Abstract
Mutations of the thyroid hormone receptor α gene (THRA) cause hypothyroidism in patients with growth and developmental retardation, and skeletal dysplasia. Genetic evidence indicates that the dominant negative activity of TRα1 mutants underlies pathological manifestations. Using a mouse model of hypothyroidism caused by a dominant negative TRα1PV mutant and its derived mouse model harboring a mutated nuclear receptor corepressor (NCOR1ΔID) (Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice), we recently showed that aberrant release of TRα1 mutants from the NCOR1 repressor complex mediates dominant negative actions of TRα1 mutants in vivo. We tested the hypothesis that deacetylation of nucleosomal histones associated with aberrant recruitment of corepressors by TRα1 mutants underlies pathological phenotypic expression. We treated Thra1PV/+and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice with a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxyamic acid (SAHA). SAHA significantly ameliorated the impaired growth, bone development and adipogenesis of Thra1PV/+ mice. In Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, SAHA improved these abnormalities even further. We focused our molecular analyses on how SAHA improved the impaired adipogenesis leading to the lean phenotype. We found that SAHA reverted the impaired adipogenesis by de-repressing the expression of the two master regulators of adipogenesis, C/ebpα and Pparγ, as well as other adipogenic genes at both the mRNA and protein levels. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses indicated SAHA increased the extent of acetylation of nucleosomal H4K5 and H3 to re-activate adipogenic genes to reverting adipogenesis. Thus, HDAC confers in vivo aberrant actions of TRα1 mutants. Importantly, for the first time, the present studies show that HDAC inhibitors are clearly beneficial for hypothyroidism and could be therapeutics for treatment.
INTRODUCTION
In humans, growth, development and metabolic homeostasis are critically regulated by the thyroid hormone T3. The genomic signaling by T3 is via the thyroid hormone receptor (TR) isoforms, α1, β1 and β2, which are encoded by the THRA and THRB genes located on two different chromosomes (1,2). These TR isoforms share extensive sequence homology in the DNA and T3 binding domains, but differ in the amino terminal A/B domains (3). The transcriptional activity of TRs is regulated by the type of thyroid hormone response element (TRE) located on the target genes and by a host of nuclear co-regulatory proteins. The unliganded TR isoforms recruit the nuclear corepressor [NCOR1 or silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptor (SMRT)/NCOR2]–histone deacetylase (HDAC) corepressor complexes for transcriptional repression on the T3-positively-regulated genes. Binding of T3 releases corepressors from the liganded TRs, allowing recruitment of nuclear receptor coactivators (e.g. SRC1)–histone acetyltransferase complexes to facilitate transcription activation (4–6).
The critical roles of TR in mediating biological functions of T3 are clearly evident in that mutations of the THRB gene cause resistance to thyroid hormone (RTH) (7). RTH was initially recognized in 1967 (8), but the first causative mutation of the THRB gene was identified only after the cloning of the THRB gene (9). So far, over 1000 RTH families have been reported. The affected heterozygous individuals have mildly increased serum thyroid hormone levels with an inappropriately normal or elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) concentration because of dysregulation of the hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid feedback axis (7).
In contrast, the identification of patients with mutations of the THRA gene was reported only very recently (10,11). Patients with mutations of the THRA gene exhibit classical features of hypothyroidism: severe growth and developmental retardation, skeletal dysplasia and constipation, but only borderline-abnormal thyroid hormone levels (10,11). That these patients are heterozygotes indicates TRα1 mutants act in a dominant negative manner to mediate the clinical manifestations. Indeed, the mutated TRα1E403X (10), TRα1F397fs406X (11) and TRα1A397PfsX7 (12) identified in patients have lost T3 binding activity, and in a reporter system they were shown to interfere with the transcriptional activity of wild-type TRs in a dominant negative manner. Moreover, in vitro, TRα1E403X and TRα1A397PfsX7 mutants fail to dissociate from nuclear corepressors and binds minimally with SRC-1 (10,12). However, the detailed molecular mechanisms by which these TRα1 mutants act in vivo in a dominant-negative fashion are not clear.
The availability of a mouse model (the Thra1PV mouse) that faithfully recapitulates the hypothyroidism exhibited in patients with mutations of the THRA gene allows the elucidation of the in vivo molecular mechanisms behind clinical manifestations. The PV mutation, identified from an RTH patient, has a frameshift mutation in the C-terminal 14 amino acids, resulting in a total loss of T3 binding activity and transcription capacity (13). Targeting the PV mutation into the Thrb gene of a mouse (the ThrbPV mouse) faithfully reproduces human RTH (14). The PV mutation was subsequently targeted to the position in the Thra gene that corresponds to that in the TRβ1 to create the Thra1PV mouse (15). Because no known patients with the mutations of the THRA gene were found at the time the Thra1PV mouse was created in 2001, the Thra1PV mouse was created to address the intriguing question why no mutations of the THRA gene were ever detected in RTH patients. Interestingly, the Thra1PV mouse exhibits phenotypes distinct from that of RTH, including severe growth retardation (dwarfism), impaired bone development (16,17), decreased survival and reduced fertility (15,18). These phenotypes are reminiscent of clinical manifestations in patients with TRα1 mutations (10,11). Importantly, these findings revealed that mutations of the THRA gene are not embryonic lethal, but confer different clinical manifestations from those of RTH. Remarkably, after the discovery of patients with mutations of the THRA gene, comparison of the mutated sequences shows that TRα1PV (TRα1-T394Hfs406X) has the same mutated C-terminal sequence (-TLPRGL) with truncated termination at amino acid L406 as did the two patients with frameshift mutations of the THRA gene [TRα1-F397fs406X; (11)]. Thus, the Thra1PV mouse represents an excellent disease model to elucidate the molecular basis underlying the clinical manifestations due to the mutations of the THRA gene.
Indeed, recently, to demonstrate that severe hypothyroidism in patients with THRA mutations is caused by an inability of TRα1 mutants to properly release NCOR1, thereby inhibiting T3-mediated transcription activity, we crossed Thra1PV mice with mice expressing a mutant Ncor1 allele (Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice). The NCOR1 mutant, NCOR1ΔID, cannot recruit the TR or PV mutant (19–21). We found that NCOR1ΔID completely ameliorates abnormalities in the thyroid–pituitary axis of Thra1PV/+ mice. The severe retarded growth and delayed bone development were also partially reverted in Thra1PV/+ mice expressing NCOR1ΔID (21). Molecular analyses show that TRα1PV-mediated repressed TR target genes were de-repressed in target tissues of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice as a result of the inability of TRα1PV to recruit NCOR1ΔID (21). These findings provided direct in vivo evidence to indicate that the constitutive recruitment of the NCOR1 by TRα1 mutants could lead to clinical hypothyroidism in humans.
However, the direct role of HDACs associated with NCOR1 in mediating the hypothyroidism caused by TRα1 mutants had not been elucidated in vivo. Moreover, we also wished to ask the question whether HDAC inhibitors could be potential therapeutics for treatment of hypothyroidism caused by the mutations of the THRA gene. Recently, inhibitors of HDAC (HDACIs) have been increasingly used to treat many diseases, including cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, and metabolic disorders (22,23). In the present study, we chose vorinostat, or suberoylanilide hydroxyamic acid (SAHA), as the HDACI for our study. Class I HDACs, including HDAC-3, are the substrates for SAHA. HDAC-3 has been shown to associate with NCOR1/SMRT in a multiprotein complex (24–27). This second generation of HDACIs has been approved for the treatment of refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) (28,29) and is currently in different phases of clinical trials for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (30), hormone therapy-resistant breast cancer (31), non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma (32). We found that treatment of Thra1PV/+ mice with SAHA significantly ameliorated the abnormalities in growth, bone development and adipogenesis. In Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, where the impairment in growth, bone development and adipogenesis was less severe as a result of the expression of NCOR1ΔID, SAHA treatment further improved these abnormalities. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analyses show that SAHA treatment increased the extent of acetylation of nucleosomal histones to activate the expression of target genes. These results provided the in vivo evidence to demonstrate the direct role of HDACs in mediating the pathological manifestation caused by mutations of TRα1 mutants. Importantly, HDAC inhibitors are potential therapeutics for the treatment of hypothyroidism caused by mutations of the THRA gene.
RESULTS
SAHA treatment decreased thyroid growth, but had no effects on the mild dysregulation of the pituitary–thyroid axis of Thra1PV/+ mice
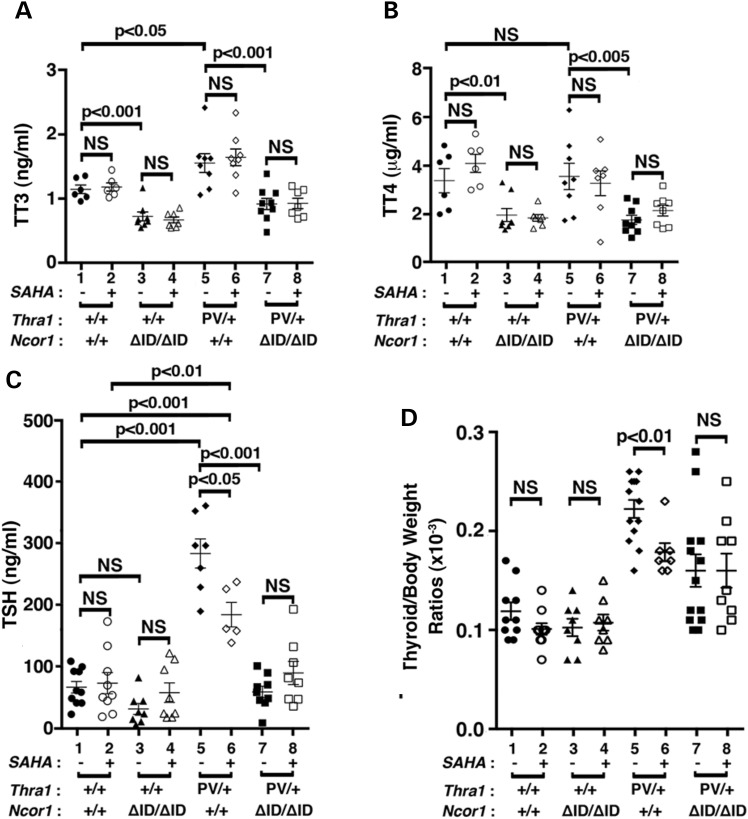
Similar to the patients with mutations in the THRA gene (10,11), Thra1PV/+ mice exhibit mild dysregulation of the pituitary–thyroid axis with elevated total serum T3 (TT3) and mildly elevated TSH (15,21). Figure 1A shows the effects of SAHA treatment on the thyroid function tests of Thra1PV/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice. SAHA treatment did not significantly affect the mildly elevated total T3 [1.6 ± 0.39 ng/ml, n = 8, data group 6 (SAHA treated) versus 1.7 ± 0.34 ng/ml, n = 8, data group 5 (vehicle treated), Fig. 1A] or total serum T4 (3.2 ± 1.3 μg/dl, n = 7, data group 6 versus 3.5 ± 1.4 μg/dl, n = 8, data group 5, Fig. 1B) in Thra1PV/+ mice. In Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, the expression of NCOR1ΔID, which cannot be recruited by TRα1PV, normalized the total serum T3 to that of Thra1+/+Ncor1+/+ mice (WT) mice [1.2 ± 0.2 ng/ml, n = 6, data group 1 and 0.92 ± 0.25 ng/ml, n = 9, data group 7, Fig. 1A; (21)]. SAHA treatment did not change the total T3 (data group 7 versus data group 8, Fig. 1A) or total T4 (data group 7 versus data group 8, Fig. 1B). Similarly, no effects of SAHA on the total T3 and total T4 of WT and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice were observed (data groups 1–4, Fig. 1A and B, respectively).
Figure 1.
Comparison of thyroid function tests and thyroid weights of Thra1PV/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice with or without SAHA treatment. Serum levels of total T3 (A) (n = 6–9 mice per group), total T4 (B) (n = 6–9 mice per group), TSH (C) (n = 8–15 mice per group) and thyroid weights (D) were determined in adult mice (3–3.5 months old) as described in Materials and Methods. In (D), ratios of thyroid weight versus body weight were determined. The data are expressed as mean ± SEM with P-values indicated (n = 8–15 mice per group).
Consistent with findings in patients, Figure 1C shows that the serum TSH level was higher in Thra1PV/+ mice than WT mice (175.7 ± 83.2, n = 15, data group 5 versus 64.7 ± 27.4, n = 10, data group 1). SAHA treatment significantly decreased the elevated serum TSH levels 13% in Thra1PV/+ mice (145.6 ± 59.4, n = 12, data group 6 versus 175.7 ± 83.2, n = 15, data group 5, Fig. 1C). In Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, the expression of NCOR1ΔID normalized the abnormally elevated TSH to a level near that of WT mice (57.3 ± 25.5, n = 9, data group 7 versus data group 1, Fig. 1C). SAHA treatment did not significantly change the serum TSH level (data group 7 versus data group 8, Fig. 1C). Likewise, no significant effects of SAHA on the serum TSH levels of WT and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice were observed (data groups 1–4, Fig. 1C). Taken together, these data indicate that SAHA had selective effects on the pituitary–thyroid axis to lower the TSH levels, not on the TT3 and TT4 levels.
We next examined the effect of SAHA on thyroid growth. SAHA treatment had no significant effects on the thyroid weight of WT and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (data groups 1–4; Fig. 1D). However, compared with WT mice, Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ mice had a 1.8-fold increase in thyroid weight (0.22 ± 0.009, n = 13, data group 5 versus 0.11 ± 0.009, n = 10, data group 1). With SAHA treatment, the extent of increase was lowered to 1.5-fold (0.17 ± 0.009, n = 7, data group 6 versus 0.22 ± 0.009, n = 13, data group 5). Consistent with our findings earlier (21), the expression of NCOR1ΔID partially corrected the abnormal thyroid weight by lowering it to a 1.3-fold enlargement (0.16 ± 0.02, n = 13, data group 7 versus data group 1). However, SAHA treatment had no effects on the thyroid weight of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (data group 8 versus data group 7). These findings suggest that while SAHA partially corrected the abnormally enlarged thyroid growth in Thra1PV/+ mice, it did not correct mildly abnormal thyroid function tests of mutant mice.
SAHA treatment lessened the extent of retarded growth in Thra1PV/+ mice
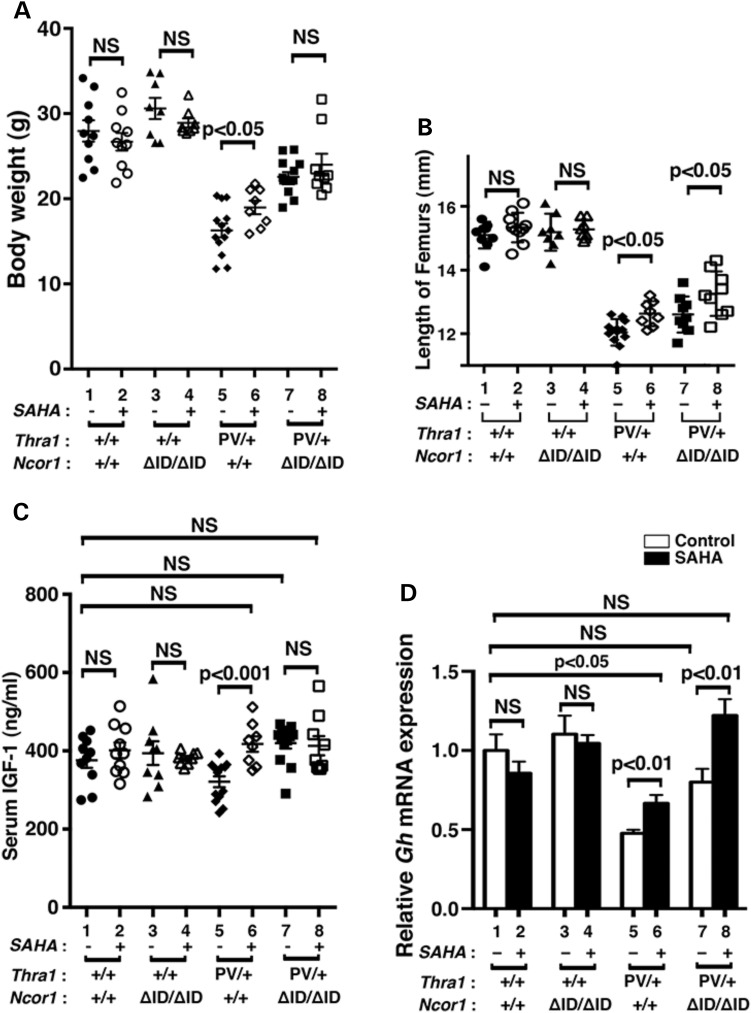
One of the debilitating symptoms in patients with mutations of the THRA gene is severe retardation in growth and bone development (10–12). Similar to those patients, Thra1PV/+ mice exhibit growth retardation (15). As juveniles, Thra1PV/+ mice are dwarfs with a body weight 40–50% less than their wild-type siblings, a size difference that persists into adulthood (15). Figure 2A shows that at 3–3.5 months of age, the impaired weight gain of Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ mice (16.2 ± 0.8 g, n = 13, data group 5; 42% lower than Thra1+/+mice: 27.9 ± 1.2 g, n = 10, data group 1) was partially reverted by SAHA treatment with a significant 12% weight increase (18.9 ± 0.8 g, n = 8, data group 6). In mice expressing two alleles of the Ncor1ΔID gene, the impaired weight gain of Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ mice was partially corrected with a significant 13% weight increase in Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (22.5 ± 0.6 g, n = 12, data group 7). However, the weight of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice was not significantly affected by SAHA treatment (23.92 ± 1.3 g, n = 9, data group 8). It is important to note that SAHA treatment had no effects on the weight gain of WT mice (data groups 1 and 2: 27.89 ± 1.3 g, n = 10, and 26.62 ± 1.03 g, n = 10, respectively) and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (data groups 3 and 4: 30.54 ± 1.23 g, n = 8, and 28.84 ± 0.53 g, n = 8, respectively).
Figure 2.
Effects of SAHA on growth of Thra1PV/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice. (A) Comparison of body weights among adult mice (3–3.5 months old) with indicated genotypes. The difference between the body weight in Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ mice with or without SAHA treatment is significant (P < 0.05), (n = 8–13 animals per group). (B) Increased length of femurs in Thra1PV/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice by SAHA treatment is significant (P < 0.05) (n = 8–13 mice per group). (C) Serum IGF1 concentrations in four different genotypes (Thra1+/+Ncor1+/+, Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID, Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID) with or without SAHA treatment were determined as described in Materials and Methods (n = 8–13 animals per group). (D) Comparison of the mRNA expression of the growth hormone gene (Gh) in the pituitary of Thra1PV/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice with or without SAHA treatment. The mRNA expression was determined by real-time RT/PCR as described in Materials and Methods (n = 5–8 mice per group). The data are expressed as mean ± SEM with P-value indicated.
Similar to patients (10–12), Thra1PV/+ mice also display skeletal abnormalities with severe and persistent postnatal linear growth impairment (15–17). Figure 2B shows the lengths of femurs of Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ mice (12.04 ± 0.11 mm, n = 13, data group 5) were ∼20% shorter than those of Thra1+/+ mice (15.10 ± 0.13 mm, n = 10, data group 1). SAHA treatment led to a significant 5% reversal of the defect in bone growth in Thra1PV/+ mice (12.63 ± 0.13 mm, n = 8, data group 6). The expression of NCOR1ΔID partially corrected the delayed bone growth by ∼5% in Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (12.60 ± 0.18 mm, n = 9, data group 7). Interestingly, SAHA treatment further reverted delayed bone growth by an additional ∼6% in Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (13.26 ± 0.23 mm, n = 9, data group 8). However, no significant effects of SAHA were detected in Thra1+/+Ncor1+/+ mice (data groups 1 and 2: 15.10 ± 0.13 mm, n = 10, and 15.34 ± 0.15 mm, n = 10, respectively) and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (data groups 3 and 4: 19.10 ± 0.20 mm, n = 8 and 15.28 ± 0.11 mm, n = 8, respectively). Taken together, these results suggest SAHA lessens the impaired growth and bone development of Thra1PV/+ mice.
It is known that patients with mutations of the THRα gene have lower than normal serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) (10–12). Consistently in our study, serum IGF-1 levels were 15% lower in Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ mice than in WT mice (Fig. 2C; 375.6 ± 19.4 ng/ml, n = 10, data group 5 versus 320.5 ± 13.9 ng/ml, n = 13, data group 1). SAHA treatment normalized the serum IGF-1 concentrations of Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ mice (Fig. 2C, data group 6, 417.0 ± 19.7 ng/ml, n = 8), to levels not significantly different from those of the WT mice (data group 6 versus data group 1). Similar to what we have shown previously (21), the expression of NCOR1ΔID corrected abnormally decreased IGF-1 in Thra1PV/+ mice to the levels of WT mice (Fig. 2C; data group 7, 419.1.0 ± 13.8 ng/ml, n = 13 for Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice). Treatment of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice with SAHA did not further elevate the serum IGF-1 levels (data group 8). SAHA treatment had no effects on the serum IGF-1 levels of WT and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (Fig. 2C; data groups 1–4).
The finding that the growth of Thra1PV/+ mice was partially corrected by SAHA treatment (Fig. 2A) prompted us also to examine whether the expression of the growth hormone (Gh) mRNA in the pituitary was affected by SAHA treatment. Gh is a TR-directly regulated gene in which the TRE is well defined (33). Figure 2D shows that SAHA treatment had no significant effects on the expression of the Gh gene in WT and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (Fig. 2D; data groups 1–4). However, the decreased expression of the Gh mRNA in Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ mice was partially reverted from a 53% reduction to a 33% reduction (compare bar 6 to bar 5). Consistent with our previous findings, the expression of NCOR1ΔID corrected abnormally decreased Gh mRNA in Thra1PV/+ mice to levels that were not significantly different from those in WT mice (compare bar 7 to bar 1). Interestingly, SAHA treatment further elevated the Gh mRNA expression 22% higher than that in the pituitary of WT mice (compare bar 8 to bar 1). Taken together, these data suggest that partial correction of the retarded growth of Thra1PV/+ mice by SAHA could be accounted for by the SAHA-induced elevation of IGF-1 levels and the increased expression of the Gh gene.
SAHA treatment ameliorated impaired adipogenesis in Thra1PV/+ mice
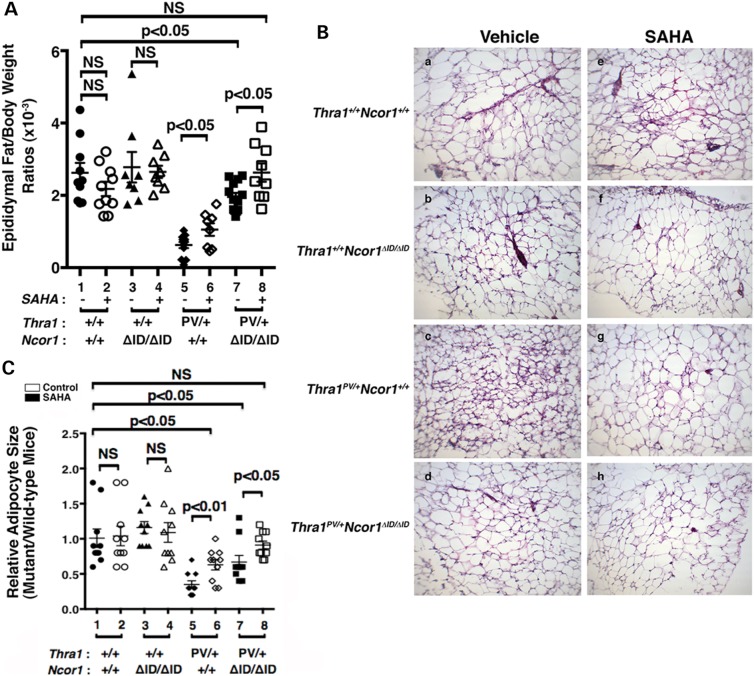
We have previously shown that Thra1PV/+ mice exhibit abnormalities in lipid metabolism (34–36). One of the striking abnormal features is a severe defect in adipogenesis of the white adipocytes (WAT). The WAT mass, such as the epididymal fat, is reduced with a markedly smaller cell size [∼77–80% reduction when compared with that of WT mice; (21)]. The impairment, in part, is caused by the repression in the expression of two master regulators of adipogenesis, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (Ppar γ) and CCAAT/enhance-binding protein α (C/ebpα) TRα1PV (21). We therefore determined whether SAHA treatment might correct this impairment. Figure 3A shows that SAHA treatment partially corrected the epididymal/body weight ratios from a 77% reduction to a 60% reduction (compare data group 5 to data group 6). Consistent with our previous findings (21), expression of NCOR1ΔID further corrected the impaired epididymal/body weight ratios from a 77% reduction (data group 5) to a 25% reduction (data group 7). Remarkably, SAHA treatment normalized the epididymal/body weight ratios to levels not significantly different from those in the WT mice (compare data group 8 with data group 1). In contrast, SAHA treatment had no apparent effects on the epididymal/body weight ratios of WT (data groups 1 and 2) and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (data groups 3 and 4). These results showed that SAHA treatment alleviated the repressive effects of TRα1PV on WAT adipogenesis of Thra1PV/+ mice.
Figure 3.
Effects of SAHA on adipogenesis of the epididymal fat of Thra1PV and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice. (A) Comparison of epididymal fat weights among adult mice (3–3.5 months old) with indicated genotypes with or without treatment of SAHA (3–3.5 months old; n = 8–13 mice per group). Ratios of fat mass versus body weight were determined. Data are expressed as mean values ± SEM with P-values shown. (B) Representative histological features of the epididymal fat of four different genotypes (Thra1+/+Ncor1+/+, Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID, Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID) with or without SAHA treatment. (C) Adipocyte size was measured for each genotype shown in (B) using NIH IMAGE software (ImageJ) and plots were presented to reflect the size distribution (n = 8–9 mice per genotype).
That SAHA treatment improved the impaired adipogenesis of Thra1PV/+ mice was further confirmed by examining the size of adipocytes. Figure 3B shows that SAHA treatment had no apparent effects on the cell size of WT (panels a and e) and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (panels b and f). In contrast, the cell size was clearly markedly larger in the SAHA-treated adipocytes (panel g) than in the vehicle-treated Thra1PV/+ mice (panel c). Consistent with our recent report (21), Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice expressing NCOR1ΔID had larger adipocytes than did Thra1PV/+ mice (compare panel d with c). SAHA treatment further enlarged the size of adipocytes of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (compare panel h with d). The areas of adipocytes were measured and the quantitative data are shown in Figure 3C. It is clear that although SAHA treatment had no effect on the size of adipocytes of WT and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (bars 1–4, Fig. 3C), it enlarged the adipocyte size in Thra1PV/+ mice and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice 2-fold and 1.3-fold, respectively (bar 6 versus bar 5 and bar 8 versus bar 7). These findings taken together indicate that SAHA treatment reverted the TRα1PV-mediated impaired adipogenesis.
SAHA de-repressed the TRα1PV-mediated repression of adipogenic genes
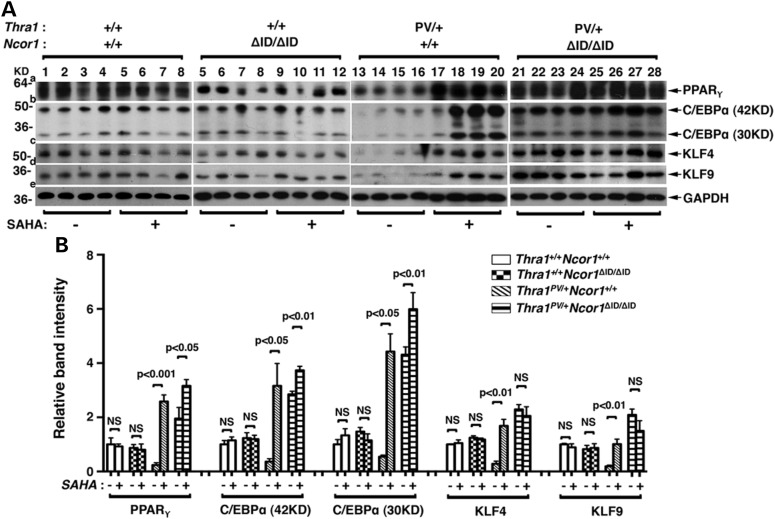
To understand the mechanisms by which SAHA treatment ameliorated the impaired adipogenesis, we evaluated the expression of transcription factors involved in adipogenesis. Adipogenesis is a complex process controlled by a network of transcription factors (37,38). We first analyzed the protein abundance of the two master regulators of adipogenesis: the PPARγ and the C/EBPα and their key upstream positive regulators, kruppel-like transcription factors (KLFs) (39). Figure 4A shows that consistent with the phenotypic expression of reduced fat mass and decreased cell size (shown in Fig. 3), the protein abundance of PPARγ (panel a, lanes 13–16; from four mice), C/EBPα (panel b, lanes 13–16), KLF4 (panel c, lanes 13–16) and KLF9 (panel d, lanes 13–16) in the epididymal fat pad of Thra1PV/+ mice were lower than the respective factors in the WT mice (lanes 1–4; four mice for each genotype). SAHA treatment (lanes 17–20) markedly elevated the protein abundance of PPARγ (panel a), C/EBPα (panel b), KLF4 (panel c) and KLF9 (panel d). The expression of NCOR1ΔID led to higher protein abundance of these four adipogenic transcription factors in the epididymal fat pad of vehicle-treated Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice than in the vehicle-treated Thra1PV/+ mice (compare lanes 21–24 with lanes 13–16). SAHA treatment of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice did not further increase the protein abundance of these four adipogenic transcription factors [lanes 25–28 (40), Figure 4A]. Neither did SAHA treatment affect the protein abundance of four adipogenic factors in the epididymal fat pad of WT and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (compare lanes 1–4 with lanes 5–8; lanes 5–8 with 9–12). The changes in the protein abundance could be clearly seen in the quantitative analysis of the band intensities detected (see Fig. 4B). Figure 4B clearly shows that SAHA treatment led to 10.9-, 8.4-, 5.9- and 5.3-fold increases in the protein abundance of PPARγ, C/EBPα, KLF4 and KLF9, respectively, in the epididymal fat pad of Thra1PV/+ mice. These data indicate that elevated transcription factors induced by SAHA treatment led to the reversal of TRα1PV-mediated impaired adipogenesis.
Figure 4.
SAHA treatment increased expression levels of proteins involved in adipogenesis of epididymal fat tissues in Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice. (A) Western blot analysis was performed with tissue lysate obtained from four different genotypes (Thra1+/+Ncor1+/+, Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID, Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID) with or without treatment of SAHA and the protein expression level of PPARγ, C/EBPα, KLF4 and KLF9 was determined. GAPDH was used as a loading control (n = 4 mice per group). (B) Quantification of relative expression of proteins associated with adipogenesis of fat tissue after normalization by using GAPDH as loading control.
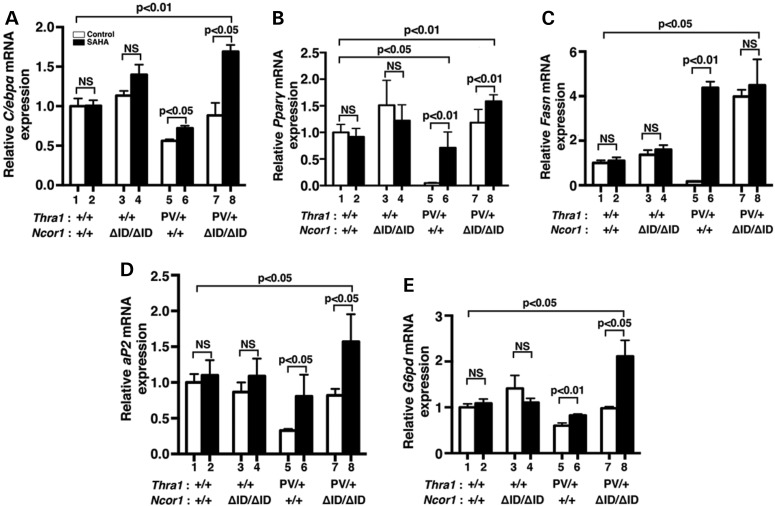
We further analyzed the expression of the C/ebpα and Pparγ genes at the transcription level. We have previously shown that both the C/ebpα and Pparγ genes are the T3 target genes (35). While SAHA treatment did not significantly affect the expression of C/ebpα mRNA in the epididymal fat pad of WT (bars 1 and 2, Fig. 5A) and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (bars 3 and 4, Fig. 5A), it de-repressed the C/ebpα mRNA expression in the epididymal fat pad of Thra1PV/+ mice (compare bar 6 with bar 5). In Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, the expression of NCOR1ΔID partially reverted the repressed expression of the C/ebpα mRNA (compare bar 7 with bar 5). Interestingly, SAHA treatment further increased the mRNA expression by an additional 1.5-fold (compare bar 8 with bar 7). A similar trend was also observed for the expression of the Pparγ mRNA (Fig. 5B) in the epididymal fat pad of four different genotypes. Notably, SAHA treatment of Thra1PV/+ mice reverted the Pparγ mRNA to a level only ∼20% lower than that of WT mice (compare bar 6 with bar 1). This level was in contrast to that of the vehicle-treated Thra1PV/+ mice where the Pparγ mRNA was only 5% of that for WT mice (compare bar 5 with bar 1). These results indicate that SAHA treatment of Thra1PV/+ mice led to the de-repression of the two master regulators of adipogenesis.
Figure 5.
Effects of SAHA on TRα1PV-repressed lipogenic genes in the epididymal fat of Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice. Comparison of the mRNA expression of (A) CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α (C/ebpα), (B) peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (Pparγ), (C) fatty acid synthase (Fasn), (D) fatty acid-binding protein gene (aP2) and (E) glucose-6P-dehydrogenase gene (G6pd) was determined by real-time RT/PCR as described in Materials and Methods. The data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3–9) and P-values are indicated.
We further analyzed the effects of SAHA on the expression of other lipogenic genes downstream of PPARγ. Consistent with the repression of the Pparγ gene shown in Figure 5B, the effects of SAHA on the expression patterns of the fatty acid synthase gene (Fasn) (Fig. 5C), the fatty acid-binding protein gene (aP2) (Fig. 5D) and the glucose-6P-dehydrogenase gene (G6pd) (Fig. 5E) were repressed in the vehicle-treated Thra1PV/+ mice (bar 5), but were increased 25-, 2.5-, and 1.4-fold, respectively, by SAHA treatment. SAHA treatment caused no significant changes in the expression of the Fasn, aP2 and G6pd mRNA in the epididymal fat pad of WT and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (bars 1 and 2, bars 3 and 4, Fig. 5C, D, E). However, treatment of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice with SAHA led to an additional 1.6- to 2.1-fold increase in the expression of aP2 and G6pd mRNA (bar 8 versus bar 7, Fig. 5D and E), with the levels significantly higher than those of WT (1.6-fold and 2.1-fold, respectively; bars 8 versus bar 1). Thus, the elevated expression of these lipogenic genes by SAHA treatment led to the increased white fat pad of Thra1PV/+ mice and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice shown in Figure 3.
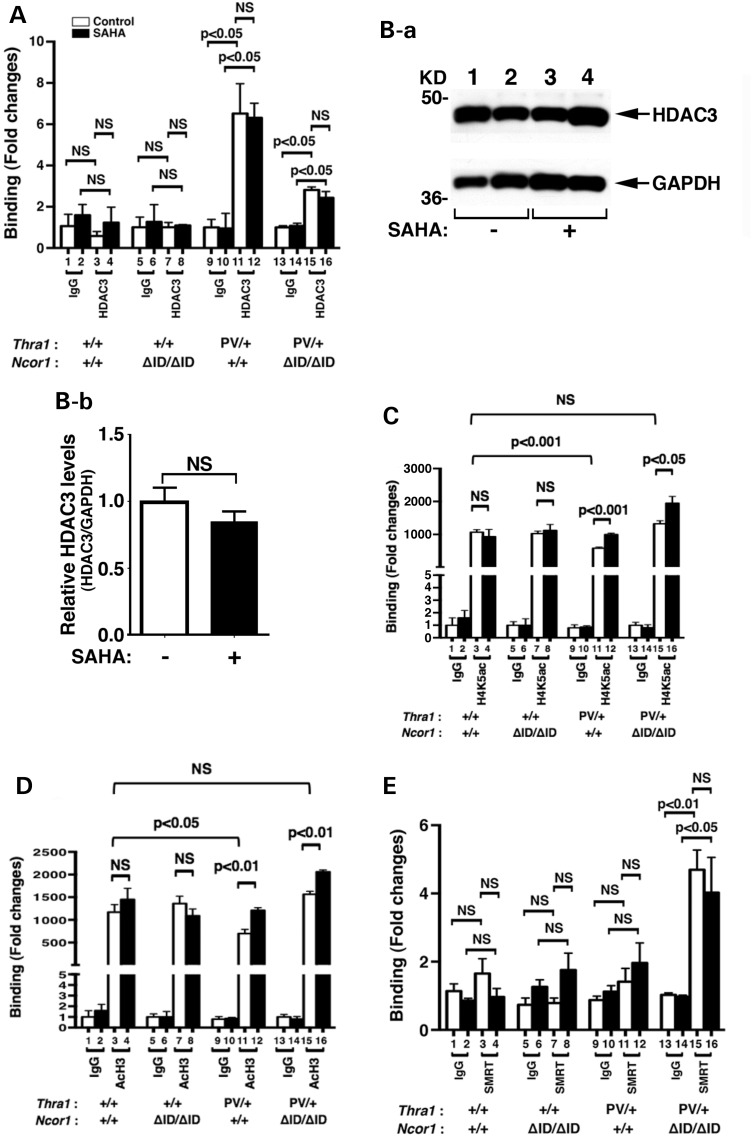
We have previously shown that the C/ebpα gene is directly regulated by TRs. An everted-repeat TRE was identified in the proximal promoter −580 to −608 of the mouse C/ebpα gene (40). That the C/ebpα gene is a TR-direct target gene allowed us to explore whether SAHA treatment altered the recruitment of acetylated core histones to the promoter of the C/ebpα gene. Accordingly, we first assessed the recruitment of HDAC-3 to the promoter of the C/ebpα gene by ChIP assays. Figure 6A shows that in the epididymal fat pad of euthyroid WT and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, no significant recruitment of HDAC-3 above the background to the promoter of the C/ebpα gene was detected (compare bars 3 and 7 to bars 1 and 5, respectively). SAHA treatment did not change the background recruitment level (bars 3 and 4; 7 and 8). In contrast, in the epididymal fat pad of vehicle-treated Thra1PV/+ mice, we detected a strong signal of HDAC-3 recruitment, which was a significant 5-fold above the background (compare bar 11 with bar 9; Fig. 6A). The extent of the HDAC-3 recruitment was not affected in SAHA-treated Thra1PV/+ mice (compare bar 12 with bar 11). In the epididymal fat pad of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice in which we have shown previously that no mutated NCOR1 is recruited to the promoter of the C/ebpα gene (21), a significant recruitment of HDAC-3 two-fold above the background was observed with or without SAHA treatment (bars 13–16; Fig. 6A).
Figure 6.
HDAC-3 regulated the histone acetylation on the promoter of the C/ebpα gene. (A) SAHA did not affect the recruitment of HDAC-3 to the TRE-bound TRα1PV on the promoter of the C/ebpα gene. ChIP assay was carried out using normal rabbit IgG (lanes 1, 2, 5, 6, 9, 10, 13 and 14) or anti-HDAC-3 antibody (lanes 3, 4, 7, 8, 11, 12, 15 and 16) as described in Materials and Methods. (B). Western blot analysis of the HDAC-3 was carried using epididymal tissue lysates of Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ mice with or without SAHA treatment as described in Materials and Methods. GAPDH was used as a loading control (n = 2 mice per group) (B-a). Quantification of the band intensities in B-a normalized to the GAPDH loading control is shown in (B-b). The inhibition of HDAD3 activities by treatment with SAHA increased the level of acetylation of H4K (C) and H3 (D) in Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ and in Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3–5). The fold of changes in binding was based on using IgG as ‘1’ (C and D). (E) SMRT was recruited to the TRE-bound TRα1PV in the epididymal tissues of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice. ChIP assay was carried out using normal rabbit IgG (lanes 1, 2, 5, 6, 9, 10, 13 and 14) or anti-SMRT antibody (lanes 3, 4, 7, 8, 11, 12, 15 and 16) as described in Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3). NS, not significant.
To assess whether the HDAC-3 protein abundance was affected by SAHA, we carried out western blot analysis to determine HDAC-3 protein levels in the epididymal fat pad of Thra1PV/+ mice. Figure 6Ba shows that there were no apparent differences in the band intensities of HDAC-3 proteins detected between mice without (lanes 1 and 2) or with SAHA treatment (lanes 3 and 4). The quantitative data shown in Figure 6Bb clearly show that the protein abundance of HDAC-3 was not affected by SAHA treatment. These data indicate that SAHA inhibited the enzymatic activity, but not the recruitment of HDAC-3 to the promoter of the C/ebpα gene in the epididymal fat pad of Thra1PV/+ mice and in Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice. Thus, the recruitment of HDAC-3 to the promoter of the C/ebpα gene in the epididymal fat pad of Thra1PV/+ mice and in Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice was independent of SAHA treatment. The findings are consistent with the reports that HDAC-3 is directly associated with NCOR1/SMRT in a multiprotein–corepressor complex (25,41,42) and that HDAC-3 is critical for TR-mediated repression (43,44).
We next examined which nucleosomal acetylated histones were affected by SAHA treatment. Histone 4 lysine5 (H4K5) has been identified to be the preferential acetylated site by HDAC-3 (27). We therefore used ChIP analysis to assess the extent of the acetylation of nucleosomal H4K5 associated with the C/ebpα gene before and after SAHA treatment. Figure 6C shows that in the epididymal fat pad of euthyroid WT and Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, no significant differences in the recruitment of nucleosomal acetylated H4K5 was associated with the C/ebpα gene (bars 3 and 4, 7 and 8, Fig. 6C). However, a reduction (∼42%) in the nucleosomal acetylated H4K5 associated with the C/ebpα gene was found in the epididymal fat pad of vehicle-treated Thra1PV/+ mice (compare bar 11 with bar 3, Fig. 6C). Notably, SAHA treatment of Thra1PV/+ mice reverted the extent of acetylated H4K5 to that of the WT level (compare bar 12 with bar 4). In the epididymal fat pad of vehicle-treated Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, the expression of NCOR1ΔID increased the nucleosomal acetylated H4K5 associated with the C/ebpα gene to the level of WT mice (compare bar 15 with bar 3, Fig. 6C). Interestingly, SAHA treatment further elevated the extent of acetylated H4K5 1.8-fold higher than that of WT mice (compare bar 16 with bar 3, Fig. 6C). These data indicate that the inhibition deacetylase activity in the repressor complexes by SAHA led to the persistent acetylation of nucleosomal H4K5 associated with the C/ebpα gene.
We further examined the effect of SAHA treatment on the extent of the acetylation of lysines on nucleosomal histone (H3) associated with the C/ebpα gene by ChIP analysis. A similar profile to that of acetylated H4K5 was apparent in each genotype examined (Fig. 6D). A similar reduction in the nucleosomal acetylated H3 (AcH3) (∼46%) than that of H4K5 was detected in the epididymal fat pad of vehicle-treated Thra1PV/+ mice (compare bar 11 with bar 3, Fig. 6D). SAHA treatment of Thra1PV/+ mice reverted the extent of nucleosomal acetylated H3 to that of the WT level (compare bar 12 with bar 4, Fig. 6D). In vehicle-treated Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, the expression of NCOR1ΔID increased the nucleosomal acetylated H3 associated with the C/ebpα gene to the level of WT mice (compare bar 15 with bar 3, Fig. 6D), which was further increased by SAHA treatment (bar 16 versus bar 15). Taken together, the ChIP analysis findings show that the recruitment of HDAC-3 to the promoter of the C/ebpα gene was SAHA independent. SAHA treatment inhibited the deacetylase activity of HDAC-3 complexing with NCOR1 to de-repress the TRα1PV-mediated repressed transcriptional activity of the C/ebpα gene, thereby ameliorating the impaired adipogenesis of in the epididymal fat pad in Thra1PV/+ mice.
That the treatment of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice with SAHA led to further increase in the extent of acetylation of H4K5 and H3 prompted us to consider that in the mutant NCOR1ΔID, SMRT could be recruited to the TRE-bound TRα1PV. We therefore carried out ChIP assays to evaluate whether SMRT was recruited to the TRE-bound TRα1PV. While we found only background signals in the epididymal fat pad of WT (bars 1–4, Fig. 6E), Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (bars 5–8, Fig. 6E) and Thra1PV/+ mice (bars 9–12, Fig. 6E) with or without SAHA treatment, an ∼5-fold higher than the background signal was detected (bar 15 versus bar 13). This increased recruitment of SMRT was SAHA independent (bar 16 versus bar 15). These results indicate when NCOR1 was mutated and thus cannot be recruited to associate with the TRE-bound TRα1PV, SMRT could assume the redundant role to interact with the TRE-bound TRα1PV.
DISCUSSION
The recent discovery of patients with mutations of the THRA gene is a milestone in research highlighting the critical roles of TR mutants in diseases (10–12). Importantly, this discovery unequivocally shows that the biological consequences of TR mutations are subtype dependent, resulting in different clinical manifestations. It also re-energizes investigators to carry out further studies to understand the molecular actions of mutant TR in vivo. The availability of the Thra1PV/+ mouse model will allow such investigations to elucidate the molecular basis underlying distinct pathological features. Indeed, using the cross of Thra1PV mice with mice expressing a mutant Ncor1 allele (Ncor1ΔID mice) that cannot interact with the PV mutant (Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice), we recently showed that the aberrant recruitment of NCOR1 by TRα1 mutants can lead to clinical hypothyroidism in humans (21). In the present study, we obtained direct evidence in vivo to show that inhibiting the histone deacetylase activity of NCOR1–HDAC complexes bound to TRα1PV by SAHA maintained the hyper-acetylated nucleosomal histones, thereby reactivating the TRα1PV-mediated repression. Such reactivation of T3 target genes by SAHA ameliorated the abnormalities in target tissues in Thra1PV/+ mice. These findings provided the in vivo evidence to illustrate the direct role of HDACs in the pathological manifestation of hypothyroidism caused by mutations of TRα1 mutants. Moreover, these results indicate that inhibitors of HDAC could be beneficial as a treatment modality for patients.
The choice of SAHA for the treatment of mutant mice was based on extensive studies by others showing that HDAC-3 (HDAC Class I) is associated with NCOR1/SMRT in a multi-protein repressor complex (24,25,27,41,42). However, it is of interest to note that in Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, in which no recruitment of NCOR1ΔID/HDAC-3 repressor complexes to the promoter of the C/ebpα target gene was expected, SAHA treatment further improved the impairment in some target tissues such as delayed development in long bone (see Fig. 2B) and adipogenesis of white adipose tissues (see Fig. 3). Consistent with the latter, the expression of the adipogenetic genes, such as the C/ebpα, Pparγ, aP2 and G6pd genes, were also further activated in the white adipose tissues of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (Fig. 5A, B, D and E, respectively). These findings raised the possibility that in some target tissues, such as white adipose tissues, while NCOR1ΔID–HDAC-3 could not be recruited to the DNA-bound TRα1PV, SMRT-HDAC-3 could be recruited to the DNA-bound TRα1PV to mediate the repression of the adipogenic genes. Indeed, we found that SMRT was recruited to the promoter of DNA-bound TRα1PV in the epididymal fat pad of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice (Fig. 6E). This notion is consistent with previous studies demonstrating that NCOR1 is more preferred than SMRT to be recruited by TR to the target genes, due to the presence of the N3 interacting domain in NCOR1, which is not present in SMRT (45,46). This N3 interacting domain is specific for TR and interacts poorly with other receptors, such as the retinoic acid receptor (45). Therefore, in target tissues of Thra1PV/+ mice, NCOR1–HDAC-3 was the major repressor complexes to be recruited to the target gene-bound TRα1PV. In Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, however, NCoR1ΔID–HDAC-3 cannot interact with TRα1PV, thereby allowing DNA-bound TRα1PV to interact with the SMRT–HDAC complex. SAHA treatment thereby further improved the impaired adipogenesis of Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice by inhibiting the activity of HDAC-3 associated with SMRT recruited to DNA-bound TRα1PV. Thus, given that 7–18-fold higher NCOR1 than SMRT is expressed in the mouse white adipose tissue, (www.nursa.org/10.1621/datasets.04002), and the differential preference of TR for NCOR1 than SMRT, NCOR1 plays a dominant role in the TRα1PV-mediated impaired adipogenesis.
The present studies also showed that the effectiveness of SAHA was TR target tissue-selective in Thra1PV/+ mice. SAHA was most effective in correcting impaired adipogenesis (Fig. 3), but was only partially effective in reverting retarded growth and delayed bone development (Fig. 2). Although SAHA was able to partially reduce enlarged thyroid growth, it was ineffective in normalizing the mildly elevated serum TT3 and TSH. SAHA has been shown to have the specificity recognizing HDACs not only in Class I, but also in Classes II and IV (22). The partial phenotypic responses by SAHA treatment would suggest that other classes of HDACs could also be involved in the deacetylation of TR target genes. Therefore, the recruitment of HDACs to NCOR1 corepressor complexes on the TR target genes could not be restricted to Class I (e.g. HDAC-3). HDACs from other classes could also be involved in NCOR1–HDAC repressor complexes. Therefore, the involvement of HDACs would be broader than previously recognized. This notion is plausible as there have been 11 mammalian HDAC enzymes identified in four major classes so far (22). HDACs in each class have different tissue distributions (47). For example, HDAC-1, -2, -3 and -8 in Class I are ubiquitously distributed in tissues. HDAC-4 and -5 in Class IIA are mainly distributed in the heart, skeletal muscle and brain. HDAC-7 in Class IIA is mainly distributed in the heart, skeletal muscles, pancreas and placenta; HDAC-9 in Class IIA is distributed in the heart and skeletal muscles. HDAC-6 in Class IIB is present in the heart, liver, kidney and placenta, and HDAC-10 in Class IIB is present in the liver and the spleen. The tissue distribution patterns of the mammalian sirtuins in Class III are not clear. But it is known that HDAC-11 in Class IV is distributed mainly in the brain, heart, skeletal muscles and kidney. Thus, it is reasonable that the tissue-dependent expressed HDACs other than HDAC-3 could also be recruited to the NCOR1–HDAC repression complexes in TR target tissues. Because of inhibitor-substrate specificity, these HDACs could be resistant to the inhibitory activity of SAHA, thereby accounting for the different levels of effectiveness of SAHA in the correction of abnormalities of mutant mice.
Recently, van Mullem reported the clinical consequences of T4 treatment of two patients (father and daughter) expressing the TRα1F397fs406X mutant receptor (48). After 5 years of treatment with T4, the patients' TSH was suppressed, and serum free T4, but not T3, were normalized. In addition, dyslipidemia, constipation, nerve conductance, IGF-1 and other serum markers of thyroid status were ameliorated. However, other abnormal clinical features such as cognitive and fine motor skill defects were not affected by T4 treatment. Moreover, the parameters that were normalized returned to the pre-treatment values when T4 was briefly stopped. That refractory to T4 treatment in some target tissues was also recently reported for a patient with hypothyroidism caused by a TRα1 mutant (48). These results show that in patients with hypothyroidism due to TRα1 mutations, T4 treatment is not effective in improving the resistance in all target tissues.
While the clinical symptoms of those three patients could be partially improved by T4 treatment (48), the present studies show that HDAC inhibitors could be considered a potential option for treatment of patients with mutations of the THRA gene. Early development of HDAC inhibitors as therapeutic targets was mainly for the treatment of cancer (22,23). Recently, however, this approach has been expanded to include other diseases such as metabolic disorders, interstitial fibrosis, immune dysfunction and inflammatory diseases (23). HDAC inhibitors are a family of naturally derived and synthetically produced compounds, each with a different structure, biological activity and specificity (22,23). Our choice of SAHA in the present studies was also based on a safety consideration; namely, SAHA has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to be used in the treatment of refractory CTCL (28,29). While the mechanisms of the anti-tumorigenic effects remain to be fully elucidated, our use of ChIP assays provided evidence to show that one mechanism is via the increase in the extent of acetylation of the nuclesosomal histones, resulting in the de-repression of the TR target genes in tissues. Therefore, the therapeutic effectiveness of HDAC inhibitors could differ from that of T4. This would open the possibility of using HDAC inhibitors to complement the T4 treatment modality. With a wide range of the selection of natural and synthetic known HDAC inhibitors, and those yet to be developed for better safety and effectiveness, HDAC inhibitors offer promise for improved treatment options.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and treatment
This animal study was carried out according to the protocol approved by the National Cancer Institute Animal Care and Use Committee. Mice harboring the mutant Thra1PV gene (Thra1PV mice) were prepared and genotyped as described earlier (15). Ncor1ΔID mice were prepared as described by Astapova et al. (20). Thra1PV mice were crossed with Ncor1ΔID mice to obtain different genotypes for studies. These mice were intercrossed several generations, and littermates with a similar genetic background were used in all experiments. SAHA (Selleck Chemicals) was added to water at 10 mg/ml, heated to 95°C until dissolved and kept at −70°C and administered by oral gavage daily at a dose of 50 mg/kg body weight (49,50) starting at the age of 6 weeks for 2 months.
Hormone assays
The serum levels of total T4 and total T3 were determined using a Gamma Coat T4 and T3 assay RIA kit (Dia-Sorin). Serum TSH levels were measured as previously described (51). The serum levels of IGF-1 were determined by using an IGF-1 Mouse ELISA Kit (Alpco) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
RNA isolation and quantitative real-time RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from pituitary by using TRIzol (Invitrogen), and fat tissues were extracted using an RNeasy lipid tissue mini kit (QIAGEN) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed with a Quantitect SYBR Green RT-PCR kit (QIAGEN), according to the manufacturer's instructions and using a 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR system (AB Applied Biosystems). Total RNA (100 ng) was used in RT-PCR determinations as described previously (52). The specific primer sequences used in RT-PCR are as follows: C/ebpα forward 5′-TTACAACAGGCCAGGTTTCC-3′; reverse 5′-CTCTGGGATGGATCGATTGT-3′, Pparγ forward 5′-TTTTCAAGGGTGCCAGTTTC-3′; reverse 5′-AATCCTTGGCCCTCTGAGAT-3′, Fasn forward 5′-TGGGTTCTAGCCAGCAGAGT-3′; reverse 5′-ACCACCAGAGACCGTTATGC-3′, aP2 forward 5′-CTGGACTTCAGAGGCTCATAGCA-3′; reverse 5′-TACTCTCTGACCGGATGGTGACCAA-3′, G6pd forward 5′-GAGGAGTTCTTTGCCCGTAAT-3′; reverse 5′-CATCTCTTTGCCCAGGTAGTG-3′, Gh forward 5′-TTCGAGCGTGCCTACATT-3′; reverse 5′-GCATGTTGGCGTCAAACTTG-3′.
Western blot analysis
Frozen epididymal fat pads were homogenized on ice in lysis buffer containing 50 mm Tris⋅HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 0.5% Triton X-100, 1× protease inhibitor mixture (Roche) and western blot analysis with the lysates was similarly carried out as described (40). The antibodies used were anti-PPARγ (1:200 dilution, sc-7273, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), anti-C/EBPα (1:200 dilution, sc-61, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), anti-KLF4 (1:200 dilution, sc-20691, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) and anti-KLF9 (1:200 dilution, sc-12966, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), anti-HADC3 (1:10,000 dilution, ab 7030, abcam, MA, USA) and anti-GAPDH (1:1000 dilution, #2118, Cell Signaling, MA, USA). Band intensities were quantified by using the NIH IMAGE software (ImageJ 1.34s; Wayne Rasband, NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay
ChIP assay with fat tissue was performed as described previously (21) with slight modification. Briefly, mouse epididymal fat tissues were dissected from mice with different genotypes (Thra1+/+Ncor1+/+, Thra1+/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID, Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID) with or without treatment of SATA. Three hundred milligrams of fat tissue was chopped with scissors, fixed in 1% of formaldehyde for 10 min and quenched by addition of glycine with a 0.125 m final concentration for 5 min. Immunoprecipitation was carried out using Anti-HDAC3 (sc-11417X, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), Anti-Histone H4 (acetyl K5) (ab51997, Abcam, MA, USA), Anti-acetyl-Histone H3 (06-599, Millipore, MA, USA), Anti-SMRT (06-891, Millipore, MA, USA) or IgG as a negative control. Subsequent steps in ChIP assays were carried out as described previously (21). The ChIP primers used were C/ebpα forward, 5′-TAGAGAAGCTGGGCGAAAAGA-3′; and reverse, 5′-AGGTTGGAGACTGCTTTGGA-3′.
Histological analysis
Epididymal fat was dissected, fixed in 10% (vol/vol) neutral buffered formalin (Sigma-Aldrich) and subsequently embedded in paraffin. Sections of 5 μm thickness were prepared and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). For each animal, single random sections through the epididymal fat were examined. NIH IMAGE software was used for the measurement of the size of white adipocytes with epididymal fat of Thra1+/+Ncor1+/+ mice, Thra1+/+ Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice, Thra1PV/+Ncor1+/+ mice and Thra1PV/+Ncor1ΔID/ΔID mice with or without treatment of SAHA.
Statistical analysis
All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Differences between groups were examined for statistical significance using Student's t-test with the use of GraphPad Prism 6. P < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
FUNDING
The present research was supported by the Intramural Research Program at the Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr Anthony Hollenberg, Beth Israel Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, for the generosity of allowing us to use the Ncor1ΔID mouse in our studies.
Conflict of Interest statement. None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Sap J., Munoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennstrom B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986;324:635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Weinberger C., Thompson C.C., Ong E.S., Lebo R., Gruol D.J., Evans R.M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986;324:641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cheng S.Y. Multiple mechanisms for regulation of the transcriptional activity of thyroid hormone receptors. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2000;1:9–18. doi: 10.1023/a:1010052101214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Johnson A.B., O'Malley B.W. Steroid receptor coactivators 1, 2, and 3: critical regulators of nuclear receptor activity and steroid receptor modulator (SRM)-based cancer therapy. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012;348: 430–439. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.04.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Buzon V., Carbo L.R., Estruch S.B., Fletterick R.J., Estebanez-Perpina E. A conserved surface on the ligand binding domain of nuclear receptors for allosteric control. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012;348:394–402. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brent G.A. Mechanisms of thyroid hormone action. J. Clin. Invest. 2012;122:3035–3043. doi: 10.1172/JCI60047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Refetoff S., Weiss R.E., Usala S.J. The syndromes of resistance to thyroid hormone. Endocr. Rev. 1993;14:348–399. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-3-348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Refetoff S., DeWind L.T., DeGroot L.J. Familial syndrome combining deaf-mutism, stuppled epiphyses, goiter and abnormally high PBI: possible target organ refractoriness to thyroid hormone. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1967;27:279–294. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-2-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sakurai A., Takeda K., Ain K., Ceccarelli P., Nakai A., Seino S., Bell G.I., Refetoff S., DeGroot L.J. Generalized resistance to thyroid hormone associated with a mutation in the ligand-binding domain of the human thyroid hormone receptor beta. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1989;86:8977–8981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bochukova E., Schoenmakers N., Agostini M., Schoenmakers E., Rajanayagam O., Keogh J.M., Henning E., Reinemund J., Gevers E., Sarri M., et al. A mutation in the thyroid hormone receptor alpha gene. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;366:243–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van Mullem A., van Heerebeek R., Chrysis D., Visser E., Medici M., Andrikoula M., Tsatsoulis A., Peeters R., Visser T.J. Clinical phenotype and mutant TRalpha1. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;366:1451–1453. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1113940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Moran C., Schoenmakers N., Agostini M., Schoenmakers E., Offiah A., Kydd A., Kahaly G., Mohr-Kahaly S., Rajanayagam O., Lyons G., et al. An adult female with resistance to thyroid hormone mediated by defective thyroid hormone receptor alpha. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013;98:4254–4261. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Parrilla R., Mixson A.J., McPherson J.A., McClaskey J.H., Weintraub B.D. Characterization of seven novel mutations of the c-erbA beta gene in unrelated kindreds with generalized thyroid hormone resistance. Evidence for two ‘hot spot’ regions of the ligand binding domain. J. Clin. Invest. 1991;88:2123–2130. doi: 10.1172/JCI115542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kaneshige M., Kaneshige K., Zhu X., Dace A., Garrett L., Carter T.A., Kazlauskaite R., Pankratz D.G., Wynshaw-Boris A., Refetoff S., et al. Mice with a targeted mutation in the thyroid hormone beta receptor gene exhibit impaired growth and resistance to thyroid hormone. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:13209–13214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.230285997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kaneshige M., Suzuki H., Kaneshige K., Cheng J., Wimbrow H., Barlow C., Willingham M.C., Cheng S. A targeted dominant negative mutation of the thyroid hormone alpha 1 receptor causes increased mortality, infertility, and dwarfism in mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2001;98:15095–15100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261565798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.O'Shea P.J., Bassett J.H., Sriskantharajah S., Ying H., Cheng S.Y., Williams G.R. Contrasting skeletal phenotypes in mice with an identical mutation targeted to thyroid hormone receptor alpha1 or beta. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005;19:3045–3059. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.O'Shea P.J., Bassett J.H., Cheng S.Y., Williams G.R. Characterization of skeletal phenotypes of TRalpha1 and TRbeta mutant mice: implications for tissue thyroid status and T3 target gene expression. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2006;4:e011. doi: 10.1621/nrs.04011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cheng S.Y. Isoform-dependent actions of thyroid hormone nuclear receptors: lessons from knockin mutant mice. Steroids. 2005;70:450–454. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2005.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Astapova I., Lee L.J., Morales C., Tauber S., Bilban M., Hollenberg A.N. The nuclear corepressor, NCoR, regulates thyroid hormone action in vivo. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:19544–19549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804604105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Astapova I., Vella K.R., Ramadoss P., Holtz K.A., Rodwin B.A., Liao X.H., Weiss R.E., Rosenberg M.A., Rosenzweig A., Hollenberg A.N. The nuclear receptor corepressor (NCoR) controls thyroid hormone sensitivity and the set point of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011;25:212–224. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fozzatti L., Kim D.W., Park J.W., Willingham M.C., Hollenberg A.N., Cheng S.Y. Nuclear receptor corepressor (NCOR1) regulates in vivo actions of a mutated thyroid hormone receptor alpha. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:7850–7855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222334110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ververis K., Hiong A., Karagiannis T.C., Licciardi P.V. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs): multitargeted anticancer agents. Biologics. 2013;7:47–60. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S29965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tang J., Yan H., Zhuang S. Histone deacetylases as targets for treatment of multiple diseases. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2013;124:651–662. doi: 10.1042/CS20120504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Guenther M.G., Barak O., Lazar M.A. The SMRT and N-CoR corepressors are activating cofactors for histone deacetylase 3. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;21:6091–6101. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.18.6091-6101.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wen Y.D., Perissi V., Staszewski L.M., Yang W.M., Krones A., Glass C.K., Rosenfeld M.G., Seto E. The histone deacetylase-3 complex contains nuclear receptor corepressors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:7202–7207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.13.7202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fischle W., Dequiedt F., Hendzel M.J., Guenther M.G., Lazar M.A., Voelter W., Verdin E. Enzymatic activity associated with class II HDACs is dependent on a multiprotein complex containing HDAC3 and SMRT/N-CoR. Mol. Cell. 2002;9:45–57. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00429-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hartman H.B., Yu J., Alenghat T., Ishizuka T., Lazar M.A. The histone-binding code of nuclear receptor co-repressors matches the substrate specificity of histone deacetylase 3. EMBO Rep. 2005;6:445–451. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Marks P.A., Breslow R. Dimethyl sulfoxide to vorinostat: development of this histone deacetylase inhibitor as an anticancer drug. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007;25:84–90. doi: 10.1038/nbt1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Duvic M., Talpur R., Ni X., Zhang C., Hazarika P., Kelly C., Chiao J.H., Reilly J.F., Ricker J.L., Richon V.M., et al. Phase 2 trial of oral vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) Blood. 2007;109:31–39. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-06-025999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ramalingam S.S., Maitland M.L., Frankel P., Argiris A.E., Koczywas M., Gitlitz B., Thomas S., Espinoza-Delgado I., Vokes E.E., Gandara D.R., et al. Carboplatin and Paclitaxel in combination with either vorinostat or placebo for first-line therapy of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010;28:56–62. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Munster P.N., Thurn K.T., Thomas S., Raha P., Lacevic M., Miller A., Melisko M., Ismail-Khan R., Rugo H., Moasser M., et al. A phase II study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat combined with tamoxifen for the treatment of patients with hormone therapy-resistant breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer. 2011;104:1828–1835. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kirschbaum M., Frankel P., Popplewell L., Zain J., Delioukina M., Pullarkat V., Matsuoka D., Pulone B., Rotter A.J., Espinoza-Delgado I., et al. Phase II study of vorinostat for treatment of relapsed or refractory indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:1198–1203. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.32.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Das P., Meyer L., Seyfert H.M., Brockmann G., Schwerin M. Structure of the growth hormone-encoding gene and its promoter in mice. Gene. 1996;169:209–213. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00815-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Araki O., Ying H., Zhu X.G., Willingham M.C., Cheng S.Y. Distinct dysregulation of lipid metabolism by unliganded thyroid hormone receptor isoforms. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009;23:308–315. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ying H., Araki O., Furuya F., Kato Y., Cheng S.Y. Impaired adipogenesis caused by a mutated thyroid hormone alpha1 receptor. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;27:2359–2371. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02189-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhu X., Cheng S.Y. New insights into regulation of lipid metabolism by thyroid hormone. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2010;17:408–413. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e32833d6d46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sarjeant K., Stephens J.M. Adipogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2012;4:a008417. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Henry S.L., Bensley J.G., Wood-Bradley R.J., Cullen-McEwen L.A., Bertram J.F., Armitage J.A. White adipocytes: more than just fat depots. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012;44:435–440. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Farmer S.R. Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 2006;4:263–273. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.07.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fozzatti L., Lu C., Kim D.W., Park J.W., Astapova I., Gavrilova O., Willingham M.C., Hollenberg A.N., Cheng S.Y. Resistance to thyroid hormone is modulated in vivo by the nuclear receptor corepressor (NCOR1) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:17462–17467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107474108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Karagianni P., Wong J. HDAC3: taking the SMRT-N-CoRrect road to repression. Oncogene. 2007;26:5439–5449. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li J., Wang J., Wang J., Nawaz Z., Liu J.M., Qin J., Wong J. Both corepressor proteins SMRT and N-CoR exist in large protein complexes containing HDAC3. EMBO J. 2000;19:4342–4350. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.16.4342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ishizuka T., Lazar M.A. The N-CoR/histone deacetylase 3 complex is required for repression by thyroid hormone receptor. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;23:5122–5131. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.15.5122-5131.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yoon H.G., Choi Y., Cole P.A., Wong J. Reading and function of a histone code involved in targeting corepressor complexes for repression. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005;25:324–335. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.1.324-335.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cohen R.N., Brzostek S., Kim B., Chorev M., Wondisford F.E., Hollenberg A.N. The specificity of interactions between nuclear hormone receptors and corepressors is mediated by distinct amino acid sequences within the interacting domains. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001;15:1049–1061. doi: 10.1210/mend.15.7.0669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Makowski A., Brzostek S., Cohen R.N., Hollenberg A.N. Determination of nuclear receptor corepressor interactions with the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003;17:273–286. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Witt O., Deubzer H.E., Milde T., Oehme I. HDAC family: what are the cancer relevant targets. Cancer Lett. 2009;277:8–21. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.van Mullem A.A., Chrysis D., Eythimiadou A., Chroni E., Tsatsoulis A., de Rijke Y.B., Visser W.E., Visser T.J., Peeters R.P. Clinical phenotype of a new type of thyroid hormone resistance caused by a mutation of the TRalpha1 receptor: consequences of LT4 treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013;98:3029–3038. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Leoni F., Zaliani A., Bertolini G., Porro G., Pagani P., Pozzi P., Dona G., Fossati G., Sozzani S., Azam T., et al. The antitumor histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid exhibits antiinflammatory properties via suppression of cytokines. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:2995–3000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052702999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Glauben R., Batra A., Fedke I., Zeitz M., Lehr H.A., Leoni F., Mascagni P., Fantuzzi G., Dinarello C.A., Siegmund B. Histone hyperacetylation is associated with amelioration of experimental colitis in mice. J. Immunol. 2006;176:5015–5022. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.8.5015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Furumoto H., Ying H., Chandramouli G.V., Zhao L., Walker R.L., Meltzer P.S., Willingham M.C., Cheng S.Y. An unliganded thyroid hormone beta receptor activates the cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent kinase/retinoblastoma/E2F pathway and induces pituitary tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005;25:124–135. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.1.124-135.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ying H., Suzuki H., Furumoto H., Walker R., Meltzer P., Willingham M.C., Cheng S.Y. Alterations in genomic profiles during tumor progression in a mouse model of follicular thyroid carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2003;24:1467–1479. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgg111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]