Abstract
The protein encoded by the yeast gene SPT14 shows high sequence similarity to the human protein, PIG-A, whose loss of activity is at the origin of the disease paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. The symptoms of this disease are apparently due to a loss of cell surface, glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins. Like PIG-A mutant cells, spt14 mutant cells are defective in GPI anchoring due to a defect in the synthesis of GlcNAc-PI, the first step of GPI synthesis. The spt14 mutant causes several other abnormalities including transcriptional defects and a downregulation of inositolphosphoceramide synthesis. We suggest that these defects are indirect results of the loss of GPI anchoring.
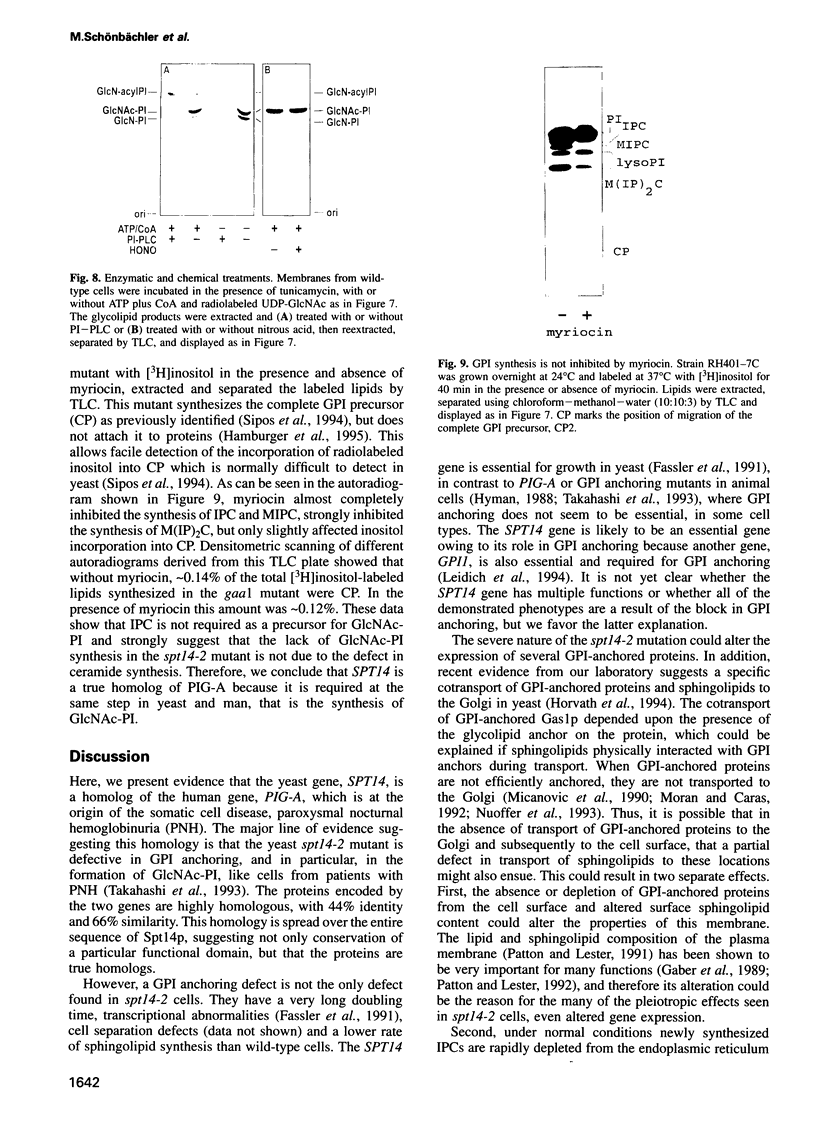
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangs J. D., Hereld D., Krakow J. L., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Rapid processing of the carboxyl terminus of a trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3207–3211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker G. W., Lester R. L. Biosynthesis of phosphoinositol-containing sphingolipids from phosphatidylinositol by a membrane preparation from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):747–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.747-754.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler M., Mason P. J., Hillmen P., Miyata T., Yamada N., Takeda J., Luzzatto L., Kinoshita T. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (PNH) is caused by somatic mutations in the PIG-A gene. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):110–117. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A., Fujimoto K., Kornfeld S. The primary glycosylation defect in class E Thy-1-negative mutant mouse lymphoma cells is an inability to synthesize dolichol-P-mannose. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4441–4446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Fankhauser C., Desponds C. Myoinositol gets incorporated into numerous membrane glycoproteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae; incorporation is dependent on phosphomannomutase (sec53). EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):653–661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Puoti A., Lester R. L., Desponds C. Two different types of lipid moieties are present in glycophosphoinositol-anchored membrane proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):457–466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05075.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Spiazzi A., Bron C. Glycolipid anchors are attached to Thy-1 glycoprotein rapidly after translation. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 15;246(3):605–610. doi: 10.1042/bj2460605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello L. C., Orlean P. Inositol acylation of a potential glycosyl phosphoinositol anchor precursor from yeast requires acyl coenzyme A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8599–8603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Glycolipid anchoring of plasma membrane proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGasperi R., Thomas L. J., Sugiyama E., Chang H. M., Beck P. J., Orlean P., Albright C., Waneck G., Sambrook J. F., Warren C. D. Correction of a defect in mammalian GPI anchor biosynthesis by a transfected yeast gene. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):988–991. doi: 10.1126/science.1978413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering T. L., Masterson W. J., Englund P. T., Hart G. W. Biosynthesis of the glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of the trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. Origin of the non-acetylated glucosamine. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11168–11173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulic V., Egerton M., Elguindi I., Raths S., Singer B., Riezman H. Yeast endocytosis assays. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:697–710. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94051-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund P. T. The structure and biosynthesis of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol protein anchors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:121–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fankhauser C., Homans S. W., Thomas-Oates J. E., McConville M. J., Desponds C., Conzelmann A., Ferguson M. A. Structures of glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchors from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26365–26374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fassler J. S., Gray W., Lee J. P., Yu G. Y., Gingerich G. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SPT14 gene is essential for normal expression of the yeast transposon, Ty, as well as for expression of the HIS4 gene and several genes in the mating pathway. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Nov;230(1-2):310–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00290682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber R. F., Copple D. M., Kennedy B. K., Vidal M., Bard M. The yeast gene ERG6 is required for normal membrane function but is not essential for biosynthesis of the cell-cycle-sparking sterol. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3447–3456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber L. D., Kodukula K., Udenfriend S. Phosphatidylinositol glycan (PI-G) anchored membrane proteins. Amino acid requirements adjacent to the site of cleavage and PI-G attachment in the COOH-terminal signal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12168–12173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güther M. L., Masterson W. J., Ferguson M. A. The effects of phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride on inositol-acylation and fatty acid remodeling in African trypanosomes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18694–18701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath A., Riezman H. Rapid protein extraction from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1994 Oct;10(10):1305–1310. doi: 10.1002/yea.320101007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath A., Sütterlin C., Manning-Krieg U., Movva N. R., Riezman H. Ceramide synthesis enhances transport of GPI-anchored proteins to the Golgi apparatus in yeast. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3687–3695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R. Somatic genetic analysis of the expression of cell surface molecules. Trends Genet. 1988 Jan;4(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Takeda J. GPI-anchor synthesis. Parasitol Today. 1994 Apr;10(4):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(94)90261-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
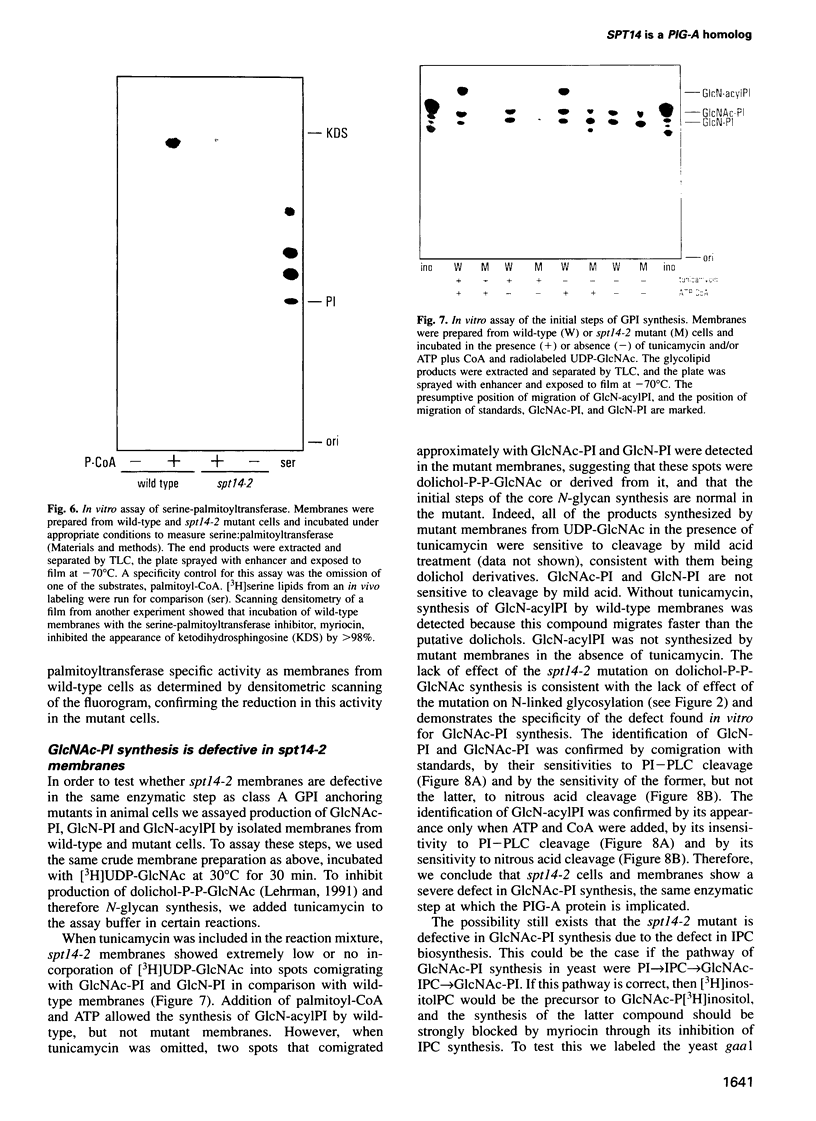
- Kodukula K., Gerber L. D., Amthauer R., Brink L., Udenfriend S. Biosynthesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored membrane proteins in intact cells: specific amino acid requirements adjacent to the site of cleavage and GPI attachment. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):657–664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A. Biosynthesis of N-acetylglucosamine-P-P-dolichol, the committed step of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide assembly. Glycobiology. 1991 Dec;1(6):553–562. doi: 10.1093/glycob/1.6.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leidich S. D., Drapp D. A., Orlean P. A conditionally lethal yeast mutant blocked at the first step in glycosyl phosphatidylinositol anchor synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10193–10196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. L., Dickson R. C. Sphingolipids with inositolphosphate-containing head groups. Adv Lipid Res. 1993;26:253–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson W. J., Doering T. L., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. A novel pathway for glycan assembly: biosynthesis of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor of the trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90684-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Ferguson M. A. The structure, biosynthesis and function of glycosylated phosphatidylinositols in the parasitic protozoa and higher eukaryotes. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 1;294(Pt 2):305–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2940305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micanovic R., Kodukula K., Gerber L. D., Udenfriend S. Selectivity at the cleavage/attachment site of phosphatidylinositol-glycan anchored membrane proteins is enzymatically determined. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7939–7943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Takeda J., Iida Y., Yamada N., Inoue N., Takahashi M., Maeda K., Kitani T., Kinoshita T. The cloning of PIG-A, a component in the early step of GPI-anchor biosynthesis. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1318–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.7680492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran P., Caras I. W. A nonfunctional sequence converted to a signal for glycophosphatidylinositol membrane anchor attachment. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):329–336. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran P., Caras I. W. Proteins containing an uncleaved signal for glycophosphatidylinositol membrane anchor attachment are retained in a post-ER compartment. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):763–772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran P., Raab H., Kohr W. J., Caras I. W. Glycophospholipid membrane anchor attachment. Molecular analysis of the cleavage/attachment site. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1250–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuoffer C., Horvath A., Riezman H. Analysis of the sequence requirements for glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchoring of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gas1 protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10558–10563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuoffer C., Jenö P., Conzelmann A., Riezman H. Determinants for glycophospholipid anchoring of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAS1 protein to the plasma membrane. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):27–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlean P., Albright C., Robbins P. W. Cloning and sequencing of the yeast gene for dolichol phosphate mannose synthase, an essential protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17499–17507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlean P. Dolichol phosphate mannose synthase is required in vivo for glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchoring, O mannosylation, and N glycosylation of protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5796–5805. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. L., Lester R. L. Phosphatidylinositol phosphate, phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate, and the phosphoinositol sphingolipids are found in the plasma membrane and stimulate the plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Jan;292(1):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. L., Lester R. L. The phosphoinositol sphingolipids of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are highly localized in the plasma membrane. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3101–3108. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3101-3108.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puoti A., Conzelmann A. Structural characterization of free glycolipids which are potential precursors for glycophosphatidylinositol anchors in mouse thymoma cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22673–22680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puoti A., Desponds C., Fankhauser C., Conzelmann A. Characterization of glycophospholipid intermediate in the biosynthesis of glycophosphatidylinositol anchors accumulating in the Thy-1-negative lymphoma line SIA-b. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21051–21059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raths S., Rohrer J., Crausaz F., Riezman H. end3 and end4: two mutants defective in receptor-mediated and fluid-phase endocytosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):55–65. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipos G., Puoti A., Conzelmann A. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: absence of ceramides from complete precursor glycolipids. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2789–2796. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T., Esmon B., Schekman R. Early stages in the yeast secretory pathway are required for transport of carboxypeptidase Y to the vacuole. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. L., Raetz C. R. Defective glycosyl phosphatidylinositol biosynthesis in extracts of three Thy-1 negative lymphoma cell mutants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10039–10042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. L. Regulation of glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis by GTP. Stimulation of N-acetylglucosamine-phosphatidylinositol deacetylation. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9718–9724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama E., DeGasperi R., Urakaze M., Chang H. M., Thomas L. J., Hyman R., Warren C. D., Yeh E. T. Identification of defects in glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis in the Thy-1 expression mutants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12119–12122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takeda J., Hirose S., Hyman R., Inoue N., Miyata T., Ueda E., Kitani T., Medof M. E., Kinoshita T. Deficient biosynthesis of N-acetylglucosaminyl-phosphatidylinositol, the first intermediate of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis, in cell lines established from patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):517–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda J., Miyata T., Kawagoe K., Iida Y., Endo Y., Fujita T., Takahashi M., Kitani T., Kinoshita T. Deficiency of the GPI anchor caused by a somatic mutation of the PIG-A gene in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90250-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. B., Taylor J. P., Webberley M. C., Turner N. J., Flitsch S. L. A novel mono-branched lipid phosphate acts as a substrate for dolichyl phosphate mannose synthetase. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 1;295(Pt 1):195–201. doi: 10.1042/bj2950195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink M. M., Edison A. M., Wells G. B., Pinto W., Lester R. L. Characterization of a novel, potent, and specific inhibitor of serine palmitoyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25032–25038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]