Abstract
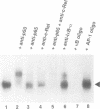
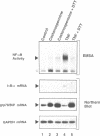
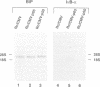
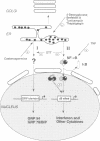
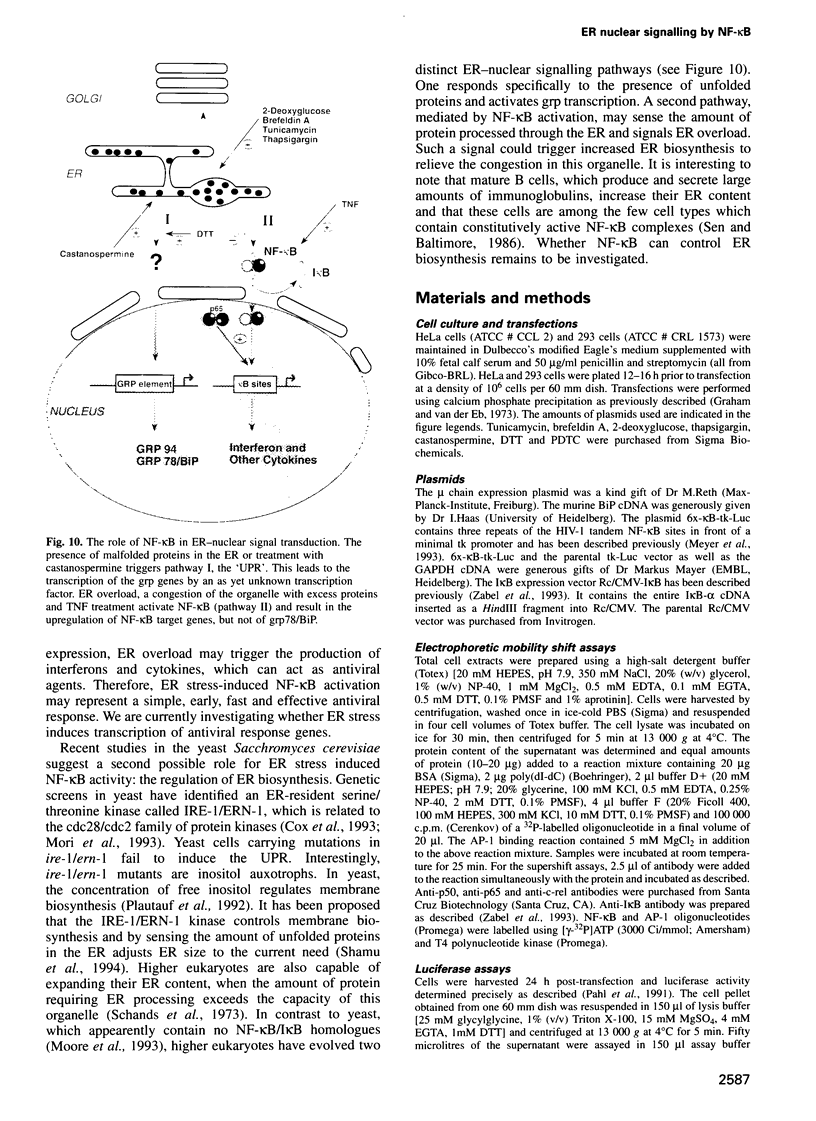
The inducible, higher eukaryotic transcription factor NF-kappa B is activated by a variety of external stimuli including inflammatory cytokines, viral and bacterial infection and UV irradiation. Here we show that internal stress, caused by the accumulation of proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), also induces NF-kappa B DNA binding as well as kappa B-dependent gene expression. This was observed upon expression of immunoglobulin mu chains in the absence of light chains and by treatment of cells with several agents known to cause ER stress, such as tunicamycin, brefeldin A, 2-deoxyglucose and thapsigsargin. The transcription factor AP-1 was weakly induced under similar conditions. Overexpression of NF-kappa B subunits did not influence expression of the gene encoding grp78/BiP, a protein induced by various forms of ER stress. Likewise, the glucosidase inhibitor castanospermine, which induced grp78/BiP expression, failed to activate NF-kappa B, while the antioxidant dithiothreitol augmented grp78/BiP expression but prevented activation of NF-kappa B. Hence, NF-kappa B participates in a novel ER-nuclear signal transduction pathway distinct from the unfolded-protein-response described previously. We provide evidence that the ER can produce at least two distinct signals in response to a functional impairment. One is emitted by the presence of unfolded proteins, the other in response to overloading of the organelle, for example through the overexpression of secretory proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Finco T. S., Nantermet P. V., Baldwin A. S., Jr Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: a mechanism for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3301–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Ruben S. M., Scheinman R. I., Haskill S., Rosen C. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr I kappa B interacts with the nuclear localization sequences of the subunits of NF-kappa B: a mechanism for cytoplasmic retention. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1899–1913. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K., Park S., Kanno T., Franzoso G., Siebenlist U. Mutual regulation of the transcriptional activator NF-kappa B and its inhibitor, I kappa B-alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2532–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. C., Erwin A. E., Lee A. S. Glucose-regulated protein (GRP94 and GRP78) genes share common regulatory domains and are coordinately regulated by common trans-acting factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2153–2162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Baker A., Saltik M., Wagner E., Buschle M. Lipopolysaccharide is a frequent contaminant of plasmid DNA preparations and can be toxic to primary human cells in the presence of adenovirus. Gene Ther. 1994 Jul;1(4):239–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. S., Shamu C. E., Walter P. Transcriptional induction of genes encoding endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins requires a transmembrane protein kinase. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90648-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duksin D., Mahoney W. C. Relationship of the structure and biological activity of the natural homologues of tunicamycin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3105–3109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Inhibitors of the biosynthesis and processing of N-linked oligosaccharide chains. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:497–534. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Oda K., Yokota S., Takatsuki A., Ikehara Y. Brefeldin A causes disassembly of the Golgi complex and accumulation of secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18545–18552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Machleidt T., Alkalay I., Krönke M., Ben-Neriah Y., Baeuerle P. A. Rapid proteolysis of I kappa B-alpha is necessary for activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):182–185. doi: 10.1038/365182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Kim K. S., Lee A. S. Regulation of the glucose-regulated protein genes by beta-mercaptoethanol requires de novo protein synthesis and correlates with inhibition of protein glycosylation. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Dec;133(3):553–559. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozutsumi Y., Segal M., Normington K., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. The presence of malfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum signals the induction of glucose-regulated proteins. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):462–464. doi: 10.1038/332462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. S., Bell J., Ting J. Biochemical characterization of the 94- and 78-kilodalton glucose-regulated proteins in hamster fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4616–4621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
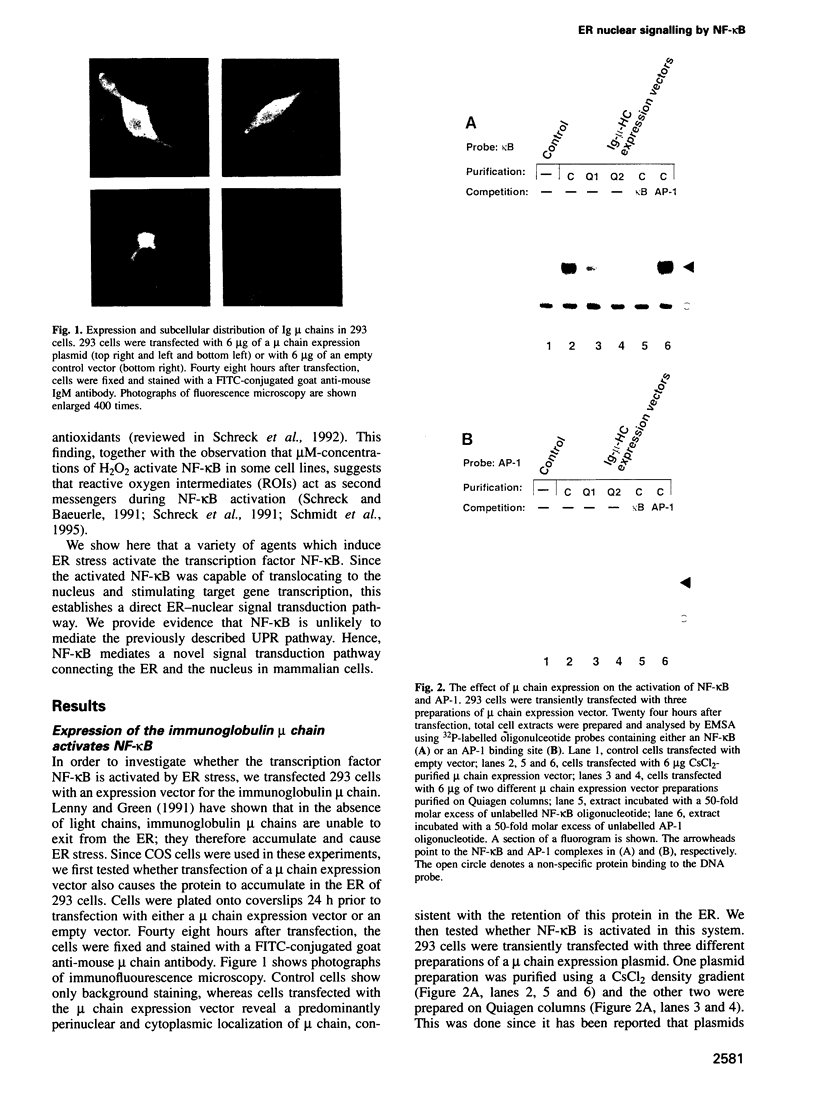
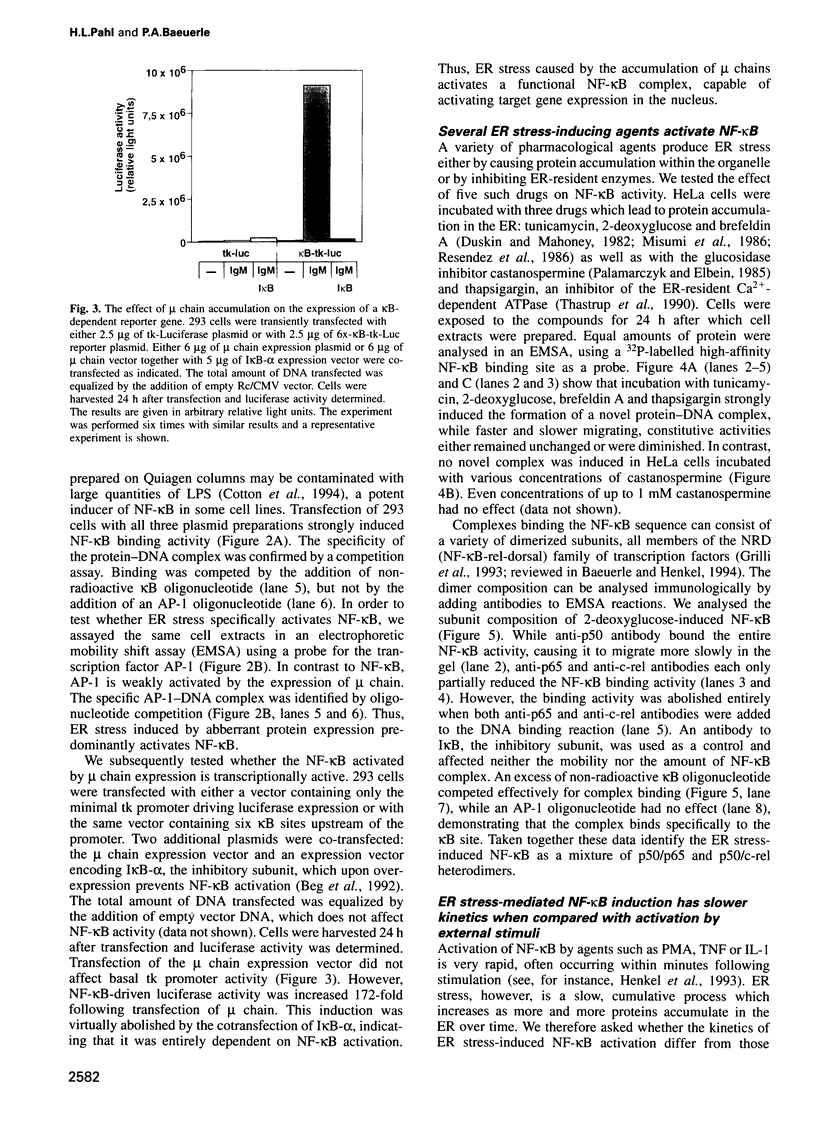
- Lenny N., Green M. Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress proteins in COS cells transfected with immunoglobulin mu heavy chain cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20532–20537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. W., Sistonen L., Morimoto R. I., Lee A. S. Stress induction of the mammalian GRP78/BiP protein gene: in vivo genomic footprinting and identification of p70CORE from human nuclear extract as a DNA-binding component specific to the stress regulatory element. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5533–5546. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2005–2015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Misumi Y., Miki K., Takatsuki A., Tamura G., Ikehara Y. Novel blockade by brefeldin A of intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. A., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Conservation of transcriptional activation functions of the NF-kappa B p50 and p65 subunits in mammalian cells and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1666–1674. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Ma W., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. A transmembrane protein with a cdc2+/CDC28-related kinase activity is required for signaling from the ER to the nucleus. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):743–756. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90521-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Sant A., Kohno K., Normington K., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. F. A 22 bp cis-acting element is necessary and sufficient for the induction of the yeast KAR2 (BiP) gene by unfolded proteins. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2583–2593. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05323.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahl H. L., Baeuerle P. A. Expression of influenza virus hemagglutinin activates transcription factor NF-kappa B. J Virol. 1995 Mar;69(3):1480–1484. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.3.1480-1484.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahl H. L., Burn T. C., Tenen D. G. Optimization of transient transfection into human myeloid cell lines using a luciferase reporter gene. Exp Hematol. 1991 Nov;19(10):1038–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palamarczyk G., Elbein A. D. The effect of castanospermine on the oligosaccharide structures of glycoproteins from lymphoma cell lines. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):795–804. doi: 10.1042/bj2270795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price B. D., Mannheim-Rodman L. A., Calderwood S. K. Brefeldin A, thapsigargin, and AIF4- stimulate the accumulation of GRP78 mRNA in a cycloheximide dependent manner, whilst induction by hypoxia is independent of protein synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Sep;152(3):545–552. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041520314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resendez E., Jr, Ting J., Kim K. S., Wooden S. K., Lee A. S. Calcium ionophore A23187 as a regulator of gene expression in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2145–2152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt K. N., Amstad P., Cerutti P., Baeuerle P. A. The roles of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide as messengers in the activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Chem Biol. 1995 Jan;2(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/1074-5521(95)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Baeuerle P. A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3805–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. A role for oxygen radicals as second messengers. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;1(2-3):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90072-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Meier B., Männel D. N., Dröge W., Baeuerle P. A. Dithiocarbamates as potent inhibitors of nuclear factor kappa B activation in intact cells. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1181–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Rieber P., Baeuerle P. A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2247–2258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamu C. E., Cox J. S., Walter P. The unfolded-protein-response pathway in yeast. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;4(2):56–60. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Peavy D. L., Smith R. T. Differential morphology of mouse spleen cells stimulated in vitro by endotoxin, phytohemagglutinin, pokeweed mitogen and staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jan;70(1):1–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Ganchi P. A., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1912–1915. doi: 10.1126/science.8096091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Ganchi P. A., Béraud C., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. Autoregulation of the NF-kappa B transactivator RelA (p65) by multiple cytoplasmic inhibitors containing ankyrin motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1346–1350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Hanley M. R., Dawson A. P. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Schulz M. F., Vassalli P. Bone marrow pre-B lymphocytes synthesize immunoglobulin mu chains of membrane type with different properties and intracellular pathways. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):361–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thévenin C., Kim S. J., Rieckmann P., Fujiki H., Norcross M. A., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S., Kehrl J. H. Induction of nuclear factor-kappa B and the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by okadaic acid, a specific inhibitor of phosphatases 1 and 2A. New Biol. 1990 Sep;2(9):793–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting J., Lee A. S. Human gene encoding the 78,000-dalton glucose-regulated protein and its pseudogene: structure, conservation, and regulation. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):275–286. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong-Starkesen S. E., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Signaling through T lymphocyte surface proteins, TCR/CD3 and CD28, activates the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):702–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traenckner E. B., Wilk S., Baeuerle P. A. A proteasome inhibitor prevents activation of NF-kappa B and stabilizes a newly phosphorylated form of I kappa B-alpha that is still bound to NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 15;13(22):5433–5441. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06878.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watowich S. S., Morimoto R. I. Complex regulation of heat shock- and glucose-responsive genes in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):393–405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooden S. K., Li L. J., Navarro D., Qadri I., Pereira L., Lee A. S. Transactivation of the grp78 promoter by malfolded proteins, glycosylation block, and calcium ionophore is mediated through a proximal region containing a CCAAT motif which interacts with CTF/NF-I. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5612–5623. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F. S., Park Y. C., Roufa D., Martonosi A. Selective stimulation of the synthesis of an 80,000-dalton protein by calcium ionophores. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5309–5312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Henkel T., Silva M. S., Baeuerle P. A. Nuclear uptake control of NF-kappa B by MAD-3, an I kappa B protein present in the nucleus. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):201–211. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martin R., Vanhove B., Cheng Q., Hofer E., Csizmadia V., Winkler H., Bach F. H. Cytokine-inducible expression in endothelial cells of an I kappa B alpha-like gene is regulated by NF kappa B. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2773–2779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]