A 30-year-old female, with no significant family history, came with complaints of intermittent, colicky abdominal pain and abdominal distension of 5 months duration, with significant weight loss. CT abdomen showed multiple polypoidal lesions in the colon. Colonoscopy revealed multiple polyps carpeting the entire colon (Fig. 1A); biopsy of which revealed adenomatous polyps. The patient underwent total proctocolectomy with J-pouch ileo-anal anastomosis and ileostomy. Gross examination is depicted in Fig. 1B. Microscopic picture is demonstrated in Fig. 2. Patient is currently doing well on a one-month follow up.
Figure 1.
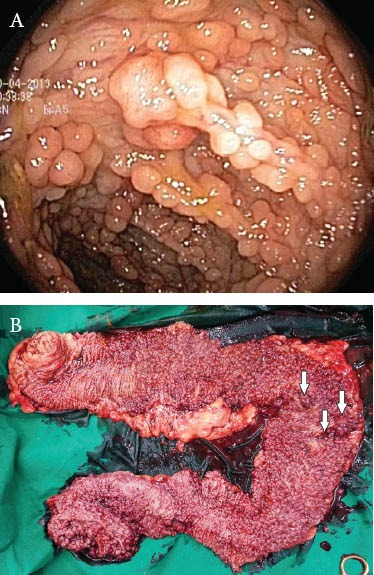
(A) Colonoscopic picture showing multiple polyps (B) Gross examination of the total proctocolectomy specimen, show-ing numerous polyps, varying in size from 0.1 to 1.8 cm, with areas suspicious for malignancy as indicated by the arrows
Figure 2.
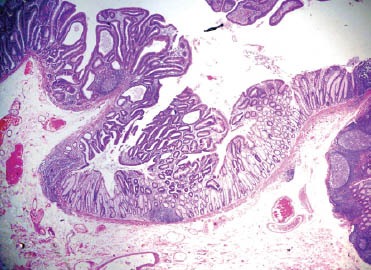
Microscopic picture, ×10, stained with eosin and hematoxylin, showing an adenomatous polyp with evidence of well-differentiated adenocarcinoma with infiltration beyond the muscularis mucosae but restricted to the submucosa
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant, inheritable condition, characterized by over a hundred adenomatous polyps in the large intestine. It is linked to mutations of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene located on chromosome 5q21. Adenomatous polyps are present in nearly 100% by 40 years of age [1]. The lifetime risk of colorectal malignancy in untreated patients with FAP is near 100% with a median age of 39 years [2].
Surgical options include total abdominal colectomy with ileorectostomy, proctocolectomy with ileal pouch anal reconstruction, and total proctocolectomy with Brooke ileostomy [1-3].
Biography
PD Hinduja Hospital, Mumbai, India
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: None
References
- 1.Beech D, Pontius A, Muni N, Long WP. Familial adenomatous polyposis: a case report and review of the literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2001;93:208–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ellis CN. Colonic adenomatous polyposis syndromes: clinical management. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2008;21:256–262. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1089940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Al-Sukhni W, Aronson M. Gallinger Hereditary colorectal cancer syndromes: familial adenomatous polyposis and Lynch syndrome. Surg Clin N Am. 2008;88:819–844. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2008.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


