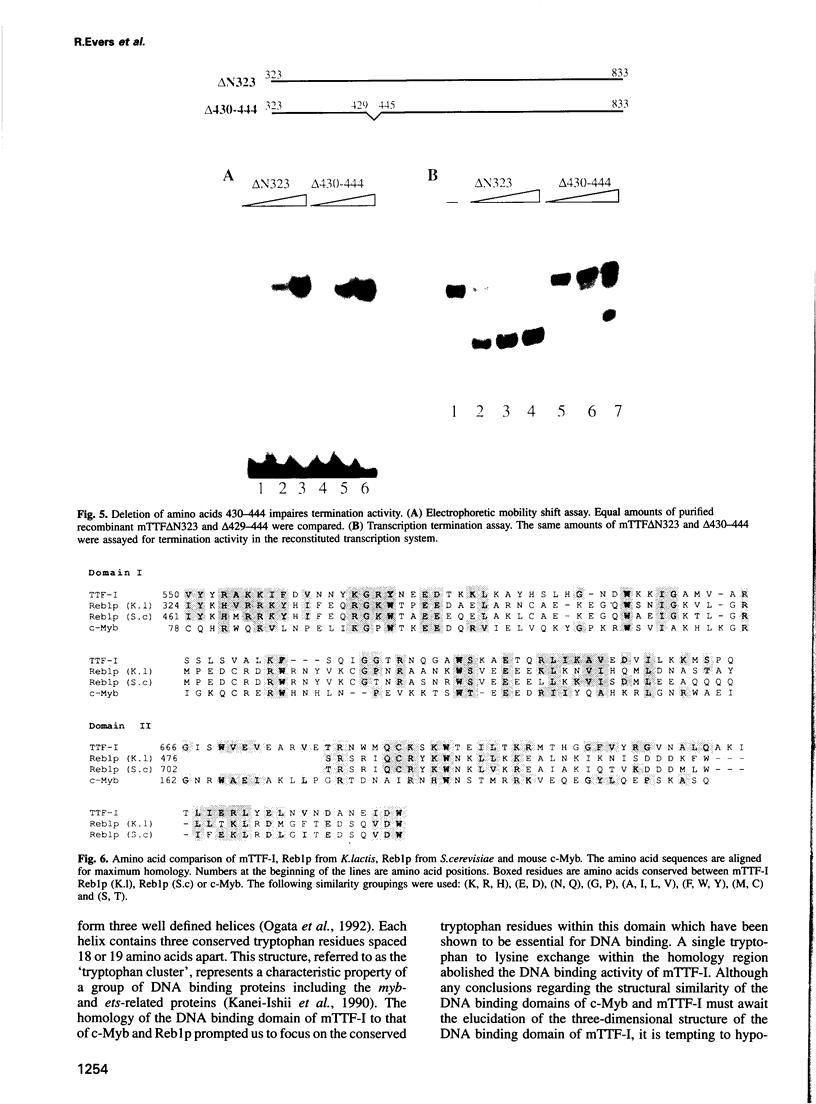
Abstract
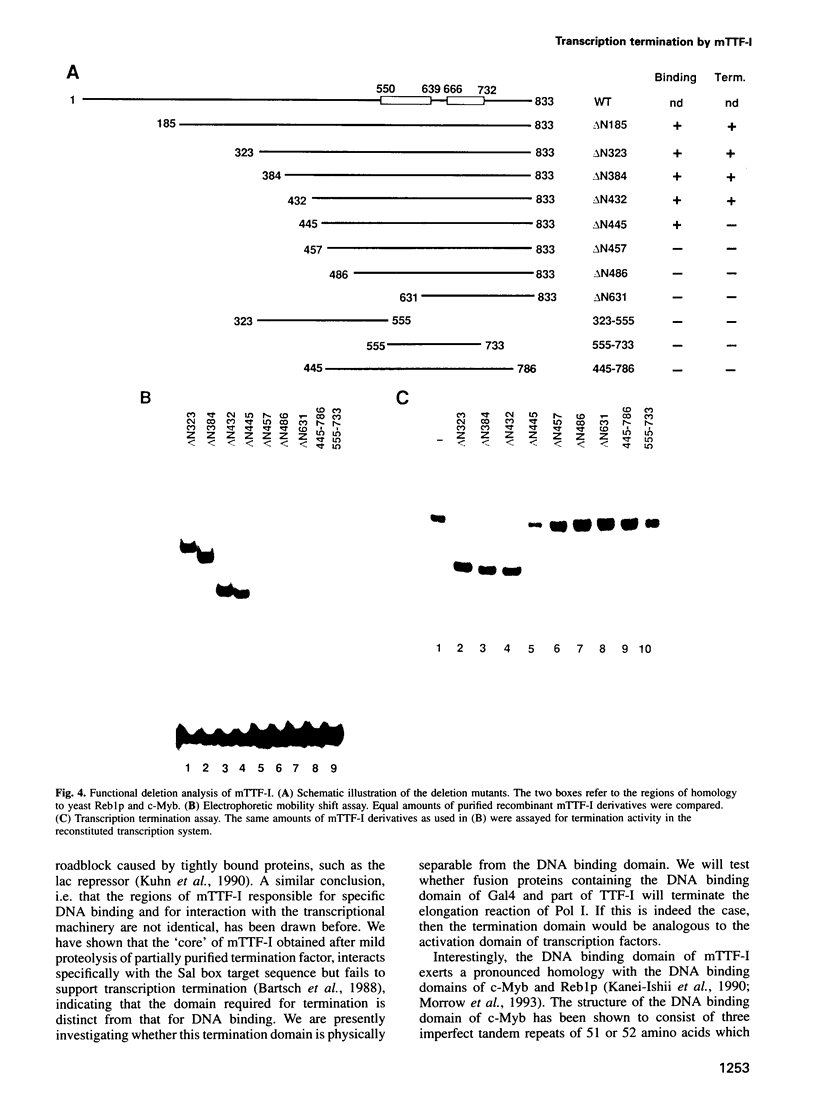
Termination of mouse ribosomal gene transcription by RNA polymerase I (Pol I) requires the specific interaction of a DNA binding protein, mTTF-I, with an 18 bp sequence element located downstream of the rRNA coding region. Here we describe the molecular cloning and functional characterization of the cDNA encoding this transcription termination factor. Recombinant mTTF-I binds specifically to the murine terminator elements and terminates Pol I transcription in a reconstituted in vitro system. Deletion analysis has defined a modular structure of mTTF-I comprising a dispensable N-terminal half, a large C-terminal DNA binding region and an internal domain which is required for transcription termination. Significantly, the C-terminal region of mTTF-I reveals striking homology to the DNA binding domains of the proto-oncogene c-Myb and the yeast transcription factor Reb1p. Site-directed mutagenesis of one of the tryptophan residues that is conserved in the homology region of c-Myb, Reb1p and mTTF-I abolishes specific DNA binding, a finding which underscores the functional relevance of these residues in DNA-protein interactions.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell V. J., Treisman R. The POZ domain: a conserved protein-protein interaction motif. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1664–1677. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch I., Schoneberg C., Grummt I. Purification and characterization of TTFI, a factor that mediates termination of mouse ribosomal DNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3891–3897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Maier U., Ohrlein A., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Transcription of mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3' spacer. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Rosenbauer H., Niedermeyer I., Maier U., Ohrlein A. A repeated 18 bp sequence motif in the mouse rDNA spacer mediates binding of a nuclear factor and transcription termination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):837–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe K. M., Reakes C. F., Watson R. J. Characterization of the sequence-specific interaction of mouse c-myb protein with DNA. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):161–169. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju Q. D., Morrow B. E., Warner J. R. REB1, a yeast DNA-binding protein with many targets, is essential for growth and bears some resemblance to the oncogene myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5226–5234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanei-Ishii C., Sarai A., Sawazaki T., Nakagoshi H., He D. N., Ogata K., Nishimura Y., Ishii S. The tryptophan cluster: a hypothetical structure of the DNA-binding domain of the myb protooncogene product. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19990–19995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Grummt I. Specific interaction of the murine transcription termination factor TTF I with class-I RNA polymerases. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):559–562. doi: 10.1038/344559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Grummt I. 3'-end formation of mouse pre-rRNA involves both transcription termination and a specific processing reaction. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):224–231. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Normann A., Bartsch I., Grummt I. The mouse ribosomal gene terminator consists of three functionally separable sequence elements. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1497–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. A 12-base-pair sequence is an essential element of the ribosomal gene terminator in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1900–1905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang W. H., Reeder R. H. The REB1 site is an essential component of a terminator for RNA polymerase I in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Ju Q., Warner J. R. A bipartite DNA-binding domain in yeast Reb1p. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1173–1182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Hojo H., Aimoto S., Nakai T., Nakamura H., Sarai A., Ishii S., Nishimura Y. Solution structure of a DNA-binding unit of Myb: a helix-turn-helix-related motif with conserved tryptophans forming a hydrophobic core. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6428–6432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfleiderer C., Smid A., Bartsch I., Grummt I. An undecamer DNA sequence directs termination of human ribosomal gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4727–4736. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Rho and RNA: models for recognition and response. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Mar;11(6):983–990. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remacle J. E., Holmberg S. A REB1-binding site is required for GCN4-independent ILV1 basal level transcription and can be functionally replaced by an ABF1-binding site. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5516–5526. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Transcription termination. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1993;28(1):1–30. doi: 10.3109/10409239309082571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. W., Baker H. V. Concerted action of the transcriptional activators REB1, RAP1, and GCR1 in the high-level expression of the glycolytic gene TPI. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):543–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Broyles S. S., Moss B. Purification and characterization of a transcription termination factor from vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12372–12380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smid A., Finsterer M., Grummt I. Limited proteolysis unmasks specific DNA-binding of the murine RNA polymerase I-specific transcription termination factor TTFI. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90213-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. Has the breast cancer gene been found? Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90393-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Nicholson P. R., Stillman D. J. Identification of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA-binding protein involved in transcriptional regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1743–1753. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]