Abstract
Despite a high heritability, a genetic diagnosis can only be established in a minority of patients with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), characterized by persistent deficits in social communication and interaction and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests or activities1. Known genetic causes include chromosomal aberrations, such as the duplication of the 15q11-13 region, and monogenic causes, such as the Rett and Fragile X syndromes. The genetic heterogeneity within ASD is striking, with even the most frequent causes responsible for only 1% of cases at the most. Even with the recent developments in next generation sequencing, for the large majority of cases no molecular diagnosis can be established 2-7. Here, we report 10 patients with ASD and other shared clinical characteristics, including intellectual disability and facial dysmorphisms caused by a mutation in ADNP, a transcription factor involved in the SWI/SNF remodeling complex. We estimate this gene to be mutated in at least 0.17% of ASD cases, making it one of the most frequent ASD genes known to date.
Recent developments in next-generation sequencing (NGS), in particular whole-exome sequencing (WES), have substantially increased our insights in the genetic causes of neurodevelopmental disorders. By trio analysis of patients with intellectual disability, a causal de novo mutation can be identified in 16-50% of cases8-11. Interestingly, intellectual disability shows a high comorbidity with ASD, which is present in up to 40% of intellectual disability cases and may be caused by defects in the same genes or pathways12-14. This observation prompted the analysis of existing ASD cohorts with WES2,3,5,6,15. Although mutations were identified in a significant percentage of ASD patients, most mutations seem to be unique and recurrently mutated genes are scarce16.
In an initial cohort of 10 patients with intellectual disability, ASD and facial dysmorphisms, we identified a patient with a de novo mutation in the transcription factor ADNP using WES (Supplementary Fig. 1). De novo loss of function mutations in this gene had previously been identified in two patients by WES2 and targeted resequencing16 of patients with ASD. In those studies however, causal relationship did not reach locus-specific significance. Based on these initial findings and the association of ADNP with neuronal cell differentiation and maturation17, as well as the cognitive abnormalities observed in a mouse model18, we considered ADNP a strong candidate gene. We subsequently identified three mutations in ADNP in 240 patients from three independent WES studies (Table 1). Next, we targeted ADNP using molecular inversion probes (MIPs) or high resolution melt curve analysis (HRM) in a cohort of 2,891 patients with syndromic ASD and identified four more patients with mutations in this gene. In total, ten mutations were found in 5,776 patients. For nine patients the parents were available for testing and in each case the mutation appeared de novo (Table 1). We found no additional non-synonymous de novo variants. Neither did we find X-chromosomal, compound or homozygous variants in known intellectual disability/ASD genes. Autism and comorbidity with mild to severe intellectual disability is a consistent feature in all patients (Table 2, Supplementary Note). Other frequent findings include hypotonia, feeding problems in infancy and congenital heart defects. A seizure disorder was noted in two patients. Additional neuropsychiatric features are relatively common, including attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, anxiety disorder and obsessive compulsive behavior. Dysmorphic features include a prominent forehead, high hairline, eversion or notch of the eyelid, broad nasal bridge, thin upper lip and smooth/long philtrum (Figure 1).
Table 1.
Summary of mutations, detection methods and cohorts compositions for the reported patients. All genomic coordinates relate to genome build GRCh37. WES: Whole Exome Sequencing, HRM: High Resolution Melting, MIPs: Molecular Inversion Probes
| Patient | Patient ID | Origin | Screening method | Cohort composition | Cohort size | mutation in genomic DNA (chr20) | mutation in cDNA (NM_015339.2) | Protein | Mutation Type | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 111294 | Antwerp | WES | Moderate to severe intellectual disability and/or autism + dysmorphic features | 10 | g.49508752_49508755delTTTA | c.2496_2499delTAAA | p.Asp832Lysfs*80 | Frameshift | de novo |
| 2 | 11-08612 | Nijmegen | WES | Non-syndromic severe intellectual disability | 100 | g.49510040G>T | c.1211C>A | p.Ser404* | Nonsense | de novo |
| 3 | 12130.p1 | Seattle | WES2,16 | ASD from the Simon Simplex Collection | 189 | g.49510028_49510029delTT | c.1222_1223delAA | p.Lys408Valfs*31 | Frameshift | de novo |
| 4 | 1050237 | Westmead | WES | Non-syndromic severe intellectual disability | 95 | g.49509086_49509098delATTTGCTCGTAAG | c.2153_2165delCTTACGAGCAAAT | p.Thr718Glyfs*12 | Frameshift | de novo |
| 5 | 3061-08D | Stockholm | WES | Moderate to severe intellectual disability and/or autism + dysmorphic features | 45 | g.49509094G>C | c.2157C>G | p.Tyr719* | Nonsense | de novo |
| 6 | 122793 | Antwerp | HRM | Autism | 148 | g.49508757_49508760delTTAA | c.2491_2494delTTAA | p.Lys831Ilefs*81 | Frameshift | de novo |
| 7 | 07-06960 | Nijmegen | MIPs | Intellectual disability and/or autism | 2743* | g.49508443delG | c.2808delC | P.Tyr936* | Frameshift | de novo |
| 8 | 2376 | Troina | MIPs | Intellectual disability and/or autism | 2743* | g.49508757_49508760delTTAA | c.2491_2494delTTAA | p.Lys831Ilefs*81 | Frameshift | de novo |
| 9 | 2533 | Troina | MIPs | Intellectual disability and/or autism | 2743* | g.49509321G>A | c.1930C>T | p.644Arg* | Nonsense | parents not available |
| 10 | 13545.p1 | Seattle | MIPs16 | ASD from the Simon Simplex Collection | 2446 | g.49509094_49509095insT | c.2156_2157insA | p.Tyr719* | Frameshift | de novo |
patients 7, 8 and 9 from the same cohort
Table 2.
Clinical characteristics of the patients with ADNP mutations
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 | Patient 7 | Patient 8 | Patient 9 | Patient 10 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | M | F | F | M | M | M | F | M | F | M | |
| Developmental delay (motor) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | 9/10 |
| Developmental delay (speech) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | 8/9 | |
| Intellectual Disability | mild | mild | mild | severe | severe | severe | mild | severe | mild | severe | 10/10 |
| ASD | + | + | + | + | + | + | ± | + | ± | + | 10/10 |
| ADHD | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | 2/9 | |
| Hypotonia | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | - | 7/9 | |
| Growth retardation / Short stature | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | 5/8 | ||
| Feeding problems | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | + | 5/8 | ||
| Recurrent infections | + | + | - | + | - | - | + | + | 5/8 | ||
| Congenital heart defect | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | 3/8 | ||
| Hyperlaxity | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | 6/8 | ||
| Obesity | - | - | + | + | - | ± | + | 4/7 | |||
| Hypermetropia | + | + | + | + | + | + | 6/6 | ||||
| Seizures | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | 2/7 | |||
| Behavior | + | + | - | + | - | + | + | 5/7 | |||
| Insensitivity to pain | - | + | + | - | - | 2/5 | |||||
| MRI brain abnormality | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | 5/9 | |
| Prominent forehead | + | + | - | + | - | + | + | - | 5/8 | ||
| High hairline | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | 7/8 | ||
| Eversion/notch eyelid | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | 3/7 | |||
| Hypertelorism | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1/8 | ||
| Broad nasal bridge | + | + | + | - | + | - | + | + | 6/8 | ||
| Short nose | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | 2/8 | ||
| Thin upper lip | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | 6/7 | |||
| Hand abnormalities | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | 6/8 | ||
| Constipation | - | + | + | - | - | - | 2/6 |
Figure 1.
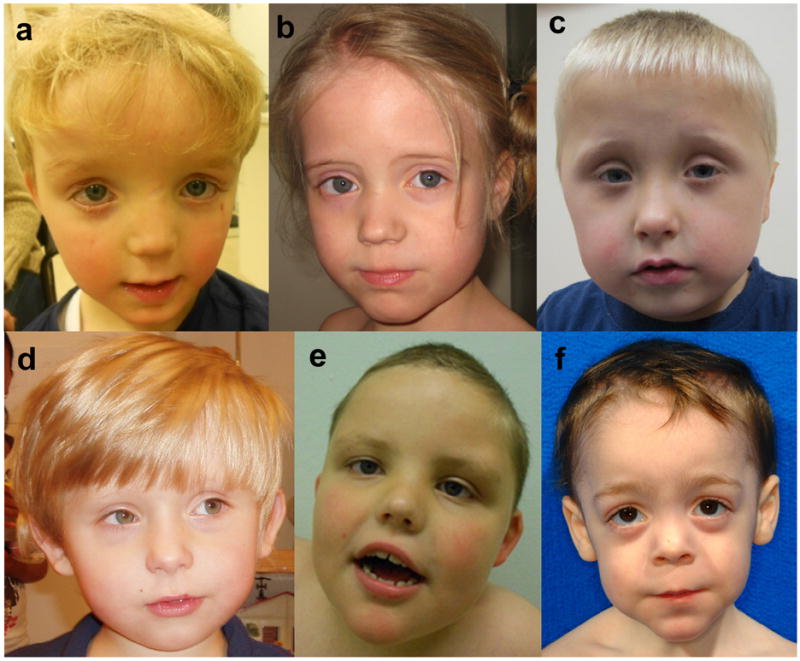
Frontal facial photographs of patient 1 (a),2 (b), 4 (c), 5 (d), 6 (e) and 8 (f) at young age. Note the clinical similarities, including a prominent forehead, a thin upper lip and a broad nasal bridge. Consent for the publication of photographs was obtained for these patients (1, 2, 4, 5, 6 and 8).
All mutations are heterozygous frameshift or nonsense variants in the C-terminal part of the last exon of ADNP and result in a premature termination codon (Table 1). None were present in the 1,000 Genomes Project19, in 1,728 MIP sequenced unaffected siblings form the Simons Simplex Collection, or in 192 HRM analyzed chromosomes from healthy Belgian controls. Putative truncating mutations for ADNP are in fact rare. Only one p.Q361* nonsense mutation upstream of all our mutations was reported in the 13,006 alleles of the Exome Sequencing Project (ESP). An inherited p.Gly1094Profs*5 mutation was identified by MIP sequencing16 but the reported frameshift is the ninth amino acid from the C-terminal end of the protein and not associated with any protein domains. Typically, variations that close to the end of a protein are unlikely to affect function. The frequency of truncating mutations in ADNP is significantly higher (p: 0.001852, odds ratio 13.24668, one-sided Fisher’s exact test) in patients compared to the ESP and Simons Siblings controls. In addition to the case-control analysis, we calculated a locus-specific enrichment for truncating variation using a probabilistic model derived from human-chimpanzee fixed difference and sequence context as described16. Under a de novo rate of 1.2 non-synonymous coding variants per individual, we estimate the probability of detecting eight or more de novo truncating events in ADNP within our cohort as p = 2.65e-18 (binomial test).
The mutated gene, ADNP (chr20:49506883-49547527, GRCh37/hg19), contains five exons, of which the last three are translated (Figure 2). The protein consists of 1,102 amino acids and contains nine zinc fingers and three other functional domains, including NAP, an eight amino acid neuroprotectant peptide (NAPVSIPQ)20,21. Administration of NAP ameliorated the short-term memory deficits in ApoE knockout mice, a model for Alzheimer’s disease22. In ADNP+/- mice, NAP treatment restores learning and memory and reduces neurodegeneration18. Further downstream a DNA binding homeobox domain is present, homologous to the HOX gene family homeobox domains (InterPro, EBI). A P*V*L motif, which can bind the HP1 protein is located just downstream of the homeobox domain. The HP1 protein binds to and mediates H3 lysine 9 trimethylation histone posstranslational modification23-25. The homeobox domain and the HP1-binding motif are responsible for the transcription factor function of ADNP.
Figure 2.
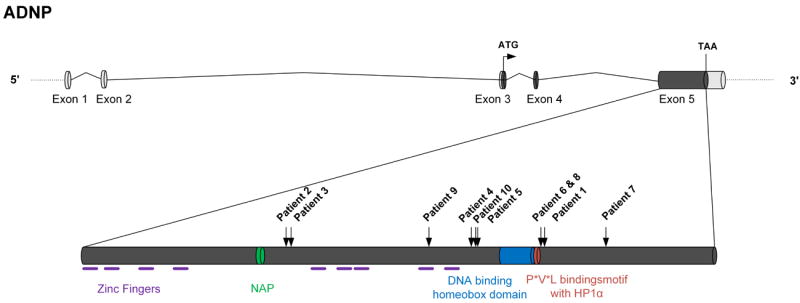
Schematic overview of the ADNP gene structure and functional domains. Identified mutations and corresponding patients are indicated by black arrows.
Almost the complete 1.6Kb sequence spanned by the mutations is conserved in mammals (PhyloP M=1.52, s=1.25)26. All mutations result in the loss of at least the 166 last C-terminal amino acids. Strikingly, the identified mutations appear to cluster at specific positions. The 4bp de novo deletions in both patient 6 and 8 are identical even though these patients are unrelated and were born and live in different countries. This mutation is separated by only one nucleotide from the 4bp deletion in patient 1. Additonally, the mutations observed in patients 5 and 10 fall within the 13bp deletion in patient 4. Clustering of de novo, rare variants is suggestive of a mutation predisposition mechanism, potentially as a result of a particular local genomic architecure. We found no evidence for the presence of simple or tandem repeats in this region. Mfold analysis (web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction)27 showed that the clustered 4bp deletions of patients 1, 6 and 8 are located in the stem of the same short hairpin (Supplementary Fig. 2). Hence, we suggest that the underlying mechanism of the mutations may involve a DNA repair defect following pausing of a replication fork at these hairpins.
Since no exon-exon boundary in the ADNP mRNA is present downstream from any of the mutations, nonsense mediated RNA decay (NMD) is unlikely28-30. Indeed, the mutations were present in the cDNA generated from lymphoblastoid cell lines of patients 1, 2, 6 and 8. To quantify the impact of truncating mutations on the expression of ADNP, we performed expression analysis. Also included in the expression analysis is a set of selected genes previously shown to interact or to be coregulated with ADNP18,23,31,32. The total level of ADNP mRNA was significantly increased by 41% in patients 1, 2, 6 and 8 (Supplementary Fig. 3b, Table 3). A single assay specific for the wildtype but not the mutant ADNP allele could be generated for patients 1, 6 and 8 to discriminate between wildtype and mutant mRNA expression. The expression of this ADNPwt amplicon was not different from controls, demonstrating that the excess ADNP mRNA in patients corresponds to the mRNA transcribed from the mutant allele. Since ADNP expression is under control of an autoregulatory negative feedback loop33, the overall upregulation might be a consequence of the inability of the mutant protein to bind the ADNP promoter. This suggests a deregulation of the negative feedback leading to increased levels of ADNP mRNA in order to restore homeostasis. Expression of ADNP2 (Supplementary Fig. 3c) was also significantly upregulated in patients, which is in line with the reported high correlation between the expression levels of ADNP and ADNP231. Of the other genes reported as differentially expressed in Adnp-/-23 and Adnp+/-18 mice (down: CCNC, TMPO, PLAGL2; up: ABCF3), only PLAGL2 was found to be differentially regulated in our patients (Supplementary Fig. 3e). This may be the consequence of differences in tissue and developmental stage between the knockout mice and the human cell lines. Expression levels of TP53, reported upregulated in HT29 cells incubated with ADNP antioligodeoxynucleotide32, were significantly increased (Supplementary Fig. 3g), possibly as a result of augmented cellular stress due to an overall deregulation of genes under transcriptional control of ADNP.
Table 3.
Realtime quantitative expression analysis of mRNA from EBV transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines of patients 1, 2, 6 and 8 compared to 8 control samples.
| Gene | Relative Expression (%) | S.E.M. | P-value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCF3 | 94.03 | 14.31 | 0.6507 | |
| ADNP | 141.67 | 13.4 | 0.0101 | * |
| ADNP2 | 148.52 | 17.58 | 0.0060 | ** |
| ADNPwt | 74.28 | 4.14 | 0.0729 | |
| CCNC | 87.98 | 6.72 | 0.2857 | |
| PLAGL2 | 153.49 | 21.4 | 0.0040 | ** |
| TMPO | 80.26 | 11.24 | 0.2462 | |
| TP53 | 164.81 | 6.17 | 0.0003 | *** |
: p < 0.05,
: p< 0.01,
:p<0.001, according to Linear Mixed Models.
ADNP has multiple cellular functions that seem compatible with the clinical presentation of our patients. A role in neuronal cell differentiation and maturation was suggested after observing a substantial decrease in the number and size of embryoid bodies and the number of neurites after knockdown of ADNP with shRNA in P19 cells17. Furthermore, Adnp-/- mice are not viable due to failure of the neural tube closure, while ADNP+/- mice show tauopathy, neuronal cell death and abnormalities in social behaviour and cognitive functioning18,34. The severity of the phenotype in our cohort varies, but all patients exhibit various degrees of ASD and all are intellectually disabled. Dysmorphic features vary from patient to patient, but a prominent forehead, broad nasal bridge, thin upper lip and smooth philtrum are frequently present. Cardiac, brain and behavioral abnormalities are more frequent in our patients than in the general population. At the moment, there are no indications for a correlation between the individual mutations and the clinical presentation. The mutations in patients 6 and 8 are identical and differ only by a single amino acid from the mutation in patient 1. Yet, these three patients do not share more clinical characteristics amongst each other than with other patients. However, at this moment it is not possible to draw firm conclusions on a possible genotype:phenotype correlation due to the small sample size. No patients with a pure deletion of ADNP have been reported. In our own databases and in DECIPHER35, five deletions with sizes 313Kb-3.31Mb, taking away 5-23 genes including (part of) ADNP, have been described. In the four cases where the parents were tested, the deletion was de novo. The patients with ADNP deletions all share some clinical characteristics with the patients reported here, carrying truncating mutations (Supplementary Fig. 4, Supplementary Table 1).
The C-terminal part of ADNP directly interacts with ARID1A, SMARCA4 and SMARCC2, three essential components of the BAF complexes, the functional eukaryotic equivalent of the SWI/SNF complex in yeast that is involved in the regulation of gene expression36. These ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling complexes consist of 15 subunits, including one of both ATPase core subunits SMARCA4 or SMARCA237. A switch of complex composition is essential for initiation of post-mitotic activity-dependent dendritic outgrowth and axonal development. This transition of neural progenitor cells to mature neurons occurs in all neurons and highlights the fundamental role of BAF complexes in neural development38. Interestingly, mutations in patients with intellectual disability have been reported in six components of these complexes (SMARCB1, SMARCA4, SMARCA2, SMARCE1, ARID1A and ARID1B). The phenotype associated with mutations in these genes ranges from non-syndromic intellectual disability with hypotonia and speech delay to recognizable syndromes such as the Coffin-Siris syndrome and Nicolaides-Baraitser syndrome. These disorders are sometimes refered to as “SWI/SNF-related intellectual disability syndromes”39-41. It has been proposed that the syndromic features might be explained by the role of BAF complexes in developmental processes in the affected tissues42. It is believed that most reported mutations in these genes have a dominant negative effect on the functioning of the BAF complex as a whole43-46. As we were able to detect mutant RNA in our patients, we hypothesize that the mutant ADNP protein competes with the wildtype protein in aberrant interaction with the BAF complex. Wildtype ADNP directly binds target genomic regions and mediates the recruitment of the BAF complex through the C-terminal end. Hence, it can be hypothesised that the mutant protein with an altered C-terminal structure will hamper the recruitment of the BAF complex, while it still occupies DNA binding sites. This will lead to a diminished functionality of the complex and ultimately to deregulation of several cellular processes.
In summary, we identified a recurrent SWI/SNF-related ASD syndrome, caused by mutations in ADNP. These findings expand the phenotypic spectrum of SWI/SNF-related disorders, several of which are caused by mutations in direct interaction partners of ADNP. Mutations in ADNP may explain the etiology of 0.17% of patients with ASD (95% binomial confidence interval: 0.083% - 0.32%) and thus constitute one of the most frequent known causes of autism. Our findings will increase the diagnostic yield in this population and studies on the role of ADNP in development may raise hope for treatment of these patients in the long term.
Methods
Patients
Patients were selected for inclusion in this study from different cohorts tested on either family-based WES, targeted resequencing or high-resolution melting analysis (Table 1). Clinical evaluation was performed by at least one expert clinical geneticist. Written informed consent for inclusion in the study was obtained for all patients and consent for the publication of photographs was obtained for patients 1, 2, 4, 5, 6 and 8.
Sanger sequencing
Primers were designed using Primer347,48. PCR was performed using GOTaq polymerase (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) on DNA from peripheral blood and on cDNA from lymphoblastoid cells, using standard protocol. Capillary electrophoresis sequencing (ABI 3130 genetic analyzer; Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was performed using the ABI BigDye terminator V3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA), following standard protocol. Data was analysed in CLC DNA Workbench (CLC Bio, Aarhus, Denmark).
Whole-exome sequencing (WES)
Patient 1 was detected in a family-based WES study (unpublished data (CH, GV, Filip Van Nieuwerburg, NVdA, RFK)). Patient DNA was fragmented using Covaris® M220 Focused-ultrasonicator™ (Covaris, MA, USA), followed by TruSeq DNA Sample Preparation (Illumina Inc, San Diego, CA, USA), enrichment using the SeqCap EZ Human Exome Library v3.0 kit (NimbleGen, Roche, Penzberg, Germany), and sequencing on HiSeq 2000 (Illumina Inc, San Diego, CA, USA), all following standard protocols. Data analysis was performed using Galaxy (see URLs)49-51. Variants were filtered by VariantDB (see URLs, manuscript in preparation) to exclude variants with (1) low quality, using thresholds based on correlation between NGS data and SNP-chip genotyping; (2) intronic or intergenic location, except splice sites; and (3) inheritance from the parents. WES sequencing of patients 2, 3 and 4 was performed as described2,8. The mutation in patient 5 was identified in a family trio based study. WES was performed using Illumina technology (Illumina Inc, San Diego, CA, USA), and sequence data was returned and analysed using software supplied from Oxford Gene Technology. Presence of reported (de novo) mutations were confirmed by an independent technique such as Sanger sequencing. Raw sequence data will be uploaded in The European Genome-phenome Archive (EMBL-EBI) database.
Molecular inversion probes (MIPs)
Patients 7, 8 and 9 were discovered from a MIP based screen of 2743 probands with intellectual disability and/or ASD). Patient 10 was included from a MIP based screen of 2446 autism patients from the Simon Simplex Collection (SSC)16. The MIP screening and analysis was performed as previously described, and MIP probe sequences for ADNP are available in O’Roak et al, 201216. Inheritance determination and validation were performed by Sanger sequencing.
High-resolution melting (HRM)
192 control chromosomes were screened for the presence of the mutations identified in the 10 patients using HRM. Primers were designed using the HRMA Assay Design module of Beacon Designer™ 8.10 (Premier Biosoft, CA, USA). HRM was performed on a LightCycler 480 (Roche, Penzberg, Germany) with the LCGreen+ incorporating dye (Idaho Technology Inc., Salt Lake City, UT, USA). Meltcurve analysis performed by the Gene Scanning module of the LightCycler software. Samples with deviating curves were analysed by Sanger sequencing. The mutation in patient 6 was identified using the same protocol, as part of the cohort of 148 probands with idiopathic ASD, for which microarray analysis did not reveal any abnormalities.
Real-time quantitative PCR
RNA isolation, cDNA synthesis and quality control were performed as described earlier52. mRNA expression was examined by an optimized three-step real-time quantitative PCR assay following the protocol described before53. Besides ADNP itself, ADNP2 was included based on the reported correlation of expression in human brain tissue31. TMPO, CCNC and PLAGL2 were reported to be significantly downregulated in homozygous Adnp knockout mice embryos, while ABCF3 was reported to be upregulated in heterozygous Adnp knockout mice embryos18,23. Finally, TP53 is upregulated in HT29 cells incubated with ADNP antioligodeoxynucleotide32. YWHAZ and HPRT were selected as reference genes, according to geNorm calculations54. qPCR primers were selected from literature31,55, the RTPrimerDB56 or designed using an in-house automated pipeline (see URLs), conforming to requirements of intron-spanning location, no SNP content, no dimer formation at the 3’ end of the primers, and low amplicon folding, with no folding in primer binding sites. The amplification efficiency of the different primers was assessed and confirmed to be above 1.85. Primer sequences are available on request. Expression values of two cDNA syntheses originating from two different RNA isolations per patient were compared to the values obtained from eight control individuals. Statistical testing was performed using linear mixed models in order to investigate significant differences in expression levels of the patients compared to controls.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Belgian National Fund for Scientific Research-Flanders (FWO) to GV and RFK, the Special Research Fund of the University of Antwerp (Bijzonder Onderzoeksfonds (BOF-IWT)) to CH, by grants from the Dutch Organization for Health Research and Development (917-86-319 and 40-00812-98-12109 to BBAdV and 907-00-365 to TK), the EU-funded GENCODYS project (EU-7th-2010-241995 to ATVvS, BBAdV and TK), Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative award (SFARI191889EE to EEE) and NIH (MH101221 to EEE). We acknowledge Drs. Rosa Pettinato and Maurizio Elia for the first enrolling of patients 8 and 9, respectively and Drs. Jay Shendure and Brian O’Roak for details regarding ADNP molecular inversion probe design. EEE. is an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Footnotes
Author contributions
The study was designed and the results were interpreted by ATVvS, BBAdV, TK, BPC, EEE, CH, GV, NVdA, RFK. Subject ascertainment and recruitment were carried out by ATVvS, JHMSH, CLM, MHW, BBAdV, TK, CR, JvdE, NVdA, AN, GA, MB, MW. Sequencing, validation and genotyping were carried out and interpreted by CH, LR, GV, HM, KTW, PB, BPC, LELMV, MF, KTW and HGY. The manuscript was drafted by CH, GV, NVdA and RFK. All authors contributed to the final version of the paper.
Competing financial interests
EEE is on the scientific advisory boards for Pacific Biosciences, Inc., SynapDx Corp., and DNAnexus, Inc.
URLs
Clinical information: http://www.adnpgene.com
Galaxy pipeline: http://biominavm-galaxy.biomina.be/galaxy/u/geert-vandeweyer/w/adnp
VariantDB: http://www.biomina.be/app/variantdb
Realtime PCR design tool: http://biomina.be/apps/qpcr-primers
Exome Variant Server: http://evs.gs.washington.edu/EVS/
References
- 1.Network, A.a.D.D.M. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders--Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 14 sites, United States, 2008. Morbidity and mortality weekly report. Surveillance summaries. 2012;61:1–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.O’Roak BJ, et al. Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations. Nature. 2012;485:246–50. doi: 10.1038/nature10989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Neale BM, et al. Patterns and rates of exonic de novo mutations in autism spectrum disorders. Nature. 2012;485:242–5. doi: 10.1038/nature11011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yu TW, et al. Using whole-exome sequencing to identify inherited causes of autism. Neuron. 2013;77:259–73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sanders SJ, et al. De novo mutations revealed by whole-exome sequencing are strongly associated with autism. Nature. 2012;485:237–41. doi: 10.1038/nature10945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.O’Roak BJ, et al. Exome sequencing in sporadic autism spectrum disorders identifies severe de novo mutations. Nat Genet. 2011;43:585–9. doi: 10.1038/ng.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Devlin B, Scherer SW. Genetic architecture in autism spectrum disorder. Current opinion in genetics & development. 2012;22:229–37. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.de Ligt J, et al. Diagnostic exome sequencing in persons with severe intellectual disability. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1921–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1206524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rauch A, et al. Range of genetic mutations associated with severe non-syndromic sporadic intellectual disability: an exome sequencing study. Lancet. 2012;380:1674–82. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61480-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yang Y, et al. Clinical Whole-Exome Sequencing for the Diagnosis of Mendelian Disorders. N Engl J Med. 2013 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1306555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vissers LELM, et al. A de novo paradigm for mental retardation. Nat Genet. 2010;42:1109–1112. doi: 10.1038/ng.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gillberg C, Billstedt E. Autism and Asperger syndrome: coexistence with other clinical disorders. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2000;102:321–30. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2000.102005321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pinto D, et al. Functional impact of global rare copy number variation in autism spectrum disorders. Nature. 2010;466:368–72. doi: 10.1038/nature09146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Talkowski ME, et al. Sequencing Chromosomal Abnormalities Reveals Neurodevelopmental Loci that Confer Risk across Diagnostic Boundaries. Cell. 2012;149:525–37. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Iossifov I, et al. De novo gene disruptions in children on the autistic spectrum. Neuron. 2012;74:285–99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.O’Roak BJ, et al. Multiplex targeted sequencing identifies recurrently mutated genes in autism spectrum disorders. Science. 2012;338:1619–22. doi: 10.1126/science.1227764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mandel S, Spivak-Pohis I, Gozes I. ADNP differential nucleus/cytoplasm localization in neurons suggests multiple roles in neuronal differentiation and maintenance. J Mol Neurosci. 2008;35:127–41. doi: 10.1007/s12031-007-9013-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Vulih-Shultzman I, et al. Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein snippet NAP reduces tau hyperphosphorylation and enhances learning in a novel transgenic mouse model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;323:438–49. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.129551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Abecasis GR, et al. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature. 2012;491:56–65. doi: 10.1038/nature11632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gozes I, et al. NAP: research and development of a peptide derived from activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) CNS drug reviews. 2005;11:353–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2005.tb00053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bassan M, et al. Complete sequence of a novel protein containing a femtomolar-activity-dependent neuroprotective peptide. Journal of neurochemistry. 1999;72:1283–93. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0721283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gozes I, et al. Protection against developmental retardation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by a fatty neuropeptide: implications for early treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of neurobiology. 1997;33:329–42. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4695(199709)33:3<329::aid-neu10>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mandel S, Rechavi G, Gozes I. Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) differentially interacts with chromatin to regulate genes essential for embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 2007;303:814–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.11.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mosch K, Franz H, Soeroes S, Singh PB, Fischle W. HP1 recruits activity-dependent neuroprotective protein to H3K9me3 marked pericentromeric heterochromatin for silencing of major satellite repeats. PloS one. 2011;6:e15894. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Smothers JF, Henikoff S. The HP1 chromo shadow domain binds a consensus peptide pentamer. Current biology : CB. 2000;10:27–30. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)00260-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pollard KS, Hubisz MJ, Rosenbloom KR, Siepel A. Detection of nonneutral substitution rates on mammalian phylogenies. Genome research. 2010;20:110–21. doi: 10.1101/gr.097857.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zuker M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3406–3415. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nagy E, Maquat LE. A rule for termination-codon position within intron-containing genes: when nonsense affects RNA abundance. Trends Biochem Sci. 1998;23:198–9. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(98)01208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schoenberg DR, Maquat LE. Regulation of cytoplasmic mRNA decay. Nature reviews. Genetics. 2012;13:246–59. doi: 10.1038/nrg3160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kervestin S, Jacobson A. NMD: a multifaceted response to premature translational termination. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology. 2012;13:700–12. doi: 10.1038/nrm3454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dresner E, Agam G, Gozes I. Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) expression level is correlated with the expression of the sister protein ADNP2: deregulation in schizophrenia. European neuropsychopharmacology : the journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;21:355–61. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2010.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zamostiano R, et al. Cloning and characterization of the human activity-dependent neuroprotective protein. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2001;276:708–14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007416200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Aboonq MS, Vasiliou SA, Haddley K, Quinn JP, Bubb VJ. Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein modulates its own gene expression. J Mol Neurosci. 2012;46:33–9. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9562-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pinhasov A, et al. Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein: a novel gene essential for brain formation. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2003;144:83–90. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(03)00162-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Firth HV, et al. DECIPHER: Database of Chromosomal Imbalance and Phenotype in Humans Using Ensembl Resources. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;84:524–533. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mandel S, Gozes I. Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein constitutes a novel element in the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2007;282:34448–56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704756200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ronan JL, Wu W, Crabtree GR. From neural development to cognition: unexpected roles for chromatin. Nature reviews. Genetics. 2013;14:347–59. doi: 10.1038/nrg3413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lessard J, et al. An essential switch in subunit composition of a chromatin remodeling complex during neural development. Neuron. 2007;55:201–15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.06.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kosho T, et al. Clinical correlations of mutations affecting six components of the SWI/SNF complex: detailed description of 21 patients and a review of the literature. Am J Med Genet. 2013;161A:1221–1237. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Santen GW, et al. Coffin-Siris Syndrome and the BAF Complex: Genotype-Phenotype Study in 63 Patients. Human mutation. 2013;34:1519–28. doi: 10.1002/humu.22394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hoyer J, et al. Haploinsufficiency of ARID1B, a member of the SWI/SNF-a chromatin-remodeling complex, is a frequent cause of intellectual disability. American journal of human genetics. 2012;90:565–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.02.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ho L, Crabtree GR. Chromatin remodelling during development. Nature. 2010;463:474–84. doi: 10.1038/nature08911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.de la Serna IL, Carlson KA, Imbalzano AN. Mammalian SWI/SNF complexes promote MyoD-mediated muscle differentiation. Nat Genet. 2001;27:187–90. doi: 10.1038/84826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kemper JK, Kim H, Miao J, Bhalla S, Bae Y. Role of an mSin3A-Swi/Snf chromatin remodeling complex in the feedback repression of bile acid biosynthesis by SHP. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:7707–19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7707-7719.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Choi EY, Park JA, Sung YH, Kwon H. Generation of the dominant-negative mutant of hArpNbeta: a component of human SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex. Exp Cell Res. 2001;271:180–8. doi: 10.1006/excr.2001.5355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tsurusaki Y, et al. Mutations affecting components of the SWI/SNF complex cause Coffin-Siris syndrome. Nat Genet. 2012;44:376–8. doi: 10.1038/ng.2219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Untergasser A, et al. Primer3--new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic acids research. 2012;40:e115. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Koressaar T, Remm M. Enhancements and modifications of primer design program Primer3. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:1289–91. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Giardine B, et al. Galaxy: a platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis. Genome Res. 2005;15:1451–5. doi: 10.1101/gr.4086505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Blankenberg D, et al. Galaxy: a web-based genome analysis tool for experimentalists. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2010;Chapter 19(Unit 19):10 1–21. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb1910s89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Goecks J, Nekrutenko A, Taylor J, Galaxy T. Galaxy: a comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biol. 2010;11:R86. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-8-r86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Van der Aa N, et al. Fourteen new cases contribute to the characterization of the 7q11.23 microduplication syndrome. Eur J Med Genet. 2009;52:94–100. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2009.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Vandeweyer G, Van der Aa N, Reyniers E, Kooy RF. The Contribution of CLIP2 Haploinsufficiency to the Clinical Manifestations of the Williams-Beuren Syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90:1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.04.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Vandesompele J, et al. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002;3:34.1–34.11. doi: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Yang MC, Weissler JC, Terada LS, Deng F, Yang YS. Pleiomorphic adenoma gene-like-2, a zinc finger protein, transactivates the surfactant protein-C promoter. American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology. 2005;32:35–43. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2003-0422OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lefever S, Vandesompele J, Speleman F, Pattyn F. RTPrimerDB: the portal for real-time PCR primers and probes. Nucleic acids research. 2009;37:D942–5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


