Abstract
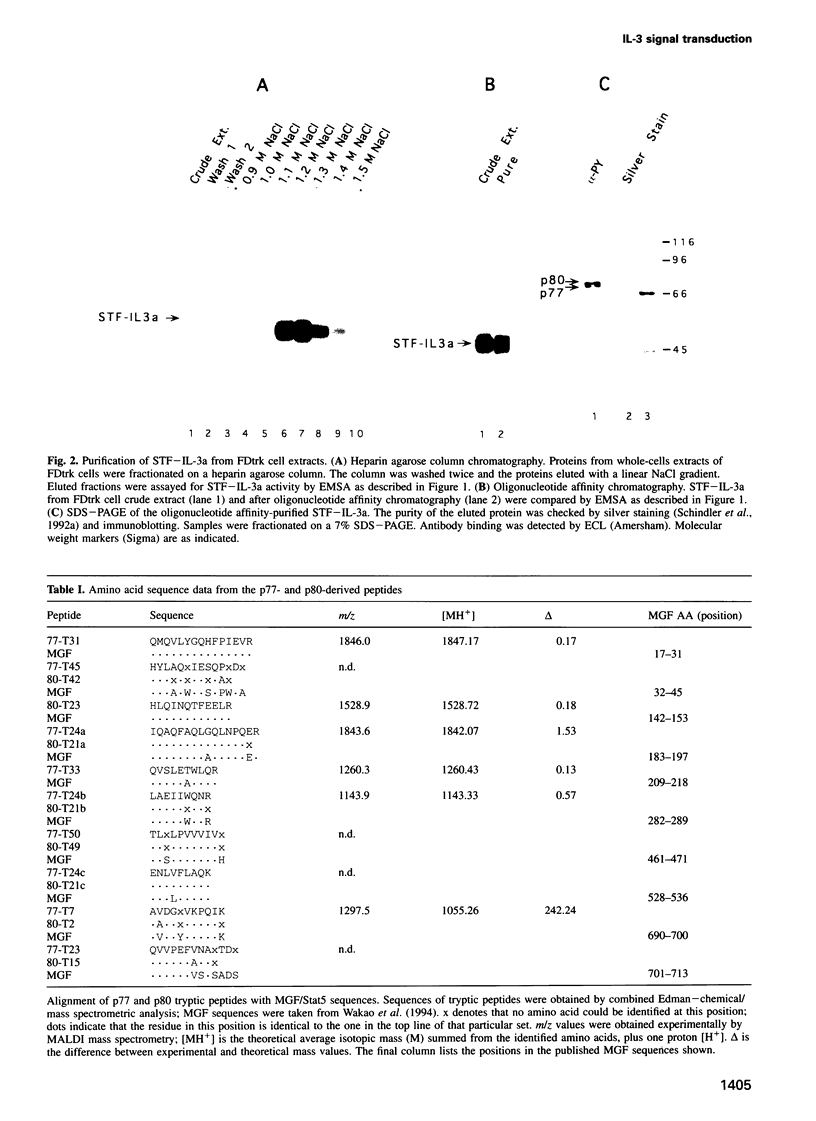
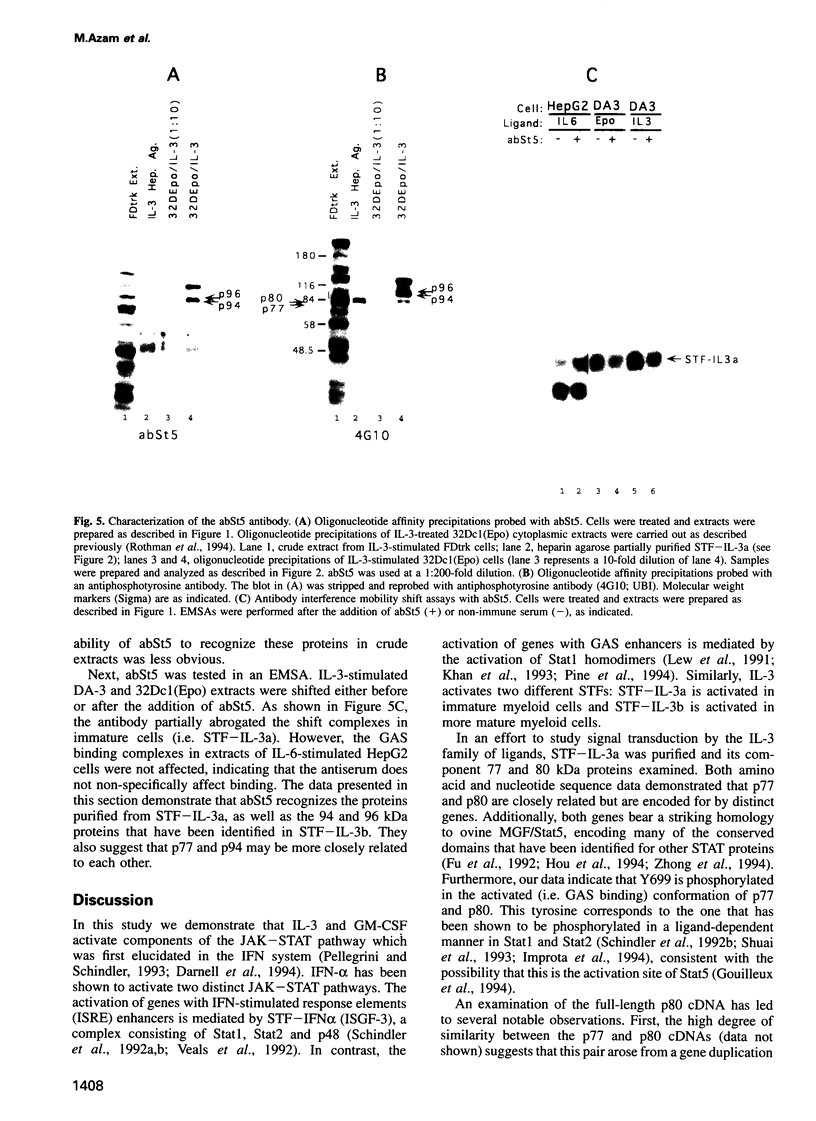
The interleukin (IL)-3 family of cytokines mediates its numerous effects on myeloid growth and maturation by binding a family of related receptors. It has been shown recently that IL-3 induces the activation of two distinct cytoplasmic signal transducing factors (STFs) that are likely to mediate the induction of immediate early genes. In immature myeloid cells, IL-3 activates STF-IL-3a, which comprises two tyrosine-phosphorylated DNA binding proteins of 77 and 80 kDa. In mature myeloid cells, IL-3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor activate STF-IL-3b, which consists of a 94 and 96 kDa tyrosine-phosphorylated DNA binding protein. Peptide sequence data obtained from the purified 77 and 80 kDa proteins (p77 and p80) indicate that they are closely related but are encoded by distinct genes. Both peptide and nucleotide sequence data demonstrate that these two proteins are the murine homologs of ovine mammary gland factor (MGF)/Stat5. The peptide data also indicate that p77 and p80 are phosphorylated on tyrosine 699, a position analogous to the tyrosine that is phosphorylated in Stat1 and Stat2 in response to interferon. Additionally, antiserum raised against bacterially expressed p77/p80 recognizes the 94 and 96 kDa protein components of STF-IL-3b, suggesting that these may be additional isoforms of Stat5. These studies indicate that the IL-3 family of ligands is able to activate multiple isoforms of the signal transducing protein Stat5.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Nishio Y., Inoue M., Wang X. J., Wei S., Matsusaka T., Yoshida K., Sudo T., Naruto M., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonni A., Frank D. A., Schindler C., Greenberg M. E. Characterization of a pathway for ciliary neurotrophic factor signaling to the nucleus. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1575–1579. doi: 10.1126/science.7504325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. S., Argetsinger L. S., Ihle J. N., Kelly P. A., Rillema J. A., Carter-Su C. Activation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase by prolactin receptors in Nb2 cells and mouse mammary gland explants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5232–5236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DaSilva L., Howard O. M., Rui H., Kirken R. A., Farrar W. L. Growth signaling and JAK2 association mediated by membrane-proximal cytoplasmic regions of prolactin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18267–18270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domen J., van der Lugt N. M., Laird P. W., Saris C. J., Clarke A. R., Hooper M. L., Berns A. Impaired interleukin-3 response in Pim-1-deficient bone marrow-derived mast cells. Blood. 1993 Sep 1;82(5):1445–1452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio V., Clark-Lewis I., Federsppiel B., Wieler J. S., Schrader J. W. Tyrosine phosphorylation of receptor beta subunits and common substrates in response to interleukin-3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21856–21863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusanter-Fourt I., Muller O., Ziemiecki A., Mayeux P., Drucker B., Djiane J., Wilks A., Harpur A. G., Fischer S., Gisselbrecht S. Identification of JAK protein tyrosine kinases as signaling molecules for prolactin. Functional analysis of prolactin receptor and prolactin-erythropoietin receptor chimera expressed in lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2583–2591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06548.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers A., Seegert D., Schindler C., Baccarini M., Decker T. The response of gamma interferon activation factor is under developmental control in cells of the macrophage lineage. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3245–3254. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elicone C., Lui M., Geromanos S., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P. Microbore reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic purification of peptides for combined chemical sequencing-laser-desorption mass spectrometric analysis. J Chromatogr A. 1994 Jul 29;676(1):121–137. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(94)00089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdjument-Bromage H., Lui M., Sabatini D. M., Snyder S. H., Tempst P. High-sensitivity sequencing of large proteins: partial structure of the rapamycin-FKBP12 target. Protein Sci. 1994 Dec;3(12):2435–2446. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Schindler C., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr The proteins of ISGF-3, the interferon alpha-induced transcriptional activator, define a gene family involved in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7840–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Bagley C. J., Vadas M. A., Lopez A. F. A model for the interaction of the GM-CSF, IL-3 and IL-5 receptors with their ligands. Growth Factors. 1993;8(2):87–97. doi: 10.3109/08977199309046929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilleux F., Wakao H., Mundt M., Groner B. Prolactin induces phosphorylation of Tyr694 of Stat5 (MGF), a prerequisite for DNA binding and induction of transcription. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4361–4369. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J., Schindler U., Henzel W. J., Ho T. C., Brasseur M., McKnight S. L. An interleukin-4-induced transcription factor: IL-4 Stat. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1701–1706. doi: 10.1126/science.8085155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Askew D. Origins and properties of hematopoietic growth factor-dependent cell lines. Int J Cell Cloning. 1989 Mar;7(2):68–91. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530070202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Improta T., Schindler C., Horvath C. M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription factor ISGF-3 formation requires phosphorylated Stat91 protein, but Stat113 protein is phosphorylated independently of Stat91 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4776–4780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzav S., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M., Hedge A. M., Isfort R., Ihle J. N. The trk oncogene abrogates growth factor requirements and transforms hematopoietic cells. Oncogene. 1989 Sep;4(9):1129–1135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan K. D., Shuai K., Lindwall G., Maher S. E., Darnell J. E., Jr, Bothwell A. L. Induction of the Ly-6A/E gene by interferon alpha/beta and gamma requires a DNA element to which a tyrosine-phosphorylated 91-kDa protein binds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6806–6810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Taga T., Akira S. Cytokine signal transduction. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., David M., Feldman G. M., Igarashi K., Hackett R. H., Webb D. S., Sweitzer S. M., Petricoin E. F., 3rd, Finbloom D. S. Tyrosine phosphorylation of DNA binding proteins by multiple cytokines. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1730–1733. doi: 10.1126/science.8378773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Strehlow I., Darnell J. E. Overlapping elements in the guanylate-binding protein gene promoter mediate transcriptional induction by alpha and gamma interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütticken C., Wegenka U. M., Yuan J., Buschmann J., Schindler C., Ziemiecki A., Harpur A. G., Wilks A. F., Yasukawa K., Taga T. Association of transcription factor APRF and protein kinase Jak1 with the interleukin-6 signal transducer gp130. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.8272872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuguchi T., Salgia R., Hallek M., Eder M., Druker B., Ernst T. J., Griffin J. D. Shc phosphorylation in myeloid cells is regulated by granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interleukin-3, and steel factor and is constitutively increased by p210BCR/ABL. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5016–5021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliaccio G., Migliaccio A. R., Kreider B. L., Rovera G., Adamson J. W. Selection of lineage-restricted cell lines immortalized at different stages of hematopoietic differentiation from the murine cell line 32D. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):833–841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura O., D'Andrea A., Kabat D., Ihle J. N. Induction of tyrosine phosphorylation by the erythropoietin receptor correlates with mitogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4895–4902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Pollard J. W., Stanley E. R. Isolation and characterization of a cloned growth factor dependent macrophage cell line, BAC1.2F5. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Mar;130(3):420–427. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041300316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mui A. L., Wakao H., O'Farrell A. M., Harada N., Miyajima A. Interleukin-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor and interleukin-5 transduce signals through two STAT5 homologs. EMBO J. 1995 Mar 15;14(6):1166–1175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata Y., Yamaguchi N., Hitoshi Y., Tominaga A., Takatsu K. Interleukin 5 and interleukin 3 induce serine and tyrosine phosphorylations of several cellular proteins in an interleukin 5-dependent cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1102–1108. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80899-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Briscoe J., Laxton C., Guschin D., Ziemiecki A., Silvennoinen O., Harpur A. G., Barbieri G., Witthuhn B. A., Schindler C. The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in interferon-alpha/beta and -gamma signal transduction. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):129–135. doi: 10.1038/366129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini S., Schindler C. Early events in signalling by interferons. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):338–342. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Canova A., Schindler C. Tyrosine phosphorylated p91 binds to a single element in the ISGF2/IRF-1 promoter to mediate induction by IFN alpha and IFN gamma, and is likely to autoregulate the p91 gene. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):158–167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle F. W., Sato N., Witthuhn B. A., Inhorn R. C., Eder M., Miyajima A., Griffin J. D., Ihle J. N. JAK2 associates with the beta c chain of the receptor for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and its activation requires the membrane-proximal region. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4335–4341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman P., Kreider B., Azam M., Levy D., Wegenka U., Eilers A., Decker T., Horn F., Kashleva H., Ihle J. Cytokines and growth factors signal through tyrosine phosphorylation of a family of related transcription factors. Immunity. 1994 Sep;1(6):457–468. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. The cellular and molecular environment in leukemia. Blood Cells. 1993;19(3):709–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamaki K., Wang H. M., Miyajima I., Kitamura T., Todokoro K., Harada N., Miyajima A. Ligand-dependent activation of chimeric receptors with the cytoplasmic domain of the interleukin-3 receptor beta subunit (beta IL3). J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15833–15839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Fu X. Y., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr Proteins of transcription factor ISGF-3: one gene encodes the 91-and 84-kDa ISGF-3 proteins that are activated by interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7836–7839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Kashleva H., Pernis A., Pine R., Rothman P. STF-IL-4: a novel IL-4-induced signal transducing factor. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1350–1356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Shuai K., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):809–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1496401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M., Darnell J. E., Jr A single phosphotyrosine residue of Stat91 required for gene activation by interferon-gamma. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1744–1746. doi: 10.1126/science.7690989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Ihle J. N., Schlessinger J., Levy D. E. Interferon-induced nuclear signalling by Jak protein tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):583–585. doi: 10.1038/366583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen P. H., Mui A. L., Murthy S. C., Krystal G. Interleukin-3, GM-CSF, and TPA induce distinct phosphorylation events in an interleukin 3-dependent multipotential cell line. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):406–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Boulton T. G., Farruggella T., Ip N. Y., Davis S., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Barbieri G., Pellegrini S. Association and activation of Jak-Tyk kinases by CNTF-LIF-OSM-IL-6 beta receptor components. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8272873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempst P., Link A. J., Riviere L. R., Fleming M., Elicone C. Internal sequence analysis of proteins separated on polyacrylamide gels at the submicrogram level: improved methods, applications and gene cloning strategies. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jul;11(7):537–553. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veals S. A., Schindler C., Leonard D., Fu X. Y., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr, Levy D. E. Subunit of an alpha-interferon-responsive transcription factor is related to interferon regulatory factor and Myb families of DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3315–3324. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez L., Fellous M., Stark G. R., Pellegrini S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakao H., Gouilleux F., Groner B. Mammary gland factor (MGF) is a novel member of the cytokine regulated transcription factor gene family and confers the prolactin response. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2182–2191. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06495.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling D., Guschin D., Müller M., Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Rogers N. C., Schindler C., Stark G. R., Ihle J. N. Complementation by the protein tyrosine kinase JAK2 of a mutant cell line defective in the interferon-gamma signal transduction pathway. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):166–170. doi: 10.1038/366166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witthuhn B. A., Silvennoinen O., Miura O., Lai K. S., Cwik C., Liu E. T., Ihle J. N. Involvement of the Jak-3 Janus kinase in signalling by interleukins 2 and 4 in lymphoid and myeloid cells. Nature. 1994 Jul 14;370(6485):153–157. doi: 10.1038/370153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):95–98. doi: 10.1126/science.8140422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]