Abstract
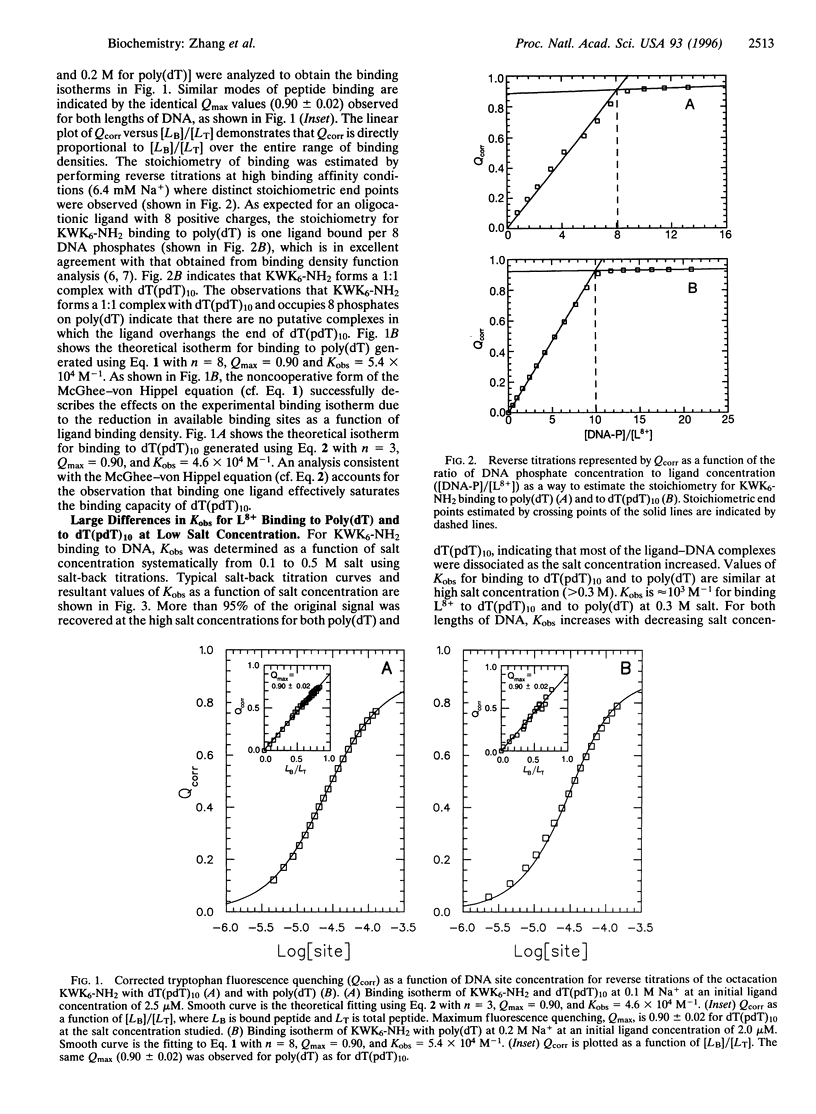
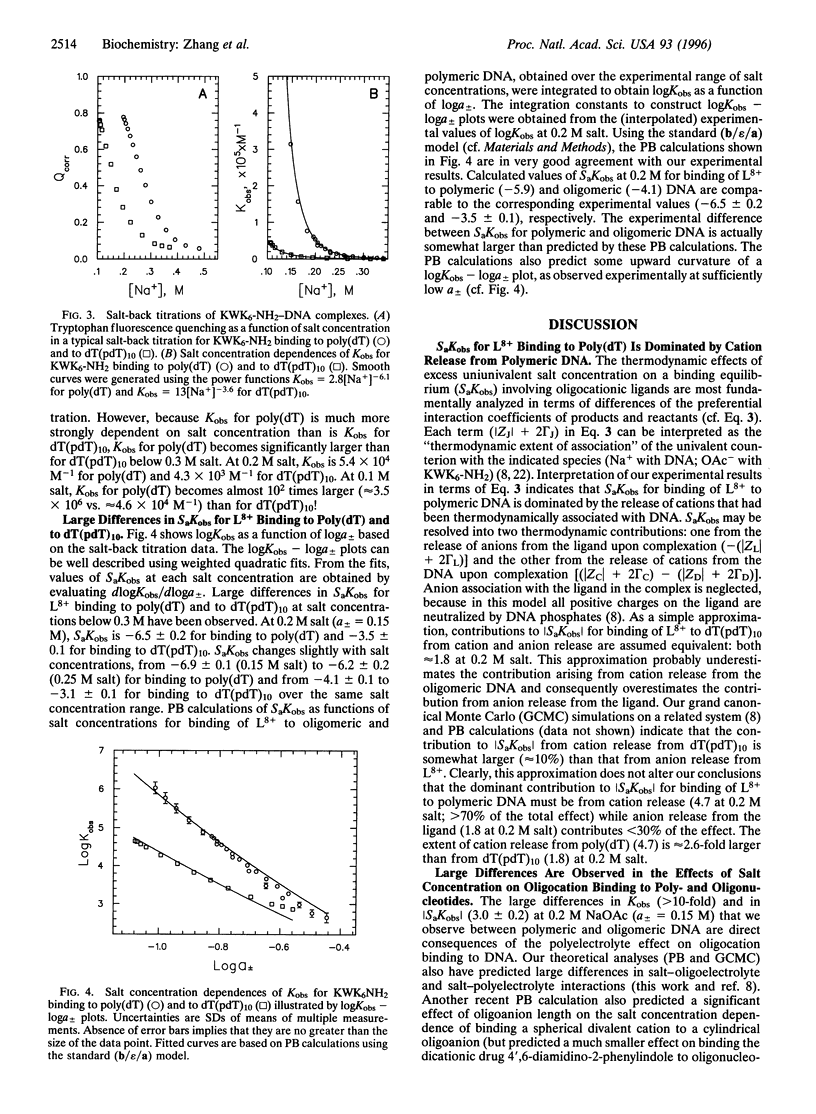
Results presented here demonstrate that the thermodynamics of oligocation binding to polymeric and oligomeric DNA are not equivalent because of long-range electrostatic effects. At physiological cation concentrations (0.1-0.3 M) the binding of an oligolysine octacation KWK6-NH2 (+8 charge) to single-stranded poly(dT) is much stronger per site and significantly more salt concentration dependent than the binding of the same ligand to an oligonucleotide, dT(pdT)10 (-10 charge). These large differences are consistent with Poisson-Boltzmann calculations for a model that characterizes the charge distributions with key preaveraged structural parameters. Therefore, both the experimental and the theoretical results presented here show that the polyelectrolyte character of a polymeric nucleic acid makes a large contribution to both the magnitude and the salt concentration dependence of its binding interactions with simple oligocationic ligands.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Salt-nucleic acid interactions. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1995;46:657–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.46.100195.003301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bujalowski W., Lohman T. M. A general method of analysis of ligand-macromolecule equilibria using a spectroscopic signal from the ligand to monitor binding. Application to Escherichia coli single-strand binding protein-nucleic acid interactions. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 2;26(11):3099–3106. doi: 10.1021/bi00385a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenley M. O., Manning G. S., Olson W. K. Approach to the limit of counterion condensation. Biopolymers. 1990;30(13-14):1191–1203. doi: 10.1002/bip.360301305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Nicholls A. Classical electrostatics in biology and chemistry. Science. 1995 May 26;268(5214):1144–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.7761829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C., Lonberg N., Newport J. W., von Hippel P. H. Interactions of bacteriophage T4-coded gene 32 protein with nucleic acids. I. Characterization of the binding interactions. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):75–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A., Sober H. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions. 3. Cation effect on binding strength and specificity. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3307–3314. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., Ferrari M. E. Escherichia coli single-stranded DNA-binding protein: multiple DNA-binding modes and cooperativities. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:527–570. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., Mascotti D. P. Nonspecific ligand-DNA equilibrium binding parameters determined by fluorescence methods. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:424–458. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12027-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascotti D. P., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamic extent of counterion release upon binding oligolysines to single-stranded nucleic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3142–3146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascotti D. P., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamics of single-stranded RNA and DNA interactions with oligolysines containing tryptophan. Effects of base composition. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 12;32(40):10568–10579. doi: 10.1021/bi00091a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., von Hippel P. H. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions: co-operative and non-co-operative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V. K., Hecht J. L., Sharp K. A., Friedman R. A., Honig B. Salt effects on protein-DNA interactions. The lambda cI repressor and EcoRI endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 29;238(2):264–280. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V. K., Sharp K. A., Friedman R. A., Honig B. Salt effects on ligand-DNA binding. Minor groove binding antibiotics. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 29;238(2):245–263. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted M. C., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Importance of oligoelectrolyte end effects for the thermodynamics of conformational transitions of nucleic acid oligomers: a grand canonical Monte Carlo analysis. Biopolymers. 1991 Nov;31(13):1593–1604. doi: 10.1002/bip.360311314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted M. C., Bond J. P., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Grand canonical Monte Carlo molecular and thermodynamic predictions of ion effects on binding of an oligocation (L8+) to the center of DNA oligomers. Biophys J. 1995 Feb;68(2):634–647. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80224-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overman L. B., Lohman T. M. Linkage of pH, anion and cation effects in protein-nucleic acid equilibria. Escherichia coli SSB protein-single stranded nucleic acid interactions. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 11;236(1):165–178. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J. L., Dewey J., Rae J. S., Nesler M., Cooper K. Single potassium channels in corneal epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990 Sep;31(9):1799–1809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Anderson C. F. Interpretation of preferential interaction coefficients of nonelectrolytes and of electrolyte ions in terms of a two-domain model. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):786–794. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80254-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Anderson C. F., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamic analysis of ion effects on the binding and conformational equilibria of proteins and nucleic acids: the roles of ion association or release, screening, and ion effects on water activity. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):103–178. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000202x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Lohman M. L., De Haseth P. Ion effects on ligand-nucleic acid interactions. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 25;107(2):145–158. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp K. A., Friedman R. A., Misra V., Hecht J., Honig B. Salt effects on polyelectrolyte-ligand binding: comparison of Poisson-Boltzmann, and limiting law/counterion binding models. Biopolymers. 1995 Aug;36(2):245–262. doi: 10.1002/bip.360360211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



