc site stabilizes the higher-order crystal packing. The sites are consistent with a requirement for zinc during crystal growth. A likely site for p13suc1-protein interaction is immediately evident on one face of the p13suc1 surface. This region comprises a group of conserved, exposed aromatic and hydrophobic residues below a flexible negatively charged loop. A conserved positively charged area would also present a notable surface feature in the monomer, but is buried at the dimer interface. p13suc1 is larger than its recently solved human homologue p9CKS2, with the extra polypeptide forming a helical N-terminal extension and a surface loop between alpha-helices 3 and 4. Notably, p13suc1 does not show the unusual beta-strand exchange that creates an intimate p9CKS2 dimer. p13suc1 cannot oligomerize to form a stable hexamer as has been proposed for p9CKS2.
Full text
PDF

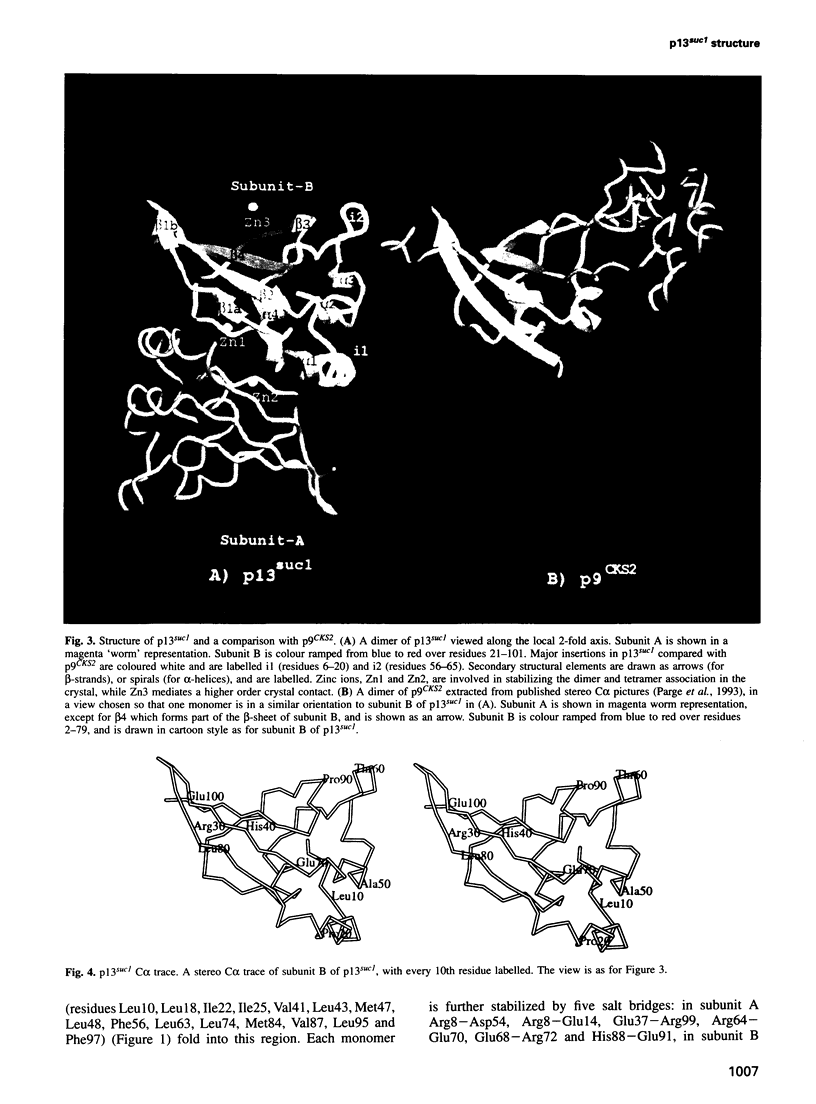
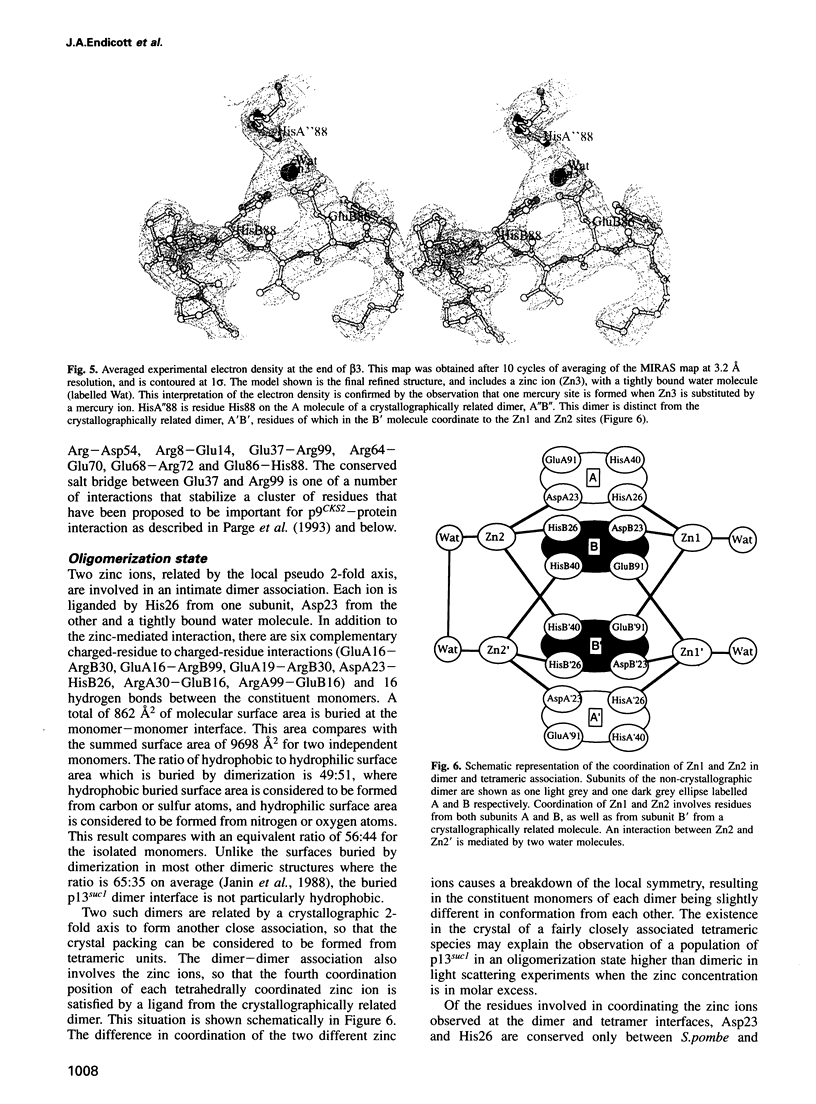
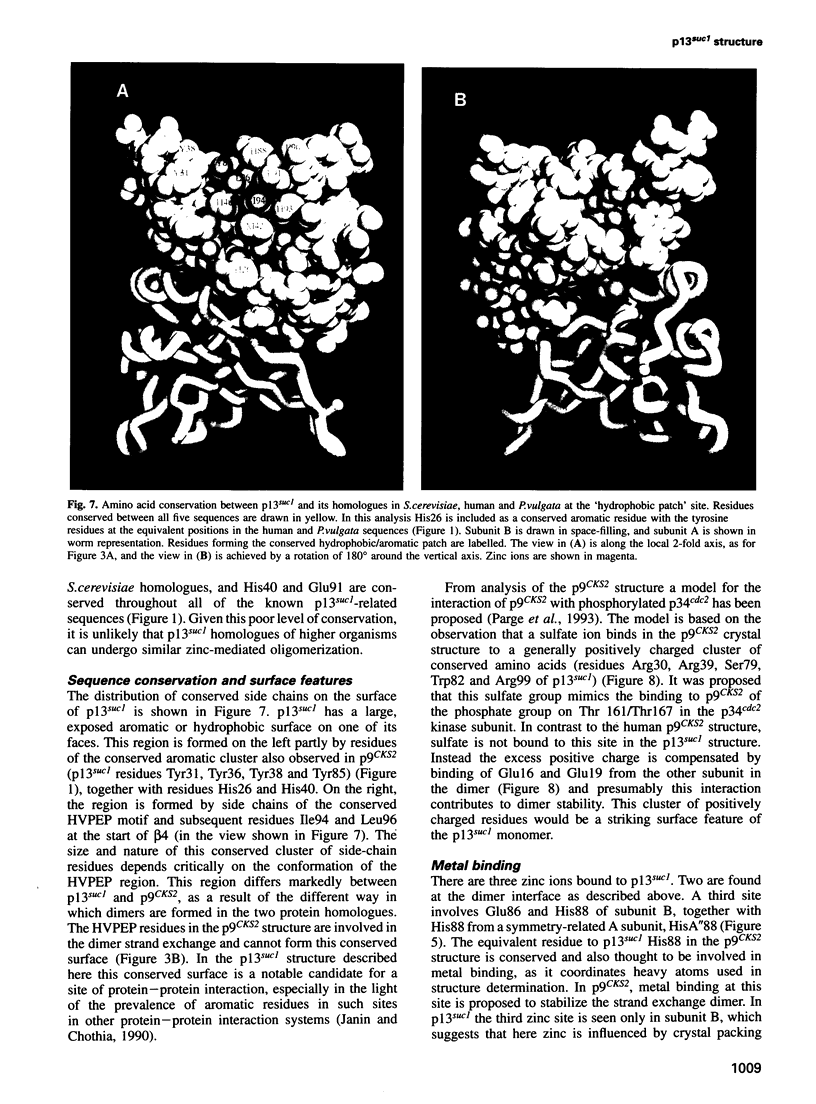
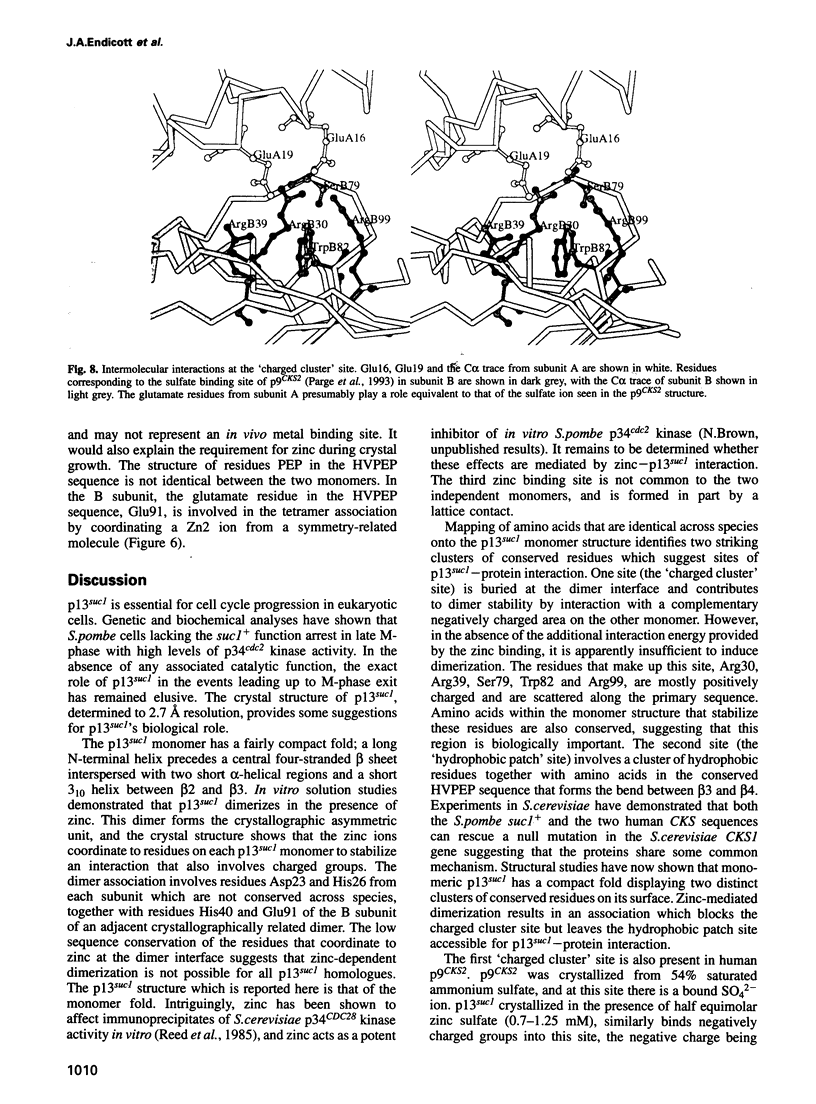



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arion D., Meijer L., Brizuela L., Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton G. J. ALSCRIPT: a tool to format multiple sequence alignments. Protein Eng. 1993 Jan;6(1):37–40. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R. N., Alfa C. E., Hyams J. S., Beach D. H. The fission yeast cdc2/cdc13/suc1 protein kinase: regulation of catalytic activity and nuclear localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):485–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizuela L., Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of human CDC2 protein as a histone H1 kinase is associated with complex formation with the p62 subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4362–4366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizuela L., Draetta G., Beach D. p13suc1 acts in the fission yeast cell division cycle as a component of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3507–3514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colas P., Serras F., Van Loon A. E. Microinjection of suc1 transcripts delays the cell cycle clock in Patella vulgata embryos. Int J Dev Biol. 1993 Dec;37(4):589–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bondt H. L., Rosenblatt J., Jancarik J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):595–602. doi: 10.1038/363595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Draetta G. Mutations at sites involved in Suc1 binding inactivate Cdc2. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6177–6184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Kumagai A. The cdc25 protein contains an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90582-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Fission yeast p13 blocks mitotic activation and tyrosine dephosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc2 protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Unraveling of mitotic control mechanisms. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):925–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J. A., Nurse P., Johnson L. N. Mutational analysis supports a structural model for the cell cycle protein kinase p34. Protein Eng. 1994 Feb;7(2):243–253. doi: 10.1093/protein/7.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesquet D., Labbé J. C., Derancourt J., Capony J. P., Galas S., Girard F., Lorca T., Shuttleworth J., Dorée M., Cavadore J. C. The MO15 gene encodes the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that activates cdc2 and other cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) through phosphorylation of Thr161 and its homologues. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3111–3121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L., Nurse P. Cell cycle regulation in the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:227–256. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Tonks N. K., Nurse P. Complementation of the mitotic activator, p80cdc25, by a human protein-tyrosine phosphatase. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1573–1576. doi: 10.1126/science.1703321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Mendenhall M. D., Reed S. I. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae CKS1 gene, a homolog of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe suc1+ gene, encodes a subunit of the Cdc28 protein kinase complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2034–2041. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayles J., Aves S., Nurse P. suc1 is an essential gene involved in both the cell cycle and growth in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3373–3379. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04653.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayles J., Beach D., Durkacz B., Nurse P. The fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2: isolation of a sequence suc1 that suppresses cdc2 mutant function. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Feb;202(2):291–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00331653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Phear G., Stein M., Beach D. Sucl+ encodes a predicted 13-kilodalton protein that is essential for cell viability and is directly involved in the division cycle of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):504–511. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann I., Clarke P. R., Marcote M. J., Karsenti E., Draetta G. Phosphorylation and activation of human cdc25-C by cdc2--cyclin B and its involvement in the self-amplification of MPF at mitosis. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):53–63. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway S. L., Glotzer M., King R. W., Murray A. W. Anaphase is initiated by proteolysis rather than by the inactivation of maturation-promoting factor. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1393–1402. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90364-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Chothia C. The structure of protein-protein recognition sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16027–16030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Miller S., Chothia C. Surface, subunit interfaces and interior of oligomeric proteins. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90606-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Mutations of p34cdc2 phosphorylation sites induce premature mitotic events in HeLa cells: evidence for a double block to p34cdc2 kinase activation in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3331–3341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusubata M., Tokui T., Matsuoka Y., Okumura E., Tachibana K., Hisanaga S., Kishimoto T., Yasuda H., Kamijo M., Ohba Y. p13suc1 suppresses the catalytic function of p34cdc2 kinase for intermediate filament proteins, in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20937–20942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé J. C., Capony J. P., Caput D., Cavadore J. C., Derancourt J., Kaghad M., Lelias J. M., Picard A., Dorée M. MPF from starfish oocytes at first meiotic metaphase is a heterodimer containing one molecule of cdc2 and one molecule of cyclin B. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3053–3058. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMaster D. M., Richards F. M. 1H-15N heteronuclear NMR studies of Escherichia coli thioredoxin in samples isotopically labeled by residue type. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7263–7268. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Hayes M. K., Maller J. L. Purification of maturation-promoting factor, an intracellular regulator of early mitotic events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorca T., Labbé J. C., Devault A., Fesquet D., Capony J. P., Cavadore J. C., Le Bouffant F., Dorée M. Dephosphorylation of cdc2 on threonine 161 is required for cdc2 kinase inactivation and normal anaphase. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2381–2390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05302.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Walworth N., Booher R., Dembski M., Kirschner M., Beach D. mik1 and wee1 cooperate in the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1111–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcote M. J., Knighton D. R., Basi G., Sowadski J. M., Brambilla P., Draetta G., Taylor S. S. A three-dimensional model of the Cdc2 protein kinase: localization of cyclin- and Suc1-binding regions and phosphorylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):5122–5131. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.5122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan C. H., Russell P. Human Wee1 kinase inhibits cell division by phosphorylating p34cdc2 exclusively on Tyr15. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):75–85. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Arion D., Golsteyn R., Pines J., Brizuela L., Hunt T., Beach D. Cyclin is a component of the sea urchin egg M-phase specific histone H1 kinase. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2275–2282. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meikrantz W., Suprynowicz F. A., Halleck M. S., Schlegel R. A. Identification of mitosis-specific p65 dimer as a component of human M phase-promoting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9600–9604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Hayles J., Nurse P. Regulation of p34cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90850-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Nurse P., Russell P. Regulation of mitosis by cyclic accumulation of p80cdc25 mitotic inducer in fission yeast. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):549–552. doi: 10.1038/344549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Draetta G., Beach D., Wang J. Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. L., MacArthur M. W., Hutchinson E. G., Thornton J. M. Stereochemical quality of protein structure coordinates. Proteins. 1992 Apr;12(4):345–364. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Blow J., Nurse P. Regulatory phosphorylation of the p34cdc2 protein kinase in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3321–3329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parge H. E., Arvai A. S., Murtari D. J., Reed S. I., Tainer J. A. Human CksHs2 atomic structure: a role for its hexameric assembly in cell cycle control. Science. 1993 Oct 15;262(5132):387–395. doi: 10.1126/science.8211159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Piwnica-Worms H. p107wee1 is a dual-specificity kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2 on tyrosine 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2917–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggott J. R., Rai R., Carter B. L. A bifunctional gene product involved in two phases of the yeast cell cycle. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):391–393. doi: 10.1038/298391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon R. Y., Yamashita K., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., Shuttleworth J. The cdc2-related protein p40MO15 is the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that can activate p33cdk2 and p34cdc2. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3123–3132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Hadwiger J. A., Lörincz A. T. Protein kinase activity associated with the product of the yeast cell division cycle gene CDC28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4055–4059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Wittenberg C. Mitotic role for the Cdc28 protein kinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5697–5701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Stueland C. S., Thomas J., Russell P., Reed S. I. Human cDNAs encoding homologs of the small p34Cdc28/Cdc2-associated protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1332–1344. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J. Activation of the various cyclin/cdc2 protein kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):180–186. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Harper J. W., Shuttleworth J. CAK, the p34cdc2 activating kinase, contains a protein identical or closely related to p40MO15. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausfeld U., Labbé J. C., Fesquet D., Cavadore J. C., Picard A., Sadhu K., Russell P., Dorée M. Dephosphorylation and activation of a p34cdc2/cyclin B complex in vitro by human CDC25 protein. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):242–245. doi: 10.1038/351242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surana U., Amon A., Dowzer C., McGrew J., Byers B., Nasmyth K. Destruction of the CDC28/CLB mitotic kinase is not required for the metaphase to anaphase transition in budding yeast. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1969–1978. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05846.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surana U., Robitsch H., Price C., Schuster T., Fitch I., Futcher A. B., Nasmyth K. The role of CDC28 and cyclins during mitosis in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):145–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90416-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang Y., Reed S. I. The Cdk-associated protein Cks1 functions both in G1 and G2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):822–832. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Radzio-Andzelm E. Three protein kinase structures define a common motif. Structure. 1994 May 15;2(5):345–355. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Th'ng J. P., Wright P. S., Hamaguchi J., Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Nurse P., Bradbury E. M. The FT210 cell line is a mouse G2 phase mutant with a temperature-sensitive CDC2 gene product. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90164-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]