Abstract
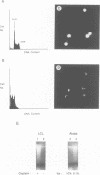
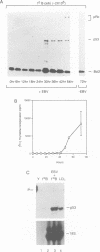
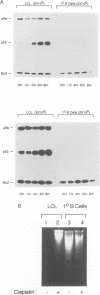
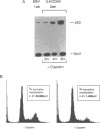
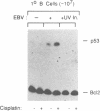
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) efficiently converts resting human B cells into actively cycling, immortal, lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs). Here we show that LCLs expressing the full complement of latent viral genes are very sensitive to DNA-damaging agents such as cisplatin. The response includes a rapid accumulation of the tumour suppressor protein p53 and induction of the cellular genes mdm2 and WAF1/p21. Although the levels of Bcl2 protein and Bax mRNA appear unaltered by the activation of p53, within 24 h the majority of cells undergo apoptosis. Over-expression of wild-type p53 in an LCL also resulted in apoptosis; this was preceded by the dephosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product, pRb. Primary resting B cells showed no response to cisplatin and even after drug treatment, p53 remained undetectable. However, after infection with EBV, p53 gene expression was induced to a similar level to that found in mitogen-activated B cells. When the physiologically activated primary B cells were exposed to cisplatin, although p53 accumulated as in LCLs, the outcome was growth-arrest rather than gross cell death. We conclude that, in contrast to the transformation of fibroblasts by adenovirus, SV40 or HPV, when B cells become activated and immortalized by EBV they are sensitized to the p53-mediated damage response. When the resulting LCLs are treated with genotoxic agents such as cisplatin, they are unable to arrest like normal cells because they are driven to proliferate by EBV and consequently undergo apoptosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfieri C., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):595–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90893-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allday M. J., Crawford D. H., Thomas J. A. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 6 induces expression of the EBV latent membrane protein and an activated phenotype in Raji cells. J Gen Virol. 1993 Mar;74(Pt 3):361–369. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-3-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allday M. J., Farrell P. J. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA3C/6 expression maintains the level of latent membrane protein 1 in G1-arrested cells. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3491–3498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3491-3498.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banchereau J., de Paoli P., Vallé A., Garcia E., Rousset F. Long-term human B cell lines dependent on interleukin-4 and antibody to CD40. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1702555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Oliner J. D., Zhan Q., Fornace A. J., Jr, Vogelstein B., Kastan M. B. Interactions between p53 and MDM2 in a mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2684–2688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou S. K., Rao L., White E. Bcl-2 blocks p53-dependent apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2556–2563. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbas M., White E. Wild-type p53 mediates apoptosis by E1A, which is inhibited by E1B. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):546–554. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Kaufmann W. K., Wilson S. J., Tlsty T. D., Lees E., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J., Reed S. I. p53-dependent inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase activities in human fibroblasts during radiation-induced G1 arrest. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1013–1023. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duthu A., Debuire B., Romano J., Ehrhart J. C., Fiscella M., May E., Appella E., May P. p53 mutations in Raji cells: characterization and localization relative to other Burkitt's lymphomas. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2161–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman A. Activation of programmed cell death by anticancer agents: cisplatin as a model system. Cancer Cells. 1990 Aug-Sep;2(8-9):275–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Allan G. J., Shanahan F., Vousden K. H., Crook T. p53 is frequently mutated in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2879–2887. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finke J., Fritzen R., Ternes P., Trivedi P., Bross K. J., Lange W., Mertelsmann R., Dölken G. Expression of bcl-2 in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines: induction by latent Epstein-Barr virus genes. Blood. 1992 Jul 15;80(2):459–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche M., Haessler C., Brandner G. Induction of nuclear accumulation of the tumor-suppressor protein p53 by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):307–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funderud S., Erikstein B., Asheim H. C., Nustad K., Stokke T., Blomhoff H. K., Holte H., Smeland E. B. Functional properties of CD19+ B lymphocytes positively selected from buffy coats by immunomagnetic separation. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):201–206. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Dive C., Henderson S., Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Gordon J., Rickinson A. B. Activation of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes protects human B cells from death by apoptosis. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):612–614. doi: 10.1038/349612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Rowe M., Gregory C., Croom-Carter D., Wang F., Longnecker R., Kieff E., Rickinson A. Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90007-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermeking H., Eick D. Mediation of c-Myc-induced apoptosis by p53. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2091–2093. doi: 10.1126/science.8091232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Braking the cycle. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):839–841. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90528-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley E. A., Thorley-Lawson D. A. B cell activation and the establishment of Epstein-Barr virus latency. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2059–2075. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessis T. D., Slebos R. J., Nelson W. G., Kastan M. B., Plunkett B. S., Han S. M., Lorincz A. T., Hedrick L., Cho K. R. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 expression disrupts the p53-mediated cellular response to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3988–3992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. The regulation of p53 function: Steiner Award Lecture. Int J Cancer. 1994 Jun 1;57(5):623–627. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau R., Packham G., Farrell P. J. Differential splicing of Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early RNA. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6233–6236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6233-6236.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E., Jacks T., Housman D. E. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):957–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90719-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E. Stabilization of the p53 tumor suppressor is induced by adenovirus 5 E1A and accompanies apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):535–545. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W. Interactions between SV40 large-tumor antigen and the growth suppressor proteins pRB and p53. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):866–871. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8344486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. P., Staunton D., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded protein found in plasma membranes of transformed cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):710–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.710-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. M., Veis D., Korsmeyer S. J., Sugden B. Latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus induces cellular phenotypes independently of expression of Bcl-2. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5269–5278. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5269-5278.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy S. A., Symonds H. S., Van Dyke T. Regulation of apoptosis in transgenic mice by simian virus 40 T antigen-mediated inactivation of p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3979–3983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Unger T., Huibregtse J. M., Howley P. M. The transcriptional transactivation function of wild-type p53 is inhibited by SV40 large T-antigen and by HPV-16 E6 oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5013–5020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Krajewski S., Krajewska M., Wang H. G., Lin H. K., Liebermann D. A., Hoffman B., Reed J. C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1799–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E. Interaction of adenoviral proteins with pRB and p53. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):880–885. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8344487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltvai Z. N., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picksley S. M., Vojtesek B., Sparks A., Lane D. P. Immunochemical analysis of the interaction of p53 with MDM2;--fine mapping of the MDM2 binding site on p53 using synthetic peptides. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2523–2529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L., Debbas M., Sabbatini P., Hockenbery D., Korsmeyer S., White E. The adenovirus E1A proteins induce apoptosis, which is inhibited by the E1B 19-kDa and Bcl-2 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7742–7746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentman C. L., Shutter J. R., Hockenbery D., Kanagawa O., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2 inhibits multiple forms of apoptosis but not negative selection in thymocytes. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):879–888. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. J., Palmero I., Peters G., Farrell P. J. EBNA-2 and EBNA-LP cooperate to cause G0 to G1 transition during immortalization of resting human B lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3321–3328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Jacks T., Cory S. DNA damage can induce apoptosis in proliferating lymphoid cells via p53-independent mechanisms inhibitable by Bcl-2. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekely L., Selivanova G., Magnusson K. P., Klein G., Wiman K. G. EBNA-5, an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen, binds to the retinoblastoma and p53 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Ono Y. Synchronous and sequential activation of latently infected Epstein-Barr virus genomes. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.445-449.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Haecker G., Strasser A. An evolutionary perspective on apoptosis. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):777–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtesek B., Bártek J., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. An immunochemical analysis of the human nuclear phosphoprotein p53. New monoclonal antibodies and epitope mapping using recombinant p53. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Jul 6;151(1-2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90122-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Crook T., Farrell P. J. Biological activities of p53 mutants in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. J Gen Virol. 1993 May;74(Pt 5):803–810. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-5-803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. Interactions of human papillomavirus transforming proteins with the products of tumor suppressor genes. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):872–879. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8393818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Szekely L., Okan I., Klein G., Wiman K. G. Wild-type p53-triggered apoptosis is inhibited by bcl-2 in a v-myc-induced T-cell lymphoma line. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3427–3431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., Smith C. A. Molecular regulation of apoptosis: genetic controls on cell death. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):777–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90457-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Levine A. J. p53 and E2F-1 cooperate to mediate apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3602–3606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis. Death gets a brake. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):272–273. doi: 10.1038/369272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
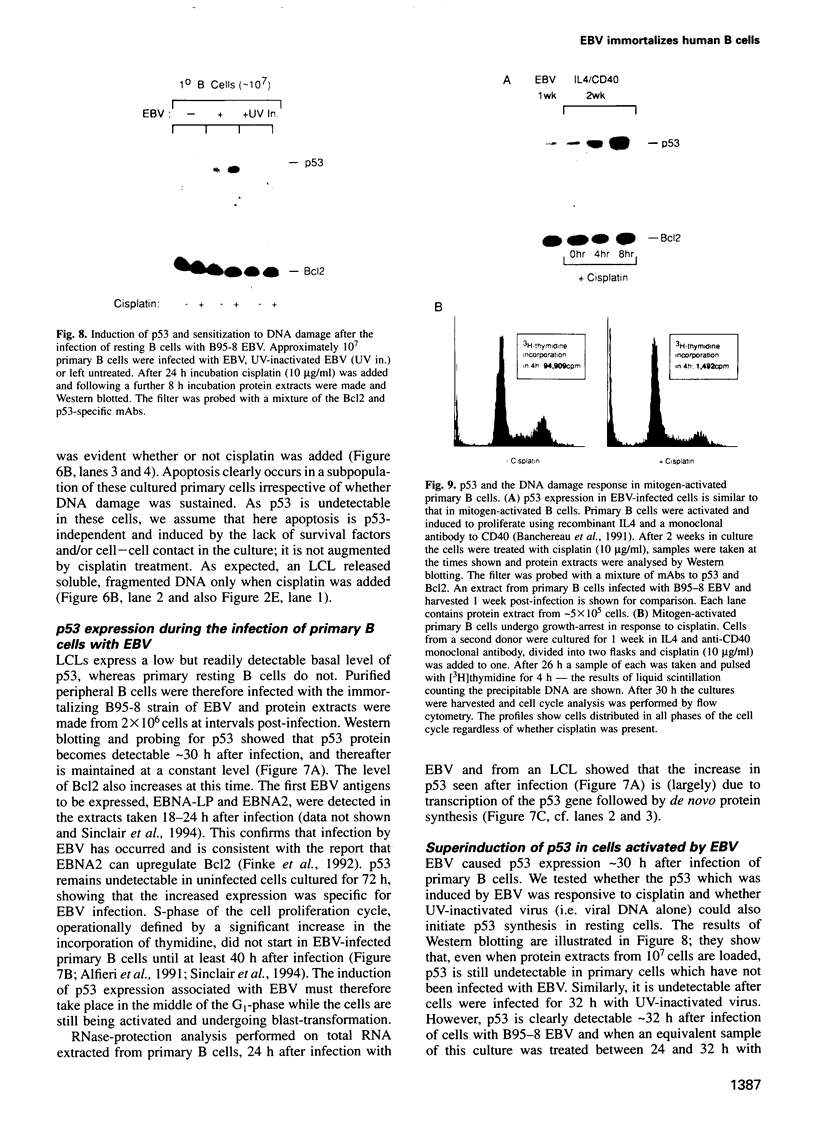
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]