Summary
The R2TP cochaperone complex plays a critical role in the assembly of multisubunit machines, including small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins (snoRNPs), RNA polymerase II, and the mTORC1 and SMG1 kinase complexes, but the molecular basis of substrate recognition remains unclear. Here, we describe a phosphopeptide binding domain (PIH-N) in the PIH1D1 subunit of the R2TP complex that preferentially binds to highly acidic phosphorylated proteins. A cocrystal structure of a PIH-N domain/TEL2 phosphopeptide complex reveals a highly specific phosphopeptide recognition mechanism in which Lys57 and 64 in PIH1D1, along with a conserved DpSDD phosphopeptide motif within TEL2, are essential and sufficient for binding. Proteomic analysis of PIH1D1 interactors identified R2TP complex substrates that are recruited by the PIH-N domain in a sequence-specific and phosphorylation-dependent manner suggestive of a common mechanism of substrate recognition. We propose that protein complexes assembled by the R2TP complex are defined by phosphorylation of a specific motif and recognition by the PIH1D1 subunit.
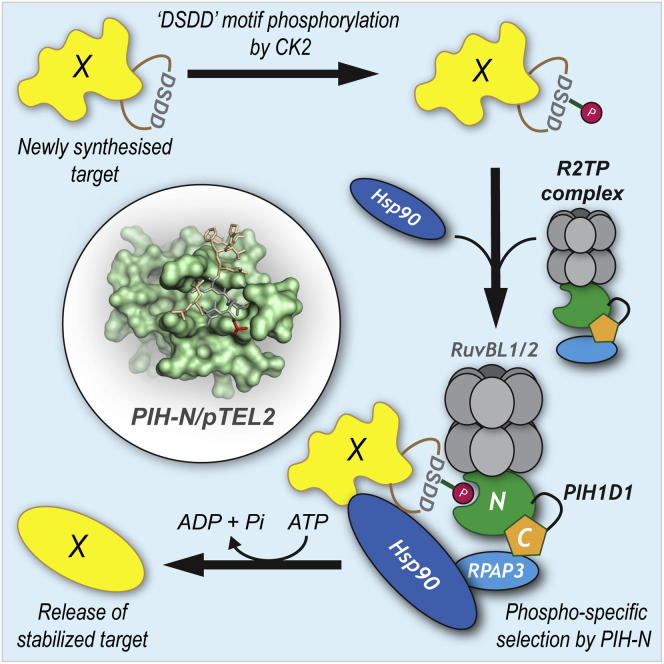
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
-
•
Phosphopeptide binding domain binds pTEL2, but not R2TP, complex components
-
•
PIH-N domain structure reveals the mechanism of pTEL2 interaction
-
•
DpSDD is a minimal consensus sequence for PIH-N domain binding
-
•
Newly identified phosphopeptide-specific interacting partners of PIH1D1
The R2TP complex is an HSP90 cochaperone that facilitates the assembly of large protein and ribonucleoprotein complexes, but the molecular basis of substrate recognition was not known. Now, Hořejší et al. identify a phosphopeptide binding domain (PIH-N) in the PIH1D1 subunit of the R2TP complex. Structural and proteomic analysis of PIH-N reveals that substrates of the R2TP complex are designated by phosphorylation and recognized by the phosphopeptide binding function of the PIH1D1 subunit.
Introduction
Molecular chaperones facilitate the folding and unfolding of polypeptides and are essential for the assembly of large protein complexes (Macario and Conway de Macario, 2005). The R2TP complex was discovered as an HSP90 cochaperone in budding yeast. The human complex consists of four subunits: RUVBL1, RUVBL2, PIH1D1, and RPAP3 (Zhao et al., 2005). RUVBL1 (also known as Pontin, Ruv1, and Tip49a) and RUVBL2 (also known as Reptin, Ruv2, and Tip49b) are essential and highly conserved ATPases that belong to the adenosine triphosphatases associated with multiple activities (AAA+) family. Both possess ATPase and protein and nucleic acid binding activity and are involved in many biological processes, including chromatin remodeling, transcription regulation, ribonucleoprotein complex biogenesis, nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, and the DNA damage response. In the majority of these processes, RUVBL1 and RUVBL2 function as components of larger complexes, such as the R2TP (Jha and Dutta, 2009). RPAP3 contains tetratricopeptide repeats involved in HSP90 binding (Back et al., 2013, Jiménez et al., 2012) and potentially other protein-protein interactions. The last member of the R2TP complex (PIH1D1) contains a predicted structural domain with unknown function. Evidence supports a role for the R2TP complex along with HSP90 in the assembly of a number of multisubunit molecular machines, including small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins (snoRNPs), spliceosomal snRNP U4, RNA polymerase II, and mTORC1 and SMG1 complexes (Ahn et al., 2013, Boulon et al., 2008, Boulon et al., 2010, Horejsí et al., 2010, Kim et al., 2013, Zhao et al., 2008). Nonetheless, a molecular explanation of how the R2TP complex recognizes such diverse substrates remains elusive (Machado-Pinilla et al., 2012). We previously reported that PIH1D1 binds to a casein kinase 2 (CK2)-phosphorylated form of the cochaperone TEL2. TEL2, along with TTI1 and TTI2, forms the TTT complex, which is critical for the assembly of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinases (Hurov et al., 2010, Takai et al., 2010). Our previous study revealed that CK2 phosphorylation of TEL2 is essential for direct binding to PIH1D1, and its disruption leads to the destabilization of mTOR, SMG1, and, to a lesser extent, ATM, ATR, and DNA-PKcs (Horejsí et al., 2010). Given that PIH1D1 is not predicted to contain any of the known phosphopeptide binding domains, such as 14-3-3, FHA, BRCT, WD40, WW, and Polo box domains, it is unclear how it recognizes phosphorylated TEL2 (pTEL2). Furthermore, whether phosphorylation-dependent binding represents a universal substrate recognition mechanism for the R2TP complex has not been previously explored.
Here, we demonstrate that the N-terminal PIH1D1 region PIH-N is a phosphopeptide binding domain structurally unrelated to previously reported phosphopeptide binding proteins that is required for recognition of phosphorylated substrates, whereas the C-terminal region of PIH1D1 binds to the other components of the R2TP complex. The crystal structure of PIH-N domain fragment bound to the phosphorylated TEL2 peptide suggests that the major interacting site for the PIH-N domain is a short conserved DpS491DD motif, previously described as a CK2 phosphorylation site (Ahn et al., 2013, Horejsí et al., 2010). The PIH-N domain contains two conserved residues (Lys57 and Lys64) that directly interact with the TEL2 pSer491 and are essential for binding in vitro and in vivo. Proteomic and in silico screens identified several PIH1D1 phosphorylation-dependent binding partners. Among these, we have confirmed a direct phosphorylation-dependent interaction with human ecdysoneless (ECD), previously implicated in the stabilization of the tumor suppressor p53, mediated by a motif identical to the TEL2 DpSDD sequence.
Results
PIH1D1 Functional Domains
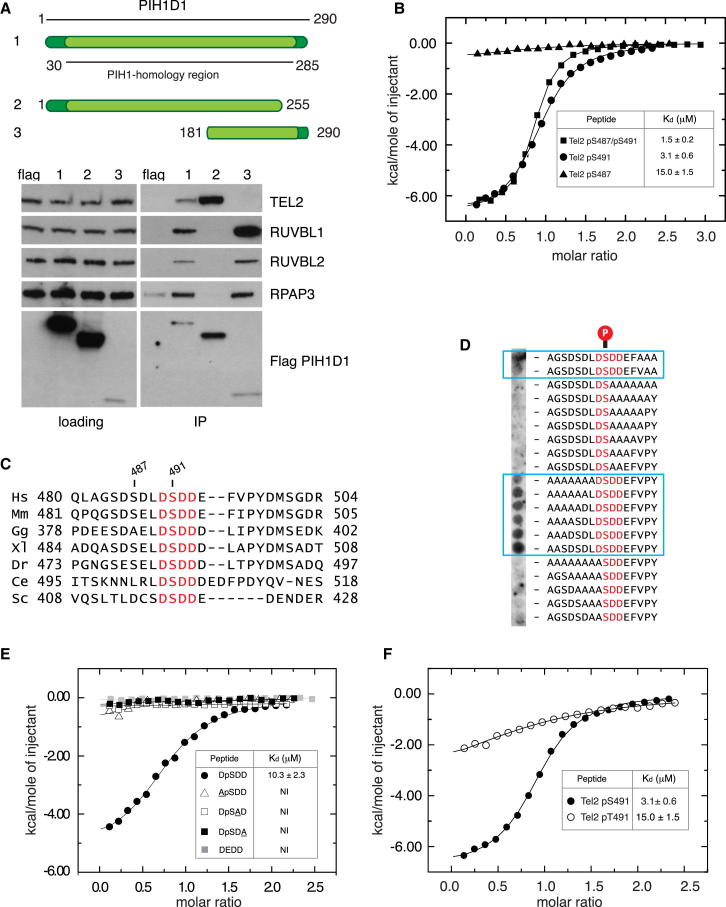
First, to gain insight into the apparent phosphopeptide binding activity of human PIH1D1 and its interactions with R2TP complex components, we performed domain-mapping experiments. Immunoprecipitation studies mapped the binding of phosphorylated TEL2 to a region within the N-terminal ∼250 amino acids of PIH1D1, whereas RUVBL1, RUVBL2, and RPAP3 interacted via a separate region in its C terminus (Figure 1A). Additional sequence homology and limited proteolysis analysis (Figure S1A), coupled with isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) measurements on a series of truncation mutants, was initially used to define a smaller, stable fragment (1–180) that was sufficient to bind to a TEL2 peptide phosphorylated on Ser491 with an affinity of 3.5 μM, comparable to the affinity of other phosphopeptide binding domains for their substrates (Figures 1B and S1C; Table S1) (Lloyd et al., 2009). A diphosphorylated peptide incorporating Ser487 located just upstream of Ser491 bound with ∼2- to 3-fold higher affinity, whereas binding to a peptide phosphorylated only at Ser487 was substantially weaker. Additional removal of the poorly conserved N-terminal region did not detectably compromise interactions (Table S1). Although it has previously been shown that Ser487 and Ser491 are both phosphorylated by CK2 in vivo, Ser487 is not conserved in TEL2 orthologs (Figure 1C), suggesting that CK2 phosphorylation of Ser491 constitutes the switch for TEL2 recognition by PIH1D1 and its orthologs in all eukaryotes. Furthermore, sequence comparison reveals that Ser491 in human TEL2 is embedded in an absolutely conserved DpSDD motif (Figure 1C), and, accordingly, “pep-spot” analysis showed that PIH1D1 interacts only with TEL2 phosphopeptides in which the DpSDD motif is intact (Figure 1D). In order to further probe interactions with the conserved acidic CK2 substrate motif within TEL2, and based on our structural studies described below, all subsequent ITC titrations used shorter (8-mer) peptides (Table S1). In these experiments, phosphopeptides in which each of the three aspartate residues were individually substituted by alanine all failed to show any significant quantifiable binding, and replacement of pSer491 with Glu as a phosphopeptide mimic also severely compromised interactions (Figure 1E). Indeed, substitution of pSer491 with pThr significantly reduced binding, even in the context of longer TEL2 peptides, revealing a marked discrimination in favor of phosphoserine-containing motifs (Figure 1F). Altogether, these data show that the PIH1 homology region encompasses two structurally and functionally separable domains—hereafter referred to as PIH-N and PIH-C—which are linked by an intervening region of variable length and sequence (Figure S1). Furthermore, they suggest that the major interacting site for the PIH-N domain of PIH1D1 (and budding yeast Pih1) is a short DpSDD motif that encompasses the only amino acids conserved between TEL2 orthologs from humans to yeast.
Figure 1.
PIH-N Domain Is Responsible for Binding of PIH1D1 to Phosphorylated TEL2 but Not Components of R2TP Complex
(A) Top, schematic representation of the WT and truncated PIH1D1 proteins. The region of highest homology with budding yeast PIH1 is highlighted in light green. Bottom, interaction of PIH1D1 with components of R2TP complex and TEL2. RUVBL1, RUVBL2, RPAP3, and TEL2 were immunoprecipitated from human embryonic kidney 293T (HEK293T) cells transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged PIH1D1 proteins or empty vector expressing FLAG.
(B) Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) analysis of PIH1D1 1–180 binding to singly and doubly phosphorylated TEL2 peptides.
(C) A core DSDD motif is absolutely conserved in TEL2 orthologs from yeast humans (Hs, Homo sapiens; Mm, Mus musculus; Gg, Gallus gallus; Dr, Danio rerio; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae).
(D) 1D pep-spot array containing TEL2 phosphopeptides in which polyalanine tracts were substituted for regions flanking the core DpS491DD motif.
(E) ITC analysis of PIH1D1 51–180 binding to WT and mutant 8-mer peptides encompassing the core conserved DpSDD TEL2 motif. NI, no quantifiable interaction.
(F) ITC analysis of WT TEL2 peptide and a variant in which pSer491 was substituted with pThr.
Crystal Structure of PIH1-N Domain Alone and Bound to TEL2 pSer491 Peptide
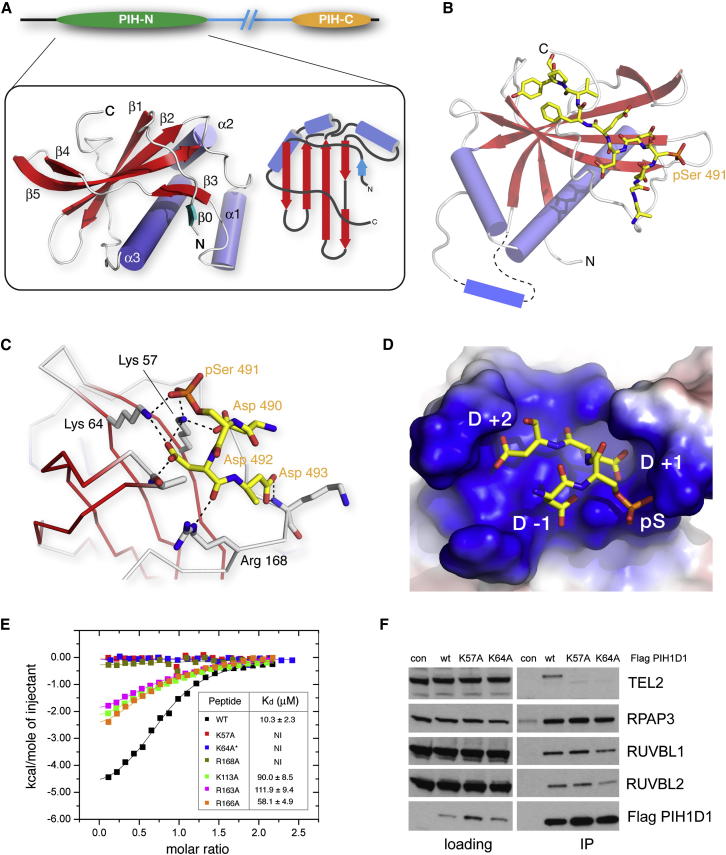
To investigate the molecular basis of the phosphopeptide-specific binding activity of the PIH-N domain, we solved the crystal structures of PIH1D1 domain fragments alone and bound to the TEL2 pSer491 peptide (Table S2). The structure of the peptide-free PIH1D1 51–180 fragment shows that the PIH-N domain adopts an unusual ββαβββαα topology (Figure 2A) that is unique among previously reported phosphopeptide-interacting proteins and modules. The structure of the PIH-N domain in the PIH1D1-pTEL2 phosphopeptide complex (Figure 2B) is essentially identical except for the fact that helix α1 located between β2 and β3 is disordered. In the structure of the PIH1D1-pTEL2 complex, 11 residues of the peptide are defined in the electron density maps and bind to a shallow, positively charged groove formed by the β sheet and an extended C-terminal segment (Figures 2B and S2). Five N-terminal residues, including pSer487, are disordered, suggesting that the small binding contribution of the additional phosphosite results from weak, nonspecific electrostatic interactions that are not associated with a single defined conformation. The most significant interactions of PIH1D1 are formed with the core DpSDD motif in TEL2, to the extent that the only intermolecular hydrogen bonds seen in the complex involve these four residues (Figure 2C). Indeed, the structure nicely explains the high degree of conservation of the DpSDD motif. Although it appears that substitution of aspartate in the pSer −1 position with glutamate could be accommodated, the pattern of hydrogen bonding of the aspartates in the +1 and +2 positions along with their steric environment indicates that even conservative substitution with glutamate would be detrimental to binding (Figure 2D).
Figure 2.
PIH-N Domain Structure and Tel2 Interactions
(A) Left, ribbons representation of the uncomplexed PIH1D1 PIH-N domain. Right, schematic representation of the overall α + β topology. β0 (cyan) contains four residues of vector encoded sequence that most likely mimics the conformation of native sequence that was removed in construction of the crystallizable fragment.
(B) Structure of the PIH-N domain of PIH1D1 bound to a TEL2 phosphopeptide. The protein is shown as ribbons and the phosphopeptide as a stick representation. The loop containing α1 is disordered in the phosphopeptide complex structure and is shown schematically.
(C) The core DpSDD motif in TEL2 is secured via a network of salt bridge and hydrogen bonding interactions with three basic residues: Lys57, Lys64, and Arg168.
(D) Aspartates in the pSer +1 and +2 positions (and, to a lesser extent the −1 position) within the TEL2 peptide pack tightly against the protein surface.
(E) ITC isotherms show that mutation of the core-motif-interacting side chains from Lys57, Lys64, and Arg168 are most deleterious to TEL2 binding. The asterisk shows that the titration with K64A was carried out at higher concentration/molar ratio, but, nonetheless, no interaction was detectable.
(F) Lys57 and Lys64, but not R2TP, are essential for TEL2 binding components in vivo. RUVBL1, RUVBL2, RPAP3, and TEL2 were immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged WT PIH1D1 or PIH1D1 with K64A and K57A mutations.
From the perspective of the PIH-N domain itself, only three (Lys57, Lys64, and Arg168) of the five basic residues that contribute to the positively charged binding surface make hydrogen bonding interactions with TEL2. Of these, only Lys57 and Lys64 interact directly with the TEL2 pSer491 phosphoryl group and constitute the only basic residues conserved across PIH1D1 orthologs from yeast to humans (Figure S1B). Arg168 forms the base of the phosphopeptide binding site, making hydrogen bonds with main-chain atoms of the bound ligand in a manner reminiscent of the binding mode observed in BRCA1 C terminus phosphopeptide complexes (BRCA1 Arg1699 and MDC1 Arg1933) (Clapperton et al., 2004, Stucki et al., 2005). Accordingly, mutation of each of these residues to alanine (K57A, K64A, and R168A) essentially abolished TEL2 phosphopeptide binding as judged by ITC, and smaller but nonetheless significant effects were observed for mutations of basic residues at more peripheral positions (Figure 2E; Table S1). In addition, both K57A and K64A mutants of full-length PIH1D1 failed to immunoprecipitate endogenous TEL2 from whole-cell extract but nonetheless retained binding to the other components of the R2TP complex mediated through the PIH-C region (Figure 2F).
Interestingly, both phosphopeptide-interacting lysines are absent in PIH1D2 but are substituted with arginine in another PIH1D1 ortholog, Kintoun, a regulator of dynein assembly (Omran et al., 2008). Although we have been unable to test PIH1D2-pTEL2 interactions by ITC, the lack of conservation at these crucial positions renders a phosphopeptide binding activity unlikely. However, the PIH-N domain of Kintoun does show some weak, but nonetheless significant, binding to the pTEL2 peptide (Figure S3), suggestive of a phosphopeptide binding capacity that is, presumably, associated with an altered overall target sequence specificity.
Proteomic Analysis of PIH1D1 Phosphopeptide-Specific Interactions
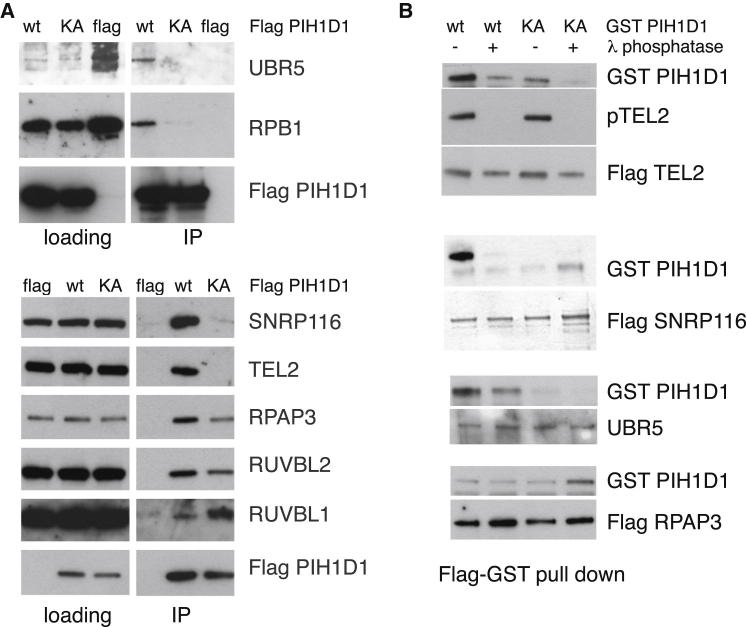
Our data raised the intriguing possibility that R2TP complex substrates may be defined by their ability to bind to PIH1D1 in a phosphopeptide-specific manner. To investigate this further and identify previously unreported R2TP complex substrates, we conducted a comparative proteomic analysis of wild-type (WT) PIH1D1 and the K64A mutant, which is compromised for phosphopeptide binding (Table S3). Among others, TEL2, SNRP116, UBR5, and RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1 were identified by mass spectrometry specifically with WT PIH1D1, but not the K64A mutant, and were confirmed by immunoprecipitation and western blotting (Figure 3A). Immunoaffinity purified SNRP116 and UBR5 also bound to WT PIH1D1 fused to glutathionine S-transferase (GST) but not GST-K64A PIH1D1. Furthermore, lambda phosphatase treatment of the immunoprecipitated SNRP116 and UBR5 disrupted their binding to GST-WT PIH1D1, indicating that the interactions are phosphorylation dependent, whereas RPAP3 bound to the GST-tagged PIH1D1 regardless of phosphorylation status or the integrity of Lys64 (Figure 3B). These results reveal that, analogous to TEL2 binding, SNRP116 and UBR5 interact with the PIH domain of PIH1D1 in a phosphorylation-dependent manner.
Figure 3.
Identification of Phosphopeptide-Specific Interacting Partners of PIH1D1
(A) FLAG-tagged WT PIH1D1 and K64A mutant immunoprecipitates with RPAP3, RUVBL1, and RUVBL2 subunits of the R2TP complex from HEK293T cells. FLAG-tagged WT PIH1D1, but not the K64A phosphopeptide binding mutant, immunoprecipitates UBR5, RPB1, SNRP116, and TEL2. Proteins were immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged PIH1D1 proteins or empty vector expressing FLAG.
(B) FLAG-tagged TEL2, SNRP116, and UBR5 untreated with lambda phosphatase bind to recombinant GST-tagged WT PIH1D1 but not K64A mutant. Interactions with GST-tagged WT PIH1D1 are disrupted by lambda phosphatase treatment. FLAG-tagged RPAP3 untreated or treated with lambda phosphatase binds to GST-tagged WT PIH1D1 and K64A mutant.
Minimal PIH-N Consensus Sequence and In Silico Identification of Potential Substrates
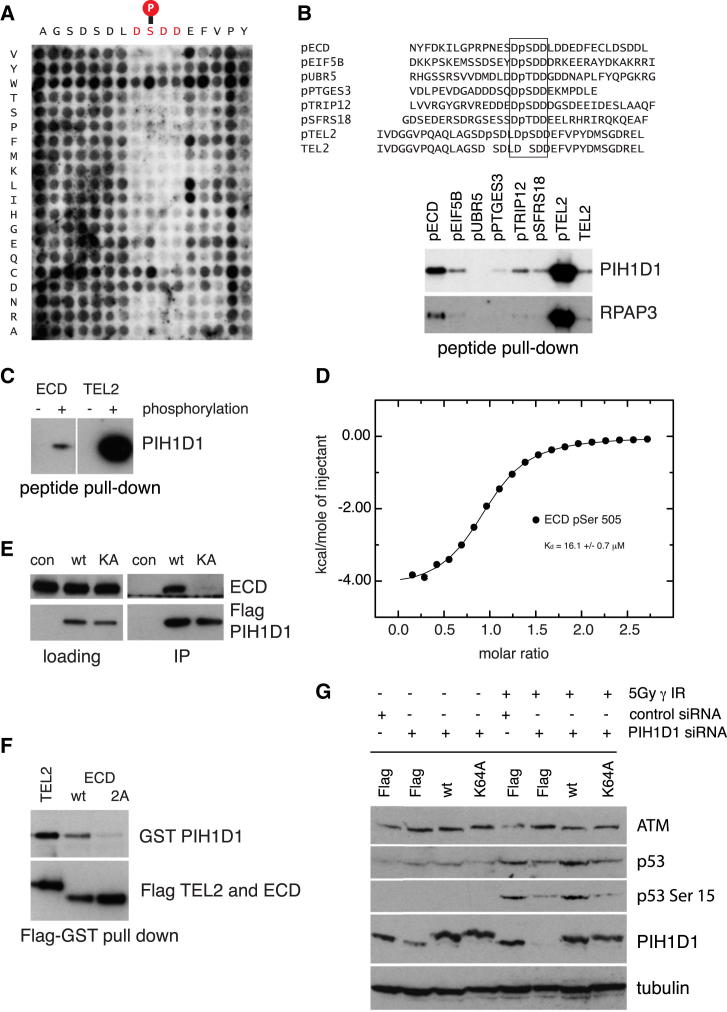
Next, we determined a minimal consensus sequence necessary for TEL2 phosphopeptide interaction with the PIH-N domain (Figure 4A). To this end, we assayed binding to a TEL2 pep-spot substitution array in which each residue in the polypeptide was substituted by all other amino acids. From this analysis, we derived a phosphopeptide binding consensus motif (D[S/T]DD[D/E]) that was then used in an in silico screen to identify additional potential substrates of the R2TP complex. Proteins containing the PIH-N domain binding consensus sequence included ECD, UBR5, PTGES3, EIF5B, TRP12, and SFRS18 (Figure 4B). Of these, we chose to further characterize and validate the interaction with ECD, which is involved in p53 stabilization and regulation of retinoblastoma phosphorylation (Kim et al., 2009, Zhang et al., 2006) and contains two PIH-N domain binding sequences surrounding CK2 consensus phosphorylation sites Ser505 and Ser518. In contrast to the unphosphorylated ECD peptide, an ECD peptide phosphorylated at Ser505 efficiently pulled down PIH1D1 from whole-cell extract (Figure 4C) and exhibited a binding affinity of 16 μM in ITC analysis (Figure 4D). Endogenous ECD also immunoprecipitated WT PIH1D1 but failed to interact with PIH1D1 K64A (Figure 4E). Conversely, mutation of the predicted CK2 sites in ECD (Ser505 and Ser518) abolished interaction with PIH1D1 (Figure 4F). Thus, like TEL2, ECD is recruited to the R2TP complex through interactions of the PIH-N domain of PIH1D1 with the conserved DSDD motif, possibly in a CK2 phosphorylation-dependent manner. Given that ECD, UBR5, and TEL2 are important for the regulation of p53 (Ling and Lin, 2011, Reid et al., 2013, Smits, 2012, Takai et al., 2007), we sought to determine if PIH1D1 also impacts on p53 function. To this end, we depleted PIH1D1 and analyzed p53 stability and phosphorylation on Ser15 after DNA damage. Depletion of PIH1D1 with two different small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) resulted in reduced p53 levels and a loss of Ser15 phosphorylation after DNA damage (Figures S4A and S4B). To determine whether this effect is dependent on PIH-N phosphopeptide binding activity, we stably transfected retinal pigment epithelium cells with WT PIH1D1, PIH1D1 K64A mutant, or empty vector and selected single clones expressing PIH1D1 at levels similar to endogenous (Figure S4C). Depletion of PIH1D1 with siRNA targeting the 5′ untranslated region of PIH1D1 from cells reconstituted with WT PIH1D1 rescued levels of p53 protein and phosphorylation after DNA damage to normal levels, which was in contrast to PIH1D1 K64A. Therefore, we conclude that the phosphopeptide binding ability of PIH1D1 is crucial for the function of R2TP complex (Figure 4G).
Figure 4.
A Minimal Consensus Sequence for PIH1 Domain Binding Reveals Potential R2TP Substrates
(A) A pep-spot array was synthesized in which each residue in the TEL2 phosphopolypeptide (16 amino acids) was substituted with all other amino acids. Peptides were spotted on a peptide array and incubated with purified 6× His-tagged PIH1D1 fragment 1–180.
(B) Peptide pull-down of PIH1D1 from HEK293T whole-cell extract. PIH1D1 and RPAP3 were pulled down from whole-cell extract by biotinylated peptides containing the phosphorylated consensus PIH-N domain binding sequence. Negative control (line 8) was unphosphorylated TEL2 peptide.
(C) ECD peptide binds PIH1D1 in a phosphopeptide-specific manner. PIH1D1 was pulled down from HEK293T whole-cell extract by biotinylated ECD peptide containing phosphorylated Ser505 but not with nonphosphorylated ECD peptide.
(D) ITC analysis of ECD binding (RPNESDpS505DDLDDY) to PIH1D1 1–180.
(E) FLAG-tagged WT PIH1D1, but not K64A mutant, immunoprecipitates ECD from HEK293T whole-cell extract. Proteins were immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged PIH1D1 proteins or empty vector expression FLAG.
(F) Mutation of ECD Ser505 and Ser518 to Ala disrupt binding of FLAG-tagged ECD to GST-tagged WT PIH1D1.
(G) Mutation of PIH1D1 leads to decreased levels of p53 after DNA damage. Retinal pigment epithelium cells were stably transfected with FLAG-tagged WT PIH1D1, PIH1D1 K64A, or empty vector expressing FLAG. The cells were treated with control siRNA (si con) or siRNA targeting 5′ untranslated region of PIH1D1 cDNA and irradiated with 5Gy. Samples were collected 1 hr after irradiation.
Discussion
Along with HSP90, the R2TP complex has been implicated in the assembly of large protein or ribonucleoprotein complexes in the cytoplasm and the nucleus. In contrast to the two AAA+ ATPases that are present in many different multisubunit complexes (RUVBL1 and RUVBL2), PIH1D1 and RPAP3 are specific to the R2TP complex and are likely to define substrate binding, potentially via interaction with the tetratricopeptide repeats of RPAP3. Nevertheless, RUVBL1 and RUVBL2 are known to be important for assembly of R2TP complex substrates into an appropriate functional conformation (Machado-Pinilla et al., 2012). However, a mechanistic explanation that defines how the R2TP complex is able to recognize and facilitate assembly of diverse substrates is largely unknown.
The results presented here reveal a previously unrecognized phosphopeptide binding domain (PIH-N) within the PIH1D1 subunit of the R2TP complex that preferentially binds to acidic phosphorylated proteins with high specificity. Structural analysis of the PIH-N domain bound to the TEL2 phosphopeptide established a unique mechanism of phosphopeptide recognition and identified Lys57 and Lys64 in PIH1D1 as essential for phosphopeptide binding. Both lysines, as well as the CK2 phosphorylated TEL2 binding motif DpSDD, are highly conserved in PIH1D1 and TEL2 orthologs from yeasts to human, indicating a common mechanism for substrate recognition by PIH-N domain. Through proteomic and in silico analysis, we demonstrate that the PIH-N domain binds to SNRP116, UBR5, RPB1, and ECD in a phosphorylation-dependent manner analogous to TEL2. Thus, we suggest that substrates are marked for assembly by the R2TP complex through phosphorylation of a short, highly acidic motif by CK2 (or other acidophilic kinases), which is then recognized by the phosphopeptide binding function of the PIH1D1 subunit.
The emergence of HSP90 inhibitors as successful cancer therapeutics has highlighted the importance of protein complex assembly and chaperone activities in cancer cells. Given that the R2TP complex works in conjunction with HSP90 to assemble multisubunit protein and ribonucleoprotein complexes, R2TP complex inhibitors could also be of value in a clinical setting. Small molecules that block the PIH-N phosphopeptide binding domain by mimicking the DpSDD motif would be predicted to prevent the RT2P complex from recognizing its substrates. Notably, the PIH1D1 subunit is overexpressed in several breast cancer cell lines (Kamano et al., 2013), which may reflect a dependency of the tumor growth for R2TP complex activity. Therefore, it is possible that inhibitors of PIH-N domain interactions could be used as an anticancer therapeutic for tumors that are overreliant on such chaperone activities.
Experimental Procedures
X-Ray Crystallography
Recombinant selenomethionine-substituted human PIH1D1 (51–180) was crystallized in complex with a diphosphopeptide (NH2-YAGSDpSDLDpSDDEFVPY-CONH) encompassing residues 483–497 of human TEL2 by sitting drop vapor diffusion with an IMPAX nano-dispensing robot. Crystals grew from a 8 mg/ml solution of complex in 20 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, and 0.5 mM tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) equilibrated well solution containing 32% w/v polyethylene glycol (PEG) 4000, 100 mM sodium acetate, and 100 mM Tris (pH 8.5) as precipitant, transferred to a cryo-protectant containing protein buffer and mother liquor supplemented with 20% v/v glycerol, and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen. All data were collected at Diamond Light Source. Images were indexed, integrated, and scaled with MOSFLM/SCALA (CCP4). Phases for the PIH1D1-pTEL2 complex were determined by single-wavelength anomalous diffraction and were of sufficient quality to enable a partial model of the two PIH1D1-pTEL2 complexes in the crystallographic asymmetric unit to be built automatically with Buccaneer (CCP4). All manual model building was carried out with Coot (Emsley and Cowtan, 2004), and structure refinement was carried out with Phenix (Terwilliger, 2002). The structure of unbound PIH1D1 (51–180) was crystallized by microseeding and vapor diffusion from 2% PEG 400 (v/v), 20% methoxy PEG 5000, and 0.1 M imidazole (pH 7.0). The structure was determined by molecular replacement using the final refined protein coordinates derived from the structure of the complex as a search model with PHASER (McCoy, 2007) and refined against data extending to a 1.58 Å resolution. Crystallographic statistics are reported in Table S2.
Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
ITC was carried out with an ITC-200 calorimeter (MicroCal). Proteins were prepared by dialysis against 20 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, and 0.5 mM TCEP. Synthetic phosphopeptides (Cambridge Peptides) were desalted with NAP5 columns (GE Healthcare) equilibrated in 20 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, and 0.5 mM TCEP and diluted to the appropriate concentration with dialysis buffer. Protein concentrations were determined by UV spectrometry. A typical experiment involved 19 × 2 μl injections of ∼800 μM peptide from the injection syringe into ∼80 μM protein in the sample cell. All measurements were carried out at 20°C. Data were analyzed with the Origin-based software provided by the manufacturers.
Mass Spectrometry Analysis and Protein Identification
SYPRO ruby-stained polyacrylamide gel slices (1–2 mM) were excised with a scalpel and processed for mass spectrometry with the JANUS automated liquid handling system (PerkinElmer).
In Silico Screen for Proteins Containing PIH1 Binding Consensus Sequence
Proteins containing the consensus binding motif D[S/T]DD[E/D] were identified with the PROSITE database (http://prosite.expasy.org) tools. The resulting list of candidates was filtered with the criteria that the site is at least conserved in mammals and that it has previously been reported as phosphorylated in vivo. For peptide pull-down assay, we chose proteins that were functionally most likely to bind to the R2TP complex.
A detailed summary of all procedures used in this study can be found in the Supplemental Experimental Procedures.
Acknowledgments
Research in the DNA damage response laboratory of S.J.B. is funded by Cancer Research UK and an ERC Advanced Investigator Grant (RecMitMei). S.J.B. is a recipient of a Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award. S.J.S is grateful to the MRC for its continuing support (U117584228) and to Philip Walker and the staff at Diamond Light Source (UK) for assistance with X-ray data collection. L.S. is the recipient of an MRC Centenary Award, and Z.H. is funded by a long-term fellowship from the ERC and by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (14-34264S).
Published: March 20, 2014
Footnotes
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/).
Supplemental Information contains Supplemental Experimental Procedures, four figures, and three tables and can be found with this article online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.013.
Contributor Information
Stephen J. Smerdon, Email: ssmerdo@nimr.mrc.ac.uk.
Simon J. Boulton, Email: simon.boulton@cancer.org.uk.
Accession Numbers
The Protein Data Bank accession numbers for the crystal structures of the unbound PIH1D1 PIH-N domain and its complex with the pTel2 peptide reported in this paper are 4PSI and 4PSF, respectively.
Supplemental Information
References
- Ahn S., Kim J., Hwang J. CK2-mediated TEL2 phosphorylation augments nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) by increase of SMG1 stability. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013;1829:1047–1055. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back R., Dominguez C., Rothé B., Bobo C., Beaufils C., Moréra S., Meyer P., Charpentier B., Branlant C., Allain F.H., Manival X. High-resolution structural analysis shows how Tah1 tethers Hsp90 to the R2TP complex. Structure. 2013;21:1834–1847. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.07.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulon S., Marmier-Gourrier N., Pradet-Balade B., Wurth L., Verheggen C., Jády B.E., Rothé B., Pescia C., Robert M.C., Kiss T. The Hsp90 chaperone controls the biogenesis of L7Ae RNPs through conserved machinery. J. Cell Biol. 2008;180:579–595. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200708110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulon S., Pradet-Balade B., Verheggen C., Molle D., Boireau S., Georgieva M., Azzag K., Robert M.C., Ahmad Y., Neel H. HSP90 and its R2TP/Prefoldin-like cochaperone are involved in the cytoplasmic assembly of RNA polymerase II. Mol. Cell. 2010;39:912–924. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapperton J.A., Manke I.A., Lowery D.M., Ho T., Haire L.F., Yaffe M.B., Smerdon S.J. Structure and mechanism of BRCA1 BRCT domain recognition of phosphorylated BACH1 with implications for cancer. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004;11:512–518. doi: 10.1038/nsmb775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emsley P., Cowtan K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004;60:2126–2132. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904019158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horejsí Z., Takai H., Adelman C.A., Collis S.J., Flynn H., Maslen S., Skehel J.M., de Lange T., Boulton S.J. CK2 phospho-dependent binding of R2TP complex to TEL2 is essential for mTOR and SMG1 stability. Mol. Cell. 2010;39:839–850. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurov K.E., Cotta-Ramusino C., Elledge S.J. A genetic screen identifies the Triple T complex required for DNA damage signaling and ATM and ATR stability. Genes Dev. 2010;24:1939–1950. doi: 10.1101/gad.1934210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jha S., Dutta A. RVB1/RVB2: running rings around molecular biology. Mol. Cell. 2009;34:521–533. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez B., Ugwu F., Zhao R., Ortí L., Makhnevych T., Pineda-Lucena A., Houry W.A. Structure of minimal tetratricopeptide repeat domain protein Tah1 reveals mechanism of its interaction with Pih1 and Hsp90. J. Biol. Chem. 2012;287:5698–5709. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.287458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamano Y., Saeki M., Egusa H., Kakihara Y., Houry W.A., Yatani H., Kamisaki Y. PIH1D1 interacts with mTOR complex 1 and enhances ribosome RNA transcription. FEBS Lett. 2013;587:3303–3308. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J.H., Gurumurthy C.B., Naramura M., Zhang Y., Dudley A.T., Doglio L., Band H., Band V. Role of mammalian Ecdysoneless in cell cycle regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:26402–26410. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.030551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S.G., Hoffman G.R., Poulogiannis G., Buel G.R., Jang Y.J., Lee K.W., Kim B.Y., Erikson R.L., Cantley L.C., Choo A.Y., Blenis J. Metabolic stress controls mTORC1 lysosomal localization and dimerization by regulating the TTT-RUVBL1/2 complex. Mol. Cell. 2013;49:172–185. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling S., Lin W.C. EDD inhibits ATM-mediated phosphorylation of p53. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:14972–14982. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.182527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J., Chapman J.R., Clapperton J.A., Haire L.F., Hartsuiker E., Li J., Carr A.M., Jackson S.P., Smerdon S.J. A supramodular FHA/BRCT-repeat architecture mediates Nbs1 adaptor function in response to DNA damage. Cell. 2009;139:100–111. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macario A.J., Conway de Macario E. Sick chaperones, cellular stress, and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:1489–1501. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra050111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machado-Pinilla R., Liger D., Leulliot N., Meier U.T. Mechanism of the AAA+ ATPases pontin and reptin in the biogenesis of H/ACA RNPs. RNA. 2012;18:1833–1845. doi: 10.1261/rna.034942.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy A.J. Solving structures of protein complexes by molecular replacement with Phaser. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2007;63:32–41. doi: 10.1107/S0907444906045975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omran H., Kobayashi D., Olbrich H., Tsukahara T., Loges N.T., Hagiwara H., Zhang Q., Leblond G., O’Toole E., Hara C. Ktu/PF13 is required for cytoplasmic pre-assembly of axonemal dyneins. Nature. 2008;456:611–616. doi: 10.1038/nature07471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid M.A., Wang W.I., Rosales K.R., Welliver M.X., Pan M., Kong M. The B55α subunit of PP2A drives a p53-dependent metabolic adaptation to glutamine deprivation. Mol. Cell. 2013;50:200–211. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smits V.A. EDD induces cell cycle arrest by increasing p53 levels. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:715–720. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.4.19154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stucki M., Clapperton J.A., Mohammad D., Yaffe M.B., Smerdon S.J., Jackson S.P. MDC1 directly binds phosphorylated histone H2AX to regulate cellular responses to DNA double-strand breaks. Cell. 2005;123:1213–1226. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai H., Wang R.C., Takai K.K., Yang H., de Lange T. Tel2 regulates the stability of PI3K-related protein kinases. Cell. 2007;131:1248–1259. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai H., Xie Y., de Lange T., Pavletich N.P. Tel2 structure and function in the Hsp90-dependent maturation of mTOR and ATR complexes. Genes Dev. 2010;24:2019–2030. doi: 10.1101/gad.1956410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T.C. Automated structure solution, density modification and model building. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2002;58:1937–1940. doi: 10.1107/s0907444902016438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Chen J., Gurumurthy C.B., Kim J., Bhat I., Gao Q., Dimri G., Lee S.W., Band H., Band V. The human orthologue of Drosophila ecdysoneless protein interacts with p53 and regulates its function. Cancer Res. 2006;66:7167–7175. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao R., Davey M., Hsu Y.C., Kaplanek P., Tong A., Parsons A.B., Krogan N., Cagney G., Mai D., Greenblatt J. Navigating the chaperone network: an integrative map of physical and genetic interactions mediated by the hsp90 chaperone. Cell. 2005;120:715–727. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao R., Kakihara Y., Gribun A., Huen J., Yang G., Khanna M., Costanzo M., Brost R.L., Boone C., Hughes T.R. Molecular chaperone Hsp90 stabilizes Pih1/Nop17 to maintain R2TP complex activity that regulates snoRNA accumulation. J. Cell Biol. 2008;180:563–578. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200709061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.