Abstract
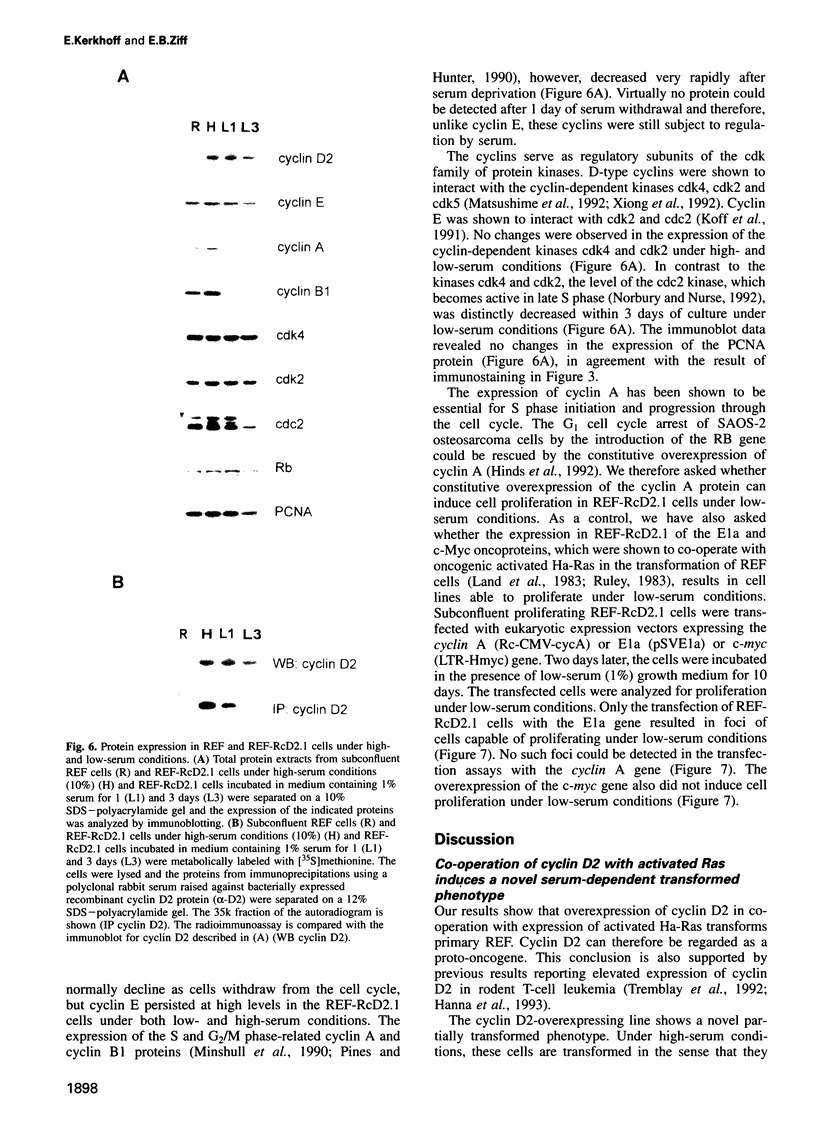
The D-type cyclins are growth factor-regulated delayed early functions which peak at the G1/S transition, are thought to regulate entry into S phase and have been implicated in tumorigenesis. Here, we show that cyclin D2 can co-operate with Ha-Ras to impose a novel transformed state on rat embryo fibroblasts (REF). While clonal cyclin D2/Ha-Ras REF transformants exhibit a characteristic transformed phenotype in high serum, in low serum they arrest cell proliferation and display profound morphological and cytological changes indicating loss of control of cell mass and deregulation of the G1/S transition. Notably, in low serum, despite re-establishment of actin cables and arrest of proliferation, cell mass continues to increase, creating giant cells up to 10 x normal size. Also, during low-serum culture the cells make a very gradual but progressive entry into S phase, reaching a 2.4N DNA content after 6 days. PCNA is expressed and 2N and 4N cells are largely absent, and thus the cells undergo a novel S phase arrest. While transfer to low serum induced the retinoblastoma protein to enter its dephosphorylated state, and cyclin A, cyclin B and cdc2 levels to decrease, all as normal, cyclin E, cdk4, cdk2 and the exogenous cyclin D2 persisted at high levels. These results indicate that cyclin D2 and Ha-Ras can transform cells when mitogenic signals from growth factors are provided. However, in low serum, co-operation of cyclin D2 and Ha-Ras provides only a subset of the progression signals and these are sufficient for G1-related cell mass increase and S phase entry, but are insufficient for full cell cycling.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldin V., Lukas J., Marcote M. J., Pagano M., Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):812–821. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Fate of immunoprecipitable protein kinase C in GH3 cells treated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15194–15199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchkovich K., Duffy L. A., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated during specific phases of the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdy S. F., Hinds P. W., Louie K., Reed S. I., Arnold A., Weinberg R. A. Physical interaction of the retinoblastoma protein with human D cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):499–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90137-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Sherr C. J., Matsushime H., Kato J., Livingston D. M. Functional interactions of the retinoblastoma protein with mammalian D-type cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90136-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadaleta G., Pepe G., De Candia G., Quagliariello C., Sbisà E., Saccone C. The complete nucleotide sequence of the Rattus norvegicus mitochondrial genome: cryptic signals revealed by comparative analysis between vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1989 Jun;28(6):497–516. doi: 10.1007/BF02602930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard F., Strausfeld U., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Cyclin A is required for the onset of DNA replication in mammalian fibroblasts. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1169–1179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich D. W., Wang N. P., Qian Y. W., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. The retinoblastoma gene product regulates progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90181-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Turck C. W., Morgan D. O. Inhibition of CDK2 activity in vivo by an associated 20K regulatory subunit. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):707–710. doi: 10.1038/366707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyuris J., Golemis E., Chertkov H., Brent R. Cdi1, a human G1 and S phase protein phosphatase that associates with Cdk2. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90498-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna Z., Jankowski M., Tremblay P., Jiang X., Milatovich A., Francke U., Jolicoeur P. The Vin-1 gene, identified by provirus insertional mutagenesis, is the cyclin D2. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1661–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Brill J. A., Fink G. R., Weinberg R. A. Collaboration of G1 cyclins in the functional inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 1;8(15):1759–1771. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.15.1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Mittnacht S., Dulic V., Arnold A., Reed S. I., Weinberg R. A. Regulation of retinoblastoma protein functions by ectopic expression of human cyclins. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):993–1006. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90249-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakawa T., Ruley H. E. Rescue of cells from ras oncogene-induced growth arrest by a second, complementing, oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1519–1523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Q. J., Bautista C., Edwards G. M., Defeo-Jones D., Jones R. E., Harlow E. Antibodies specific for the human retinoblastoma protein identify a family of related polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5792–5799. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W., Kahn S. M., Zhou P., Zhang Y. J., Cacace A. M., Infante A. S., Doi S., Santella R. M., Weinstein I. B. Overexpression of cyclin D1 in rat fibroblasts causes abnormalities in growth control, cell cycle progression and gene expression. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3447–3457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. V., Walsh M. L., Chen L. B. Localization of mitochondria in living cells with rhodamine 123. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):990–994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamb A., Gruis N. A., Weaver-Feldhaus J., Liu Q., Harshman K., Tavtigian S. V., Stockert E., Day R. S., 3rd, Johnson B. E., Skolnick M. H. A cell cycle regulator potentially involved in genesis of many tumor types. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):436–440. doi: 10.1126/science.8153634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelekar A., Cole M. D. Immortalization by c-myc, H-ras, and Ela oncogenes induces differential cellular gene expression and growth factor responses. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3899–3907. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Cross F., Fisher A., Schumacher J., Leguellec K., Philippe M., Roberts J. M. Human cyclin E, a new cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1217–1228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90044-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Giordano A., Desai D., Yamashita K., Harper J. W., Elledge S., Nishimoto T., Morgan D. O., Franza B. R., Roberts J. M. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.1388288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolch W., Heidecker G., Kochs G., Hummel R., Vahidi H., Mischak H., Finkenzeller G., Marmé D., Rapp U. R. Protein kinase C alpha activates RAF-1 by direct phosphorylation. Nature. 1993 Jul 15;364(6434):249–252. doi: 10.1038/364249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovec H., Sewing A., Lucibello F. C., Müller R., Möröy T. Oncogenic activity of cyclin D1 revealed through cooperation with Ha-ras: link between cell cycle control and malignant transformation. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):323–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Ewen M. E., Strom D. K., Kato J. Y., Hanks S. K., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Identification and properties of an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type G1 cyclins. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90360-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Quelle D. E., Shurtleff S. A., Shibuya M., Sherr C. J., Kato J. Y. D-type cyclin-dependent kinase activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2066–2076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Roussel M. F., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):701–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittnacht S., Hinds P. W., Dowdy S. F., Weinberg R. A. Modulation of retinoblastoma protein activity during the cell cycle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:197–209. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Arnold A. Cyclin D and oncogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Feb;3(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80334-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Bloom T., Kim H. G., Jüppner H., Ruderman J. V., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):512–515. doi: 10.1038/350512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. Control of the yeast cell cycle by the Cdc28 protein kinase. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):166–179. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90099-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobori T., Miura K., Wu D. J., Lois A., Takabayashi K., Carson D. A. Deletions of the cyclin-dependent kinase-4 inhibitor gene in multiple human cancers. Nature. 1994 Apr 21;368(6473):753–756. doi: 10.1038/368753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Roberts J. M. Cyclin-dependent regulation of G1 in mammalian fibroblasts. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1908–1912. doi: 10.1126/science.8384376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Theodoras A. M., Tam S. W., Draetta G. F. Cyclin D1-mediated inhibition of repair and replicative DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1627–1639. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Gibbs J. B. Pathways of Ras function: connections to the actin cytoskeleton. Adv Cancer Res. 1993;62:19–64. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle D. E., Ashmun R. A., Shurtleff S. A., Kato J. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Overexpression of mouse D-type cyclins accelerates G1 phase in rodent fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1559–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Wittenberg C., Cross F., Reed S. I. An essential G1 function for cyclin-like proteins in yeast. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90768-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Noble M., Land H. Ras-mediated cell cycle arrest is altered by nuclear oncogenes to induce Schwann cell transformation. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1635–1645. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02990.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Disappearance of Ca2+-sensitive, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in phorbol ester-treated 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Hannon G. J., Beach D. A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):704–707. doi: 10.1038/366704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton D. J., Park S. H., Lanier L., Weinberg R. A. Nonfunctional mutants of the retinoblastoma protein are characterized by defects in phosphorylation, viral oncoprotein association, and nuclear tethering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3033–3037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay P. J., Kozak C. A., Jolicoeur P. Identification of a novel gene, Vin-1, in murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell leukemias by provirus insertional mutagenesis. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1344–1353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1344-1353.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troppmair J., Cleveland J. L., Askew D. S., Rapp U. R. v-Raf/v-Myc synergism in abrogation of IL-3 dependence: v-Raf suppresses apoptosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;182:453–460. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77633-5_57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Yunis J., Onorato-Showe L., Erikson J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Molecular cloning of the chromosomal breakpoint of B-cell lymphomas and leukemias with the t(11;14) chromosome translocation. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1403–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.6610211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M., Tokiwa G., Futcher B. Comparison of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae G1 cyclins: Cln3 may be an upstream activator of Cln1, Cln2 and other cyclins. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1955–1968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05845.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriz S., Lemaitre J. M., Leibovici M., Thierry N., Méchali M. Comparative analysis of the intracellular localization of c-Myc, c-Fos, and replicative proteins during cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3548–3555. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:513–552. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. D type cyclins associate with multiple protein kinases and the DNA replication and repair factor PCNA. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90518-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. Subunit rearrangement of the cyclin-dependent kinases is associated with cellular transformation. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1572–1583. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]