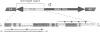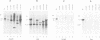Abstract
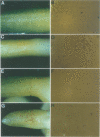
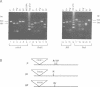
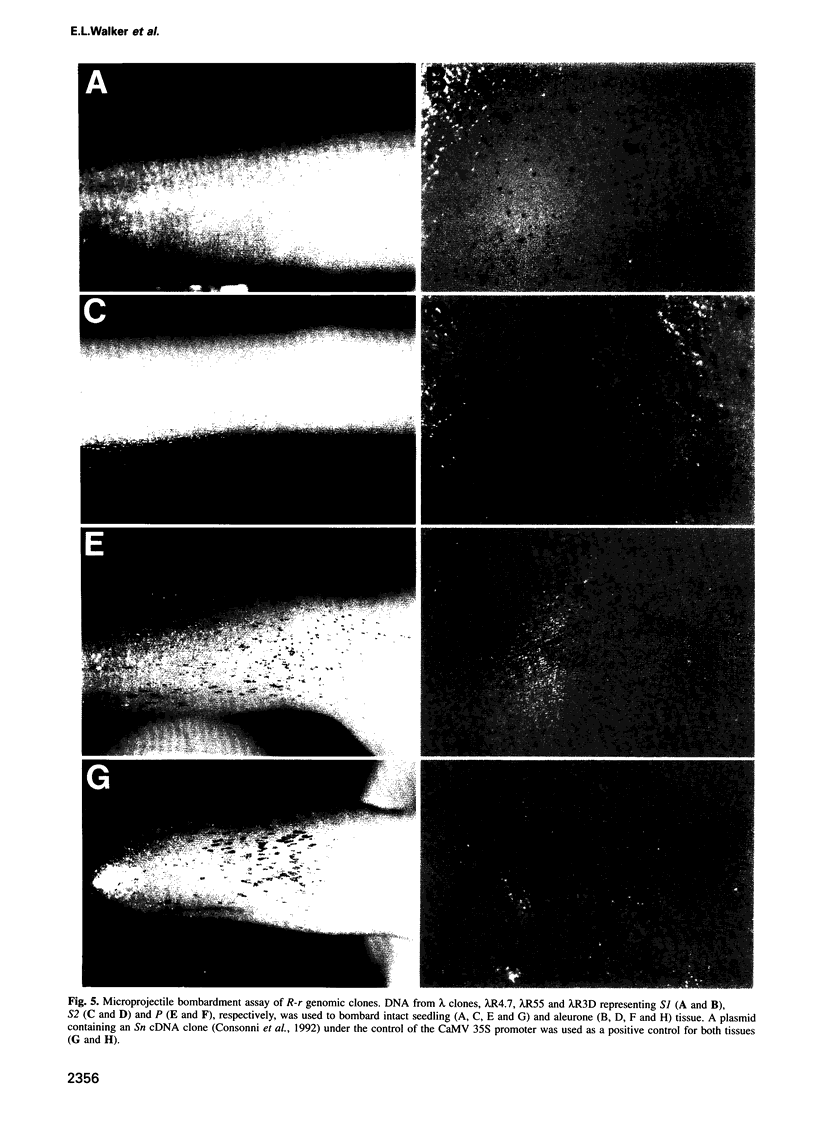
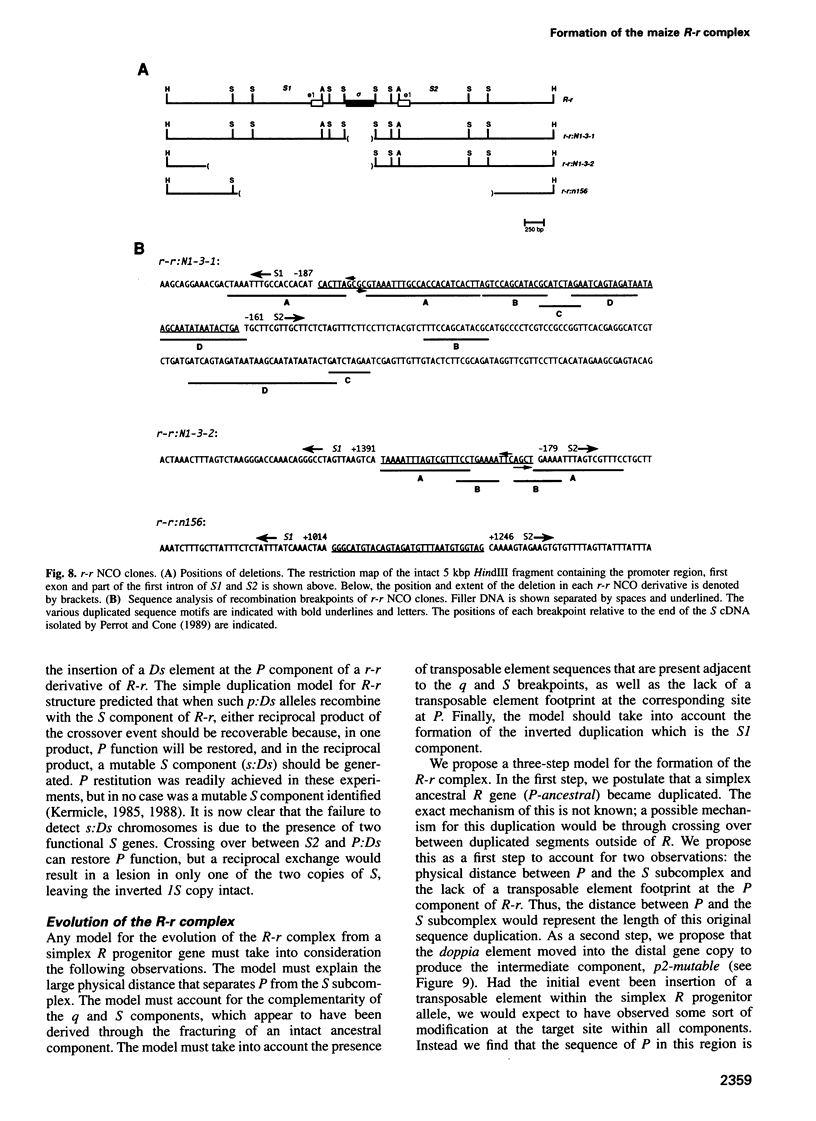
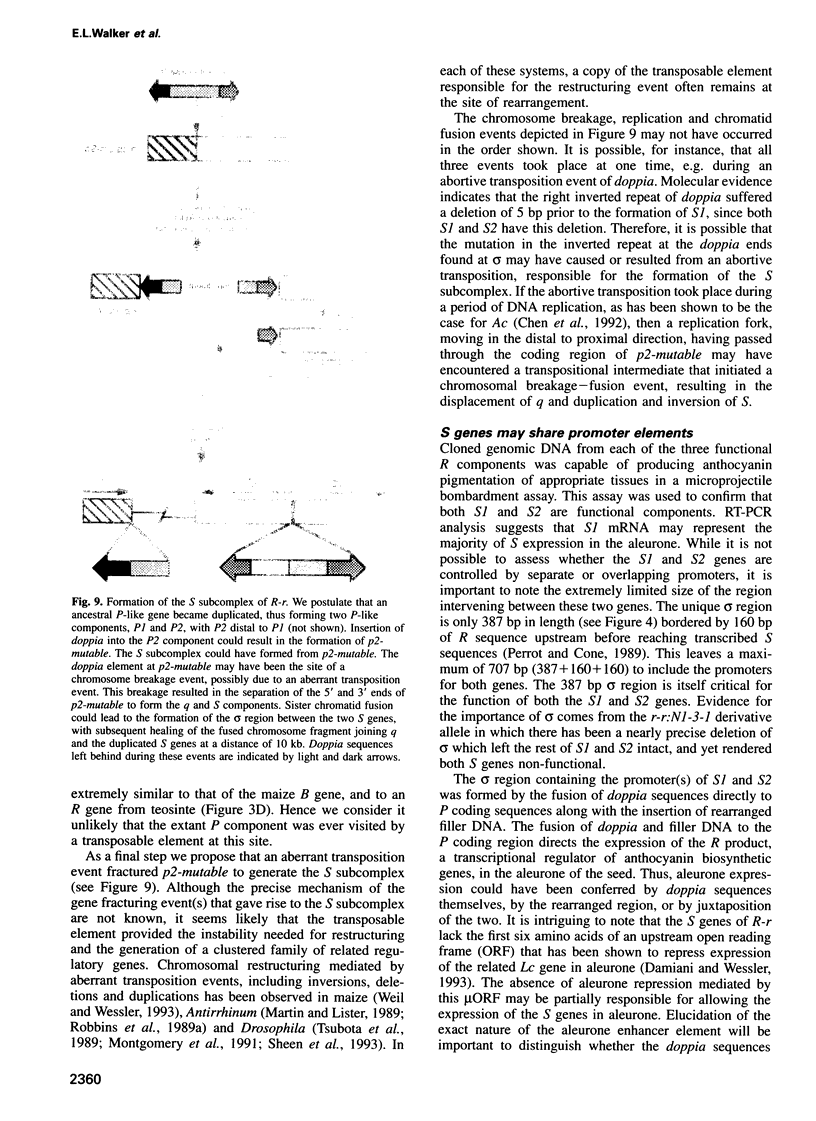
R-r controls the production of anthocyanin pigment in plant parts and the aleurone layer of seeds through the production of a family of related transcriptional activating proteins of the helix-loop-helix type. The R-r complex comprises a series of repeated, homologous components arranged in both direct and inverted orientations. These include the P component, a simple R gene that confers pigmentation of plant parts, and the S subcomplex that consists of a truncated inactive R gene called q, and two functional R genes, S1 and S2, that pigment the aleurone. The S genes are arranged in an unusual inverted head-to-head orientation. The identity of each functional component was confirmed by microprojectile bombardment of intact maize tissues with cloned genomic DNA and by analysis of in vivo mRNA populations. Sequence analysis suggests that the S subcomplex was derived through the rearrangement of a simple P-like progenitor element. At the rearrangement breakpoints, features typical of the CACTA family of transposable elements were found. The location and arrangement of these CACTA element sequences implies that this element may have mediated the chromosomal rearrangements that led to the formation of the R-r complex. The unusual structure of R-r explains much of the meiotic instability of the complex.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Baltimore D. Joining of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene segments: implications from a chromosome with evidence of three D-JH fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4118–4122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Radicella J. P., Robbins T. P., Chen J., Turks D. Two regulatory genes of the maize anthocyanin pathway are homologous: isolation of B utilizing R genomic sequences. Plant Cell. 1989 Dec;1(12):1175–1183. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.12.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Greenblatt I. M., Dellaporta S. L. Molecular analysis of Ac transposition and DNA replication. Genetics. 1992 Mar;130(3):665–676. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Greenblatt I. M., Dellaporta S. L. Transposition of Ac from the P locus of maize into unreplicated chromosomal sites. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):109–116. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocciolone S. M., Cone K. C. Pl-Bh, an anthocyanin regulatory gene of maize that leads to variegated pigmentation. Genetics. 1993 Oct;135(2):575–588. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.2.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone K. C., Cocciolone S. M., Moehlenkamp C. A., Weber T., Drummond B. J., Tagliani L. A., Bowen B. A., Perrot G. H. Role of the regulatory gene pl in the photocontrol of maize anthocyanin pigmentation. Plant Cell. 1993 Dec;5(12):1807–1816. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.12.1807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consonni G., Viotti A., Dellaporta S. L., Tonelli C. cDNA nucleotide sequence of Sn, a regulatory gene in maize. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):373–373. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damiani R. D., Jr, Wessler S. R. An upstream open reading frame represses expression of Lc, a member of the R/B family of maize transcriptional activators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8244–8248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooner H. K., Kermicle J. L. Reconstitution of the R compound allele in maize. Genetics. 1974 Oct;78(2):691–701. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.2.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooner H. K., Kermicle J. L. Structure of the R tandem duplication in maize. Genetics. 1971 Mar;67(3):427–436. doi: 10.1093/genetics/67.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooner H. K., Robbins T. P., Jorgensen R. A. Genetic and developmental control of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:173–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Klein T. M., Roth B. A., Fromm M. E., Cone K. C., Radicella J. P., Chandler V. L. Transactivation of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes following transfer of B regulatory genes into maize tissues. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2517–2522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau N. R., Schatz D. G., Rosa M., Baltimore D. Increased frequency of N-region insertion in a murine pre-B-cell line infected with a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase retroviral expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3237–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig S. R., Bowen B., Beach L., Wessler S. R. A regulatory gene as a novel visible marker for maize transformation. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):449–450. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4941.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig S. R., Habera L. F., Dellaporta S. L., Wessler S. R. Lc, a member of the maize R gene family responsible for tissue-specific anthocyanin production, encodes a protein similar to transcriptional activators and contains the myc-homology region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7092–7096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C., Lister C. Genome juggling by transposons: Tam3-induced rearrangements in Antirrhinum majus. Dev Genet. 1989;10(6):438–451. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020100605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery E. A., Huang S. M., Langley C. H., Judd B. H. Chromosome rearrangement by ectopic recombination in Drosophila melanogaster: genome structure and evolution. Genetics. 1991 Dec;129(4):1085–1098. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.4.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrot G. H., Cone K. C. Nucleotide sequence of the maize R-S gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):8003–8003. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.8003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston E. J., English J. J., Dooner H. K. Sequence of three bronze alleles of maize and correlation with the genetic fine structure. Genetics. 1988 May;119(1):185–197. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins T. P., Carpenter R., Coen E. S. A chromosome rearrangement suggests that donor and recipient sites are associated during Tam3 transposition in Antirrhinum majus. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):5–13. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins T. P., Walker E. L., Kermicle J. L., Alleman M., Dellaporta S. L. Meiotic instability of the R-r complex arising from displaced intragenic exchange and intrachromosomal rearrangement. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):271–283. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Chang X. B., Wilson J. H. Comparison of filler DNA at immune, nonimmune, and oncogenic rearrangements suggests multiple mechanisms of formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3049–3057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Porter T. N., Wilson J. H. Mechanisms of nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler L J, Emmerling M H. Relation of Unequal Crossing over to the Interdependence of R Elements (P) and (S). Genetics. 1956 Jan;41(1):124–137. doi: 10.1093/genetics/41.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonelli C., Consonni G., Dolfini S. F., Dellaporta S. L., Viotti A., Gavazzi G. Genetic and molecular analysis of Sn, a light-inducible, tissue specific regulatory gene in maize. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Mar;225(3):401–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00261680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubota S. I., Rosenberg D., Szostak H., Rubin D., Schedl P. The cloning of the Bar region and the B breakpoint in Drosophila melanogaster: evidence for a transposon-induced rearrangement. Genetics. 1989 Aug;122(4):881–890. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.4.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil C. F., Wessler S. R. Molecular evidence that chromosome breakage by Ds elements is caused by aberrant transposition. Plant Cell. 1993 May;5(5):515–522. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.5.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S., Tarpley A., Purugganan M., Spell M., Okagaki R. Filler DNA is associated with spontaneous deletions in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8731–8735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]