Abstract
Background. Neck/shoulder pain is a common musculoskeletal disorder among adults. The pain is often assumed to be related to muscular tenderness rather than serious chronic disease. Aim. To determine the association between neck/shoulder pain intensity and trapezius muscle tenderness in office workers. Methods. 653 employees from two large office workplaces in Copenhagen, Denmark, replied to a questionnaire on health and working conditions (mean: age 43 years, body mass index 24 kg·m−2, computer use 90% of work time, 73% women). Respondents rated intensity of neck/shoulder pain during the previous three months on a scale of 0–10 and palpable tenderness of the upper trapezius muscle on a scale of “no tenderness,” “some tenderness,” or “severe tenderness.” Odds ratios for tenderness as a function of neck/shoulder pain intensity were determined using cumulative logistic regression controlled for age, gender, and chronic disease. Results. The prevalence of “no,” “some,” and “severe” tenderness of the trapezius muscle was 18%, 59%, and 23% in women and 51%, 42%, and 7% in men, respectively (chi-square, P < 0.0001). Participants with “no,” “some,” and “severe” tenderness of the trapezius muscle, respectively, rated their neck/shoulder pain intensity to 1.5 (SD 1.6), 3.8 (SD 2.0), and 5.7 (SD 1.9) for women and 1.4 (SD 1.4), 3.1 (SD 2.2), and 5.1 (SD 1.7) for men. For every unit increase in neck/shoulder pain intensity, the OR for one unit increase in trapezius tenderness was 1.86 (95% confidence interval 1.70 to 2.04). Conclusion. In office workers, a strong association between perceived neck/shoulder pain intensity and trapezius muscle tenderness exists. The present study provides reference values of pain intensity among office workers with no, some, and severe tenderness of the trapezius muscle.
1. Introduction
Approximately a third of working-age adults are regularly bothered by neck pain [1], and every other office worker experiences neck/shoulder pain on a weekly basis [2, 3]. Musculoskeletal disorders of the neck and shoulder in office workers are likely influenced by prolonged static working positions [4], leading to continuous activity of low-threshold motor units, reduced local blood flow, accumulation of Ca2+, and other homeostatic changes in the active muscle fibers [5, 6]. Thus, pain symptoms appear to worsen during prolonged static muscle activity and repetitive job tasks [7, 8]. The associated costs are enormous, as white-collar workers with neck/shoulder pain have a 35% increased risk of long-term sickness absence [9].
Many people experience soreness of the neck/shoulder muscles after prolonged computer work. The soreness presents in different neck/shoulder muscles, for example, the trapezius, levator scapulae, neck extensors, and infraspinatus [10, 11]. For some people the soreness and pain aggravates over time and becomes chronic. Clinical research has confirmed that the most common type of neck/shoulder pain in computer workers is associated with tenderness of the muscles, that is, myalgia [12]. In a small sample of elderly computer workers with neck/shoulder pain 38% had trapezius myalgia [12]. However, a more detailed relationship between neck/shoulder pain intensity and trapezius muscle tenderness remains unclear.
The aim of the present study is to determine associations between neck/shoulder pain intensity and trapezius muscle tenderness in office workers.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
The present questionnaire survey was conducted in June 2009 as part of a randomised controlled trial [13], which was approved by the local ethical committee of Copenhagen and Frederiksberg (HC2008103). The study was registered at the Danish Data Protection Agency (registration number 2009-54-0737). The questionnaire on health and working conditions went out to 1094 employees at two large office workplaces in Copenhagen, Denmark, and 653 (60%) replied (mean: age, 43 years; body mass index, 24 kg·m−2; and computer use, 90% of work time, 27/73% men/women).
2.2. Questionnaire Survey
Participants rated average neck/shoulder pain during the last three months on a numerical rating scale from 0 to 10, where 0 is “no pain” and 10 is “worst imaginable pain.” The rating scale was horizontally oriented to represent a modified visual-analogue scale [14]. A drawing from the Nordic Questionnaire defined the neck/shoulder area [15].
Participants were asked to manually palpate the muscle between the neck and shoulder (i.e., the midportion of the upper trapezius muscle) using a light squeeze with the opposite hand as shown by a picture and to rate tenderness on a scale of “no tenderness,” “some tenderness,” and “severe tenderness.” The actual force of the squeeze was not measured, but a pilot test in our lab showed that a light squeeze corresponded to approximately 20 N for most individuals as validated by squeezing lightly on a scale. Further, typical squeeze time ranged from 4 to 6 seconds.
Participants were also asked whether they had hypertension, heart disease, stroke, spinal disorders, fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, or problems due to traumatic injury. Participants were defined as having chronic disease when replying yes to one or more of these questions.
2.3. Statistics
Neck/shoulder pain intensity and prevalence of “no,” “some,” and “severe” tenderness, respectively, of the trapezius muscle were plotted on an x-y axis, and associations were fitted with a 2nd order polynomial. Additionally, the odds ratio for tenderness as a function of neck/shoulder pain intensity was determined using cumulative logistic regression controlled for age, gender, and chronic disease (Proc Logistic of SAS version 9.2). Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated with tenderness as the dependent variables and neck pain intensity, age, gender, and chronic disease were calculated as independent variables.
3. Results
Table 1 shows demographics and neck/shoulder pain intensity of the respondents. The prevalence of “no,” “some,” and “severe” tenderness of the trapezius muscle was 18%, 59%, and 23% in women and 51%, 42%, and 7% in men, respectively, with a significant gender-difference (chi-square, P < 0.0001). Participants with “no,” “some,” and “severe” tenderness of the trapezius muscle, respectively, rated their neck/shoulder pain intensity to 1.5 (SD 1.6), 3.8 (SD 2.0), and 5.7 (SD 1.9) for women and 1.4 (SD 1.4), 3.1 (SD 2.2), and 5.1 (SD 1.7) for men.
Table 1.
Demographics and neck/shoulder pain among all men and women of the study as well as men and women with no, some, and severe tenderness, respectively, in the trapezius muscle. The percentage of men and women with tenderness is provided in parentheses next to the number of participants in each category.
| All | No tenderness | Some tenderness | Severe tenderness | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | Men | Women | Men | Women | Men | Women | |
| N = 179 | N = 474 | N = 91 (51%) | N = 88 (18%) | N = 76 (42%) | N = 278 (59%) | N = 12 (7%) | N = 108 (23%) | |
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 43.5 (12.2) | 42.7 (11.8) | 43.9 (12.3) | 44.9 (12.6) | 43.2 (12.7) | 41.7 (11.8) | 41.9 (7.8) | 43.7 (10.9) |
| Height (cm), mean (SD) | 183 (7.0) | 168 (6.2) | 184 (6.6) | 169 (6.0) | 181 (7.4) | 169 (6.0) | 182 (5.9) | 168 (6.7) |
| Weight (kg), mean (SD) | 82.8 (10.5) | 67.4 (12.1) | 84.4 (9.6) | 66.1 (11.5) | 81.1 (11.1) | 67.3 (12.6) | 81.6 (12.0) | 69.0 (11.0) |
| BMI kg (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 24.8 (2.7) | 23.8 (4.2) | 24.9 (2.6) | 23.3 (3.6) | 24.6 (2.7) | 23.6 (4.4) | 24.8 (4.1) | 24.6 (4.2) |
| Neck/shoulder pain intensity (0–10) | 2.4 (2.1) | 3.8 (2.3) | 1.4 (1.4) | 1.5 (1.6) | 3.1 (2.2) | 3.8 (2.0) | 5.1 (1.7) | 5.7 (1.9) |
In the cumulative logistic regression controlled for age, gender, and chronic disease, for every unit increase in neck/shoulder pain intensity, the OR for one unit increase in tenderness was 1.86 (95% confidence interval 1.70 to 2.04). The OR's for the other variables were 1.57 (95% confidence interval 1.07 to 2.30) for chronic disease (reference = no chronic disease), 3.11 (95% confidence interval 2.10 to 4.60) for women (reference = men), and 0.99 for age (95% confidence interval 0.98 to 1.01, n.s.).
Figure 1 shows that the association between neck/shoulder pain intensity and tenderness of the trapezius muscle could be almost perfectly fitted by a 2nd order polynomial (R 2 = 0.94–0.99) with the following equations where y equals the prevalence of trapezius muscle tenderness and x equals neck/shoulder pain intensity:
| (1) |
Figure 1.
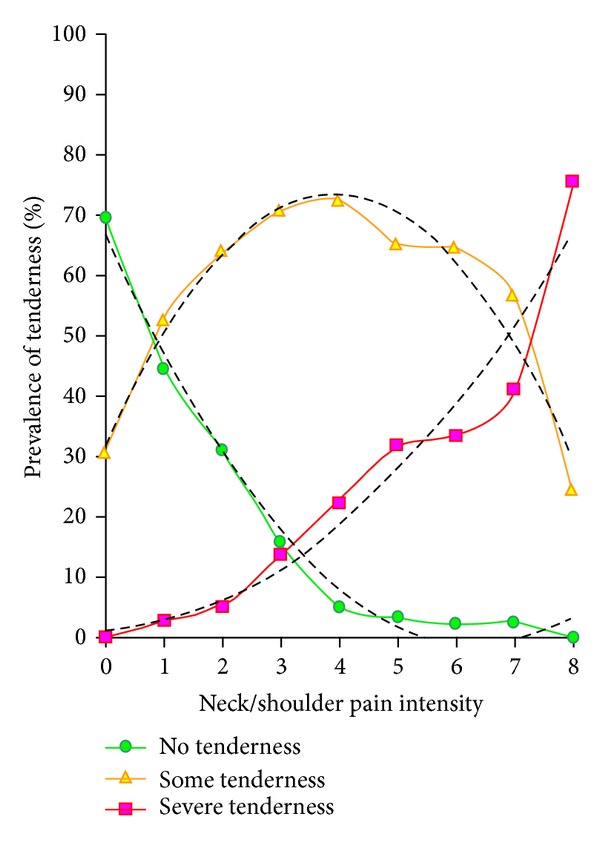
Neck/shoulder pain intensity (x-axis) and prevalence of no, some, and severe tenderness in the trapezius muscle (y-axis) among 653 office workers. The association could be almost perfectly fitted by a 2nd order polynomial (R 2 = 0.94–0.99).
4. Discussion
Our study showed a strong association between perceived neck/shoulder pain intensity and trapezius muscle tenderness in office workers. The present study provides reference values of pain intensity among office workers with no, some, and severe tenderness of the trapezius muscle. The relevance of these findings is discussed below.
Our study shows a strong relationship between neck/shoulder pain and muscle tenderness. This confirms that the majority of neck/shoulder pain is related to myalgia, that is, pain and tenderness of the muscles [10, 12]. Juul-Kristensen and coworkers showed in a small study among 42 elderly computer workers with neck/shoulder pain that 38% had trapezius myalgia, 17% had tension neck syndrome, and 17% had cervicalgia [12]. Andersen and coworkers showed from clinical examination among 198 office workers with frequent neck/shoulder pain, from the total sample of 653 participants of the present study, that more than two-thirds experienced tenderness of the upper trapezius muscle [10].
The present study elaborates on these previous findings by providing reference values of pain intensity among office workers with no, some, and severe tenderness of the trapezius muscle. Thus, women and men with severe tenderness of the trapezius muscle had on average neck/shoulder pain intensities of 5.7 and 5.1, respectively. This knowledge can be used when defining relevant cut-points of pain intensity for inclusion of participants in future studies on neck/shoulder pain. Further, this knowledge can also be used to estimate the proportion of participants with muscle tenderness in studies that assessed only pain intensity, but not palpable tenderness. For instance, a study among the general working population with 1759 blue-collar and 3337 white-collar workers defined neck/shoulder pain cases as those having pain intensities of 4 or more [9]. According to the fitted 2nd order polynomial obtained from the x-y plot in Figure 1 of the present study, the expected prevalence of no, some, and severe tenderness among office workers with a neck/shoulder pain intensity of 4 is 7.9%, 73.5%, and 18.6%, respectively. Thus, it is likely that the majority of the white-collar workers in the previous study by Andersen had trapezius muscle tenderness.
The average differences in neck/shoulder pain intensity between no, some, and severe tenderness ranged between 1.7 and 2.3 on a scale of 0–10. Previous studies have argued that a difference in pain intensity of 1 on a scale of 0–10 is considered the minimally relevant difference in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain, and a difference of 2 is considered to be moderately clinically meaningful [16]. Our study is in line with these findings by showing an approximate difference in pain intensity of 2 within each category on the tenderness scale of no, some, and severe tenderness.
Severe tenderness was more prevalent among women than men (23% versus 7%). This gender difference of tenderness is in line with findings in fibromyalgia patients [17], in workers with chronic neck/shoulder pain [10], in the hand muscles of healthy adults [18], and in the neck/shoulder muscles of healthy adults [19]. Although the exact reason for this gender difference remains unknown [20, 21], there are likely several influential mechanisms including differences in muscle size and testosterone levels. Thus, one study has shown a positive correlation between testosterone and pain thresholds; that is, higher testosterone was associated with less tenderness [22]. This may contribute to explaining the observed gender differences in the present and previous studies.
Our study has both strengths and limitations. The homogenous group of office workers reduces the risk of bias from socioeconomic confounding. However, this also limits the generalizability of our findings to office workers. Future studies should test the generalizability by including also workers with more strenuous work. Further, because all data were obtained from questionnaires, several sources of common method bias may influence the analyses. The most critical source is that information about tenderness and pain intensity has been delivered by the same person, that is, common-rater effects [23]. Controlling for chronic disease in the cumulative logistic regression analysis is a strength as it influences pain perception [24]. Thus, our study clearly shows that—even when controlling for chronic disease—there is a strong association between neck/shoulder pain intensity and trapezius muscle tenderness.
In conclusion, among office workers, a strong association between perceived neck/shoulder pain intensity and trapezius muscle tenderness exists. Further, tenderness was more common among women than men. The present study provides reference values of pain intensity among office workers with no, some, and severe tenderness of the trapezius muscle.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- 1.Andersen LL, Mortensen OS, Hansen JV, Burr H. A prospective cohort study on severe pain as a risk factor for long-term sickness absence in blue- and white-collar workers. Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2011;68(8):590–592. doi: 10.1136/oem.2010.056259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blangsted AK, Søgaard K, Hansen EA, Hannerz H, Sjøgaard G. One-year randomized controlled trial with different physical-activity programs to reduce musculoskeletal symptoms in the neck and shoulders among office workers. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment and Health. 2008;34(1):55–65. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Janwantanakul P, Pensri P, Jiamjarasrangsri V, Sinsongsook T. Prevalence of self-reported musculoskeletal symptoms among office workers. Occupational Medicine. 2008;58(6):436–438. doi: 10.1093/occmed/kqn072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van der Windt DAWM, Thomas E, Pope DP, et al. Occupational risk factors for shoulder pain: a systematic review. Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2000;57(7):433–442. doi: 10.1136/oem.57.7.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Visser B, van Dieen JH. Pathophysiology of upper extremity muscle disorders. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. 2006;16(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2005.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Staal JB, de Bie RA, Hendriks EJM. Aetiology and management of work-related upper extremity disorders. Best Practice and Research: Clinical Rheumatology. 2007;21(1):123–133. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2006.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Buckle P. Ergonomics and musculoskeletal disorders: overview. Occupational Medicine. 2005;55(3):164–167. doi: 10.1093/occmed/kqi081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Blangsted AK, Hansen K, Jensen C. Muscle activity during computer-based office work in relation to self-reported job demands and gender. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2003;89(3-4):352–358. doi: 10.1007/s00421-003-0805-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Andersen LL, Mortensen OS, Hansen JV, Burr H. A prospective cohort study on severe pain as a risk factor for long-term sickness absence in blue- and white-collar workers. Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2011;68(8):590–592. doi: 10.1136/oem.2010.056259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Andersen LL, Hansen K, Mortensen OS, Zebis MK. Prevalence and anatomical location of muscle tenderness in adults with nonspecific neck/shoulder pain. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2011;12, article 169 doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.García-Massó X, Colado JC, Moraes Filho JA. The prophylactic physical exercise for computer users: a review. Fitness & Performance Journal. 2010;9(1):16–25. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Juul-Kristensen B, Kadefors R, Hansen K, Byström P, Sandsjö L, Sjøgaard G. Clinical signs and physical function in neck and upper extremities among elderly female computer users: the NEW study. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2006;96(2):136–145. doi: 10.1007/s00421-004-1220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Andersen LL, Saervoll CA, Mortensen OS, Poulsen OM, Hannerz H, Zebis MK. Effectiveness of small daily amounts of progressive resistance training for frequent neck/shoulder pain: randomised controlled trial. Pain. 2011;152(2):440–446. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pincus T, Bergman M, Sokka T, Roth J, Swearingen C, Yazici Y. Visual analog scales in formats other than a 10 centimeter horizontal line to assess pain and other clinical data. Journal of Rheumatology. 2008;35(8):1550–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kuorinka I, Jonsson B, Kilbom A, et al. Standardised Nordic questionnaires for the analysis of musculoskeletal symptoms. Applied Ergonomics. 1987;18(3):233–237. doi: 10.1016/0003-6870(87)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dworkin RH, Turk DC, McDermott MP, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of group differences in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2009;146(3):238–244. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Maquet D, Croisier J-L, Demoulin C, Crielaard J-M. Pressure pain thresholds of tender point sites in patients with fibromyalgia and in healthy controls. European Journal of Pain. 2004;8(2):111–117. doi: 10.1016/S1090-3801(03)00082-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chesterton LS, Barlas P, Foster NE, Baxter GD, Wright CC. Gender differences in pressure pain threshold in healthy humans. Pain. 2003;101(3):259–266. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3959(02)00330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Binderup AT, Arendt-Nielsen L, Madeleine P. Pressure pain sensitivity maps of the neck-shoulder and the low back regions in men and women. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2010;11, article 234 doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-11-234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hurley RW, Adams MCB. Sex, gender, and pain: an overview of a complex field. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 2008;107(1):309–317. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0b013e31816ba437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Greenspan JD, Craft RM, LeResche L, et al. Studying sex and gender differences in pain and analgesia: a consensus report. Pain. 2007;132(1):S26–S45. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.10.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Choi JC, Chung MI, Lee YD. Modulation of pain sensation by stress-related testosterone and cortisol. Anaesthesia. 2012;67(10):1146–1151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2012.07267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Podsakoff NP. Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annual Review of Psychology. 2012;63:539–569. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Desmeules JA, Cedraschi C, Rapiti E, et al. Neurophysiologic evidence for a central sensitization in patients with fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2003;48(5):1420–1429. doi: 10.1002/art.10893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


