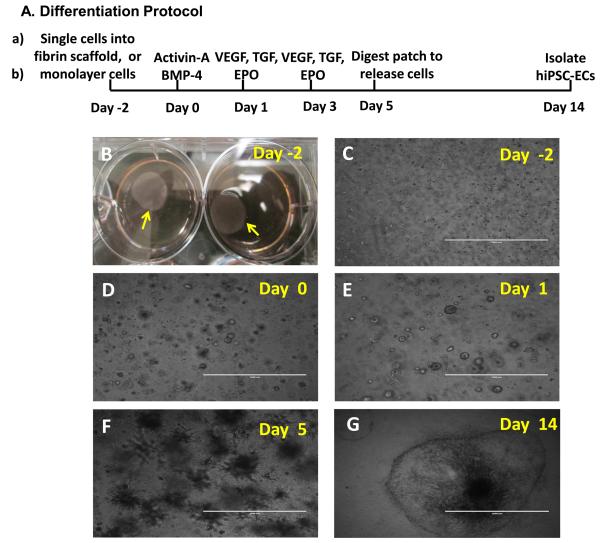
Figure 1. 3D scaffold-mediated differentiation of hiPSCs into hiPSC-ECs.
(A) A schematic diagram of the hiPSC-EC differentiation protocol is displayed. (B) Two days before the differentiation protocol was initiated (i.e., on Day -2), fibrinogen solution was loaded with hiPSCs and mixed with thrombin to form a hiPSC-containing scaffold (yellow arrow). (C) The cells self-assembled into small clusters within the patch and grew to form sphere-shaped structures on (D) Day 0, when stage 1 of differentiation was initiated by culturing the cells with activin A and BMP-4. (E) On Day 1 (i.e., 24 hours later), stage 2 of differentiation was initiated by replacing the activin A/BMP-4 medium with medium containing VEGF, EPO, and TGFβ1, and the cells were cultured for 96 hours (i.e., until Day 5). (F) After 5 days of differentiation, the spheres had grown into spike-like structures, which were released from the patch via collagenase IV digestion. (G) By Day 14, the differentiated hiPSCs (visible as a sphere attached to the cell culture surface and formed a single layer of cells. (C-F: Bar=1 mm; G: Bar=2 mm).