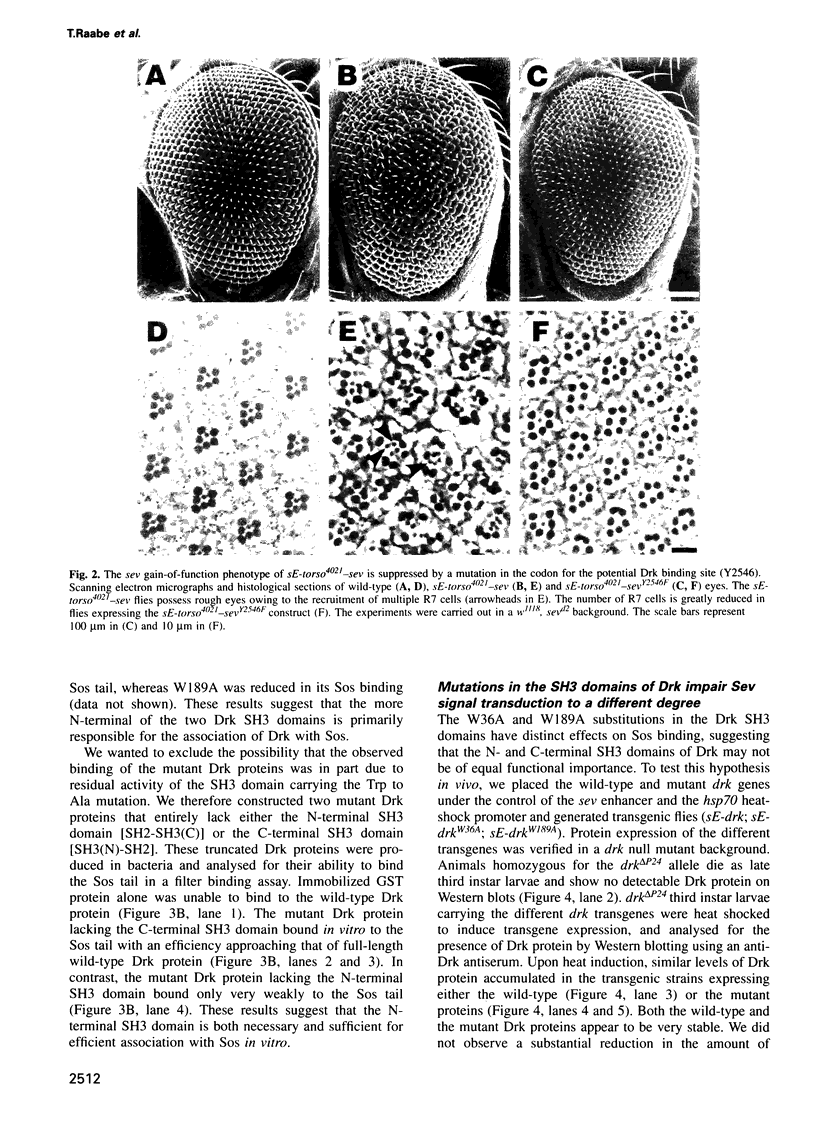
Abstract
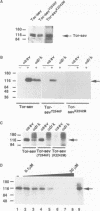
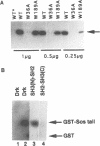
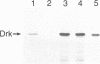
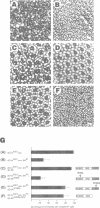
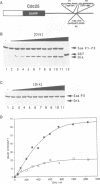
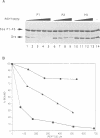
The Drk SH3-SH2-SH3 adaptor protein has been genetically identified in a screen for rate-limiting components acting downstream of the Sevenless (Sev) receptor tyrosine kinase in the developing eye of Drosophila. It provides a link between the activated Sev receptor and Sos, a guanine nucleotide release factor that activates Ras1. We have used a combined biochemical and genetic approach to study the interactions between Sev, Drk and Sos. We show that Tyr2546 in the cytoplasmic tail of Sev is required for Drk binding, probably because it provides a recognition site for the Drk SH2 domain. Interestingly, a mutation at this site does not completely block Sev function in vivo. This may suggest that Sev can signal in a Drk-independent, parallel pathway or that Drk can also bind to an intermediate docking protein. Analysis of the Drk-Sos interaction has identified a high affinity binding site for Drk SH3 domains in the Sos tail. We show that the N-terminal Drk SH3 domain is primarily responsible for binding to the tail of Sos in vitro, and for signalling to Ras in vivo.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltensperger K., Kozma L. M., Cherniack A. D., Klarlund J. K., Chawla A., Banerjee U., Czech M. P. Binding of the Ras activator son of sevenless to insulin receptor substrate-1 signaling complexes. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1950–1952. doi: 10.1126/science.8391166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Christen B., Hafen E. Ligand-independent activation of the sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase changes the fate of cells in the developing Drosophila eye. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1069–1081. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90262-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Hafen E. Control of photoreceptor cell fate by the sevenless protein requires a functional tyrosine kinase domain. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):299–311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A. M., Tang T. L., Sugimoto S., Walsh C. T., Neel B. G. Protein-tyrosine-phosphatase SHPTP2 couples platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta to Ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7335–7339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaikie P., Immanuel D., Wu J., Li N., Yajnik V., Margolis B. A region in Shc distinct from the SH2 domain can bind tyrosine-phosphorylated growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32031–32034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90146-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. G., Stern M. J., Horvitz H. R. C. elegans cell-signalling gene sem-5 encodes a protein with SH2 and SH3 domains. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):340–344. doi: 10.1038/356340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Benjumea F. J., Hafen E. The sevenless signalling cassette mediates Drosophila EGF receptor function during epidermal development. Development. 1994 Mar;120(3):569–578. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.3.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson B., Sprenger F., Hafen E. Prepattern in the developing Drosophila eye revealed by an activated torso--sevenless chimeric receptor. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2327–2339. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle H. J., Bishop J. M. Torso, a receptor tyrosine kinase required for embryonic pattern formation, shares substrates with the sevenless and EGF-R pathways in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):633–646. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Giddings B. W., Brooks M. W., Buday L., Sizeland A. M., Weinberg R. A. Association of Sos Ras exchange protein with Grb2 is implicated in tyrosine kinase signal transduction and transformation. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):45–51. doi: 10.1038/363045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Hui C. C., Pawson T. SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase as a target of protein-tyrosine kinases. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1607–1611. doi: 10.1126/science.8096088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Chen J. K., Yu H., Simon J. A., Schreiber S. L. Two binding orientations for peptides to the Src SH3 domain: development of a general model for SH3-ligand interactions. Science. 1994 Nov 18;266(5188):1241–1247. doi: 10.1126/science.7526465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gout I., Dhand R., Hiles I. D., Fry M. J., Panayotou G., Das P., Truong O., Totty N. F., Hsuan J., Booker G. W. The GTPase dynamin binds to and is activated by a subset of SH3 domains. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):25–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I., Rubin G. M. Making a difference: the role of cell-cell interactions in establishing separate identities for equivalent cells. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90470-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanaugh W. M., Williams L. T. An alternative to SH2 domains for binding tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. Science. 1994 Dec 16;266(5192):1862–1865. doi: 10.1126/science.7527937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Weber U., Gehring W. J. The white gene as a marker in a new P-element vector for gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):3947–3959. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama S., Yu H., Dalgarno D. C., Shin T. B., Zydowsky L. D., Schreiber S. L. Structure of the PI3K SH3 domain and analysis of the SH3 family. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):945–952. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90582-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Cagan R. L., Zipursky S. L. Interaction of bride of sevenless membrane-bound ligand and the sevenless tyrosine-kinase receptor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):207–212. doi: 10.1038/352207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letwin K., Yee S. P., Pawson T. Novel protein-tyrosine kinase cDNAs related to fps/fes and eph cloned using anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):621–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Nishimura R., Kashishian A., Batzer A. G., Kim W. J., Cooper J. A., Schlessinger J. A new function for a phosphotyrosine phosphatase: linking GRB2-Sos to a receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):509–517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim W. A., Richards F. M., Fox R. O. Structural determinants of peptide-binding orientation and of sequence specificity in SH3 domains. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):375–379. doi: 10.1038/372375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein E. J., Daly R. J., Batzer A. G., Li W., Margolis B., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Skolnik E. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Schlessinger J. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90167-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marengere L. E., Songyang Z., Gish G. D., Schaller M. D., Parsons J. T., Stern M. J., Cantley L. C., Pawson T. SH2 domain specificity and activity modified by a single residue. Nature. 1994 Jun 9;369(6480):502–505. doi: 10.1038/369502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. MAP kinase kinase kinase, MAP kinase kinase and MAP kinase. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier J. P., Raabe T., Henkemeyer M., Dickson B., Mbamalu G., Margolis B., Schlessinger J., Hafen E., Pawson T. A Drosophila SH2-SH3 adaptor protein implicated in coupling the sevenless tyrosine kinase to an activator of Ras guanine nucleotide exchange, Sos. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90170-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Gish G. D. SH2 and SH3 domains: from structure to function. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci G., Lanfrancone L., Grignani F., McGlade J., Cavallo F., Forni G., Nicoletti I., Grignani F., Pawson T., Pelicci P. G. A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2 domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90536-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins L. A., Larsen I., Perrimon N. corkscrew encodes a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase that functions to transduce the terminal signal from the receptor tyrosine kinase torso. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90098-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronk G. J., McGlade J., Pelicci G., Pawson T., Bos J. L. Insulin-induced phosphorylation of the 46- and 52-kDa Shc proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5748–5753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinke R., Zipursky S. L. Cell-cell interaction in the Drosophila retina: the bride of sevenless gene is required in photoreceptor cell R8 for R7 cell development. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Preston C. R., Phillis R. W., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Benz W. K., Engels W. R. A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):461–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozakis-Adcock M., Fernley R., Wade J., Pawson T., Bowtell D. The SH2 and SH3 domains of mammalian Grb2 couple the EGF receptor to the Ras activator mSos1. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):83–85. doi: 10.1038/363083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozakis-Adcock M., McGlade J., Mbamalu G., Pelicci G., Daly R., Li W., Batzer A., Thomas S., Brugge J., Pelicci P. G. Association of the Shc and Grb2/Sem5 SH2-containing proteins is implicated in activation of the Ras pathway by tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):689–692. doi: 10.1038/360689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaife R., Gout I., Waterfield M. D., Margolis R. L. Growth factor-induced binding of dynamin to signal transduction proteins involves sorting to distinct and separate proline-rich dynamin sequences. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2574–2582. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Bowtell D. D., Dodson G. S., Laverty T. R., Rubin G. M. Ras1 and a putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor perform crucial steps in signaling by the sevenless protein tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):701–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Dodson G. S., Rubin G. M. An SH3-SH2-SH3 protein is required for p21Ras1 activation and binds to sevenless and Sos proteins in vitro. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90169-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Batzer A., Li N., Lee C. H., Lowenstein E., Mohammadi M., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. The function of GRB2 in linking the insulin receptor to Ras signaling pathways. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1953–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.8316835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Lee C. H., Batzer A., Vicentini L. M., Zhou M., Daly R., Myers M. J., Jr, Backer J. M., Ullrich A., White M. F. The SH2/SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 interacts with tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS1 and Shc: implications for insulin control of ras signalling. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1929–1936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., McGlade J., Olivier P., Pawson T., Bustelo X. R., Barbacid M., Sabe H., Hanafusa H., Yi T. Specific motifs recognized by the SH2 domains of Csk, 3BP2, fps/fes, GRB-2, HCP, SHC, Syk, and Vav. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2777–2785. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger F., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Torso receptor activity is regulated by a diffusible ligand produced at the extracellular terminal regions of the Drosophila egg. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):987–1001. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90394-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Bowtell D. D., Hafen E., Rubin G. M. Localization of the sevenless protein, a putative receptor for positional information, in the eye imaginal disc of Drosophila. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Ready D. F. Sevenless: a cell-specific homeotic mutation of the Drosophila eye. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4736.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valius M., Kazlauskas A. Phospholipase C-gamma 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase are the downstream mediators of the PDGF receptor's mitogenic signal. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):321–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90232-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W., Lammers R., Huang J., Ullrich A. Activation of a phosphotyrosine phosphatase by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1611–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.7681217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittekind M., Mapelli C., Farmer B. T., 2nd, Suen K. L., Goldfarb V., Tsao J., Lavoie T., Barbacid M., Meyers C. A., Mueller L. Orientation of peptide fragments from Sos proteins bound to the N-terminal SH3 domain of Grb2 determined by NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 22;33(46):13531–13539. doi: 10.1021/bi00250a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Geer P., Hunter T. Mutation of Tyr697, a GRB2-binding site, and Tyr721, a PI 3-kinase binding site, abrogates signal transduction by the murine CSF-1 receptor expressed in Rat-2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5161–5172. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]