Abstract
Bacterial invasion of human mucosal cells is considered to be a primary event in the pathogenesis of a gonococcal infection. Here we report that cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans may play a role in the establishment of an infection, by functioning as receptors for the invasion-promoting gonococcal opacity protein adhesin. Chemical modification and enzymatic removal of proteoglycan receptors from cultured epithelial cells abolished opacity protein-associated gonococcal invasion, and mutant cell lines defective in proteoglycan synthesis were poor substrates for gonococcal attachment. The addition of purified receptor and receptor analogues totally blocked gonococcal entry into the cells. Heparin-affinity chromatography and receptor binding assays using recombinant bacteria producing defined opacity proteins and reconstituted receptor or purified receptor fragments as probes, identified one particular member of the opacity protein family (MS11-Opa30) as the primary ligand for this novel class of receptors for bacteria. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans with gonococcal binding activity were purified from various cell types derived from target tissues of gonococcal infection, including ME-180 endocervical cells and primary cultures of human corneal epithelium. The physico-chemical properties of the receptor indicate that it may belong to the syndecan proteoglycan family.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascencio F., Fransson L. A., Wadström T. Affinity of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori for the N-sulphated glycosaminoglycan heparan sulphate. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Apr;38(4):240–244. doi: 10.1099/00222615-38-4-240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Huttner W. B. Chlorate--a potent inhibitor of protein sulfation in intact cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):870–877. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belland R. J., Chen T., Swanson J., Fischer S. H. Human neutrophil response to recombinant neisserial Opa proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(13):1729–1737. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergey E. J., Stinson M. W. Heparin-inhibitable basement membrane-binding protein of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1715–1721. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1715-1721.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernfield M., Kokenyesi R., Kato M., Hinkes M. T., Spring J., Gallo R. L., Lose E. J. Biology of the syndecans: a family of transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:365–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Gotschlich E. C. Purification and partial characterization of the opacity-associated proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):452–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., Hannah J. H., Leininger E. Adhesion of Bordetella pertussis to sulfatides and to the GalNAc beta 4Gal sequence found in glycosphingolipids. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18827–18831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Weintraub H. J. Molecular modeling of protein-glycosaminoglycan interactions. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):21–32. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey D. J., Stahl R. C., Tucker B., Bendt K. A., Cizmeci-Smith G. Aggregation-induced association of syndecan-1 with microfilaments mediated by the cytoplasmic domain. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Sep;214(1):12–21. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey D. J., Todd M. S. A cytoskeleton-associated plasma membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan in Schwann cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7518–7525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Sparling P. F. Mucosal infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Bacterial adaptation and mucosal defenses. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1699–1705. doi: 10.1172/JCI115770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G. Integral membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans. FASEB J. 1993 Aug;7(11):1023–1030. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.11.8370471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Inhibitors of the biosynthesis and processing of N-linked oligosaccharide chains. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:497–534. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenius K., Jalkanen M. Function of the syndecans--a family of cell surface proteoglycans. J Cell Sci. 1994 Nov;107(Pt 11):2975–2982. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.11.2975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A. Measurement of invasion by gentamicin resistance. Methods Enzymol. 1994;236:405–420. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)36030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esko J. D. Genetic analysis of proteoglycan structure, function and metabolism. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;3(5):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esko J. D., Rostand K. S., Weinke J. L. Tumor formation dependent on proteoglycan biosynthesis. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1092–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.3137658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S. Bacterial entry into eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1099–1102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90003-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S., Isberg R. R., Portnoy D. A. The interaction of bacteria with mammalian cells. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:333–363. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frevert U., Sinnis P., Cerami C., Shreffler W., Takacs B., Nussenzweig V. Malaria circumsporozoite protein binds to heparan sulfate proteoglycans associated with the surface membrane of hepatocytes. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1287–1298. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. T., Walker A. Molecular distinctions between heparan sulphate and heparin. Analysis of sulphation patterns indicates that heparan sulphate and heparin are separate families of N-sulphated polysaccharides. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 15;230(3):665–674. doi: 10.1042/bj2300665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Hayashi M., Jalkanen M., Firestone J. H., Trelstad R. L., Bernfield M. Immunocytochemistry of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan in mouse tissues. A light and electron microscopic study. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Oct;35(10):1079–1088. doi: 10.1177/35.10.2957423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inki P., Stenbäck F., Grenman S., Jalkanen M. Immunohistochemical localization of syndecan-1 in normal and pathological human uterine cervix. J Pathol. 1994 Apr;172(4):349–355. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Tran Van Nhieu G. Binding and internalization of microorganisms by integrin receptors. Trends Microbiol. 1994 Jan;2(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(94)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Busch S. J., Cardin A. D. Glycosaminoglycans: molecular properties, protein interactions, and role in physiological processes. Physiol Rev. 1991 Apr;71(2):481–539. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
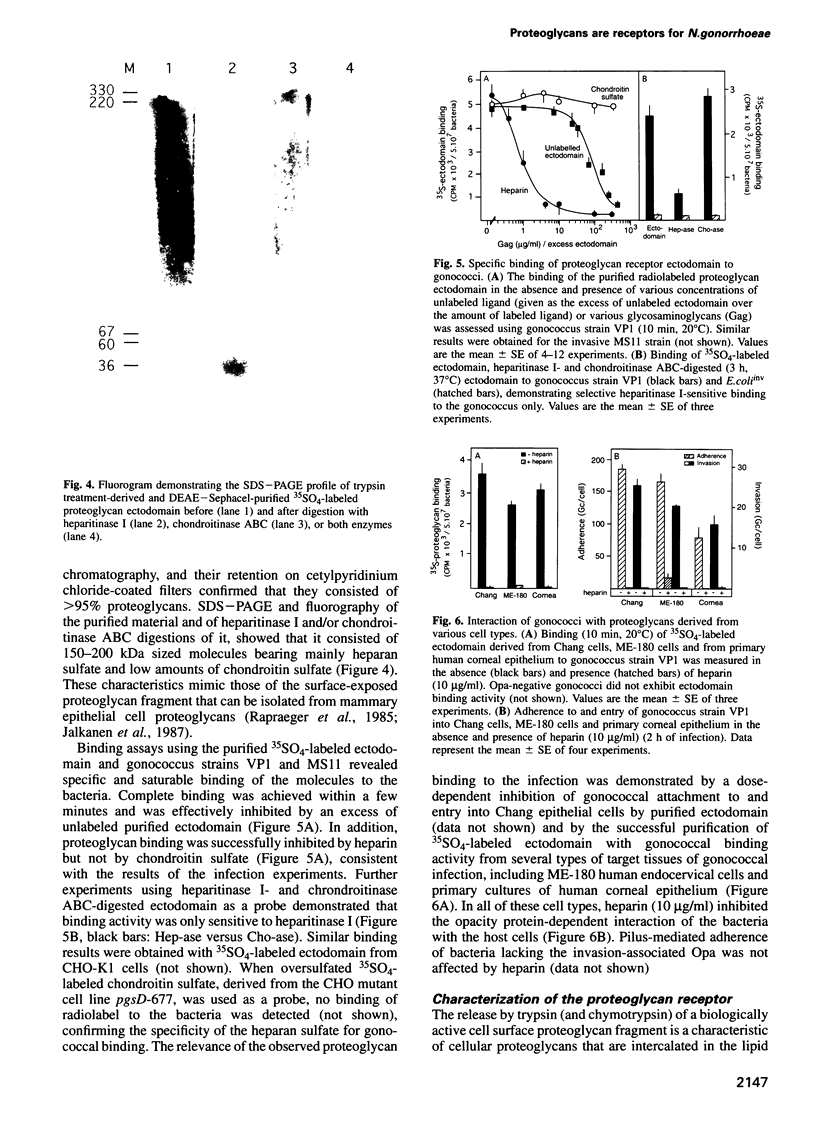
- Jalkanen M., Rapraeger A., Saunders S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan of mouse mammary epithelial cells is shed by cleavage of its matrix-binding ectodomain from its membrane-associated domain. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):3087–3096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén L., Lindahl U. Proteoglycans: structures and interactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:443–475. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén L., Oldberg A., Hök M. Cell-surface heparan sulfate. Mechanisms of proteoglycan-cell association. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10407–10413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koda J. E., Bernfield M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans from mouse mammary epithelial cells. Basal extracellular proteoglycan binds specifically to native type I collagen fibrils. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11763–11770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupsch E. M., Knepper B., Kuroki T., Heuer I., Meyer T. F. Variable opacity (Opa) outer membrane proteins account for the cell tropisms displayed by Neisseria gonorrhoeae for human leukocytes and epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):641–650. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05697.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love D. C., Esko J. D., Mosser D. M. A heparin-binding activity on Leishmania amastigotes which mediates adhesion to cellular proteoglycans. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(3):759–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.3.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Casillas F., Cheifetz S., Doody J., Andres J. L., Lane W. S., Massagué J. Structure and expression of the membrane proteoglycan betaglycan, a component of the TGF-beta receptor system. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., van Putten J. P., Meyer T. F. Phase variation of the opacity outer membrane protein controls invasion by Neisseria gonorrhoeae into human epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1307–1315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mali M., Jaakkola P., Arvilommi A. M., Jalkanen M. Sequence of human syndecan indicates a novel gene family of integral membrane proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6884–6889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menozzi F. D., Gantiez C., Locht C. Interaction of the Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin with heparin. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Feb;62(1):59–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1991.tb04417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menozzi F. D., Mutombo R., Renauld G., Gantiez C., Hannah J. H., Leininger E., Brennan M. J., Locht C. Heparin-inhibitable lectin activity of the filamentous hemagglutinin adhesin of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1994 Mar;62(3):769–778. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.3.769-778.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Pohlner J., van Putten J. P. Biology of the pathogenic Neisseriae. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1994;192:283–317. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78624-2_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen H. M., Jalkanen M. The cytoplasmic domain of syndecan-1 is not required for association with Triton X-100-insoluble material. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jun;107(Pt 6):1571–1581. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.6.1571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimms L. T., Zampighi G., Nozaki Y., Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Phospholipid vesicle formation and transmembrane protein incorporation using octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):833–840. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyts J., Snoeck R., Schols D., Balzarini J., Esko J. D., Van Schepdael A., De Clercq E. Sulfated polymers inhibit the interaction of human cytomegalovirus with cell surface heparan sulfate. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):48–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90680-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-Barria E., Pereira M. E. A novel T. cruzi heparin-binding protein promotes fibroblast adhesion and penetration of engineered bacteria and trypanosomes into mammalian cells. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90192-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannekoek Y., van Putten J. P., Dankert J. Identification and molecular analysis of a 63-kilodalton stress protein from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6928–6937. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6928-6937.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A. C., Bernfield M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans from mouse mammary epithelial cells. A putative membrane proteoglycan associates quantitatively with lipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3632–3636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan of mammary epithelial cells. Protease releases a heparan sulfate-rich ectodomain from a putative membrane-anchored domain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4103–4109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Jalkanen M., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan associates with the cytoskeleton at the basolateral cell surface of mouse mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2683–2696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Jalkanen M., Endo E., Koda J., Bernfield M. The cell surface proteoglycan from mouse mammary epithelial cells bears chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11046–11052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A. Transforming growth factor (type beta) promotes the addition of chondroitin sulfate chains to the cell surface proteoglycan (syndecan) of mouse mammary epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2509–2518. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. D., Ginsburg V. Sulfated glycolipids and cell adhesion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Dec;267(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Yamaguchi Y. Proteoglycans as modulators of growth factor activities. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):867–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90308-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Natomi H., Zhao W. L., Okuzumi K., Sugano K., Iwamori M., Nagai Y. Identification of glycolipid receptors for Helicobacter pylori by TLC-immunostaining. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 6;282(2):385–387. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson R. D., Bernfield M. Molecular polymorphism of a cell surface proteoglycan: distinct structures on simple and stratified epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9562–9566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh M. T., WuDunn D., Montgomery R. I., Esko J. D., Spear P. G. Cell surface receptors for herpes simplex virus are heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1273–1281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Rest R. F. Escherichia coli expressing a Neisseria gonorrhoeae opacity-associated outer membrane protein invade human cervical and endometrial epithelial cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5512–5516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Brown M., Nickel P., Meyer T. F. Opacity genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: control of phase and antigenic variation. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjia K. F., van Putten J. P., Pels E., Zanen H. C. The interaction between Neisseria gonorrhoeae and the human cornea in organ culture. An electron microscopic study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988;226(4):341–345. doi: 10.1007/BF02172964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran Van Nhieu G., Isberg R. R. Bacterial internalization mediated by beta 1 chain integrins is determined by ligand affinity and receptor density. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1887–1895. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Putten J. P., Weel J. F., Grassmé H. U. Measurements of invasion by antibody labeling and electron microscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1994;236:420–437. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)36031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E. The effect of protein II and pili on the interaction of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):503–512. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weel J. F., Hopman C. T., van Putten J. P. In situ expression and localization of Neisseria gonorrhoeae opacity proteins in infected epithelial cells: apparent role of Opa proteins in cellular invasion. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1395–1405. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R., Hök M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans of rat embryo fibroblasts. A hydrophobic form may link cytoskeleton and matrix components. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10872–10879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R. Syndecan 4 heparan sulfate proteoglycan is a selectively enriched and widespread focal adhesion component. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Feb;5(2):183–192. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata M., Saga S., Kato M., Bernfield M., Kimata K. Selective distributions of proteoglycans and their ligands in pericellular matrix of cultured fibroblasts. Implications for their roles in cell-substratum adhesion. J Cell Sci. 1993 Sep;106(Pt 1):55–65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Klagsbrun M., Esko J. D., Leder P., Ornitz D. M. Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90512-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. P., Stephens R. S. Mechanism of C. trachomatis attachment to eukaryotic host cells. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):861–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90296-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Putten J. P., Hopman C. T., Weel J. F. The use of immunogold-silver staining to study antigen variation and bacterial entry into eukaryotic cells by conventional light microscopy. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Sep;33(1):35–41. doi: 10.1099/00222615-33-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Putten J. P. Phase variation of lipopolysaccharide directs interconversion of invasive and immuno-resistant phenotypes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4043–4051. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]