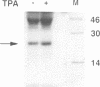
Abstract
The DNA-binding activity of c-Jun is determined by the phosphorylation state of a cluster of threonine and serine residues located near its COOH-terminus. We have analyzed the events that lead to c-Jun activation via dephosphorylation of these sites in response to phorbol esters. Our results indicate that COOH-terminal dephosphorylation is an indirect consequence of a separate phosphorylation event targeted to the NH2-terminus of c-Jun. Thus, the activation of c-Jun DNA-binding potential, caused by COOH-terminal dephosphorylation, may not require the regulation of the kinase/phosphatase system that brings about this change, but rather an alteration in the accessibility of the COOH-terminal phosphoacceptor sites of c-Jun.
Full text
PDF


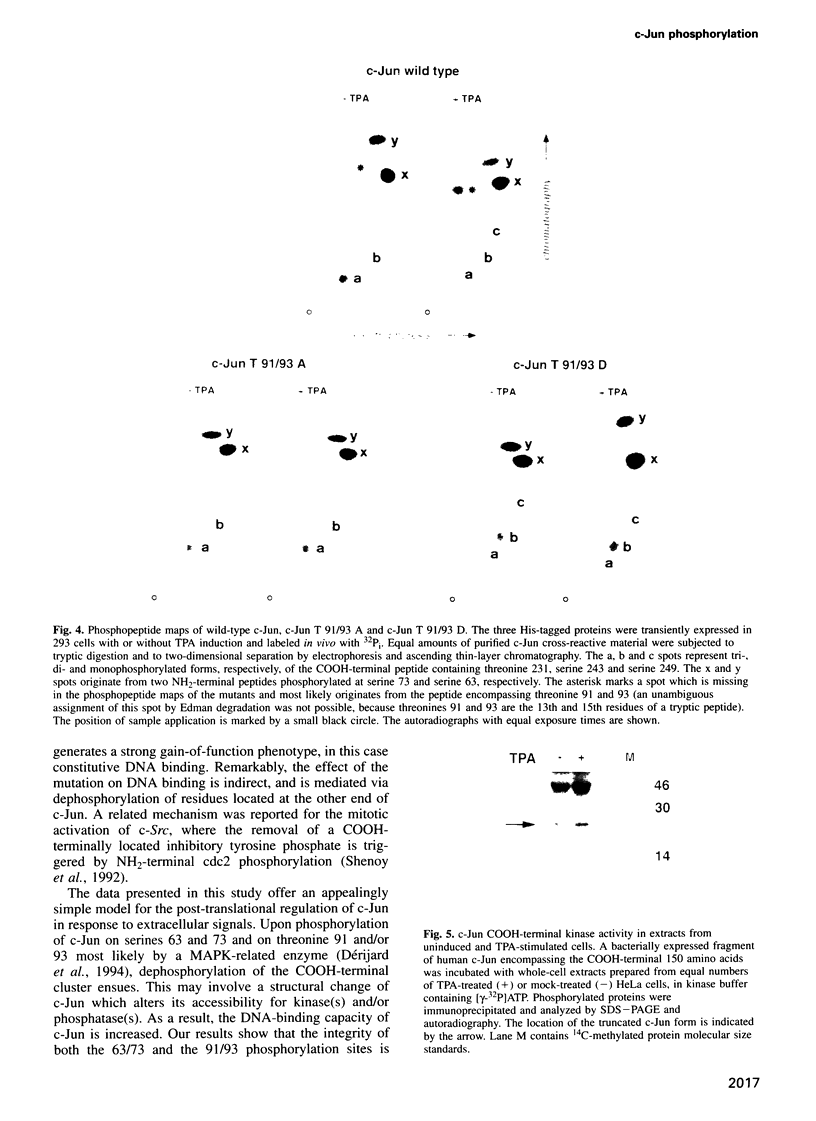


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Kerppola T. K., Luk D., Vandenberg M. T., Marshak D. R., Curran T., Abate C. Jun is phosphorylated by several protein kinases at the same sites that are modified in serum-stimulated fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4694–4705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binétruy B., Smeal T., Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):122–127. doi: 10.1038/351122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Tjian R. Biochemical analysis of transcriptional activation by Jun: differential activity of c- and v-Jun. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Smeal T., Karin M. The mammalian ultraviolet response is triggered by activation of Src tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1081–1091. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Lin A., Smeal T., Minden A., Karin M. Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2135–2148. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler W. K., Levinson A. D., Bauer E. A. Activation of c-Jun transcription factor by substitution of a charged residue in its N-terminal domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 11;22(7):1305–1312. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.7.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Signal transduction from the cell surface to the nucleus through the phosphorylation of transcription factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landt O., Grunert H. P., Hahn U. A general method for rapid site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1990 Nov 30;96(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90351-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Frost J., Deng T., Smeal T., al-Alawi N., Kikkawa U., Hunter T., Brenner D., Karin M. Casein kinase II is a negative regulator of c-Jun DNA binding and AP-1 activity. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90311-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. MAP kinase kinase kinase, MAP kinase kinase and MAP kinase. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavassiliou A. G., Bohmann K., Bohmann D. Determining the effect of inducible protein phosphorylation on the DNA-binding activity of transcription factors. Anal Biochem. 1992 Jun;203(2):302–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90317-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavassiliou A. G., Chavrier C., Bohmann D. Phosphorylation state and DNA-binding activity of c-Jun depend on the intracellular concentration of binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11562–11565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavassiliou A. G. Preservation of protein phosphoryl groups in immunoprecipitation assays. J Immunol Methods. 1994 Mar 29;170(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90246-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radler-Pohl A., Sachsenmaier C., Gebel S., Auer H. P., Bruder J. T., Rapp U., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. UV-induced activation of AP-1 involves obligatory extranuclear steps including Raf-1 kinase. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1005–1012. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy S., Chackalaparampil I., Bagrodia S., Lin P. H., Shalloway D. Role of p34cdc2-mediated phosphorylations in two-step activation of pp60c-src during mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7237–7241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D. A., Birrer M., Karin M. Oncogenic and transcriptional cooperation with Ha-Ras requires phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):494–496. doi: 10.1038/354494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Hibi M., Karin M. Altering the specificity of signal transduction cascades: positive regulation of c-Jun transcriptional activity by protein kinase A. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):6006–6010. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treier M., Staszewski L. M., Bohmann D. Ubiquitin-dependent c-Jun degradation in vivo is mediated by the delta domain. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):787–798. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90502-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]