Abstract
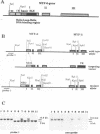
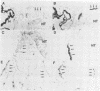
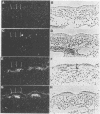
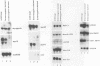
Myf-6, alternatively called MRF4 or herculin, is a member of a group of muscle-specific transcription factors which also comprises Myf-5, myogenin and MyoD. All family members show distinct expression patterns during skeletal muscle development and can convert a variety of cell lines to myocytes. We disrupted the Myf-6 gene in mice to investigate its functional role in the network of regulatory factors controlling myogenesis. Homozygous mice carrying the disrupted Myf-6 gene show pronounced down-regulation of Myf-5 transcription for reasons presently unknown. Consequently, these mice represent a double knock-out model for Myf-6 and Myf-5. The mutants resemble most of the Myf-5 phenotype with aberrant and delayed early myotome formation and lack of distal rib structures. In addition, we find a reduction in the size of axial muscles in the back. Apart from changes in the pattern of some contractile protein isoforms, the existing myofibers appear fairly normal. This suggests that Myf-6 has no major role in the maturation of myotubes, as previously proposed. Our results provide evidence that skeletal myogenesis can proceed in the absence of two myogenic factors, Myf-5 and Myf-6, therefore they must exert largely non-redundant functions in vivo.
Full text
PDF


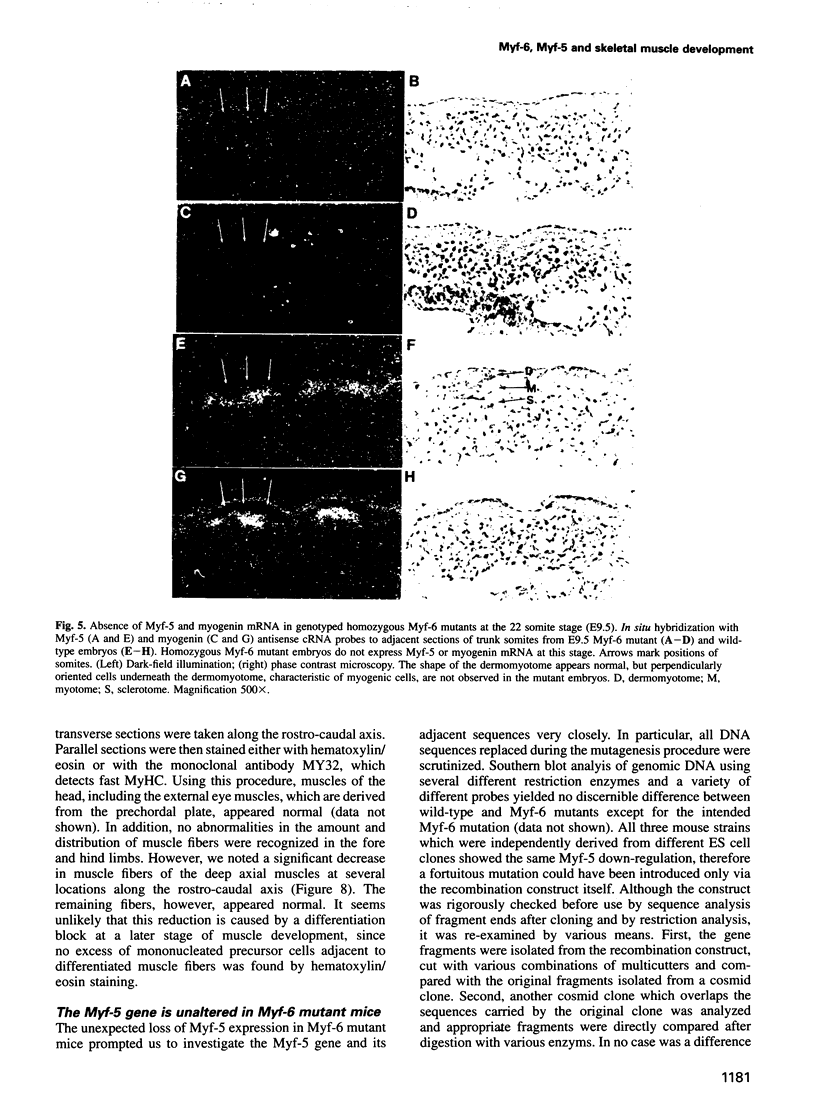





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold H. H., Braun T. The role of Myf-5 in somitogenesis and the development of skeletal muscles in vertebrates. J Cell Sci. 1993 Apr;104(Pt 4):957–960. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.4.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bober E., Brand-Saberi B., Ebensperger C., Wilting J., Balling R., Paterson B. M., Arnold H. H., Christ B. Initial steps of myogenesis in somites are independent of influence from axial structures. Development. 1994 Nov;120(11):3073–3082. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.11.3073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bober E., Franz T., Arnold H. H., Gruss P., Tremblay P. Pax-3 is required for the development of limb muscles: a possible role for the migration of dermomyotomal muscle progenitor cells. Development. 1994 Mar;120(3):603–612. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.3.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bober E., Lyons G. E., Braun T., Cossu G., Buckingham M., Arnold H. H. The muscle regulatory gene, Myf-6, has a biphasic pattern of expression during early mouse development. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1255–1265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Arnold H. H. ES-cells carrying two inactivated myf-5 alleles form skeletal muscle cells: activation of an alternative myf-5-independent differentiation pathway. Dev Biol. 1994 Jul;164(1):24–36. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Arnold H. H. The four human muscle regulatory helix-loop-helix proteins Myf3-Myf6 exhibit similar hetero-dimerization and DNA binding properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5645–5651. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Arnold H. H. Inhibition of muscle differentiation by the adenovirus E1a protein: repression of the transcriptional activating function of the HLH protein Myf-5. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):888–902. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Buschhausen-Denker G., Kohtz S., Grzeschik K. H., Arnold H. H., Kotz S. Differential expression of myogenic determination genes in muscle cells: possible autoactivation by the Myf gene products. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3617–3625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Rudnicki M. A., Jaenisch R., Arnold H. H. MyoD expression marks the onset of skeletal myogenesis in Myf-5 mutant mice. Development. 1994 Nov;120(11):3083–3092. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.11.3083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Winter B., Rosenthal N., Arnold H. H. Myf-6, a new member of the human gene family of myogenic determination factors: evidence for a gene cluster on chromosome 12. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):821–831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Rudnicki M. A., Arnold H. H., Jaenisch R. Targeted inactivation of the muscle regulatory gene Myf-5 results in abnormal rib development and perinatal death. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):369–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Winter B., Bober E., Arnold H. H. Transcriptional activation domain of the muscle-specific gene-regulatory protein myf5. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):663–665. doi: 10.1038/346663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Chakraborty T., Olson E. N. Mutagenesis of the myogenin basic region identifies an ancient protein motif critical for activation of myogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5675–5679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchberger A., Ragge K., Arnold H. H. The myogenin gene is activated during myocyte differentiation by pre-existing, not newly synthesized transcription factor MEF-2. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):17289–17296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham M. Making muscle in mammals. Trends Genet. 1992 Apr;8(4):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90373-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Brennan T., Olson E. Differential trans-activation of a muscle-specific enhancer by myogenic helix-loop-helix proteins is separable from DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2878–2882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng T. C., Hanley T. A., Mudd J., Merlie J. P., Olson E. N. Mapping of myogenin transcription during embryogenesis using transgenes linked to the myogenin control region. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1649–1656. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng T. C., Wallace M. C., Merlie J. P., Olson E. N. Separable regulatory elements governing myogenin transcription in mouse embryogenesis. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):215–218. doi: 10.1126/science.8392225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christ B., Brand-Saberi B., Grim M., Wilting J. Local signalling in dermomyotomal cell type specification. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1992 Oct;186(5):505–510. doi: 10.1007/BF00185464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duxson M. J., Usson Y., Harris A. J. The origin of secondary myotubes in mammalian skeletal muscles: ultrastructural studies. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):743–750. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson C. P., Jr Skeletal myogenesis: genetics and embryology to the fore. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90033-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiering S., Kim C. G., Epner E. M., Groudine M. An "in-out" strategy using gene targeting and FLP recombinase for the functional dissection of complex DNA regulatory elements: analysis of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8469–8473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst D. O., Osborn M., Weber K. Myogenesis in the mouse embryo: differential onset of expression of myogenic proteins and the involvement of titin in myofibril assembly. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):517–527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding M., Lumsden A., Paquette A. J. Regulation of Pax-3 expression in the dermomyotome and its role in muscle development. Development. 1994 Apr;120(4):957–971. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.4.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty P., Bradley A., Morris J. H., Edmondson D. G., Venuti J. M., Olson E. N., Klein W. H. Muscle deficiency and neonatal death in mice with a targeted mutation in the myogenin gene. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):501–506. doi: 10.1038/364501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberger T. J., Sassoon D. A., Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Expression of the muscle regulatory factor MRF4 during somite and skeletal myofiber development. Dev Biol. 1991 Sep;147(1):144–156. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(05)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H. Use of a conditional MyoD transcription factor in studies of MyoD trans-activation and muscle determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8028–8032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. G., Epner E. M., Forrester W. C., Groudine M. Inactivation of the human beta-globin gene by targeted insertion into the beta-globin locus control region. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):928–938. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
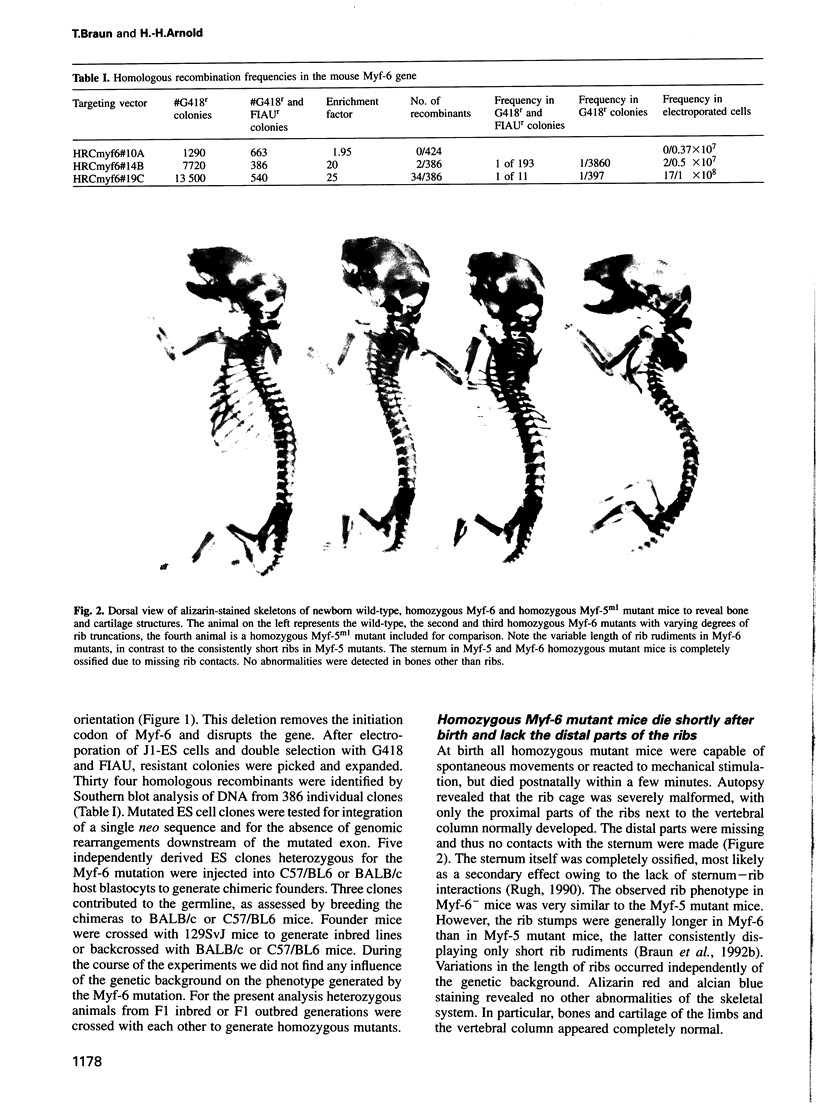
- McLeod M. J. Differential staining of cartilage and bone in whole mouse fetuses by alcian blue and alizarin red S. Teratology. 1980 Dec;22(3):299–301. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420220306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. Herculin, a fourth member of the MyoD family of myogenic regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Hanaoka K., Hayasaka M., Esumi E., Li S., Nonaka I., Nabeshima Y. Myogenin gene disruption results in perinatal lethality because of severe muscle defect. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):532–535. doi: 10.1038/364532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Klein W. H. bHLH factors in muscle development: dead lines and commitments, what to leave in and what to leave out. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):1–8. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Bober E., Lyons G., Arnold H., Buckingham M. Early expression of the myogenic regulatory gene, myf-5, in precursor cells of skeletal muscle in the mouse embryo. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1097–1107. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patapoutian A., Miner J. H., Lyons G. E., Wold B. Isolated sequences from the linked Myf-5 and MRF4 genes drive distinct patterns of muscle-specific expression in transgenic mice. Development. 1993 May;118(1):61–69. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Identification of MRF4: a new member of the muscle regulatory factor gene family. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2050–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohkamm R. Degeneration and regeneration in neurons of the cerebellum. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1977;53(6):1–118. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66818-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong P. M., Teillet M. A., Ziller C., Le Douarin N. M. The neural tube/notochord complex is necessary for vertebral but not limb and body wall striated muscle differentiation. Development. 1992 Jul;115(3):657–672. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.3.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicki M. A., Braun T., Hinuma S., Jaenisch R. Inactivation of MyoD in mice leads to up-regulation of the myogenic HLH gene Myf-5 and results in apparently normal muscle development. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90508-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicki M. A., Schnegelsberg P. N., Stead R. H., Braun T., Arnold H. H., Jaenisch R. MyoD or Myf-5 is required for the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1351–1359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90621-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. Positive autoregulation of the myogenic determination gene MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90838-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. The MyoD family and myogenesis: redundancy, networks, and thresholds. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1241–1244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90610-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A., Ordahl C. P. Pax-3 expression in segmental mesoderm marks early stages in myogenic cell specification. Development. 1994 Apr;120(4):785–796. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.4.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Rigby P. W. The regulation of myogenin gene expression during the embryonic development of the mouse. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1277–1289. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutzey K. E., Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Differential trans activation associated with the muscle regulatory factors MyoD1, myogenin, and MRF4. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3934–3944. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]